Anatomy 2320 - Axial Skeleton: Skull
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
8
How many cranial bones are there?
14
How many facial bones are there?
Calvaria
The upper dome-like portion of the skull, which forms the upper portion of the cranial cavity
Upper portion of frontal bone, parietal bones and upper portion of occipital bone
What bones form the calvaria?
Nasal septum
divides nasal cavity
mucas and cilia
What lines the hollow paranasal sinuses?
Sphenoidal, Maxillary, Frontal, Ethmoidal
The four paranasal sinuses
supraoribital margin
prominent bony ridge over orbits
supraorbital foramen
Allows for passage of nerves and blood vessels to the eyes
frontal sinuses
pair of sinuses within frontal bone
Age 6, Age 10
When do the frontal sinuses begin to appear? When do they fully develope?
frontal sinus
Which sinus has a unique pattern so it is able to be used in forensics?
Frontal crest
a midline elevation of bone on the internal anterior surface of the frontal bone
Falx Cerebri
What does the frontal crest and crista galli serve as attachments for?
Sagittal suture
What divides the two parietal bones?
Coronal suture
What separates the frontal bone from the parietal bones?
squamosal suture
What separates each parietal bone from its adjacent temporal bone?
Petrous Region
region of temporal bone that houses structures of middle and inner ear
Otitis Media
infection of the middle ear
Carotid canal
Within the petrous region of the temporal bone, allows for passage of blood vessels that supply the brain
Foramen lacerum
Located between the petrous portion of the temporal bone, sphenoid bone and occipital bone (FLOST). Closed off by connective tissue in living persons
Jugular foramen
located between the temporal and occipital bones, allows for drainage of blood from the brain via internal jugular vein
Mastoid Region
rounded portion of the temporal bone which can be easily felt as the bony knob immediately behind your earlobe
Mastoid process
location on the skull that serves as attachment for muscles that flex the neck or rotate head
Mastoiditis
Prolonged middle ear infections may spread to mastoid air cells causing...
Squamous Region
lateral flat surface of each temporal bone immediately inferior to the squamosal suture
Tympanic region
small area surrounding the outer entrance to the external auditory canal
Styloid process
serves as attachment point for muscles of tongue and ligaments connecting to hyoid bone
Lambdoidal suture
separates the occipital bone from the two parietal bones
Occipital condyles
On either side of foramen magnum, articulate with atlas. Allows head to nod "yes"
Superior nuchal line and inferior nuchal line
two prominent horizontal ridges on posterior portion of occipital bone, serve as attachment sites for neck muscles
Internal occipital crest
On the internal posterior portion of occipital bone, serves as attachment point for falx cerebri
falx cerebri
"sickle shaped" sheet of connective tissue that separate the two hemispheres of the brain
Sphenoid bone
often referred to as the bridging bone, also resembles a bat or butterfly with outstretched wings
Sphenoidal sinuses
Sinuses of sphenoid bone that drain into the nasal cavity
hollow
Because the sphenoid is ___, it may be fractured from head trauma
sella turcica
prominent depression on superior medial portion of sphenoid bone
pituitary stalk
Because the pituitary gland is so well anchored, sudden traumatic shifting may sever the...
Optic foramen
Allows passage of the optic nerve (part of sphenoid)
foramen rotundum
Allows passage of one of the three branches (second branch) of the trigeminal nerve (V) that conveys sensations from teeth and gums of maxillae
Second division nerve block
name for injection of anesthetic not far below foramen rotundum that desensitizes all upper teeth on one side of maxilla
Foramen ovale
allows passage of the third branch of the trigeminal nerve (V) that conveys sensation from the teeth and gums of the mandible
Foramen spinosum
small opening for meningeal blood vessels
Superior orbital fissure
allows passage of several cranial nerves, including first branch of trigeminal, that convey sensation the nose, forehead and anterior scalp
Cirsta galli
superior part of the ethmoid bone that exhibits a midsagittal elevation
Falx cerebri
The crista galli serves as an attachment for...
cribriform plate
immediately lateral to each side of the crista galli, has numerous foramina that allow passage for fibers of olfactory nerves (I) to travel from nose to brain
Perpendicular plate
inferior midline projection of ethmoid bone, forms superior part of nasal septum
Superior and middle nasal conchae
two projections of the ethmoid located on both lateral walls of the nasal cavity
inferior nasal conchae
Nasal conchae that is not part of the ethmoid, but are independent facial bones
mucous membrane and erectile tissue
All the nasal conchae are covered with...
