Marine Biology Exam 1
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
What is Marine Biology?
Study of organisms that live in the sea, including all water that has some degree of salinity, like the estuaries at river mouths
What is marine biology’s interdisciplinarians?
Geology
Chemistry (organic and inorganic)
Physics
Meteorology
Zoology
Botany
Marine biologist:
Study organisms that inhabit the sea
Oceanographers:
Study physical aspects of the ocean
4 branches of oceanography
Biological oceanography
Physical oceanography
Geological oceanography
Chemical oceanography
Is marine biology and oceanography the same?
No, they both have a different perspective of the marine world
Humans have been using the sea since _____ _____
early times
~ 165,000 yr old clam shells
discovered in a cave in south Africa

110,000 yr old shells
Harpoons and fishhooks

Pacific Islanders, Phoenicians
Sailed adjacent seas

Ancient Greeks
Knowledge of Med. Sea
Aristotle
Described many marine forms

Captain James Cook (1768-1780)
First Europeans to view Antarctic ice fields, + extensive mapping, and brought back many specimens
Wilkes Expedition (1832-1842)
10,000 specimens (2,000 unknown)
Confirmed Antarctica as continent
Edward Forbes
Studied seafloor around the British Isles
Discovered that species on the sea floor vary greatly dependent on depth = fundamental principle of marine biology
Challenger Expedition (1872-1876)
First major exploration devoted to the study of marine organisms
discovered ~ 4,700 new species
Published 50 volumes from data, took 19 years
Modern Marine Biology
Many marine biology research stations exist in locations around the world. Several facilities in the US:
• Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and Marine Biological Laboratory, Massachusetts
• Scripps Institution -La Jolla, California
• Friday Harbor Laboratories, Washington state
• Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute
• Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute
Remote sensing (tools in marine biology)
Using satellite technology to look at elevation, bathymetry, and ocean currents. Tells us a lot about the oceans and where they organisms are, and where life is distributed. They can follow large animals through _____ ______
Sonar (tools in marine biology)
Sound navigation and ranging. Was developed for sub warfare, but now it’s used to find animals, to figure out depth, and to fine seamounts
SCUBA (tools in marine biology)
Self-contained underwater breathing apparatus. Was developed in the late 1940’s for automobiles to run on compressed gas. Jacqu laristo modified it for underwater breathing
ROVs, AUVs, DSVs (tools in marine biology)
Remote operated vehicles
Autonomous underwater vehicles
Deep submergence vehicles
Research vessels
Vehicles made into science vessels. Boats made for research
Marine Biology is…
Survey class
Reef life'
Looks at small Benthic organisms, communities
Medicine, food, fishing, the harm, the value
Value = ~ $20 trillion per year
Dominant feature on the Earth
Ocean; 71%
61% of N Hemisphere
80% of S Hemisphere
4 Basins:
Pacific
Atlantic
Indian
Artic
Pacific
Deepest, largest, and the oldest
Atlantic
Younger, second in size
Indian
Similar to size to Atlantic, a little deeper
Artic
Smallest and shallowest
Deepest place in the Pacific
Marianas Trench
Deepest place in the Atlantic
Puerto Rico Trench
Deepest place in the Indian
Java Trench
Deepest place in the Artic
Molloy Deep
7 Seas/Oceans
N, S Pacific
N, S Atlantic
Indian
Artic
Southern (surrounds Antarctica)
Bacon (1620)
Puzzel pieces? (Structure of Basins)
Alfred Wegner
Continental Drift, 1912
A single supercontinent, Pangaea
Pangaea began breaking up 180 Mya
Not widely accepted at the time
Plate Tectonics
1950’s
Divergent Boundary -Sea Floor Creation
New from sea-floor spreading
Spreading = 2-18 cm per year, varies
Results in rifts and ridges
Normal fault
Nazca plate is one of the fastest - 5 to 18 cm per year
Mid-Atlantic plate is 2-5 cm per year
Mid-Oceanic Ridges
= Chain of submarine volcanic mountains
Sediment accumulates = floors are thicker
away from the ridges = older
Ridges is displaced by faults in crust = trans form faults
Convergent Boundary - Subduction zones
