2.6: Adaptations
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Types of selection pressures
Resource availability – Presence of sufficient food, habitat (shelter / territory) and mates
Environmental conditions – Temperature, weather conditions or geographical access
Biological factors – Predators and pathogens (diseases)
Sexual dimorphism
The differences in appearance between males and females of the same species, such as in colour, shape, size, etc.
Reproductive pressures act on the males of the species making them brighter and flashier BUT AT A COST!
Predation pressures act on the females.

Adaptation
an inherited characteristic that favors the survival or reproduction of an organism, and is the result of natural selection.
Can be:
Behavioral: Migration, hibernation
Physiological: temperature regulation (camel hump with water), release of toxins/poisons (snake venom)
Structural: body color (camouflage, seasonal change, warning vs disruptive coloration, deceptive markings), body covering, beak type, and claw type.
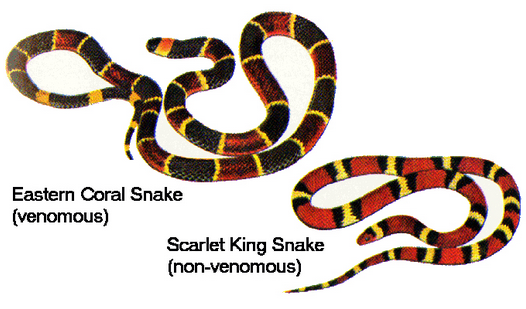
Batesian Mimicry
A harmless animal (the mimic) copies a known harmful animal (the model)
Ex. The venomous coral snake serves as a model for the harmless king snake.
Mullerian Mimicry
Both model and mimic are equally harmful to predators
Advantage:
A single taste trial by a predator will secure future protection for two or more species
Ex. The Monarch and the Viceroy

Microscale vs Macroscale
Microscale
Mutation
Recombination
Macroscale
Gene flow
Genetic drift
Bottleneck effects
Founder effects
Recombination
The genetic process by which one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome during reproductive cell division.
Gene flow
The process by which individuals move from one population to another and thereby alter the genetic composition of both populations.
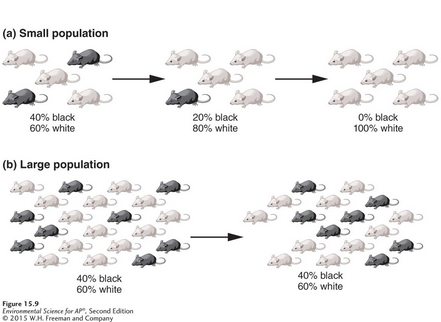
Genetic drift
A change in the genetic composition of a population over time as a result of random mating.
In a small population, some less-common genotypes can be lost
In a large population, it is more difficult for the less-common genotypes to be lost
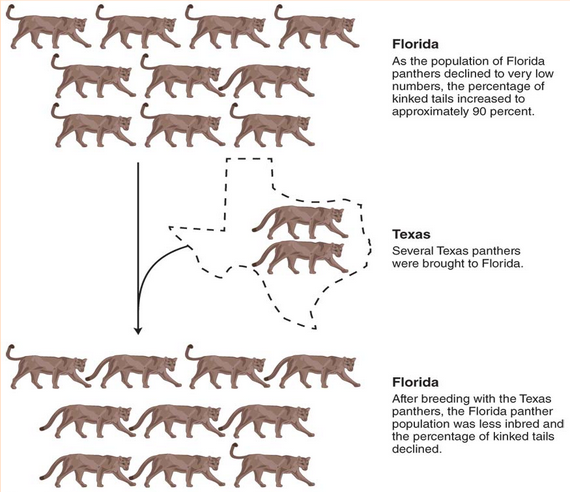
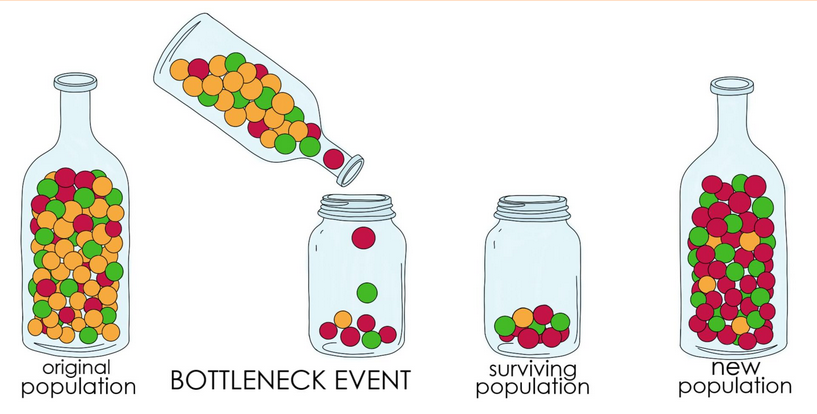
Bottleneck effect
an extreme example of genetic drift that happens when the size of a population is severely reduced.
Events like natural disasters (earthquakes, floods, fires) can decimate a population, killing most individuals and leaving behind a small, random assortment of survivors.
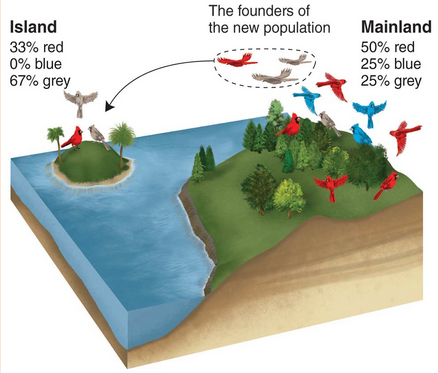
Founder effect
A change in the genetic composition of a population as a result of descending from a small number of colonizing individuals.
The genotypes on the island will represent only a subset of the genotypes present in the mainland population.