Genetics Section 1
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Genetics is the study of
heredity and variation
When two distinct individuals with different characteristics are bred to each other, the experiment is called a
cross or hybridization
gamete
haploid reproduction cells that come together to form a zygote
A variety that continues to produce the same trait after several generations of self-fertilization is called a
true breeding line or true breeding strain.
a cross where you observe one character
single factor cross
The law of segregation
the two copies of a gene segregates/separates from each other during the process that gives rise to gametes. Therefore, only one copy of each gene is found in a gamete. At fertilization, two gametes combine randomly, potentially producing different allelic combinations.
consanguineous
inbreeding
Experimental advantages of using pea plants
They came in several different varieties, They were capable of self-fertilization, They were easy to cross
With regard to Mendel’s experiments, the term cross refers to an experiment in which
the gametes come from different individuals
To avoid self-fertilization in his pea plants, Mendel had to
remove the anthers from immature flowers
two different genes will randomly assort their alleles during the process that gives rise to gametes
Mendel’s law of independent assortment
an allele of a gene that encodes an RNA or protein that is nonfunctional or compromised in function
loss of function allele
a pedigree is
a family tree
Which of the following would not be observed in a pedigree if a genetic disorder was inherited in a recessive manner?
two affected parents have an unaffected kid
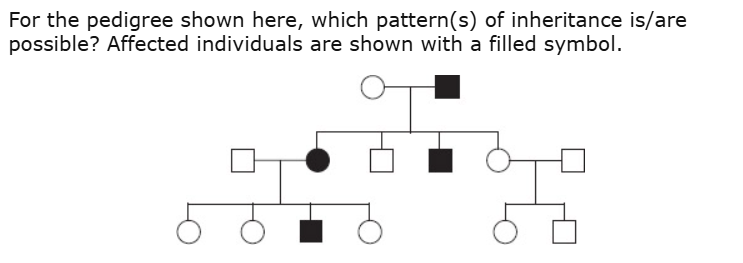
both recessive and dominant
probability
the chance that an outcome will occur in the future
which of the following could be used for hypothesis testing?
product rule, binomial expansion, chi square test, all of the above
Chi square test
for a cross between a heterozygous tall pea plant and a dwarf plant predict the ratios of the offspring’s genotypes and phenotypes
both are 1:1
Describe the significance of nonparental combinations of traits with regard to the law of independent assortment. In other words, explain how the appearance of nonparental combinations refutes the hypothesis of linked assortment.
Offspring with a nonparental phenotype are consistent with the law of independent assortment. If two different traits were always transmitted together as unit, it would not be possible to get nonparental combinations of traits. For example, if a true-breeding parent had two dominant traits and was crossed to a true-breeding parent having the two recessive traits, the F2 offspring could not have one recessive and one dominant trait. However, because independent assortment can occur, it is possible for F2 offspring to have one dominant and one recessive trait.