NPB101 Systemic Physiology
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
First Lecture Set Only
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Body Functions follow the____ of _____ and ______
laws, chemistry, physics
Cells, tissues and organs ______ in a coordinated fashion
interact/ work together
Cells, tissues and organs _____ with eachother
communicate
body function are usually _____ by 1 or more controllers
regulated
_____ drive movement of molecules
Gradients
What is a Gradient?
difference in height; ex: bowling ball going down hill
What is Homeostasis?
A body goal; body function to keep internal environment constant
What is the internal environment?
ECF, body fluids, plasma, brain ECF
What does Homeostasis keep constant?
Temperature, pH, glucose(fuel), gas concentrations, electrolytes
Why do you need to keep homeostasis constant?
Because disturbances in the internal environment can disrupt cellular function and life function
What body parameters get disturbed on a hot day?
salt levels, PO2;PCO2, Body Temp (TB), “waste” lactic acid, glucose levels
What is a Homeostatic Reflex?
A response to CORRECT the disturbance (although not completely)
Is a Homeostatic Reflex involuntary?
Yes and its reflexive
Describe the Homeostatic Reflex
Your TB is too high (39º) and a receptor detects that disturbance then transmits that info via the afferent pathway, then the C.P.U. processes the info that TB is too high and makes a decision about disturbance, then it compares the input of our set point value of 37º, then after comparing it transmits info via the efferent pathway, the efferent pathway takes info from the CPU and “talks” to effector organ, the effector organ( skin) is the sweat glands and is a (+) disturbance, then the effect is sweating that lowers the disturbance as it negates TB and this has a (-) effect on the initial disturbance of high TB → negative feedback loop since The cooling effect of sweating reduces the initial stimulus
Is sweating a Negative or Positive Feedback Loop?
Negative Feedback
Is variance narrow or wide with TB?
Narrow
Can your set point value change?
Yes
What are the Levels of Body “Organization”/ Hierarchy?
Chemical/Molecular, Cellular, Tissue-level, Organ-level, Organ System-level
What does the Plasma Membrane/Cell Membrane do?
It separates environments with walls (ex: cytoplasm & ECF)
What makes up Plasma Membrane walls?
Phospholipids
What is between PM walls?
Intercellular Space
T/F, The head of a phospholipid is hydrophobic
False, the head is hydrophilic
T/F, The tail of a phospholipid is hydrophobic
True
What is the Tail of a Phospholipid made of up?
Glycerol & Fatty Acids
Are phospholipids set up as a monolayer or bilayer?
Bilayer
Can ions and proteins pass the Phospholipid Bilayer?
No, they cannot, but they CAN with the help of a channel or transporter protein
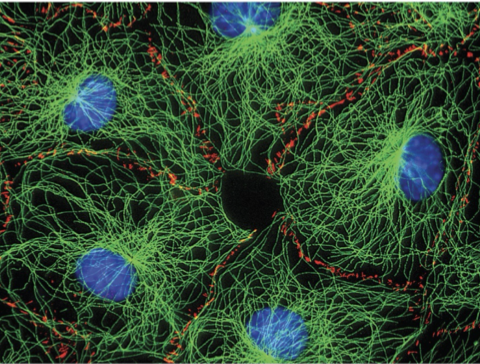
What is a Cytoskeleton?
Protein strands
What are/do Protein Strands do?
Give shape and strength to the cytoskeleton
What does the Cytoskeleton do?
use portions of protein strands to move/ “crawl” & change shape
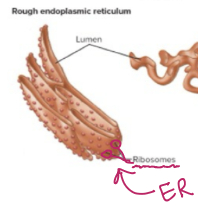
The ER has a bunch of what on it?
Ribosomes
Mitochondria does?
ATP generation, fatty acid metabolism
T/F a Organelle/ER is non membrane bound?
False, it is membrane bound
T/F a Ribosome is non membrane bound?
True, and has an entity inside

What are Tissues?