Zygomatic
forms bony prominence of cheeks
lacrimal bones
paired bones that form part of the medial wall of each orbit
lacrimal groove
A small depressed inferior opening in the lacrimal bone that provides a passageway for the nasolacrimal duct, which drains tears into the nasal cavity. Explains why nose runs when you cry
Nasal bones
paired bones where your glasses would sit
vomer
a triangular bone that joins perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone to form bony part of nasal septum
Palatine bones
forms the posterior third of the hard palate and contribute to the posterior walls and floor of nasal cavity, as well as make a small contribution to floor of orbits
Craniosynostosis
the premature fusing of the skull bones
scaphocephaly, or dolicocephaly
A child with sagittal synostosis develops a very elongated, narrow skull shape called...
Plagiocephaly
term for asymmetric head shape where one part of the skull (usually the frontal or occipital region) has an oblique flattening
Infraorbital foramen
Large hole providing passage for blood vessels and nerves on the maxilla
Palletine processes
There are two ____ ____ of the maxillae that project horizontally and form anterior portion of hard palate
Cleft palate (may be accompanied by cleft lip)
The failure of the palatine processes to join during early prenatal development (about 10-12 weeks)
Maxillary sinus
Sinus lateral to nasal cavity, drains into nasal cavity through opening high and medial within sinus that exits inferior to midline of middle nasal conchae
Crepitus
Crackling sound caused by gas or grinding broken bone pieces beneath skin, can be caused by fracture of maxillary sinus
Blowout fracture
A fracture of the bone that supports the orbit causing the eye and/or eye muscles to drop down into the maxillary sinus
Occlude
