Grade VIII - Term 2 revision
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
Manufacturing Industries
Converts raw materials into finished products on a larger scale using physical labour and mechanical power.
Manufactured goods
More valuable than the original raw material
Evolution of Industry
Industrial revolution in the 18th century
Machines operated on power generated from coal
Manual and animal labour reduced
Large scale industries
Other sources of power - Petroleum, Hydroelectricity
Stages of production in an industry
Obtaining raw material
Processing into a finished product
Distribution
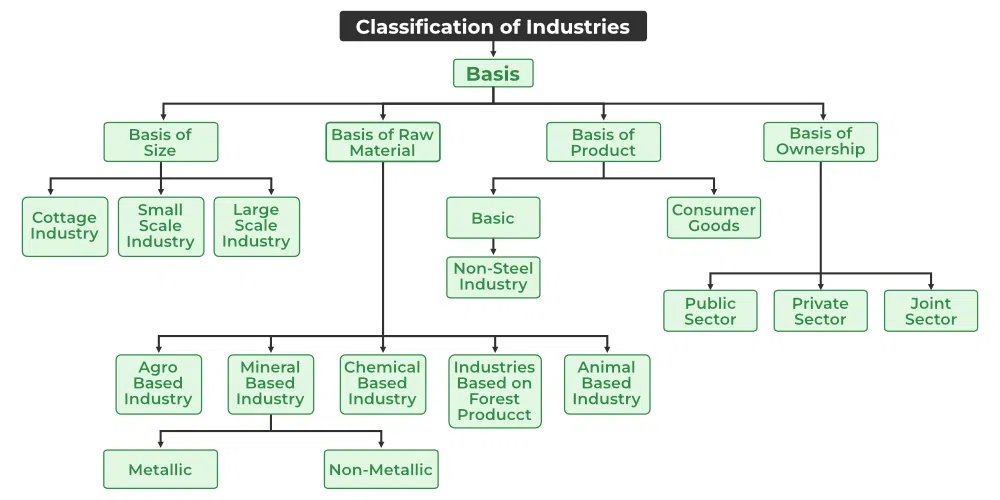
Classification of industries
Based on size
Based on raw materials
Based on ownership
Based on products
Types of industries based on size
Cottage industries
Small scale industries
Large scale industries
Cottage industries
Goods made with the help of family members at home
Little Capital
Local raw materials
Simple tools
Eg -pottery, baskets, jewelry, and jams
Small scale industries
Some labor and power-driven machinery
Raw materials from local and outside
Employ a large section of the population
Eg - Textiles, ceramics, toys, and leather goods
Large scale industries
Huge capital
Employs 1000s of labourers
Power driven heavy machinery
Imported raw materials
Finish good can be exported
Separate departments for different operations
Eg - Iron and steel, petrochemical and cement industry.
Types of industries based on raw materials
Agro-based - From agriculture. Eg - Sugar, jute textile
Mineral-based - rocks and minerals. Eg - Iron and steel.
Pastoral-based - From animals. Eg - Woolen textiles and dairy products.
Marine-based - From aquatic animals. Eg - Fish processing.
Forest-based — From forests. Eg - Timber, Paper.
Types of industries based on end products
Basic industries
Intermediate goods industries
Consumer goods industries
Types of industries based on ownership
Private
Public
Joint
Co-operative
Private sector industries
Owned and managed by an individuals or group of individuals.
Eg - Tata Iron and Steel Industry, Reliance Industries
Public sector industries
Owned and managed by central or state governments or their agencies.
Eg - Steel Authority of India Ltd. , Bharat Heavy Electricals Ltd.
Joint sector industries
Owned and managed jointly by private firms and government agencies.
Eg - Oil India Ltd. and Gujarat Alkalies
Cooperative sector industries
Owned and managed by a group of people who form their own co-operative society.
Eg - Sugar mills, Dairy cooperatives and handloom industries.