A collection of cells; Grouping/clusters of cells that work together
How many types of Tissues are there? & Name them
-5
-10
-4
-3
4 types: Muscle Tissue, Connective Tissue, Nervous Tissue, Epithelial Tissue
What are the names of the Muscle Tissues?
Skeletal, Cardiac, Smooth
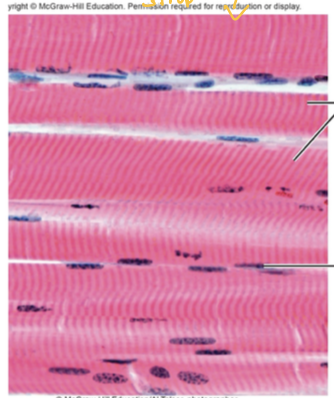
What Muscle Tissue is this?
Skeletal
Is skeletal involuntary contracting? Describe it
No, it is Voluntary contracting and has stripes
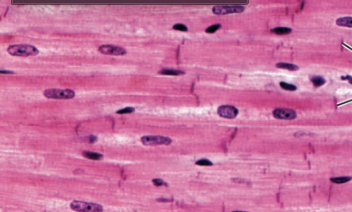
What Muscle Tissue is this?
Cardiac
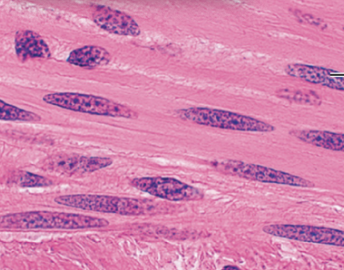
What Muscle Tissue is this?
Smooth
Is Cardiac involuntary contracting? Describe it
Yes, it is involuntary contracting and has stripes; heart tissue
Is Smooth involuntary contracting? Describe it
Yes, it is involuntary contracting, its a hollow organs~stomach, intestine
What is Contraction, Describe it, what tissue type
It is shortened(inward pull) and generates force(pulling) and generates heat(uses ATP/energy) in the Muscle Tissue
What does the Nervous Tissue do?
Communicates and Processes
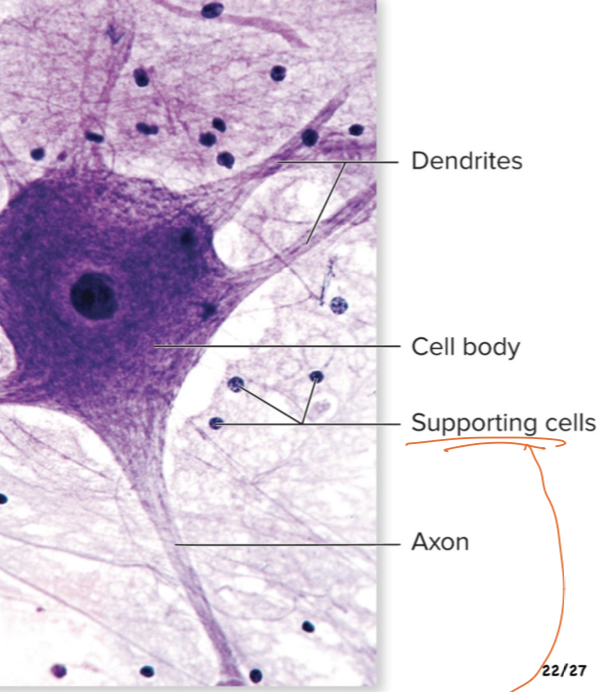
What tissue is this?
Nervous Tissue
Does the neuron Process or Communicate? Explain.