Term for the teeth of the mandible and maxilla lining up properly
Mentum
The anterior point of the mandible
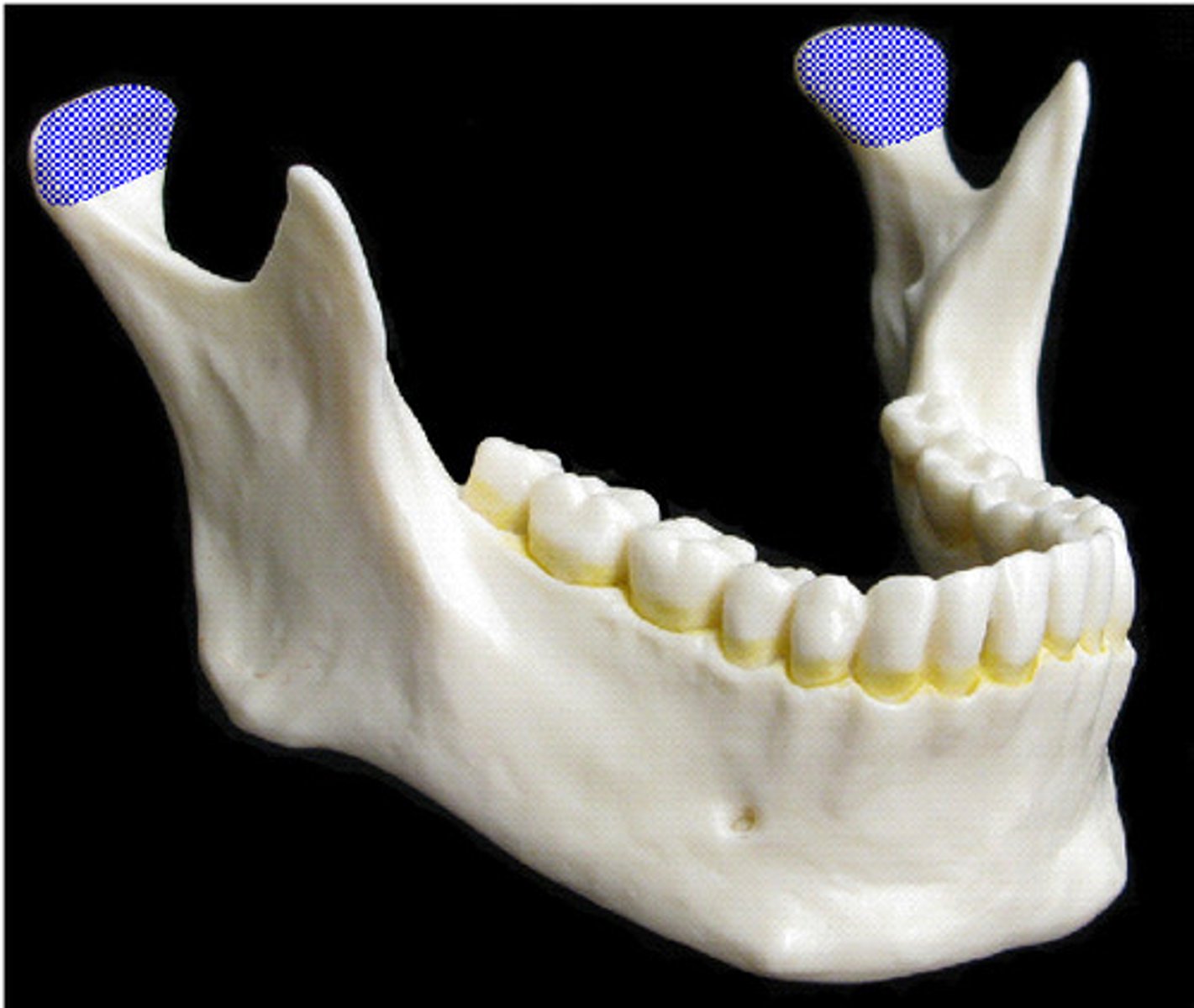
mandibular condyle
Name this highlighted bony landmark.
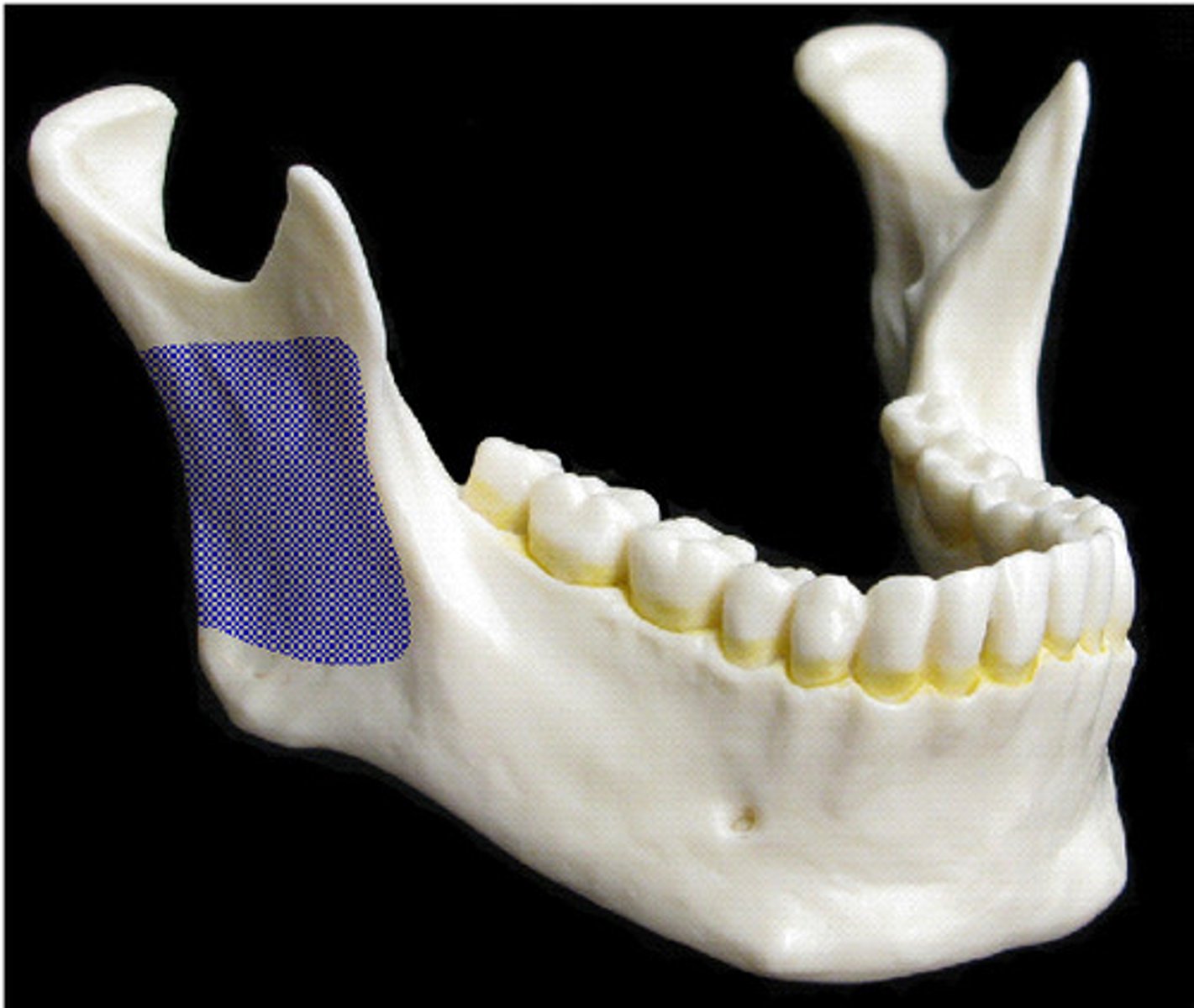
Ramus
Name this highlighted bony landmark
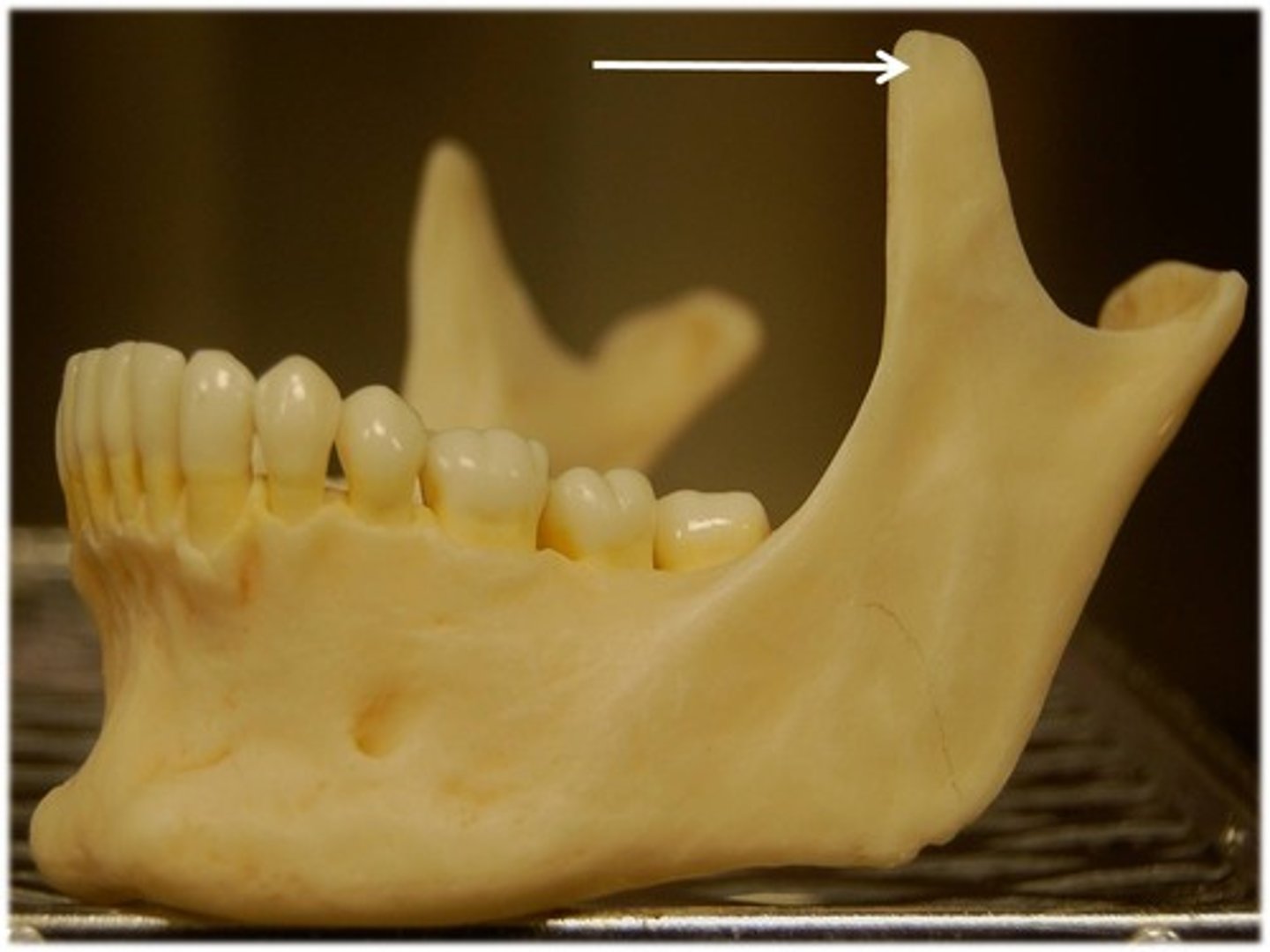
coronoid process
Name this part of the mandible
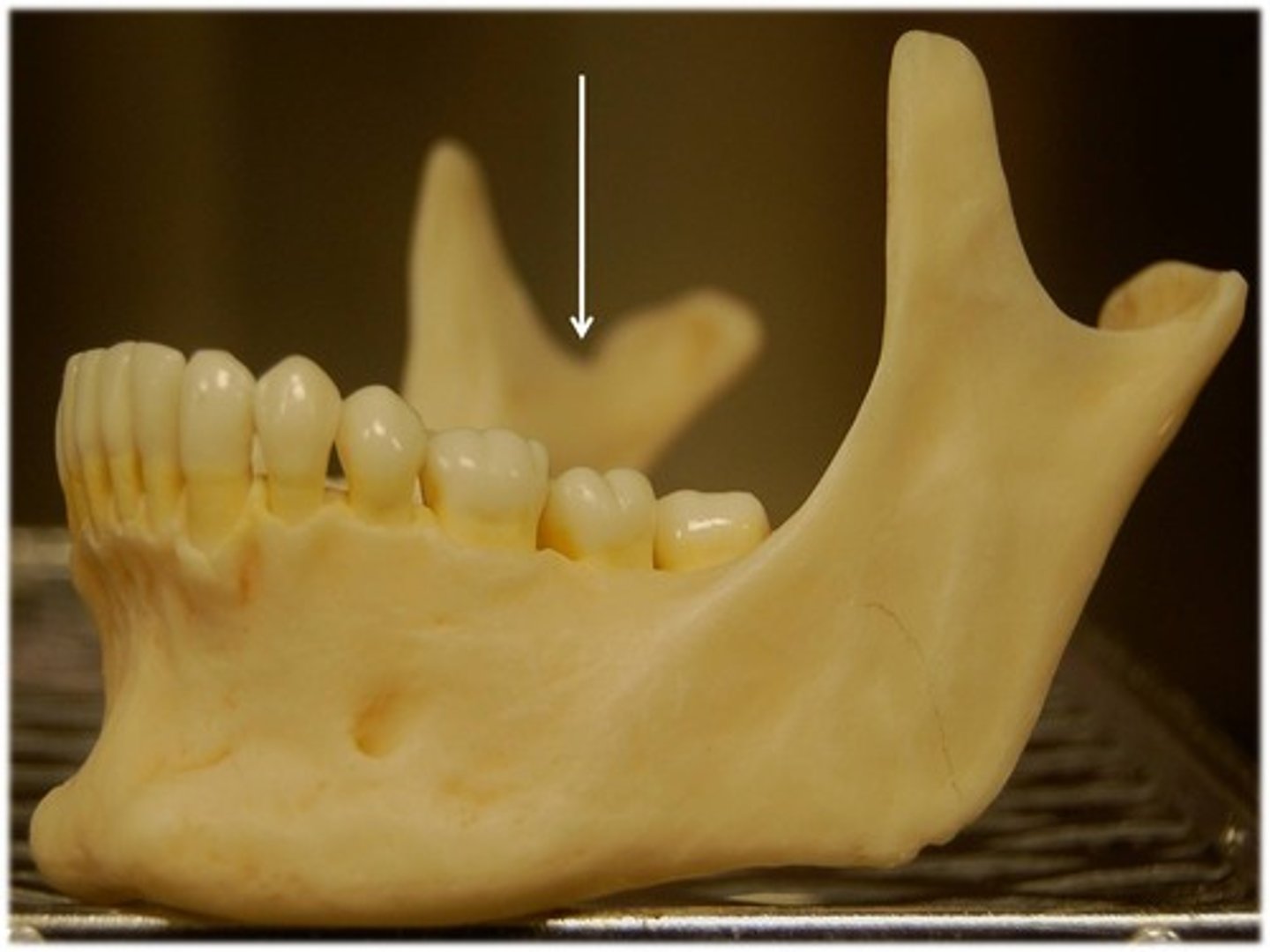
mandibular notch
Name this part of the mandible.
angle of the mandible
Name this bony landmark.
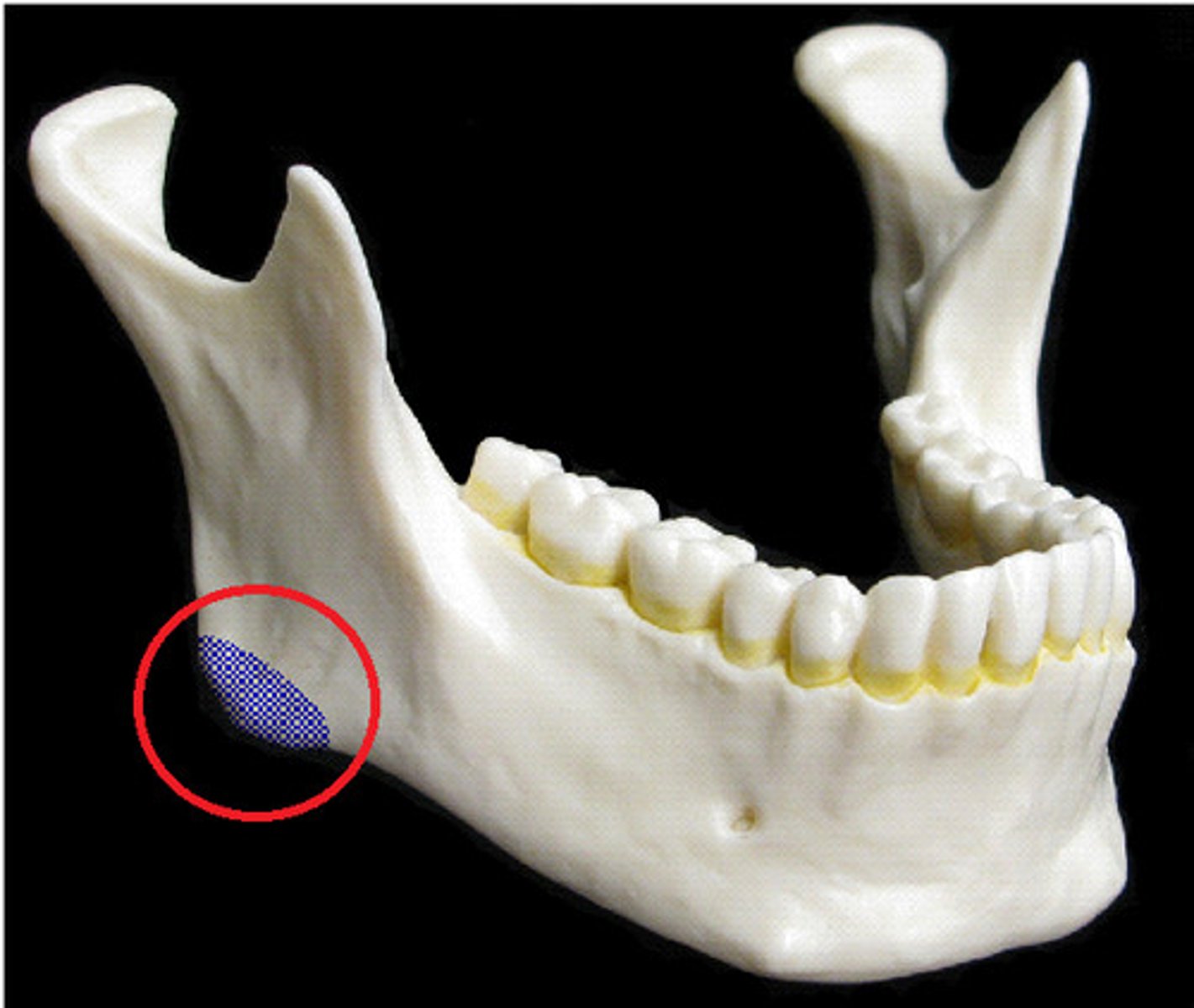
Mental foramen
Name this opening.

Mandibular foramen
Name this bony landmark.
