Lab List Midterm everything you need to know
1/220
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
221 Terms
Ventral is also reffered to as what?
Anterior
What is Ventral/Anterior
The Front or direction toward the front of the body
What is Posterior referred as?
Dorsal
What is Posterior/Dorsal
The Back. or direction toward the back.
Superior is also referedd to as what?
Cranial
What is Superior/Cranial
Describes postion above or higher than another part of the body
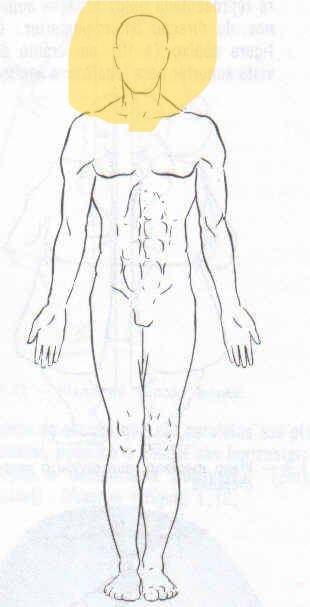
What is Inferior also referedd as ?
Caudal
What is Inferior/Caudal
a postion below. or lower than another part of the body (ex: feet becuase they are lower then the Hands.)
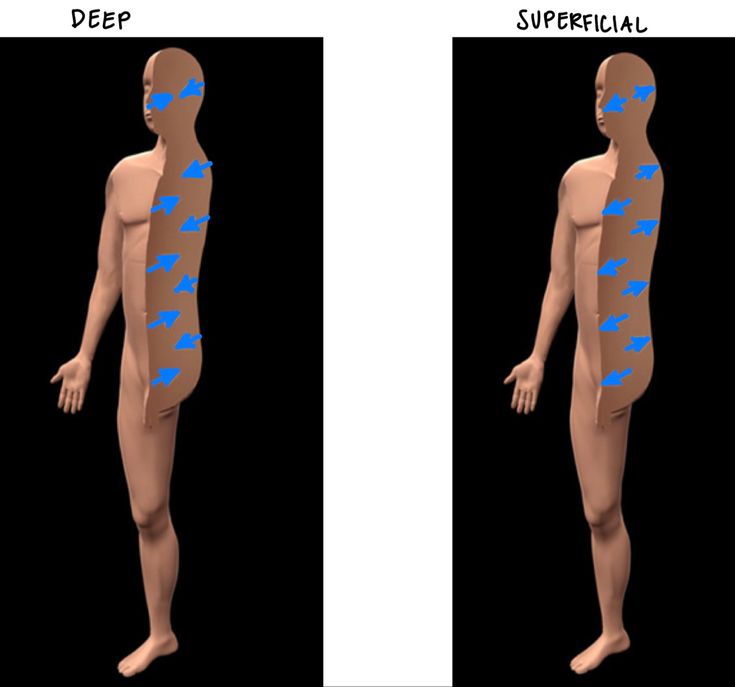
What is Superficial(External)
A postion closer to the surface of the body or at body surface. (skin is superfical to the bones.)
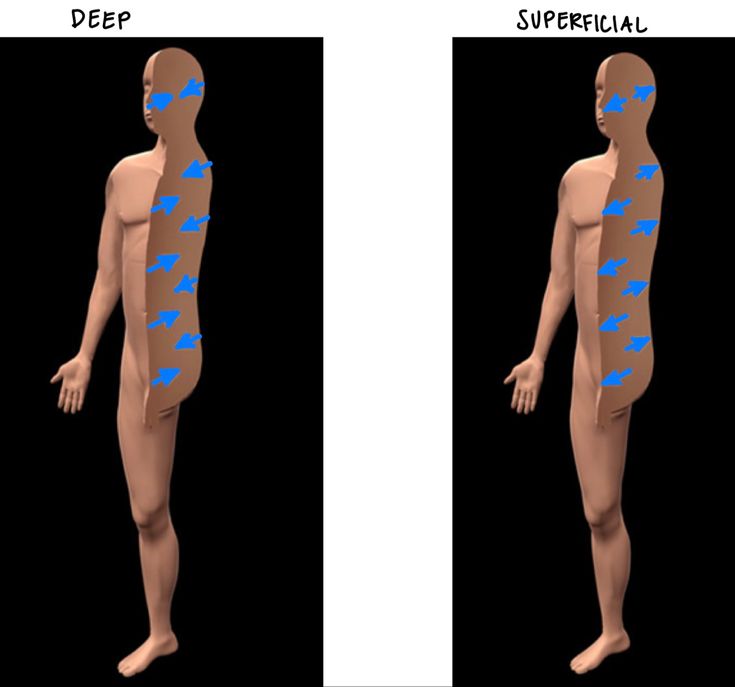
What is Deep/internal
a postion farther from the surface of the body (ex: the brain is deep to the skull)
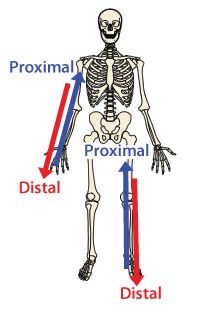
What is Proximal
postion in a limb that is nearer to the point of attachment or the body
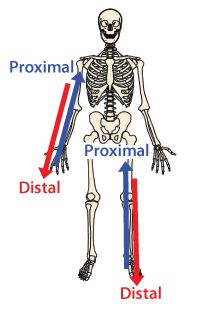
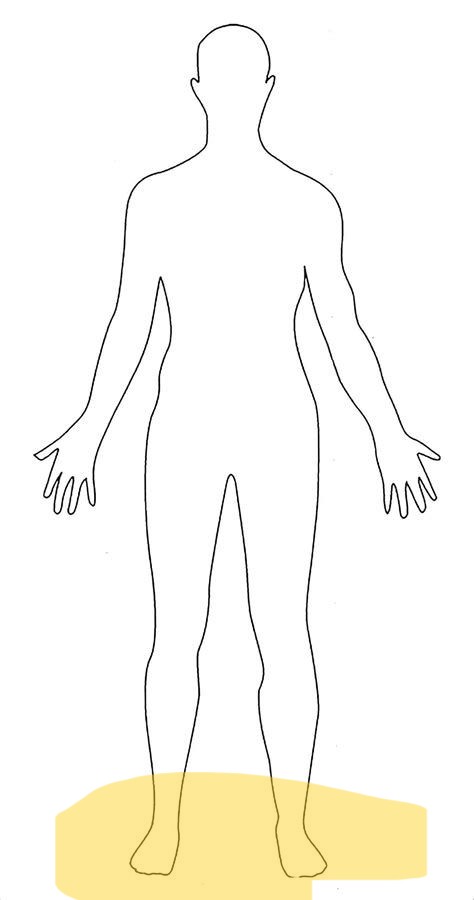
What is Distal
postion farther from the point of attachment or the body
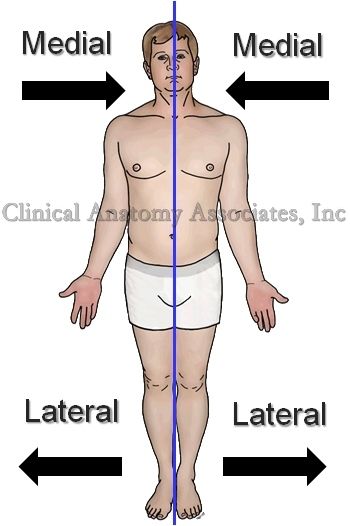
What is Medial
the middle or direction toward the middle of the body
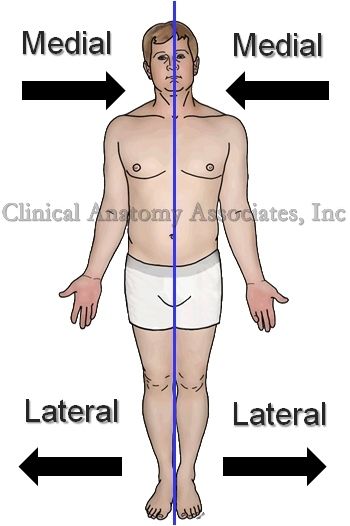
What is Lateral
The side or direction toward the side of the body
What is the Contralateral
Opposite side of the body. Meaning if a disorder is happening to the right or left. Contralateral refers to the opposite side.