It Communicates; Propagates (allow to move) the action potential
the AP is the neurons way of communicating
neuron=messenger
AP= is the message
the neuron creates the AP and sends it down the axon
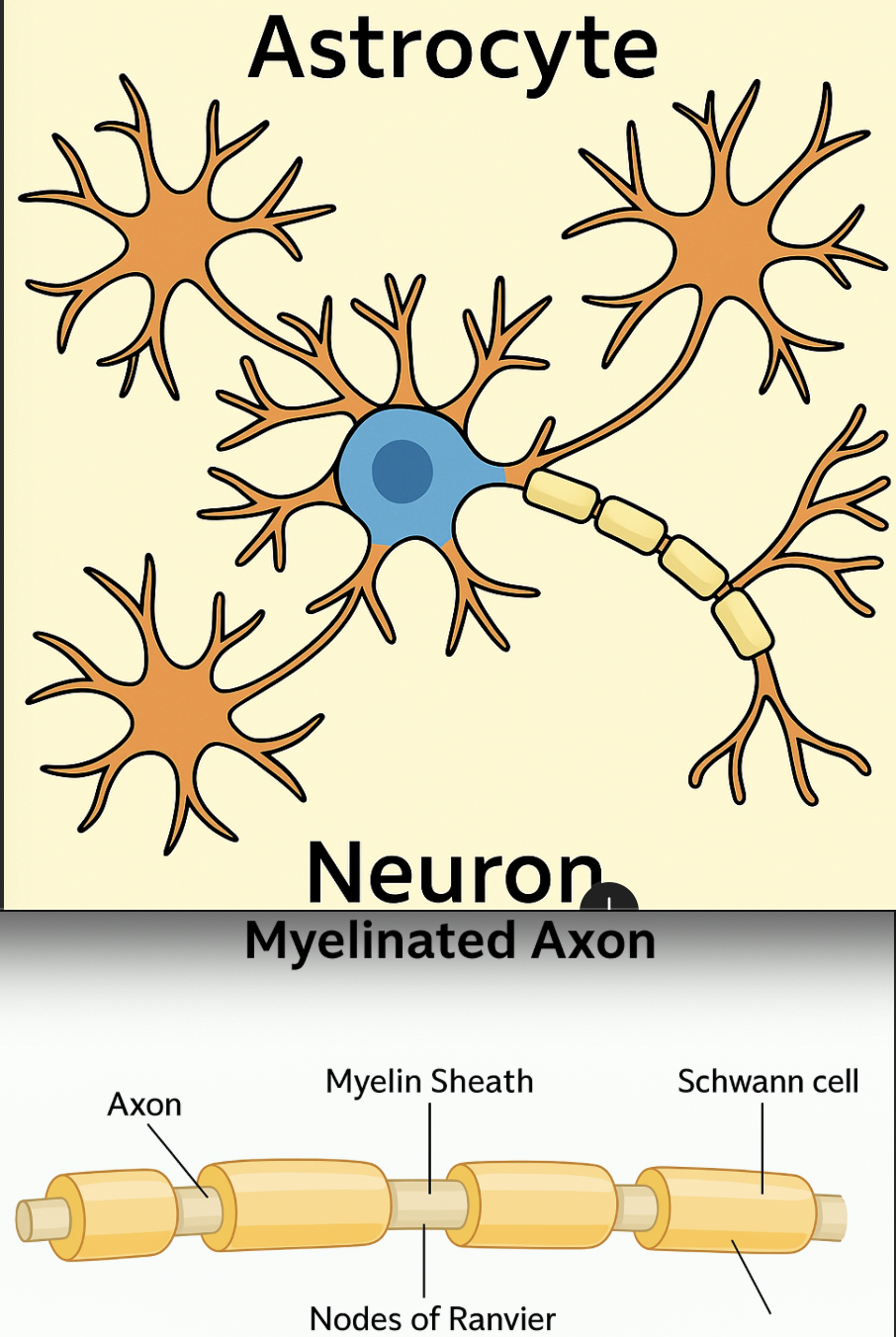
Does the Astrocytes/ Oligodendrocytes(supporting cells) Process or Communicate? Explain.
They Process as it is necessary for neuron to do its job.
they process in the sense that they perform essential support functions to make it possible for the neuron to send signals
Astrocyte: nutrient regulation
Oligodendrocytes: myelination that allows neuron to fxn properly
Myelination: wrapping a fatty layer (myelin) around axons of neurons
What Tissue is this?
