Histology: Connective Tissue and Muscle Tissue
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
4 different types of Connective Tissues are all derived from the same embryonic tissue called
mesenchyme
4 types of CT
Connective Tissue Proper, Cartilage, Bone, Blood
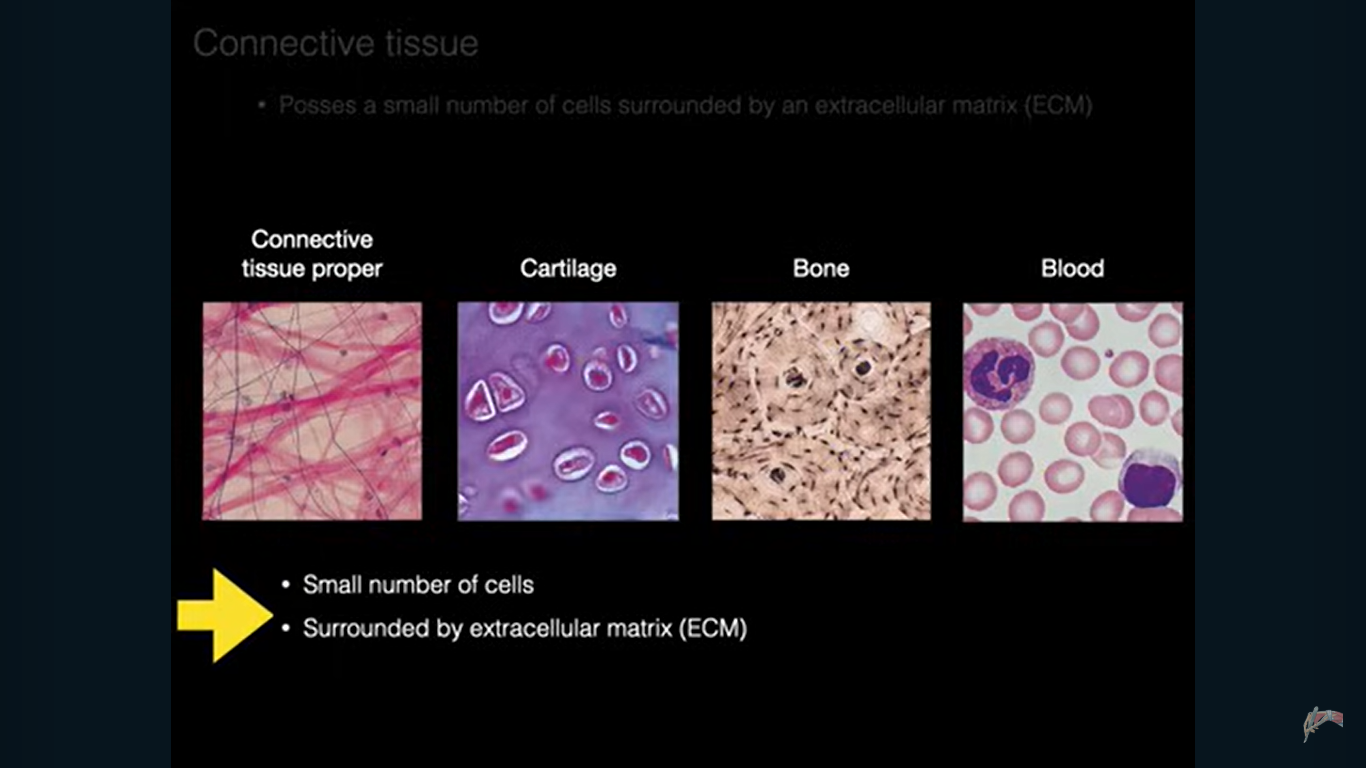
It Possess a small number of cells surrounded by large amount of extracellular matrix, opposite of epithelial tissue
connective tissue
Primary Connective Tissue Cell on connective tissue Proper
Fibroblast +
This cell synthesizes extracellular matrix made mainly collagen, elastin, and ground substance
Fibroblasts =
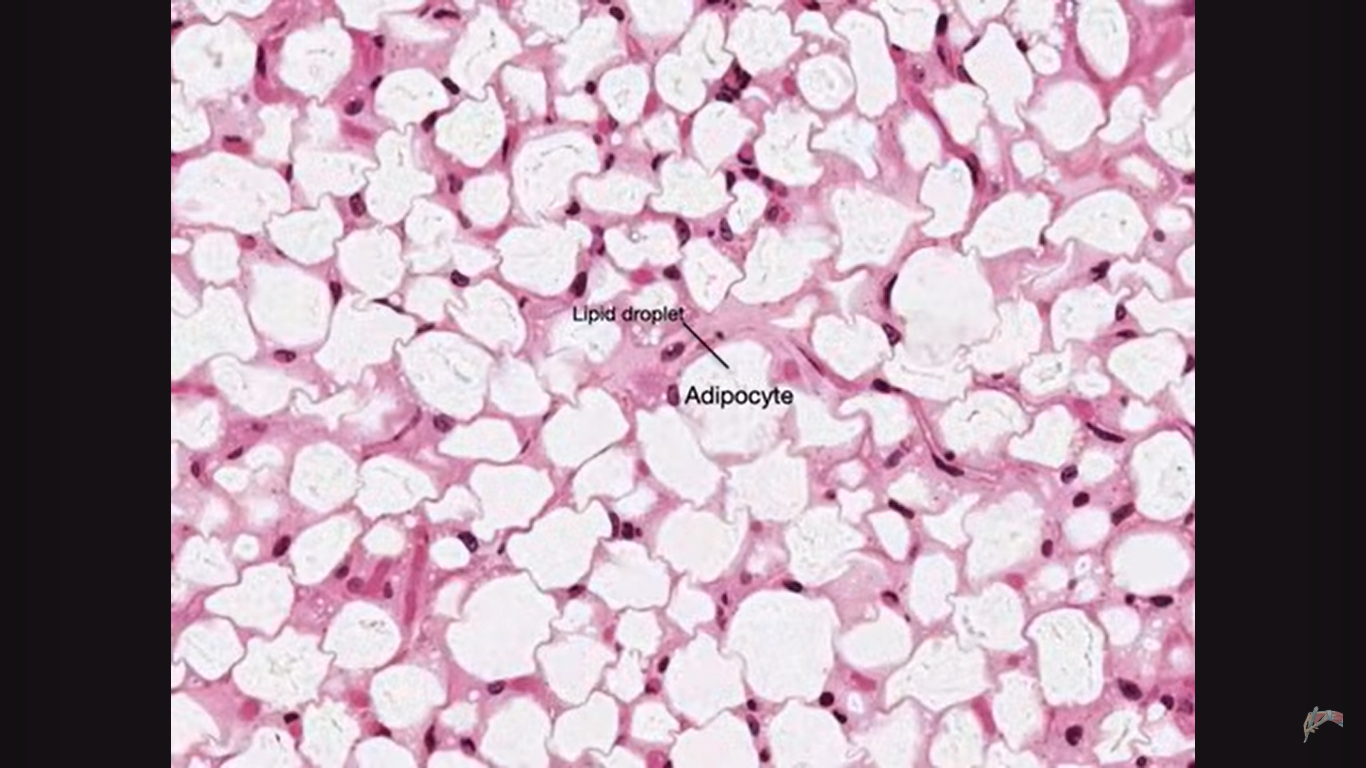
these are fat cells that store lipid in a single droplet
Adipocytes
Phagocytize and destroy microorganisms, old cells, and damaged tissues
Macrophages
Inflammatory cells that secretes histamine which promotes vascular leakiness
Mast Cells
tough, structural protein that provides tensile strength
collagen +
most abundant type of protein in connective tissue proper
collagen =
this protein allows stretch and recoil
elastin
cells present in CT Proper
fibroblast, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells
Type of CT proper that is embedded deep to all epithelial basement membrane
Loose Connective Tissue / Areolar Connective Tissue
Type of CT proper that is strong in all directions located in Dermis and submucosa of organs
Dense Irregular Collagenous Connective Tissue
Type of CT proper that is strong in one direction, located mainly in tendons
Dense regular Collagenous CT
Type of CT proper that stores energy, padding, and insulation
Adipose Tissue +
Type of CT proper is located in hypodermis
Adipose Tissue =
fx: connect, attach, and package
Connective Tissue Proper
4 types of connective tissue proper
LCT/Areolar CT, Dense Irregular Collagenous Connective Tissue, Dense Regular Collagenous Connective Tissue, Adipose Tissue
Type of Cartilage found behind of pharynx, on costal cartilages, and articular cartilages (allows bones to glide smoothly against one another)
Hyaline Cartilage
Type of Cartilage that has high concentration in the ear and epiglottis because it is firm but goes back to its original shape