What is Ipislateral
Same side of the body. (ex: Tumor on the Right side of brain may effect vision in right eye
Cephalic
Head
Cranial
Skull
Cervical
Neck
Buccal
Cheek
Frontal
Forehead
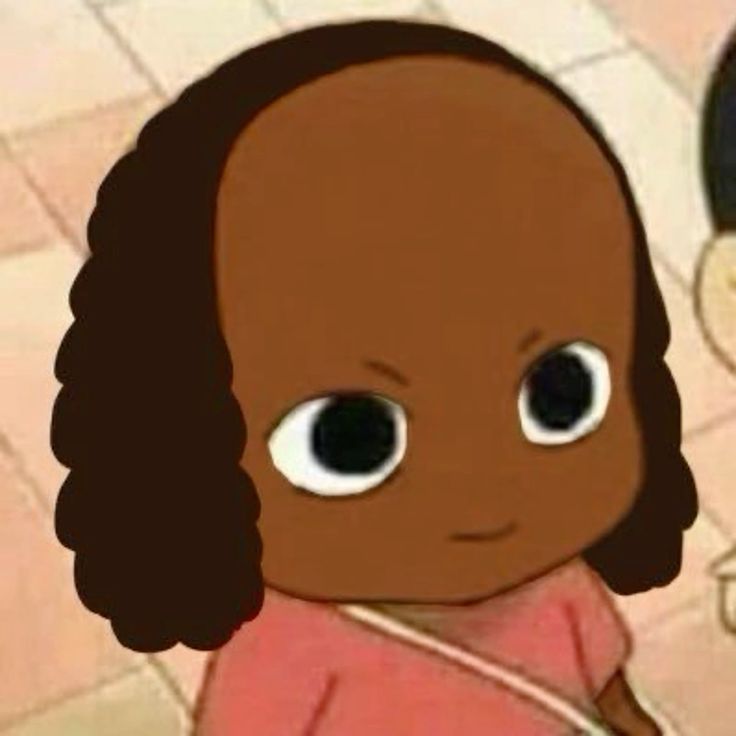

Mental
Chin

Nasal
Nose
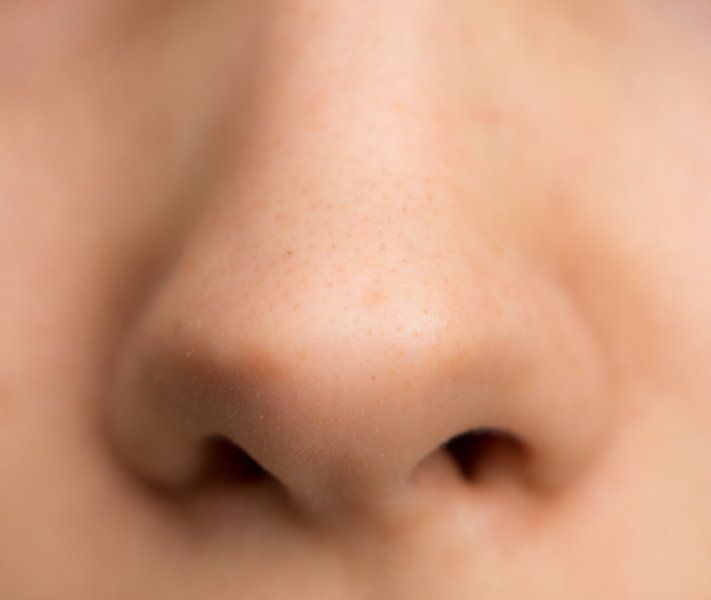
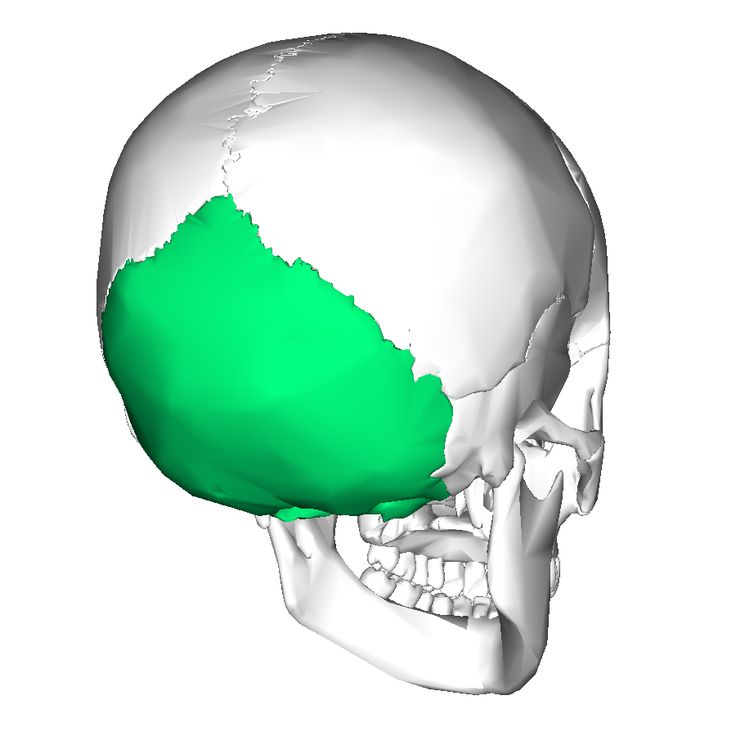
Occipital
Back of skull
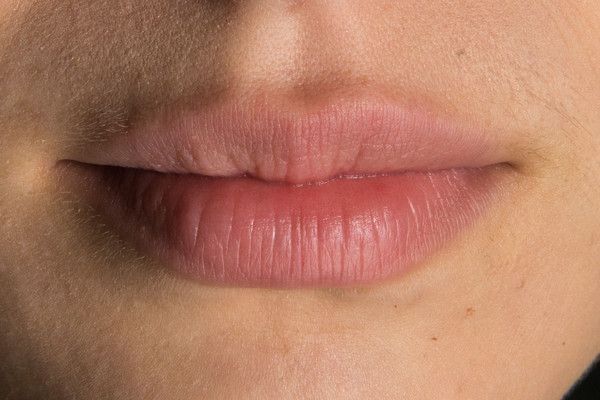
Oral
Mouth
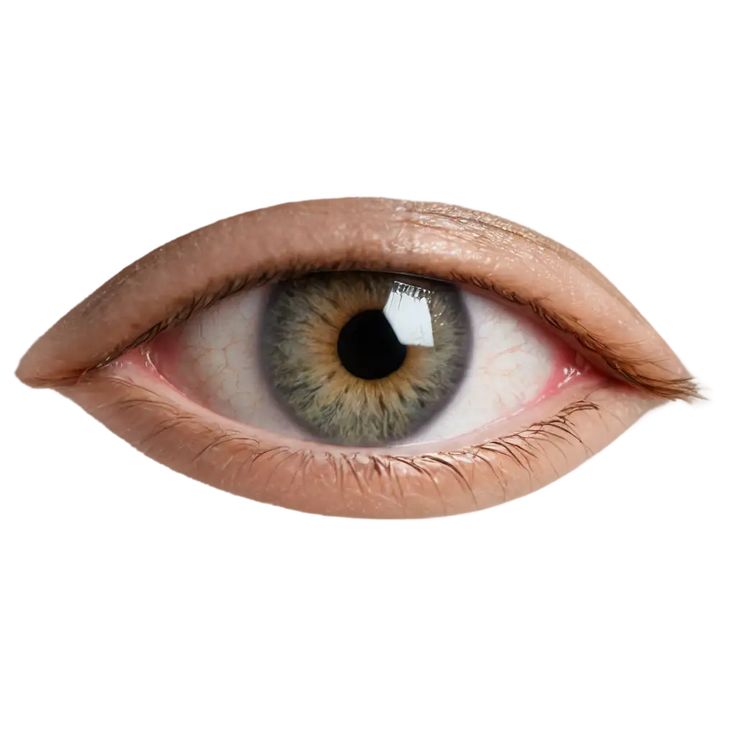
Orbital
Eye
Otic
Ear
Acromial
Shoulder
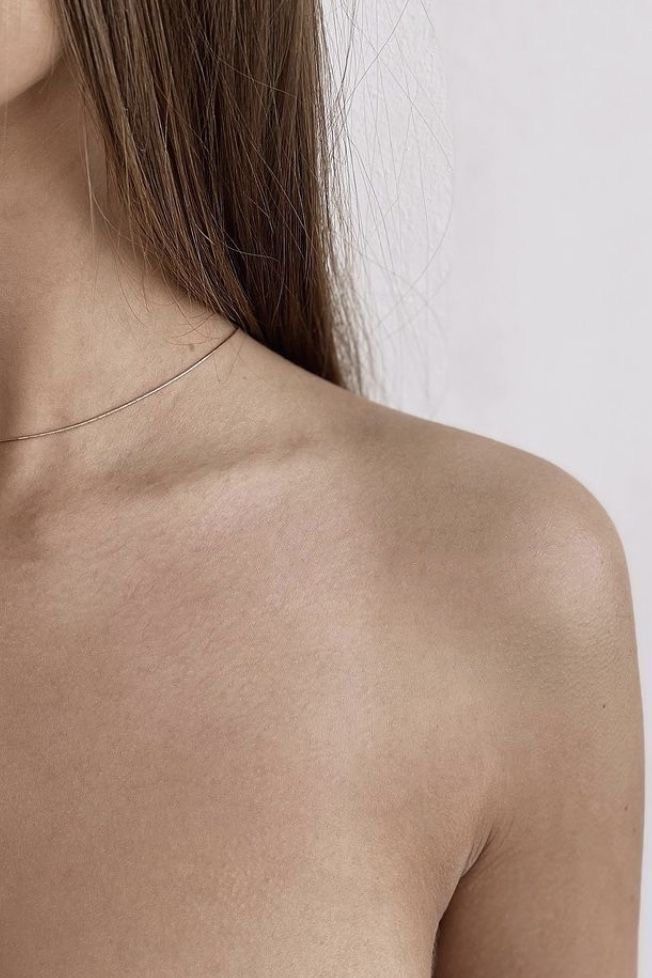

Antebrachial
Forearm
Antecubital
Front of elbow

Axillary
Armpit

Brachial
arm

Carpal
wrist
Digital
Fingers
Manual
Hand

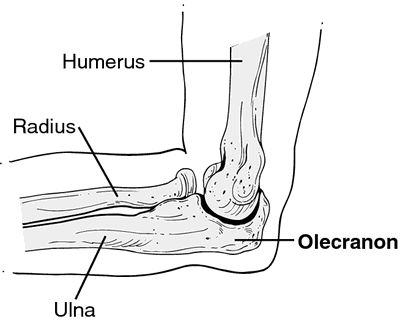
Olecranal
Elbow
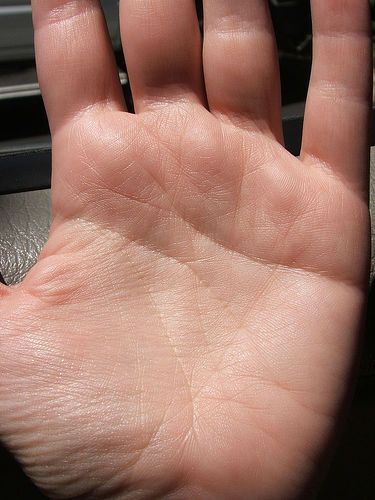
Palmar
Palms
Pollex
Thumb (connective part/ below)
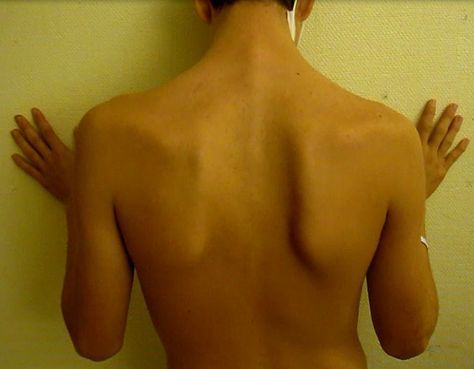
Scapular
Shoulder blades
Thoracic
Chest
Sternal
Breastbone
Mammary
Breast
Abdominopelvic
combined abdominal and pelvic cavities that extend from the diaphragm to the pelvic floor, housing organs like the stomach, liver, kidneys, and reproductive organs.