Epithelial Tissue
What does the Epithelial Tissue do?
absorbs nutrients, give rise to endocrine tissues, protects
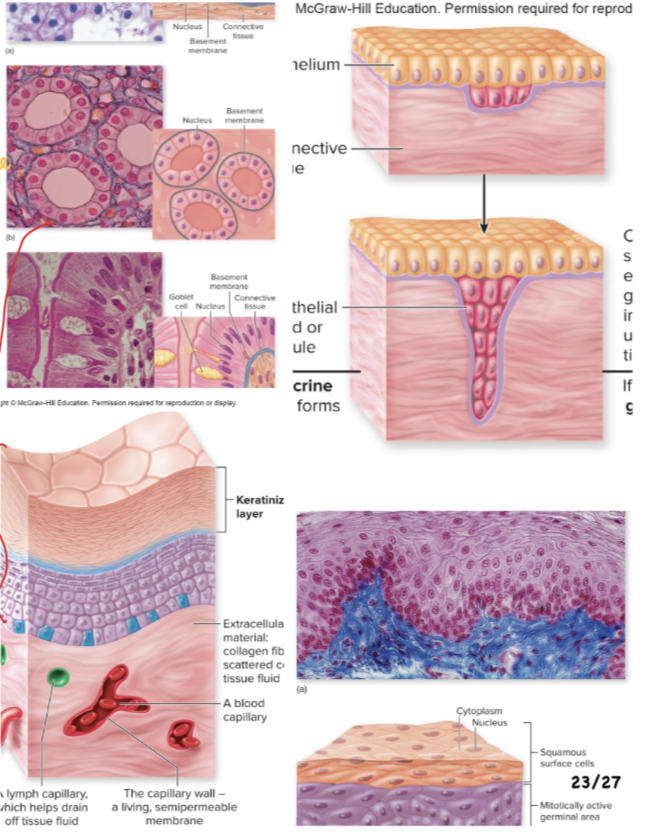
Epithelial Tissue: What does the Kidney do?
absorb water
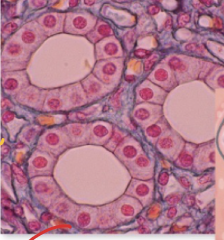
Epithelial Tissue: What’s the function of the skin ?
Scratch resistant & waterproof
What are some Connective Tissues?
Adipose, Bone, Cartilage, Blood, Loose connective tissue (a cushion/padding one on butt)
What is the Function of Connective Tissue?
It has a variety for functions
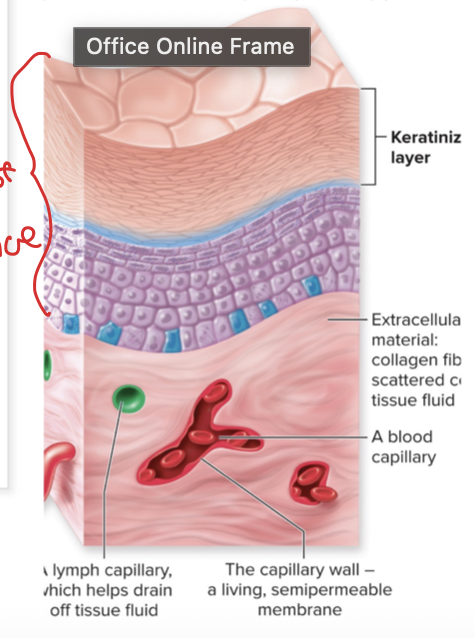
Connective Tissue: What tissue is this and the function?
Adipose Tissue & is a storage site for lipids & also cushion organs
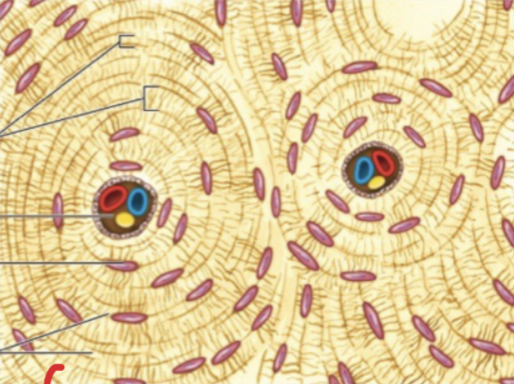
Connective Tissue: What tissue is this and the function?