Factors influencing the location of the industry
Availability of raw material
Power supply
Labour
Transport
Market
Capital
Water supply
Land
Climate
Government policy
Global industrial regions
Eastern part of North America
Western and Central Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Asia
Indian industrial regions
Mumbai - Pune region
Hugli Basin region
Bengaluru - Tamil Nadu region
Gujarat region
Chhota Nagpur region
Vishakapatnam - Guntur region
Gurgaon - Delhi - Meerut region
Kollam - Thiruvananthapuram region
Revolt of 1857
Considered the First War of independence
Political causes of revolt of 1857
Lord Dalhousie’s policy of Doctrine of Lapse curbed the adoption rights of the ruling class
The annexation of Awadh angered Hindus and Muslims
The disrespect shown towards Mughal Emperor Bahadur Shah
Exclusion of Indians from high-paying civil and military jobs
Subedar
Highest post an Indian could get in the army for 60 - 70 rupees per month
Sadar Amin
Highest post in civil services an Indian could get for Rs. 500 a month
Economic causes of Revolt of 1857
Destruction of cottage industries
Commercialization of agriculture destroyed the self-sufficient village economy
Weavers and artisans received minimal remuneration ( Salary)
Machine-made products from England flourished making the artisans unemployed
Social and religious causes of Revolt of 1857
Fear of getting converted by the Christian Missionaries who entered India through the Charter Act of 1813
Changing of customs and traditions - Abolishment of Sati and female infanticide, and encouraging widow remarriage.
Imposition of taxes on land with temples and mosques.
Military causes of Revolt of 1857
Soldiers of Bengal army were offended by the annexation of Awadh
Army was asked to take an oath that they would fight for British overseas whenever asked to ( Sea travel was not allowed in some religions)
No extra remuneration for sepoys when they fought in distant lands
Low salaries of sepoys did not fulfil their basic needs
Immediate cause of Revolt of 1857
Introduction of Enfield rifle which required the soldiers to bite the greased cartridge before usage.
Rumour - the greased cartridges were made od cow/pig fat.
Refused to work as it hurt religious sentiments.
Spread of the Revolt
Several regiments in Barrackpur and Meerut were disbanded and punished after the soldiers refused to use these cartridges.
Mangal Pandey - marched with his comrades to revolt. He was executed.
Nana Saheb - leader of the revolt in Kanpur
Rani Lakshmi Bhai - Jhansi
Kunwar Singh - Bihar
Begum Hazrat Mahal - Lucknow
Tantia Tope - Gwalior
Suppression of the Revolt
Lord Canning - Governor-General took immediate steps
Forces of Madras, Bombay, Sri Lanka, Burma and Sikh were asked to proceed to Delhi.
Two sons of Bahadur Shah were killed
Bahadur Shah was deported to Rangoon as a prisoner
Rani Lakshmi Bhai joined Tantia Tope in Gwalior.
Lakshmi Bhai - killed in a battle and Tantia Tope was executed.
Nana Saheb and Hazarat Mahal fled to Nepal and died there
Failure of the revolt
Limited scope - Delhi, Meerut, Bihar whereas Punjab and the southern regions remained aloof.
Lack of planning by a single central organization
Lack of military skills to match that of the British forces.
Rulers of Nepal, Patiala, Jind, and Hyderabad supported the British.
The educated and upper-middle-class Indians did not support the rebels, but the British.
Changes after 1857
British EIC rule came to an end
Secretary of State and the Indian Council were created
The army was reorganized with an increased proportion of British soldiers
The policy of territorial annexation ended.
The unconditional pardon was given to rebels except those responsible for the murder of British subjects.
Government of India Act 1858
Patshaalas
Network of elementary schools in India before British rule
Maktabs and madrasas
Higher education in India were conducted through these institutions before British rule
First institutions set up in India by the British
Calcutta Madrasa for Muslim law set up by Warren Hastings
Sanskrit College for Hindu Law and Philosophy was established by Jonathan Duncan
Fort William College for the training of civil servants of the company
Non-intervention policy of EIC
EIC did not want to interfere in the education system in India
Christian missionaries wanted EIC to give up this policy a it would help them lose faith in their religion and follow Christianity
Charter Act of 1813 and education
No mention of the medium of instruction
Ambiguous about the target audience
Orientalists
Supported the promotion of Indian education through the medium of classical languages like Sanskrit, Arabic, and Persian.