Elastic Cartilage
Type of Cartilage that has high concentration of collagen in intervertebral discs, pubis symphysis, and meniscus of the knee
Fibrocartilage +
this cell maintain cartilage
Chondroblasts
Mature Chondroblast turn into what?
Chondrocytes
fx: Strong yet flexible, avascular, and able to absorb shock
Cartilage
3 kinds of Cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage, Elastic Cartilage, Fibrocartilage
This cell secrete bone matrix in a bone tissue and Builds new bone
osteoblasts
mature osteoblasts that reside in lacunae and monitor and Maintain in the ECM
Osteocytes
This cell secrete enzymes that catalyze the breakdown (Crushing) of bone matrix that is made up of calcium and phosphate
Osteoclasts
extracellular Matrix of bone is made up of 2 elements
calcium and phosphate
Composed of RBCs, WBCs, Platelets, and Plasma
Blood
ECM of blood?
Plasma
Transport O2
RBCs
Immune Defense
WBCs
Clots blood
Platelet
ECM of blood
plasma
This tissue is made up of contractile type of cell
Muscle Tissue
3 types of muscle tissue
skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, smooth muscle
voluntary muscle fibers that are long, striated, and multinucleated
skeletal muscle tissue +
This type of muscle tissue are compartmentalized by CT sleeves
skeletal muscle tissue =
each muscle fiber is surrounded by loose connective tissue called ____
endomysium
bundle of muscle fibers are called ____
muscle fascicle
Muscle Fascicle is connected by dense connective tissue called ____
perimysium
bundle of muscle fascicle is called ______
skeletal muscle
Skeletal Muscle is surrounded by CT called ____
epimysium
This type of muscle tissue is located primarily within muscles that attach to bones
skeletal muscle tissue _
This type of muscle tissue is involuntarily controlled, and striated with intercalated discs
cardiac muscle tissue +
located on muscle wall of the heart or myocardium
cardiac muscle tissue =
This type of muscle tissue is involuntarily controlled, and non striated
smooth muscle tissue +
Located on wall of most hollow organs like stomach, bladder, blood vessels, fallopian tube, urethra, and so forth
smooth muscle tissue =