Bone Tissue and is protects organs, provide structure, support
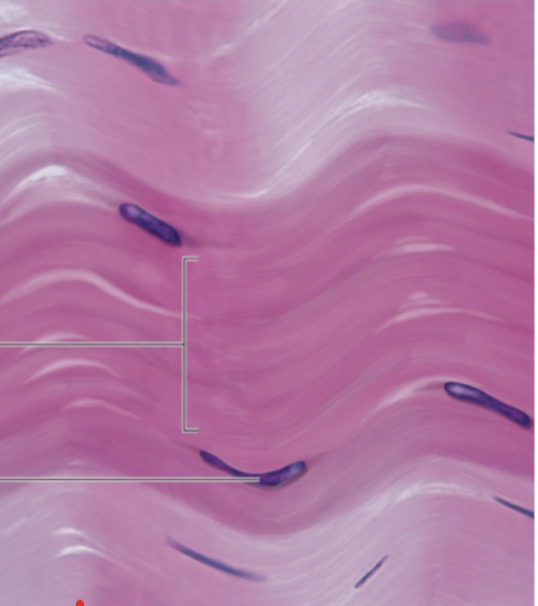
Connective Tissue: What tissue is this and the function?
Cartilage and cushions bones and provides flexibility
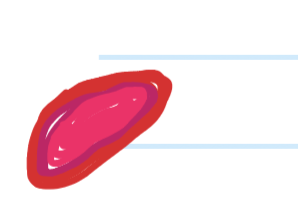
Connective Tissue: What tissue is this and the function?
Blood: transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste
FOR ALL TISSUE SYSTEMS they do NOT constitute function of body yet as they have to get into organ
for all 4 types
Organs are made up of _____ that work together
two or more tissues
Organs are organized into ______
organ system
A group of ____ perform activities that accomplish _____ _____.
organs, specific tasks
How many different organ systems do we have?
11-12
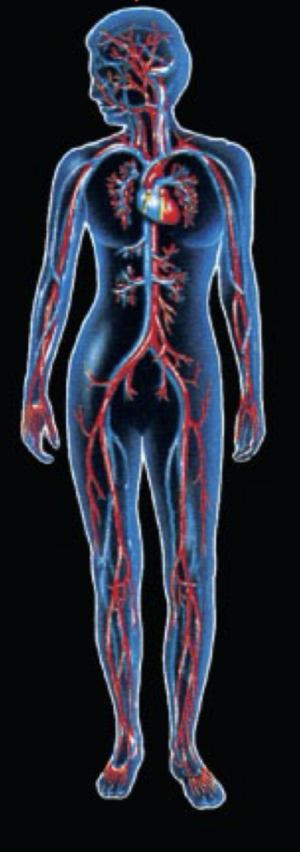
What System is this and what is the function?
Circulatory:Transports
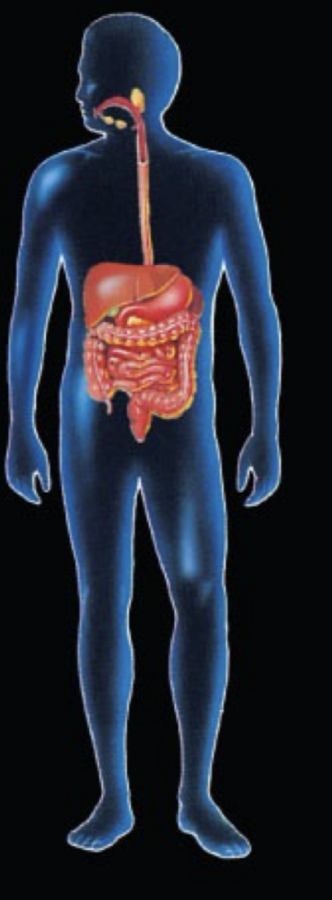
What System is this and what is the function?