William Jones, Nathaniel Halhed, and Henry Colebrooke
Anglicists
Promotion of Western languages through the medium of English
Enlightened Indians - Raja Ram Mohan Roy - saw Western education as a remedy for social, political and economic evils.
Thomas Babington Macaulay
Macaulay’s minute
Limited government resources for teaching western sciences and literature though the medium of instruction - English
Persian as court language was abolished
Printing of English books - made free
42 schools were set up
Bengal had 9 zones with one government school in each set up by Governor-General Auckland
Wood’s Despatch
Charles Wood
Magna Carta of English Education in India
Education of the masses
Graded schools with hierarchies - Universities, colleges, high school, middle school, and primary school.
English - medium for higher studies and Indian languages - school level
Emphasis on female and vocational education
Secular education in government institutions
Grants-in aids for private enterprises
Universities in Bombay, Madras and Calcutta
Hunter Commission
Under W W Hunter
To review the progress of education after Wood’s Despatch
Recommendations to primary and secondary education
Setting up of Punjab and Allahabad University
Raleigh Commission
Measure to improve the conditions of Indian universities
Indian Universities Act was passed
Nationalists were against it - as they saw it as a way to make Indians loyal to the British
Wardha scheme of education
Formation of Zakir Hussain Committee
Detailed national scheme for basic education
Main principle - “Learning through activity”
Gandhian ideas published in series of articles in the weekly journal called Harijan
Limitations of British policies for education in India
Mass education and education of women were neglected leading to widespread illiteracy ( Inefficiency of downward filtration theory)
Wide linguistic and cultural gap between the educated and the non-educated
Decline of traditional system of Indian learning
Applicants of government jobs were required to know English
No scientific or technological education for Indians
Practices - Social and religious evils
Sati
Infanticide
Purdah
Devadasi system
Polygamy
Child marriage
Illiteracy
Social reformers
Raja Ram Mohan ROy
Ishwar Chandra Vidya Sagar
Keshab Chandra Sen
Mahadev Govind Ranade
Dayanand Saraswati
Jyotibha Phule
Pandita Ramabhai
Raja Ram Mohan Roy
Social reformer
Father of modern India
Champion of women’s rights
Established Brahmo Samaj for social welfare
Campaigned against sati, child marriage polygamy, caste distinctions, and untouchability
Attacked by orthodox Hindus for his campaign against sati
Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar
Worked for female education
Set up 35 schools for girls
Set up the first Indian school for girls in Calcutta
Opposed polygamy and child marriage
Campaigned to legalise widow remarriage
He supervised the first widow remarriage of upper caste in Calcutta
Swami Vivekananda
Founder of Ramakrishna Mission
Emphasis on spiritualism and empowerment of women
Social reformers in Maharashtra
Prarthana Samaj
Mahadev Govind Ranade and R G Bhandarker
Behramji Malabari - Articles in “The Times” on the evils of child marriage and widowhood.
D K Karve - Educated women to become teachers at girls’ school in Poona
Jyotiba Phule with his wife started a girls’ school at Poona
Swami Dayanand
Found Arya Samaj
Encouraged female education by establishing Kanaya gurukuls
Pandita Ramabhai
Educated in Sanskrit texts
Widow at a young age
Worked with Arya Mahila Sabha
Established Sharda Sadan - A school for Indian widows
Sarojini Naidu
Worked for women’s right
Associated with All India Women’s Conference
Reason for the spread of caste movements
Spread of education among the oppressed classes
Forming associations that assumed all India status to safeguard themselves from oppression
Reasons for the growth of national consciousness
Economic exploitation of the Indian by the British
The rise of press and literature
Improvement in transport and communication also contributed to the emergence of nationalism
Early associations
The Landholder’s Society, Calcutta
Bengal British India Society
Madras Native Association
Bombay Association
Indian National Congress
Indian National Congress
Founded in 1885
Founded by A O Hume - a retired civil service officer
Womesh Chandra Banerjee - first president
Moderates and Extremists
Moderates
Educated classes
Submitted petitions ansd prayers to put forward concerns
Demands - Indianisation of civil service, increased participation in legislative assembly and more funds for educating Indians
Used constitutional methods
Humble and mild criticism of the British
Extremists
Lost faith in British government
Opposed the ideologies of Moderates
Highest goal - attainment of colonial form of self government
Ideal - Poorna swaraj - complete independence
Balgangadar Tilak, Bipin Chandra Pal and Lala Lajpat Rai
Partition of Bengal
Announced by Lord Curzon
Separate province for East Bengal and Assam - Muslims
West Bengal - Bengali Hindus
Purpose was told to be better administration
Swadeshi Movement
Boycott of British goods
Promotion of Indian goods
Establishment of textile mills, national banks, chemical works, and insurance companie.