Abdominal
Abdomen
Coxal
Hip
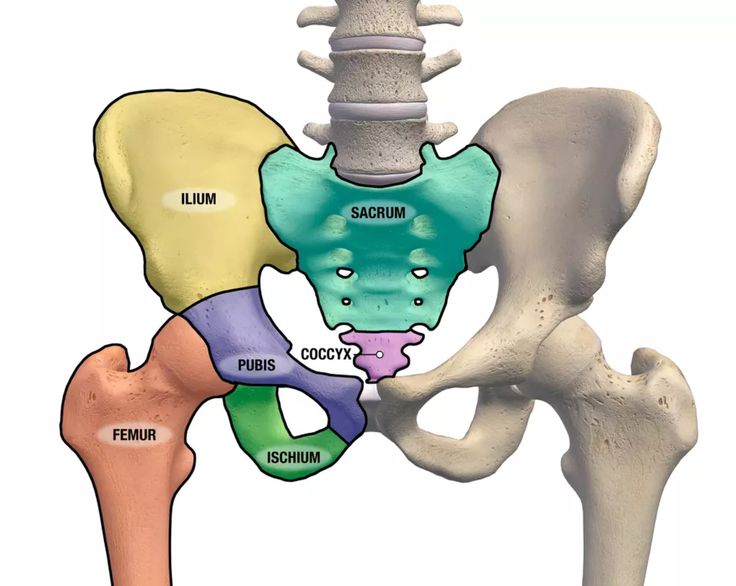
Gluteal
Buttock

Inguinal
groin
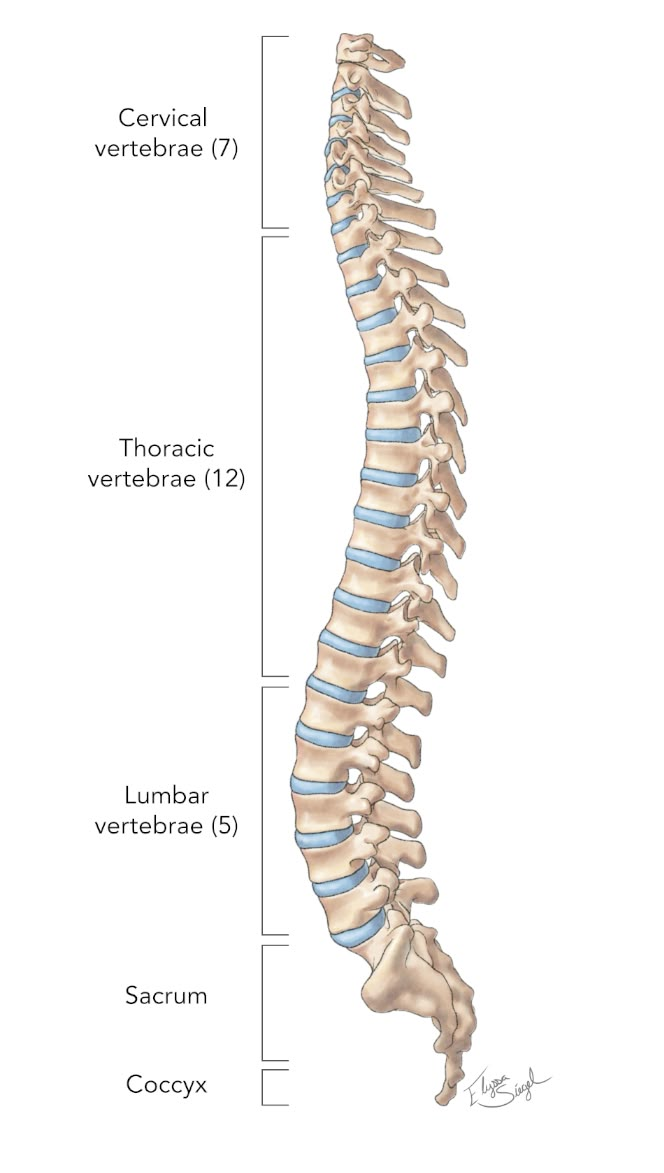
Lumbar
lower part of your back consisting of five vertebrae
Perineal
underlying muscles located between the anus and the genitals
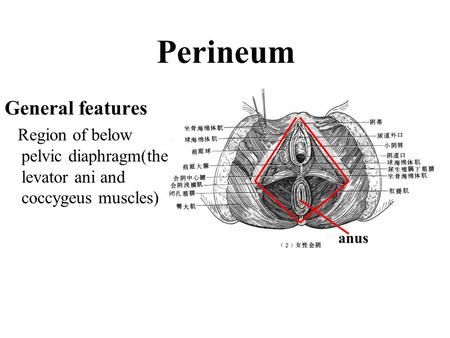
pelvic
pelvis
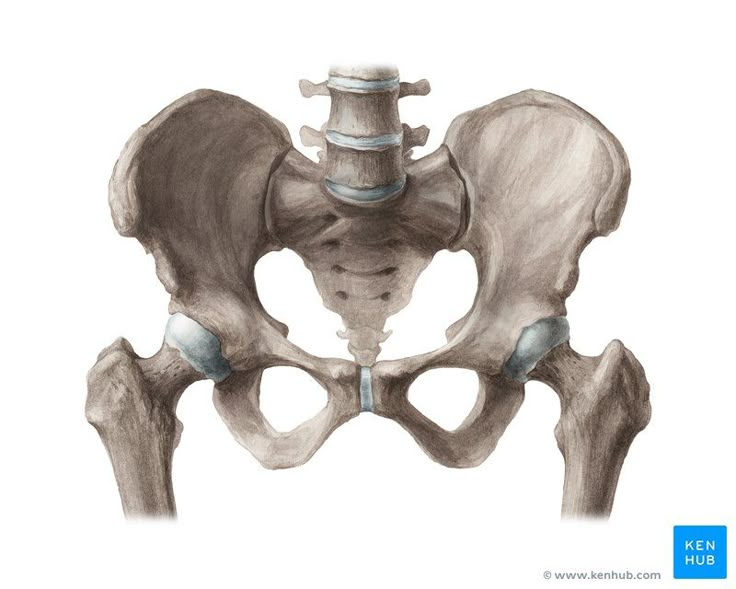
pubic
pubis (relating to the area just above a person's genitals.)