Digestive System: nutrient & water absorption

What System is this and what is the function?
Respiratory System: Gas Exchange
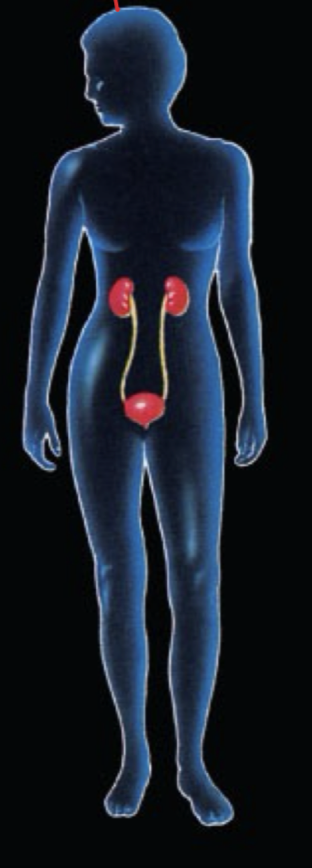
What System is this and what is the function?
Urinary/Renal System: recondition the blood—>pH & Homeostasis
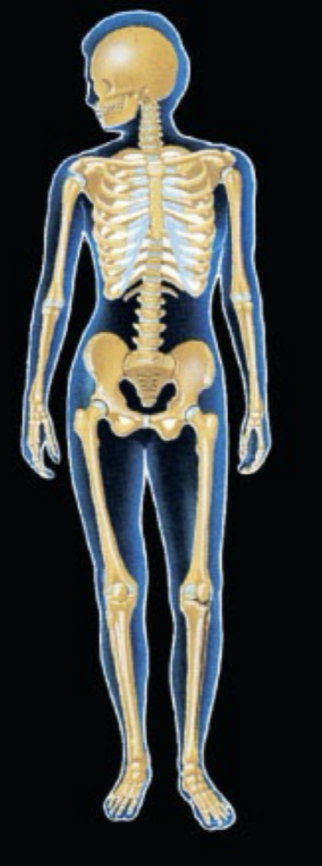
What System is this and what is the function?
Skeletal System: Support & Movement
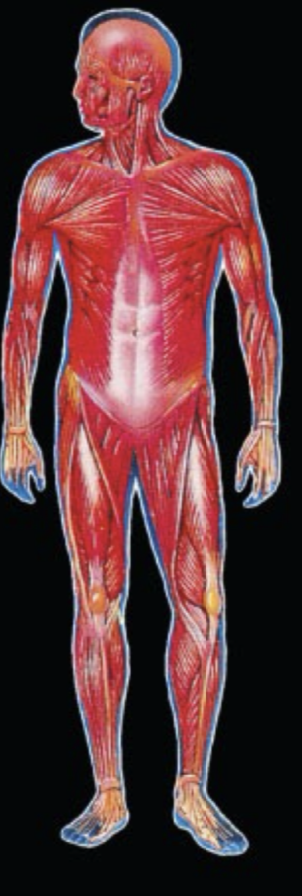
What System is this and what is the function?
Muscular System: movement, relaxation, & maintain posture

What System is this and what is the function?
Integumentary System: protect
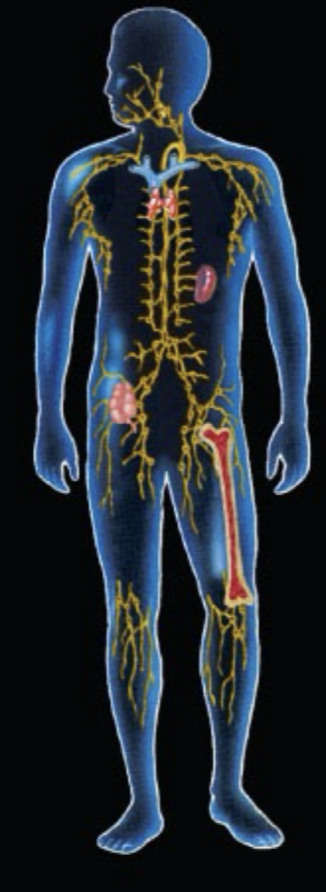
What System is this and what is the function?