Women participants
Most active - School boys and girls
Processions and meetings were banned - repression of the movement by the British
Leaders were imprisoned
Muslim League
Salimulla Khan and Aga Khan - founded the Muslim League
To get a separate electorate for Muslims
Surat Split
The Extremists left the Indian National Congress in the Surat Session
Revolutionaries
Used violent means to get independence
Formed secret societies, manufactured bombs, and imported other weapons from other countries
Assassination of British officials
spread revolutionary ideas through newspapers and pamphlets
Revolutionary Ideas outside India
Ghadar Party in America - San Francisco
Morley - Minto reforms
Increase in the number of members of legislative councils
Introduction of separate electorates for Muslims
Extremists leaders thought that seprate electorate would harm the harmony
Lucknow Pact of 1916
Muslims were upset because of the war between Britain and Turkey.
Muslim League rejoined the Indian National Congress along with the Extremists
Montague-Chelmsford Reforms
Adoption of a more liberal policy towards Indians by the British after the Indians helped Britain in the First World War
Central legislature - Council of the State( Upper House ) and Legislstive Assembly ( Lower House)
System of dyarchy - Sharing of power by Indian elected members and appointed British officials
Minorities like Sikhs, Anglo-Indians and Christians - separate electorates
Gandhi and Non-violent satyagraha movement
Champaran - fought for Indigo planters
Ahmedabad - Settlement of disputes between mill owners and employers
Kheda - struggle of revenue collection
Rowlatt Satyagraha
Government - broke processions and meetings, lathi charge and opened fire at different places
Protest at Jallianwala Bagh in Amritsar
General Dyer - opened fire and killed hundreds and injured thousands
Rabrinath Tagore and Gandhi returned their titles of Knighthood and Kesar-i-Hind.
Khilafat Movement
Khalifa - leader of Muslims all over the world
Maulana Ali and Shaukat Ali formed the Khilafat committee to organise a nation wide agitation against the compromise of the position of Khalifa
Non-Cooperation Movement
Khilafat Committee merged with the Indian National Congress
Surrendering of all titles, resigning from nominated seats in local bodies
Refusal to attend govt functions
Withdrawal of students from govt schools and colleges
Boycott of British courts by lawyers
boycott of elections and foreign goods
Suspension of Non-Cooperation Movement
Came to an end after the Chauri Chaura incident - a police station was burnt in UP
Congress Khilafat Swaraj Party
Formed by CR Das and Motilal Nehru to stand in elections to end the Act of 1919
Simon Comission
Headed by Sir John Simon to prepare a report on the wokring of dyarchy in India
Congress boycotted this committee as there was no Indian in it
Country-wide hartal/ strike with the slogan - “ GO BACK SIMON”
Nehru Report
Lord Birkenhead challenged Nehr to draft a constitution
Proposals included:
:: Dominion status for India
:: Responsible governments - centre and at state
:: Residuary powers with Central
:: Central parliament - two houses and state legislative assembly with one house
:: A committee of defense at the center
:: Joint electorates with reservation of seats:: North-West frontier reservations for non-muslims
:; Fundamental rights incorporation
Civil Disobedience Movement
Launched by Mahatma Gandhi
Dandi March or Salt Satyagraha from Sabarmati Ashram to Dandi
Government Repression
Gandhi-Irwin Pact in the Second Round Table Conference
Indian National Army
Also known as Azad Hind Fauj
Founded by Subash Chandra Bose
Gained support from Japanese army adn marched towards Delhi with the slogan Chalo Dilli
Post 1945 developments
Labour Party in power - Clement Atlee Prime Minsiter in Britain
Sympathetic towards Indians
Division of India - Pakistan and India
Lord Mountbatten -First Governor General of India
Jinnah - First Governor General of Pakistan
Dr. Rajendra Prasad - President of Constituent Assembly
B R Ambedkar - Head of Drafting Committee
Constitution of India came into force on 26 Jan 1950
Division of power between the state and union governments
Union list - Subjects on which only the union government can make laws. Eg - Finance and foreign relations
State list - Subjects on which only state governments can make laws. Eg - Housing and transport
Concurrent list - Subjects on which both the govts can make laws. If there is a clash - central law will prevail.