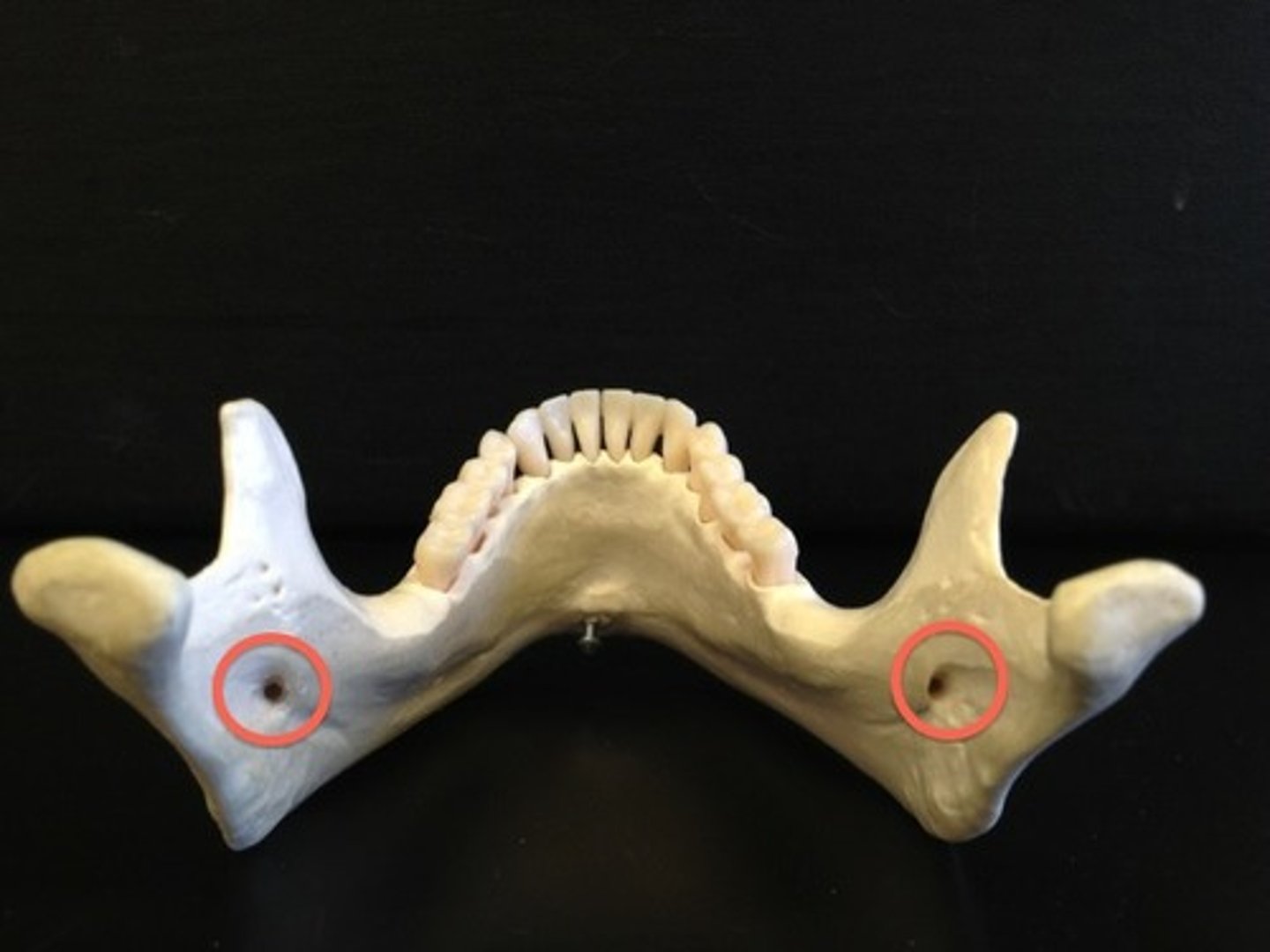
Mandibular foramen
Allows passage of the third branch of the trigeminal nerve (V) on mandible, conveys sensation from the teeth and gums of the mandible
Third division nerve block
Mandibular teeth and gums can be desensitized by an injection of anesthetic near the mandibular foramen
Roof
Part of nasal complex formed by nasal bones, cribiform plate of ethmoid, and parts of frontal and sphenoid
Floor
Part of nasal complex formed by palatine processs of maxillae and horizontal plates of palatine bones
Walls
Part of nasal complex formed by ethmoid, maxillae, inferior nasal conchae, palatine bones and lacrimal bones
Nasal septum
Area formed by septal nasal cartilage, perpendicular plate of ethmoid and vomer
Humidify/warm air, give resonance to voice, and lighten skull
What are the three purposes of the paranasal sinuses that are mentioned
Bones that contribute to the oribits
What is "many people see zebras falling like elephants" a mnemonic for
Malleus, Incus, Stapes
List the auditory ossicles from superficial to deep
Fontanelles or Fontanels
Six large membranous areas of the skull providing space space between developing bones
Molding
Term for the shifting of one parietal bone over the other and the occipital sliding underneath to shrink the head during parturition
Dehydration; Meningitis and increased intracranial pressure
____ may lead to sunken fontanels. ________ may lead to bulging fontanels.
Dental attrition
Term for when teeth begin to wear down or are lost with age
The bone that covers the alveoli and roots of teeth become less prominent and eventually disapear
Explain what happens to the mandible and maxillae when a person loses some or all of their teeth
20s to 30s, 40s, late 60s or not at all
When does the coronal suture first fuse? Sagittal suture? Squamosal suture?