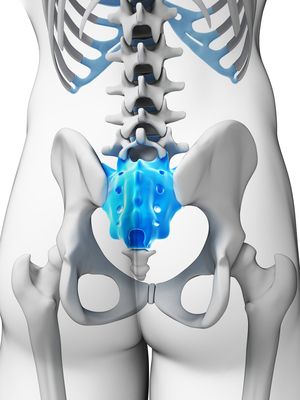
Sacral
triangular-shaped bone located at the base of the spine, between the lumbar vertebrae and the coccyx (tailbone)
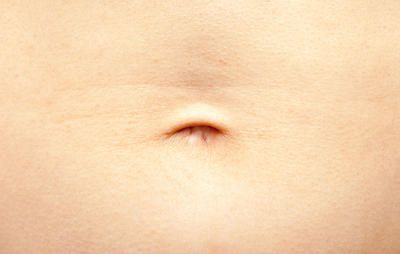
Umbilical
belly button
Vertebral
spine
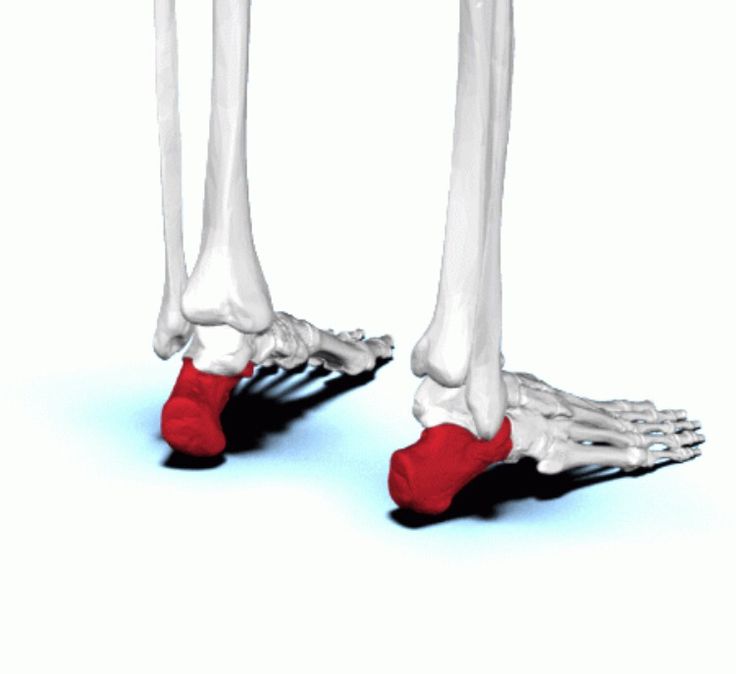
Calcaneal
Heel of foot
Crural
leg/thigh

digital (lower limbs)/ phalanges
toes

Femoral
Thigh
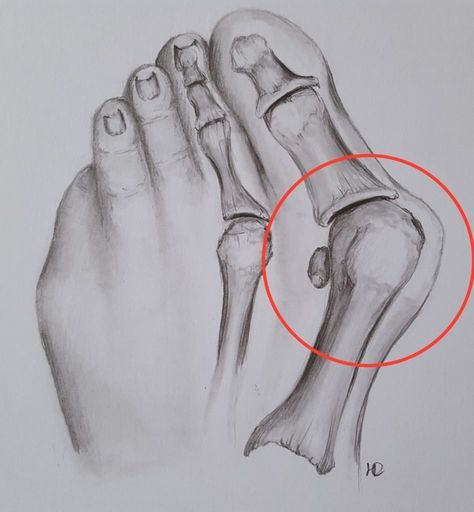
Hallux
Big toe
patellar
kneecap
Pedal
Foot
plantar
sole of foot
Popliteal
Back of knee
Sural
calf
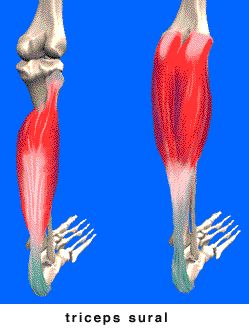
Tarsal
Ankle

What are the Posterior and Dorsal Cavity
Cranial (brain) and Vertebral(Spine)
What are the Anterior (Ventral) Cavity
Mediastinum(sternum) Pericardial cavity (within mediastinum) pleural cavity
What are the Abdominopelvic cavity
Abdominal Cavity -Stomach (largest cavity), digestive organs and Pelvic Cavity -Groin/pelvic, houses reproduction organs
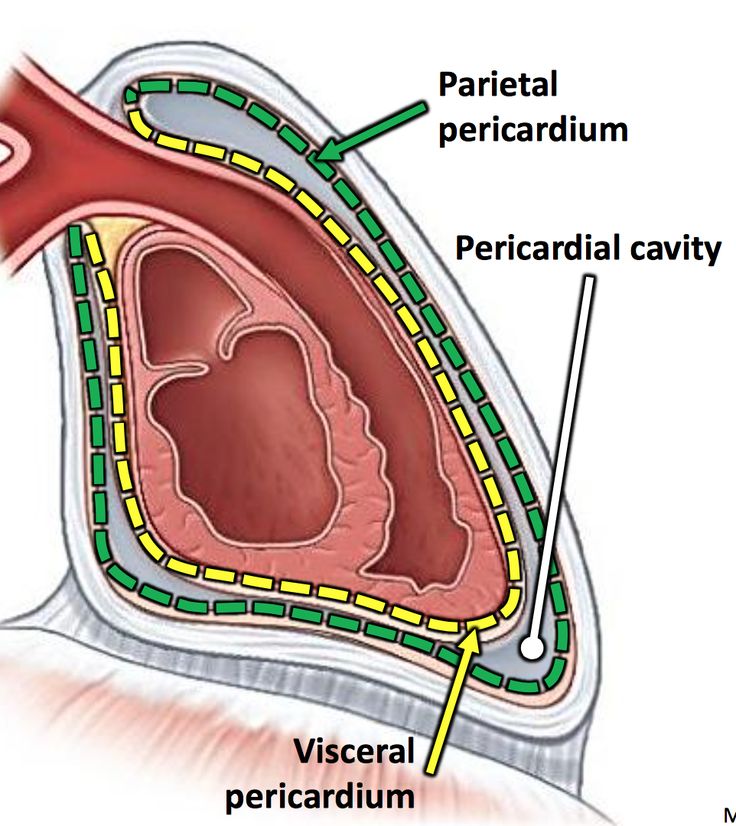
Visceral Pericardium
INNER layer of pericardium, sac like structure that surrounds and protects the heart
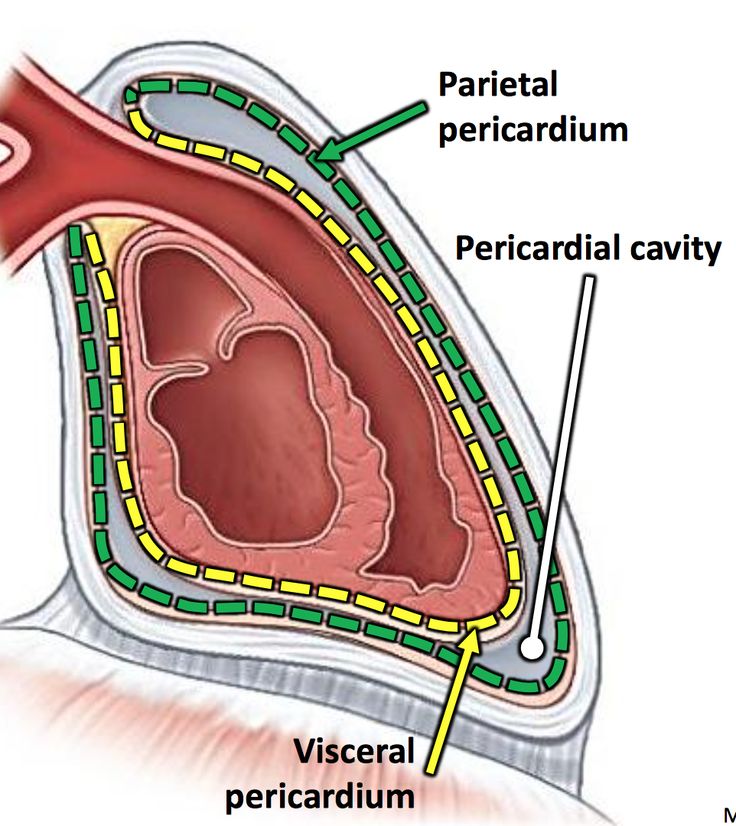
Parietal Pericardium
The OUTER layer of the pericardium, sac like membrane that surrounds and protects the heart
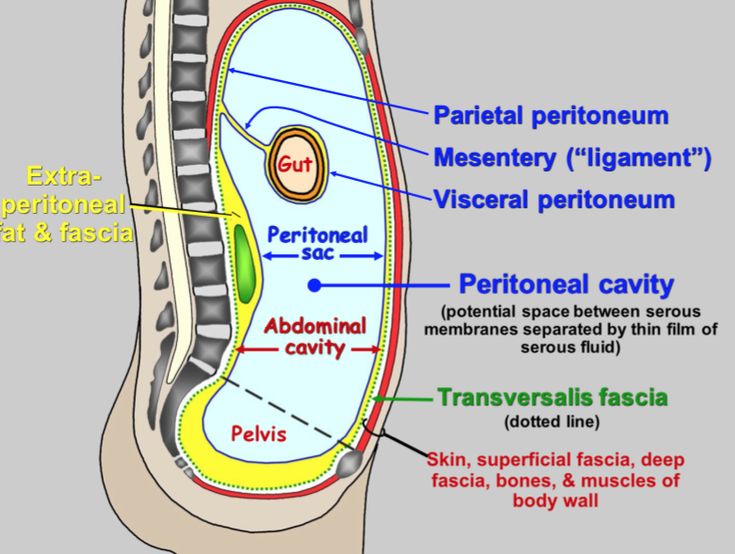
Visceral Peritoneum
Serous membrane lining and supporting abdominal organs (stomach, liver, intestines); includes the parietal peritoneum lining the abdominal wall.