The President
Head of the Indian union in whom all the executive power rests
Nominal head who acts with the aid of the council of ministers headed by the Prime Minister
The Union Legislature
The Parliament - The President, The Council of States ( Rajya Sabha/ Upper House) and The House of People ( Lok Sabha/ Lower House)
Members knowns as Members of Parliament - MPs
Has to meet atleast twice in a year.
Summoned and closed by the President
Lok Sabha
Lower House
Members elected through universal adult franchise
More powerful in a democracy as the power resides with people
Maximum - 550 members
530 - states and 20 - Union territories
Reservations for SCs and STs
Eligibility criteria to be a member of Lok Sabha
Citizen of India
At least 25 years old
Not be bankrupt or mentally unsound
Not hold any other govt job
Elections to be a member of Lok Sabha
Territories divided into constituencies
Divided based on population
Candidates can be from a political party or an independent candidate
Voting - done by secret ballot
One representative from each constituency - with maximum vites is selected
Election Commission
The independent body that conducts elections to the Indian legislature under the provisions of the Constitution
Formation of government
The party with the majority of seats - Ruling party
Leader of the ruling party - The Prime Minister
Other parties - opposition party - criticises the policies of the ruling party
Term of Lok Sabha
5 years
The President may dissolve if the ruling party loses its majority due to interim elections
The term can be extended by one year during emergency
Presiding officer of Lok Sabha
Speaker - conducts the proceedings of the house and maintains order. Exercises an vote at the end if there is a tie
Deputy Speaker - Carries out the duties of the speaker in the absence of the speaker
Rajya Sabha
Upper House
Represents the State and Union Territories
Reflect the interest of the states
Maximum members - 250
12 members nominated by the President from various fields like literature, science, art, and social service.
238 members - from States and Union Territories
The number of members from each state and UTs - Based on population
Eligibility criteria to become a member of Rajya Sabha
Citizen of India
At least 30 years old
Not be bankrupt or mentally unsound
Not hold any other govt job
Elections for Rajya Sabha
Elected by the elected representatives of the legislative assembly of the state.
Term of Rajya Sabha
Permanent House
Cannot be dissolved
1/3rd members retire every 2 years
Equal number of members elected in their place
Term - 6 years
Presiding officer of Rajya Sabha
Vice President - ex-officio chairman - presides the meeting
In case of a tie - cast a vote on decisions
Deputy chairman - elected from one of its members - exercises the proceedings in the absence of the Chairman
Legislative powers of the Parliament
Makes laws on subjects on the union, concurrent and residuary list
Law introduced in the form of a bill. ( Money/ Constitution Amendment/ Ordinary bills)
Approval of both houses - Passing of a bill
Money bill can only be initiated by the Lok Sabha
Voting in joint meeting of both houses - when there is a difference in decisions
Executive Powers of the Parliament
Questioning ministers about policies and actions during question hour in both houses
If ministers fail to give satisfactory answers - the house may pass a no-confidence against them - Minister has to resign (Only Lok Sabha)
Lok Sabha has more effective control than Rajya Sabha as it can pass a no-confidence motion and Rajya Sabha cannot
Financial Powers of the Parliament
Control over union finances
Budget is presented
Finance bill is also introduced
Proposal for new taxes and changes in existing taxes
Parliament’s Power to amend the Constitution
Some articles in the Constitution can be amended by a simple majority
2/3rd majority in both the houses needed
Judicial powers of the Constitution
The Parliament can remove the President, Vice President of India through the process of impeachment
Recommendations to remove Judge of the Supreme/ High court, Election Commissioner and the Auditor General.