Trenches = deep depressions
Marianna: 10,994 m
Earthquakes, volcanoes - higher activity in area (“Ring of Fire”)
Island Arcs = chains of islands in the ocean (e.g. W. Pacific)
Side of deep-sea tranches
Earthquakes and volcanoes all occur in ________ zones
Reverse fault
Shear (Transform) Boundary
2 plates move and slip, creating friction
Earthquakes common (i.e. San Andreas Fault)
Strike-slip fault or transform fault
Lithogenous sediment
= derived from break-down of rocks (weathering)
Red clay
Biogenous sediments
= derived from the skeletons and shells of marine organisms
aged by carbon dating
ocean temperatures
Depth - CCD CaCO3
Calcareous / siliceous ooze
CCD = Calcium compensation Depth
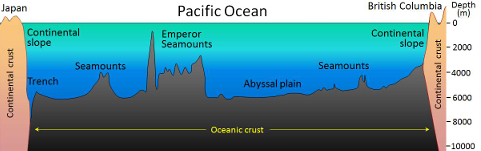
Continental margins: boundaries between
Continental crust and oceanic crust consist of:
Continental shelf (most landward)
Continental slope
Continental rise (most seaward)
Continental Shelf (most seaward)
~ 8% of ocean surface area, past exposure
Richest area of the ocean (biodiversity)
Width: 1 km - 750 km
Shelf break depth: 120-400 m (average 200 m)
International boundary
Continental Slope
“Edge” of a continent; shelf break to C. rise
Steepest part of continental margin
Continental Rise (most seaward)
Formed by sediment pushed down from the continental shelf and slope
“Underwater river delta” - deep sea fan
Active Margins
More intense: earthquakes, volcanoes, and trenches
Steep, rocky shorelines, narrow continental shelves, and steep continental slopes
Ex. West Coast
Passive margins
Relatively inactive
Flat, wide coastal plains, wide continental shelves, and gradually sloping continental slopes
Ex. East Coast
Thick C. Rise
Oceanic crust
= Sea Floor / Abyssal Plain
Seamounts, guyots, hills
Mid-oceanic ridge, trenches, channels
Hydrothermal vents
- “Black” Smokers
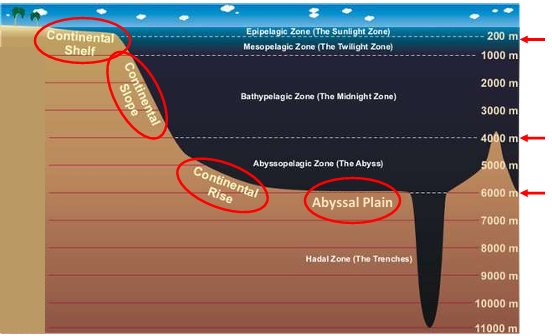
Continental Shelf (zones)
Epipelagic Zone (the sunlight zone) 200m
Mesopelagic Zone (the twilight zone) 1000m
Continental slope (zones)
Bathypelagic zone (the midnight zone) 4000m
Continental Rise (zones)
Abyssopelagic Zone (the Abyss) 6000 m
Hadal zone
Hadalpelagic - the trenches. over 6000 m
Zones
Euphotic
0-200 m
Dysphotic
200-1000 m
Photosynthesis
to 80 m
Igneous and metasediment rocks form -
Continental crust
2-6 km carbonate (limestone, dolomite) -
and evaporate sedimentary rock succession punctured by dissolution
1-150 m veneer -
Of mostly siliciclastic sands soil horizon
Florida formation
Opening up of Tethys ocean - global tropical ocean
Rifting stops in Georgia - Georgia channel seaway
Yucatan and Florida plates move away - forms Golf
Collisions, Bahamas and Florida plates become inactive - Fl straits separate platforms
Florida plates today
Earthquakes? No
FL faults = inactive; Cuba and PR = active
Resultant makeup
Karst - mostly north and central Florida - acidic water dissolving carbonate
Causes:
- Fracturing of rocks
- Too much / too little water
- Development
Silica invasion
Eroding mountains
Deposition of carbonate
In keys and everglades in Pleistocene and holocene
Resultant Sands around Florida
White, squeaky
Red streaks
Brown/tan
White, carbonate
Rocks
Palm Beach County
- Coquina - shell rich
Florida Keys
- Key Largo Limestone: reef rock (upper keys)
- Miami Limestone: Oolitic grainstone (lower keys + Miami and Boward)
- Caliche: lithified soils (paleosols); red from Saharan dust
Wetlands
Critically impt, mostly protected
Flat topography, low elevation, high water table, humidity
Everglades
Low relief, gentle slope
Laterally confined by E/W elevation (old lake/sea)
Formed 125 kya, after last glacial period
Holocene sediments: 4 m of mangrove peat; or 1 m of calcite mud; or exposed
Largely impacted by humans
Coastlines
Longests in US, 1305mi (2170km)
Variable; wide range of geomorphology
- 33% is not sand
Mainland
Open, bay, inside lagoon
Barrier Islands
Most formed in past 1000’s yrs
Largest coastline category
Vulnerable to erosion, flooding, migration - open
Developed / seawalls = required nourishment
Plant Dominated
Big Bend - marsh
Ten thousand Islands - Mangrove
Coral Reefs
3rd largest in world
Perched on older reefs
Spur / groove
Human impacted
Limited nutrients - favorable