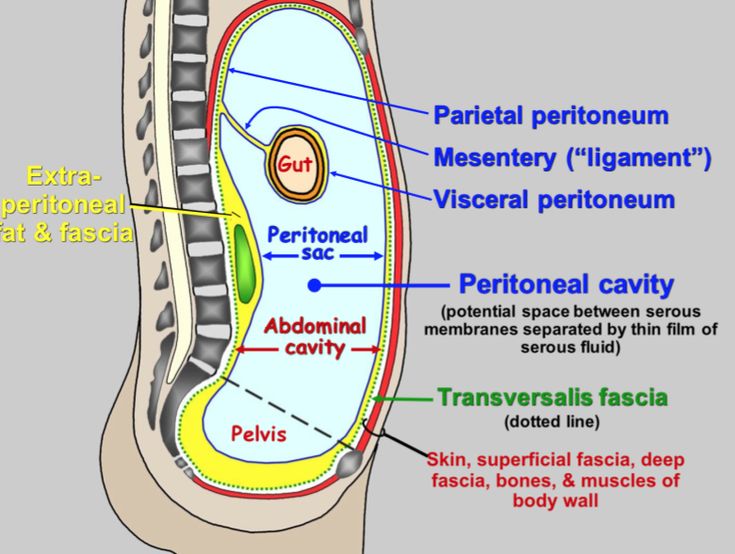
Parietal Peritoneum
OUTER layer of the peritoneum, a serous membrane that lines interal surface of the abdominal and pelvic walls
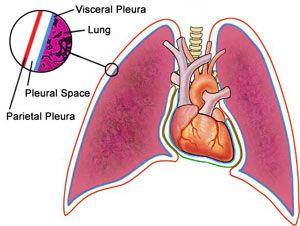
Visceral Pleura
INNER layer of the pleura two layered membrane that surrounds and separates the lungs from the chest wall
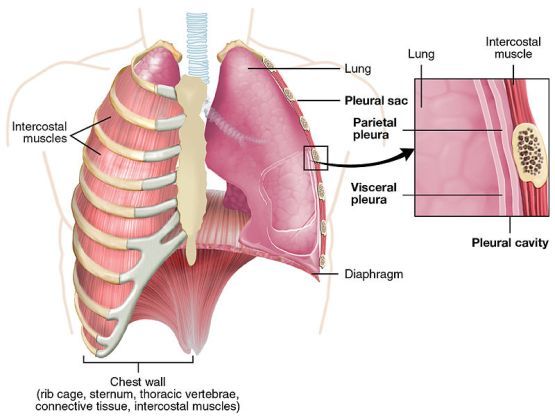
Parietal Pleura
thin serous membrane that lines the inner surface of the thoracic
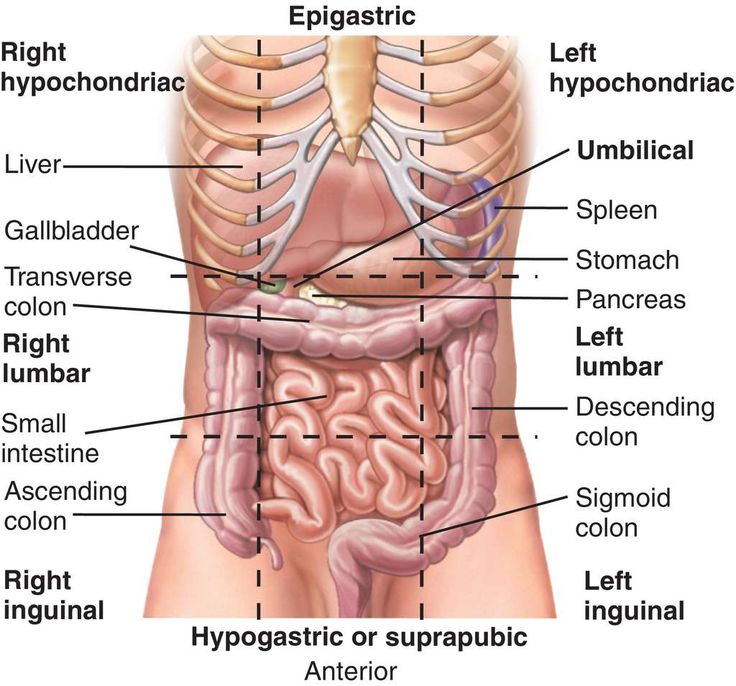
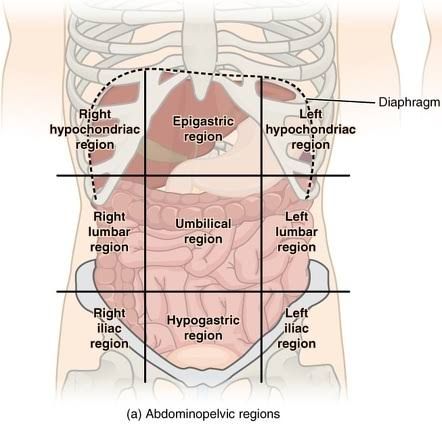
Epigastric
the upper central area of the abdomen, just below the sternum
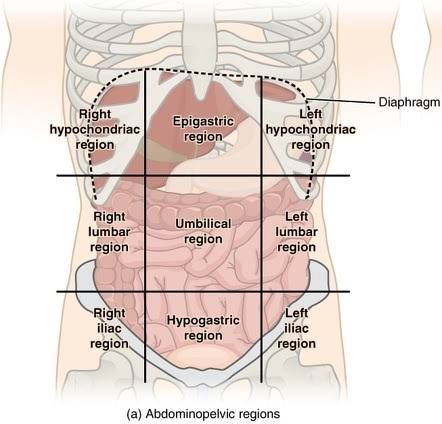
Hypogastric (pubic)
Region below the Umbilical
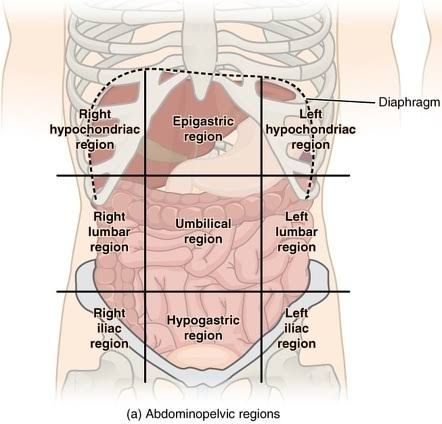
Right Hypochondriac
The ride side of the abdominal cavity on the right side of the epigastric
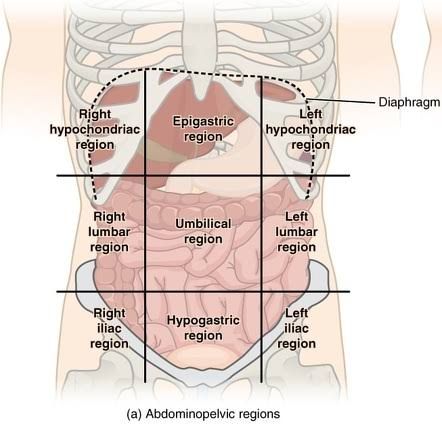
Left Hypochondriac
Left side of the stomach on the left side of the epigastric
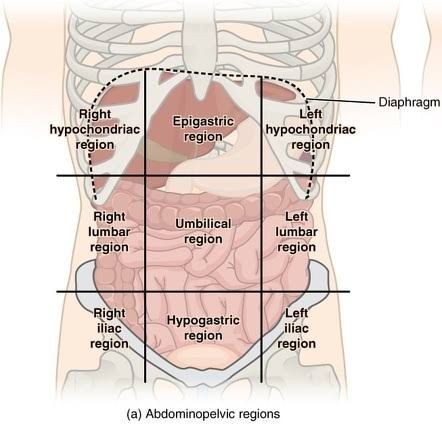
Right lliac (inguinal)
The region below the right lumbar region beside the hypogastric region
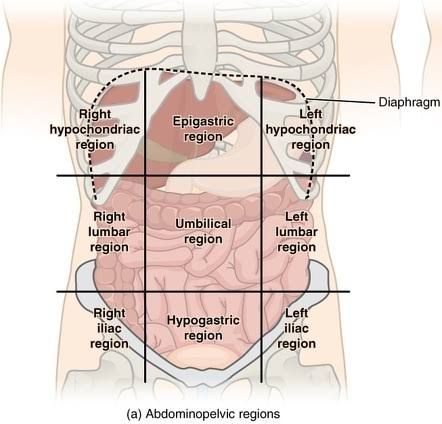
Left lliac (inguinal)
On the left side of the hypogastric region below the left lumbar
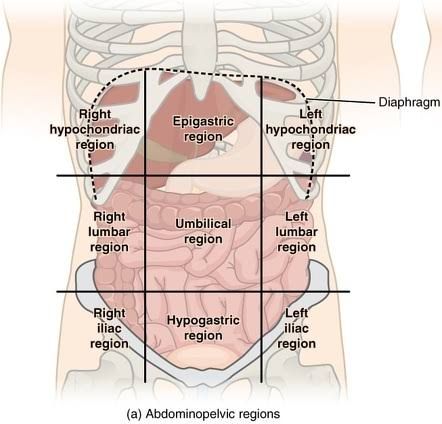
Umibilical region
Region in the middle where your naval is
Which one is Coronal (frontal)
One facing forawrd/ straight ahead. you can see the front veiw of the person
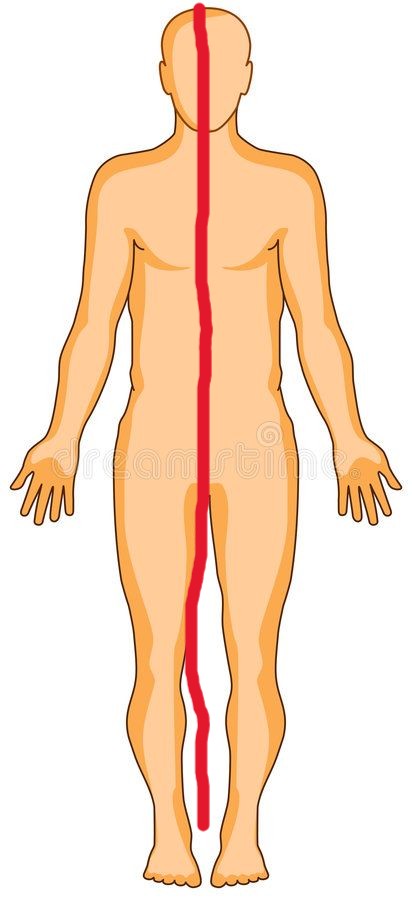
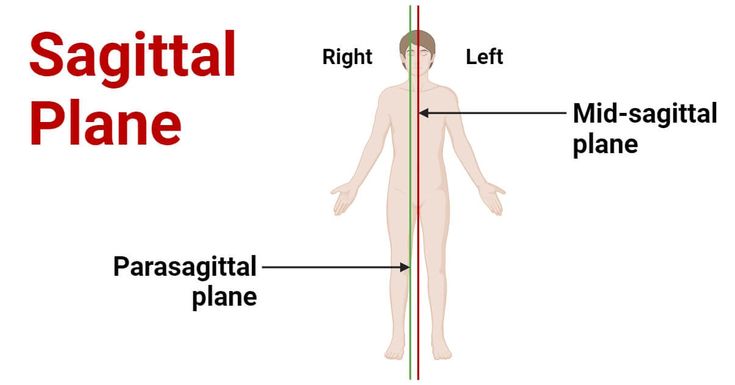
Midsagittal (median)
The a line that runs through the center of the body. straight down middle
Parasagittal
plane divides the body into unequal left and right portions, essentially running alongside the midline.