Immune System:
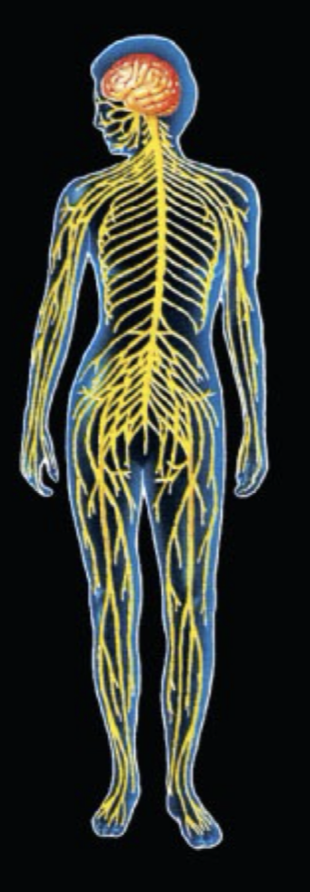
What System is this and what is the function?
Nervous System
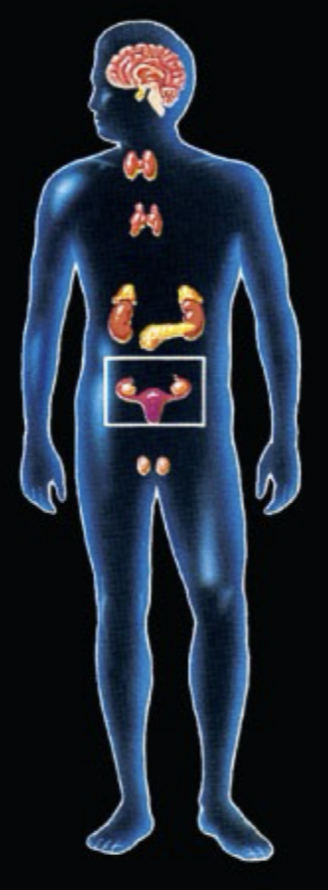
What System is this and what is the function?
Endocrine System: produces and releases hormones
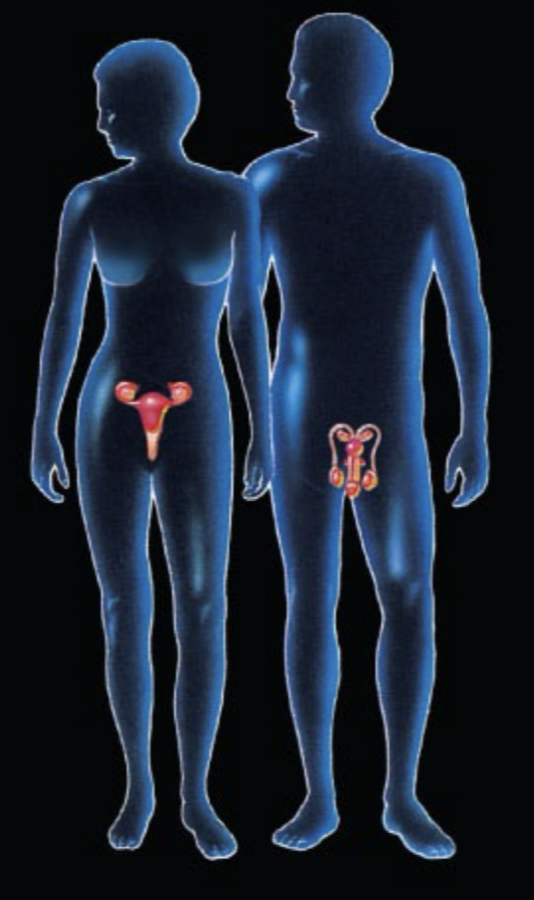
What System is this and what is the function?
Reproductive System: CAN take out and SURVIVE