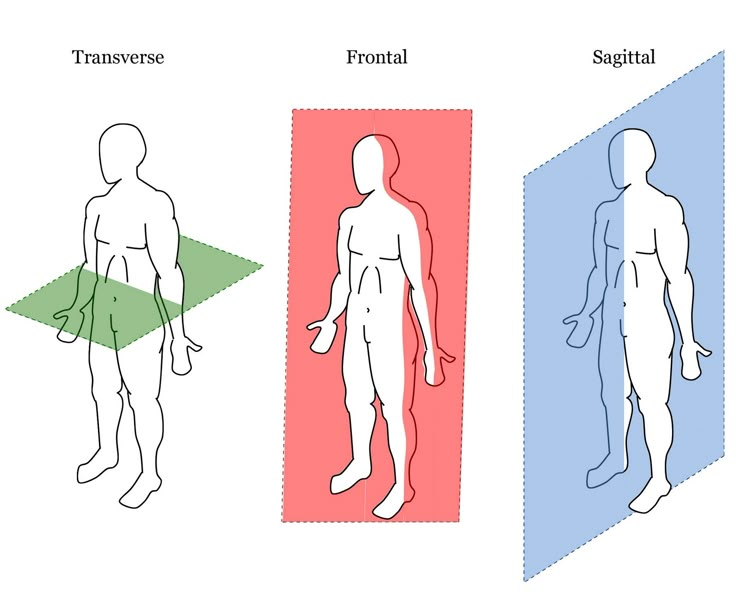
Sagittal plane
divides body vertically left and right
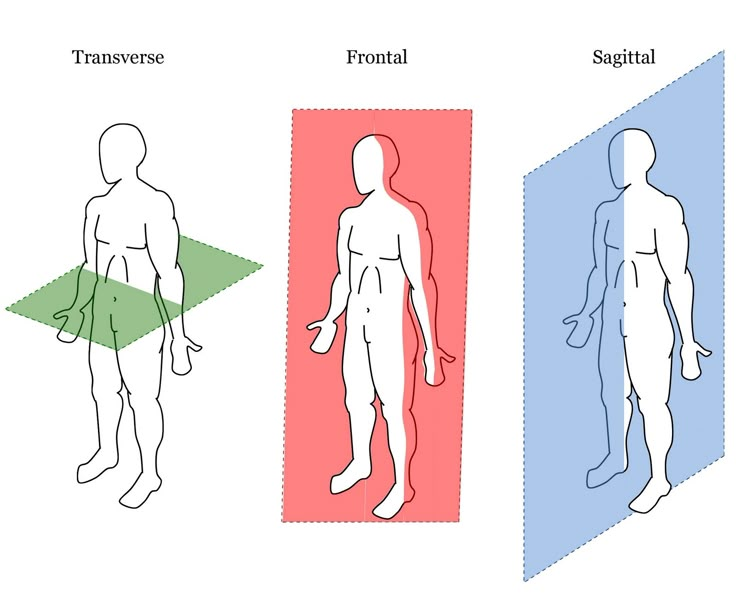
Transverse plane
divides horizontally into upper and lower sections
What are the primary organs of the Integumentry system
skin,hair,nails, sebaceous gland (oil), and sudoriferous (sweat), Apocrine gland.
What is the function of hair
protects from dust,sun and other particles. Sensory dection, thermoregulation, communication
What is the function for Nails
Protects finger tips and toes and body parts that experience maximum mechanical stress
What is the function of the Sebaceous gland (oil)
Lubricates and waterproofs the skin and hair, preventing water loss from the skin in low-humidity environments. They excrete sebum, an oily substance that keeps the skin moisturized.
What is the function of the sudoriferous gland (sweat)
cools the body, eccrine sweat gland is sweat thermoregulation, helps to maintain homeostasis.deters microbes from over colonizing the skin surface by generating dermicidin, which has antibiotic properties
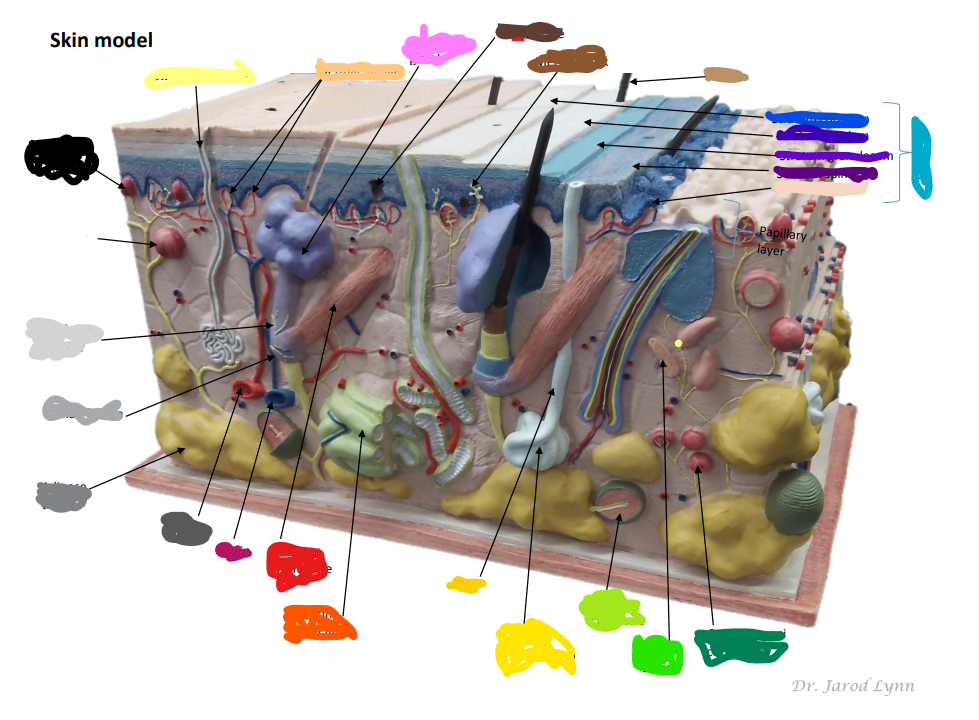
Where is the Epidermis in the model of skin
light blue by the purples -The outer layer of skin, made up of four (thin skin) or five (thick skin) layers of epithelial cells. Does not have blood vessels within. It is Avascular.
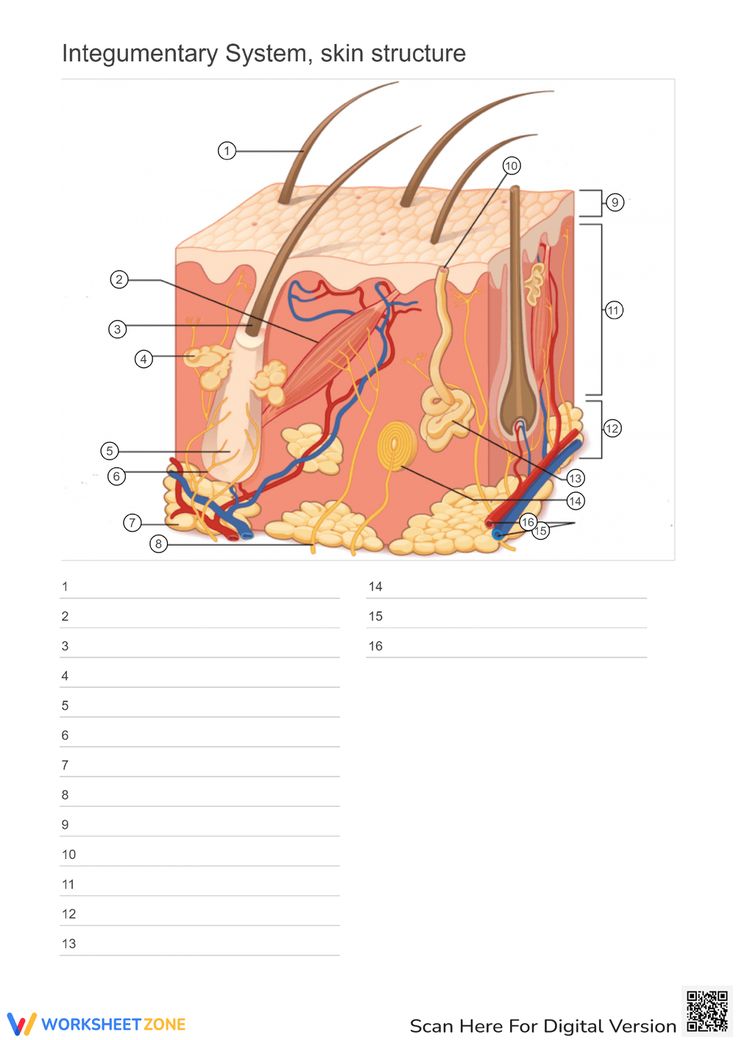
Looking at the Model Where is the Dermis in the Model of skin
11 - “core” of the integumentary system. Contains blood and lymph vessels, nerves, hair follicles, and sweat glands. Made up of 2 layers of connective tissue that compose
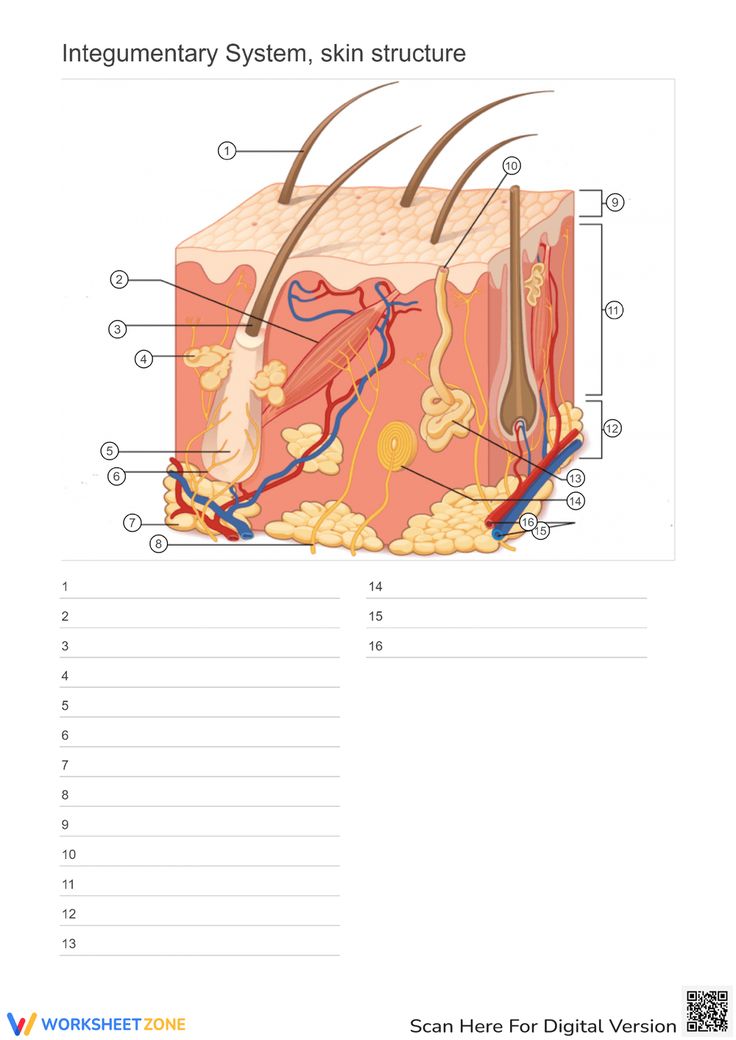
Looking at the Model Where is the Hypodermis in the Model of skin
12- The “subcutaneous layer” of “superficial fascia” is a layer below the dermis, and it serves to connect the skin to the underlying fascia (fibrous tissue) of the bones and muscle. Consists of well-vascularized, loose areolar connective tissue and adipose tissue, which function as a fat storage providing insulation and cushion for the skin/ integument.
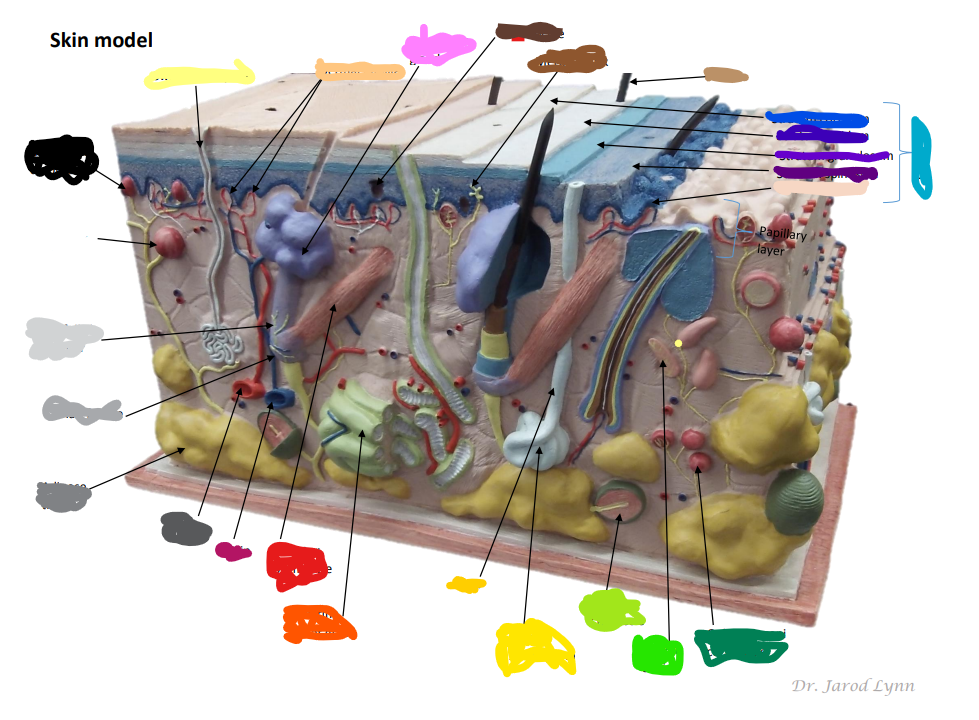
Looking at the Model Where is the Eccrine sweat gland in the Model of skin
brightest yellow closer to the green- thermoregulation which helps maintain homeostasis
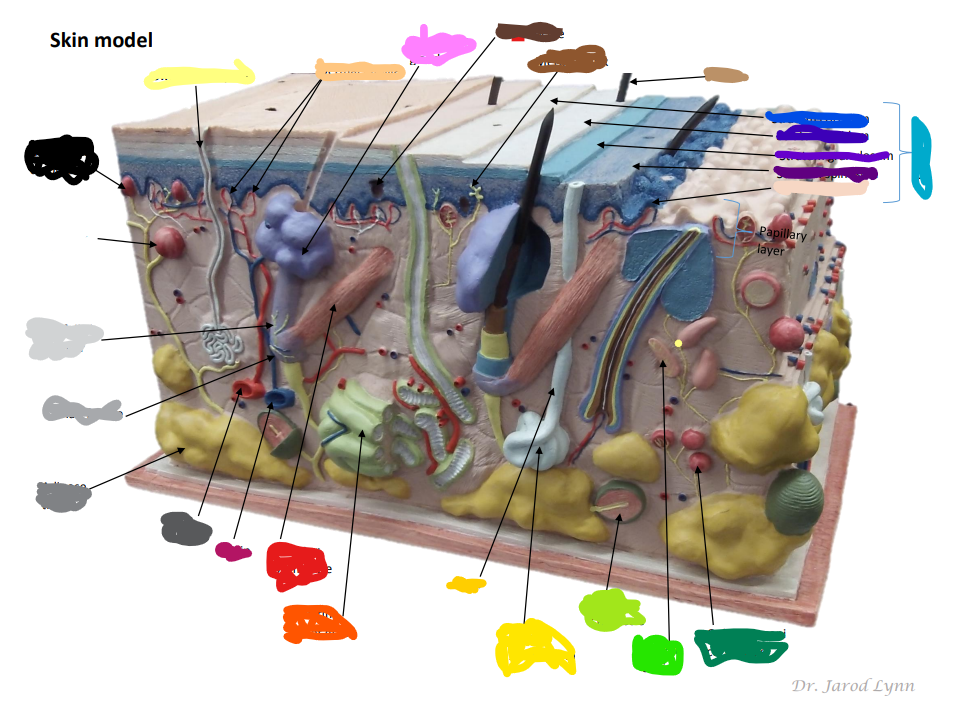
Looking at the Model Where is the Pacinian Corpuscle in the Model of skin
brightest green
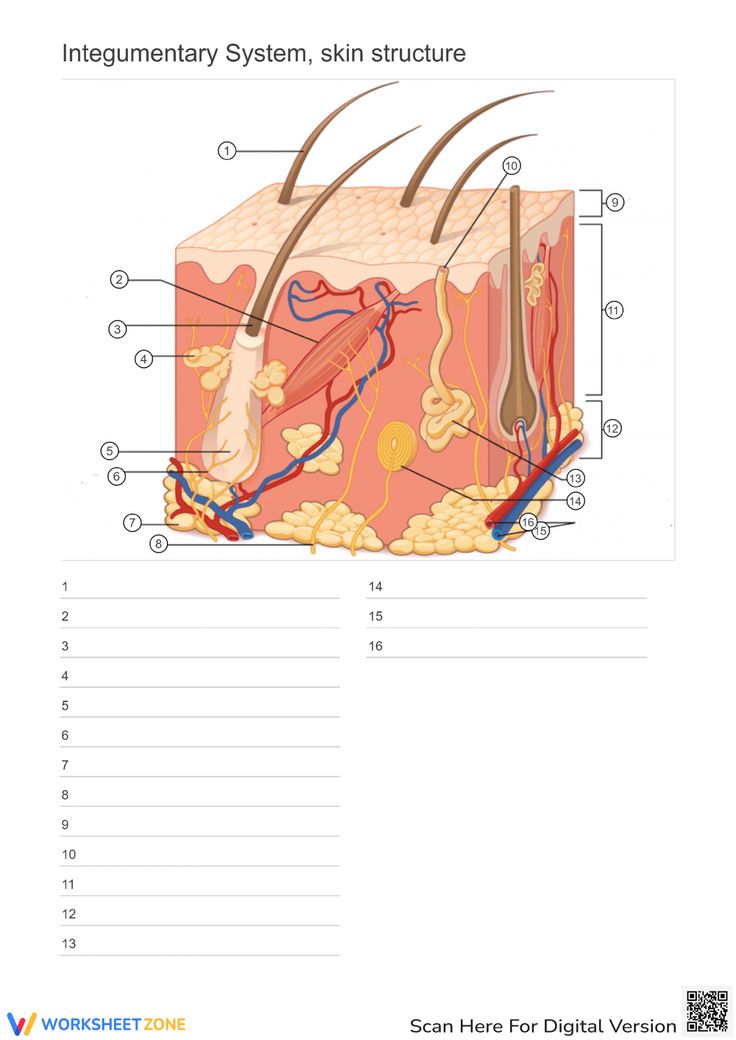
Looking at the Model Where is the Cutaneous vascular plexus in the Model of skin
14
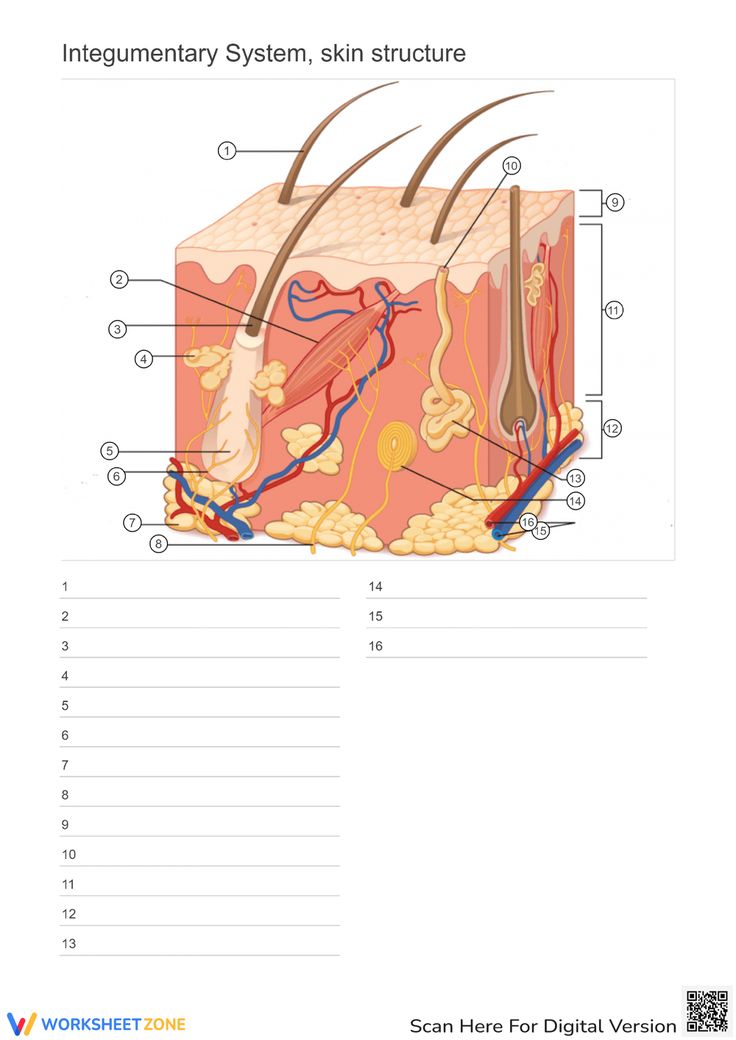
Looking at the Model Where is the sensory nerve fiber in the Model of skin
8
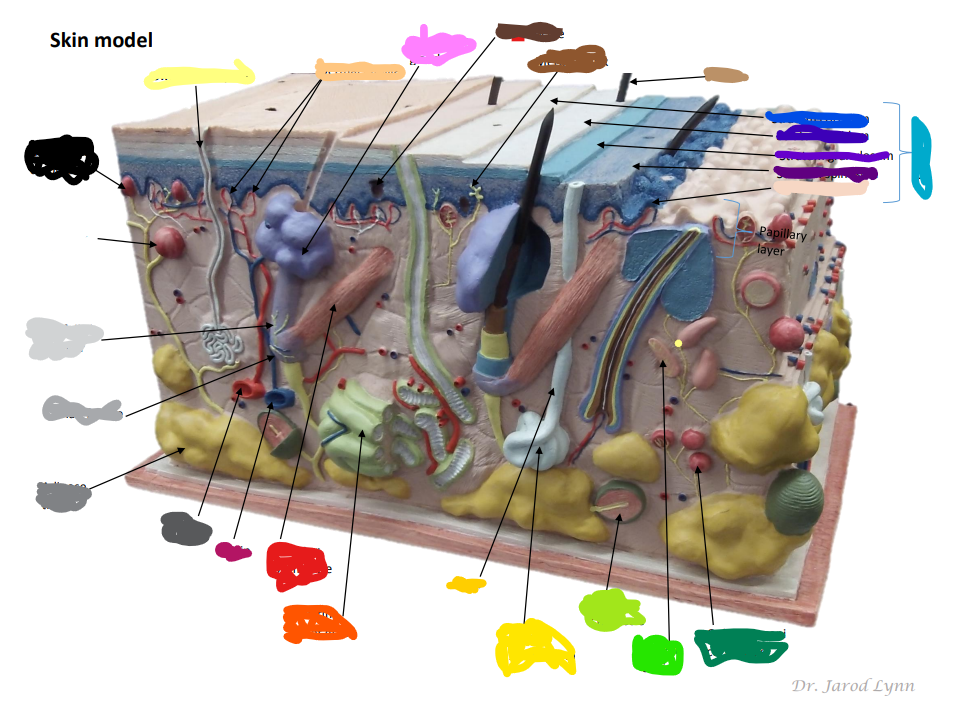
Looking at the Model Where is the adipose tissue in the Model of skin
darker grey. right below medium gray
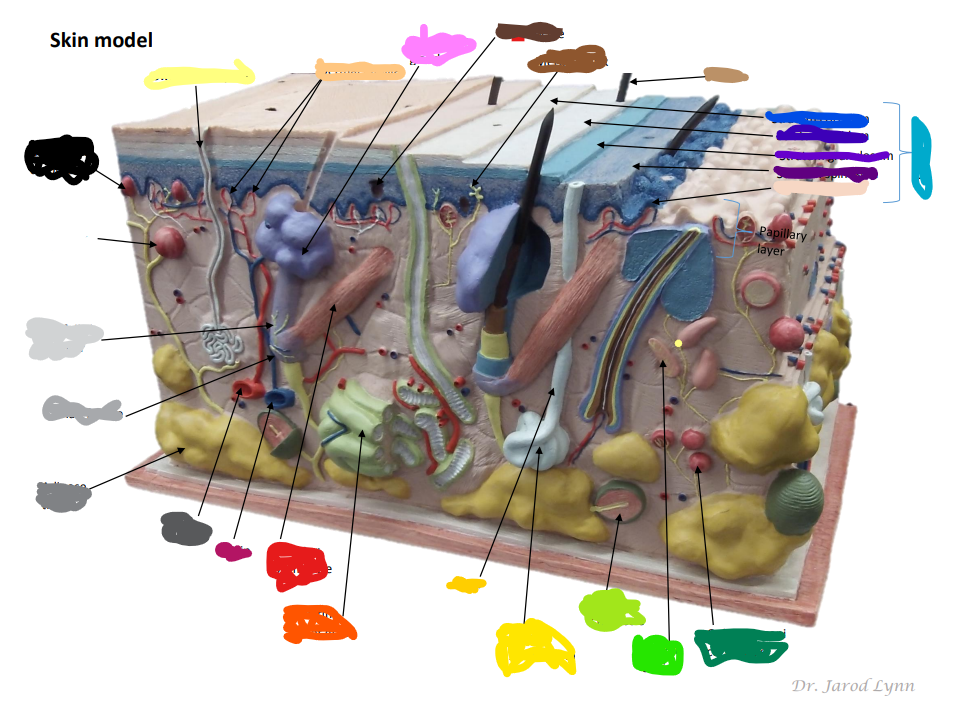
Looking at the Model Where is the hair follicle in the Model of skin
medium/light gray