ZOO 14 – Osmoregulation and Excretion
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Osmoregulation
Animals must maintain appropriate levels of solutes and water in their tissues in order to function
Osmoregulation
regulation of water volume and salt concentration inside the animal body
Osmoregulation
at the cellular level, the cell membrane regulates entry and exit of molecules
Hypotonic
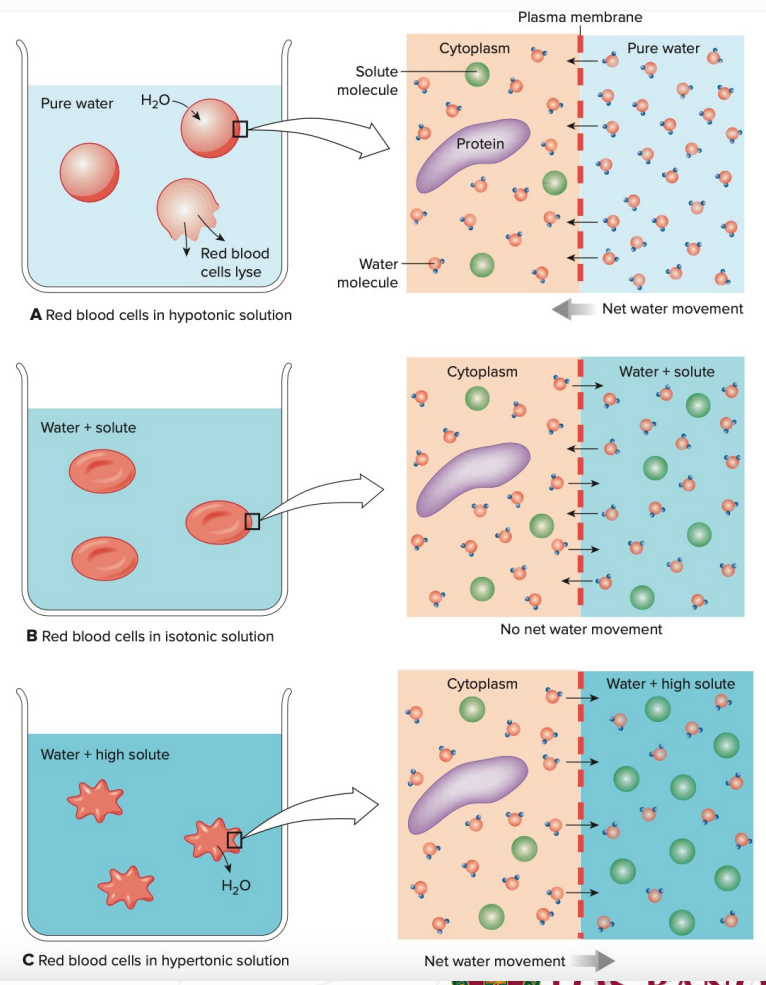
_____________ environment - cell bloats beyond its normal size
Isotonic

_______________ environment – cell maintains its shape
Hypertonic

________________ environment – cell shrinks as the net movement of water is out of the cell
Osmoconformers
Type of animals based on their osmotic regulation
match their body’s osmolarity to their environment
Osmoconformers

Type of animals based on their osmotic regulation
Most marine invertebrates
Osmoregulators

Type of animals based on their osmotic regulation
control levels of most of the ions in extracellular fluids,
Osmoregulators

Type of animals based on their osmotic regulation
employing a combination of ion absorption and excretion strategies
Stenohaline
Salinity tolerance of aquatic animals
tolerate a narrow range of salinity (freshwater or marine)
Euryhaline
Salinity tolerance of aquatic animals
tolerate a wide range of salinity
Excretion
CO2
Nitrogenous wastes
____________
Removal of metabolic wastes
_______ - removed during exhalation (external respiration)
_____________ – from breakdown of cellular proteins
Excretion
Requires water → plays a role in osmoregulation
Type of metabolic waste dependent on the animal’s habitat
Ammonia
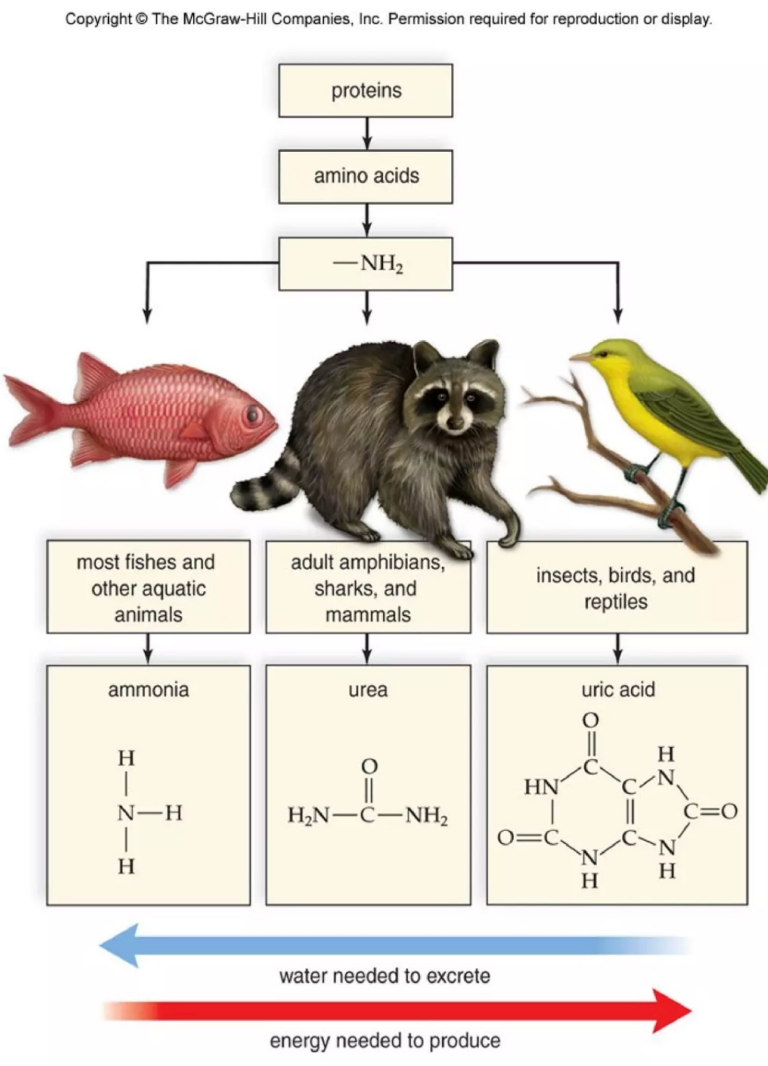
Nitrogenous wastes
Highly toxic and requires plenty of water
Ammonia

Nitrogenous wastes
Most bony fishes and many aquatic animals
Ammonia

Nitrogenous wastes
Excreted through gills and diluted by surrounding water
Urea

Nitrogenous wastes
Mammals, sharks and adult amphibians
Urea

Nitrogenous wastes
Less toxic than ammonia; can be concentrated to conserve water and eliminated in urine
Urea

Nitrogenous wastes
Requires energy to be converted from ammonia in the liver
Uric Acid

Nitrogenous wastes
Insects, reptiles, and birds
Uric Acid

Nitrogenous wastes
Can be combined with little water to form a paste
Uric Acid

Nitrogenous wastes
Requires more ATP to be produced
Sponges (porifera), cnidarians, echinoderms
Osmoregulatory and excretory structures
These phyla possess no excretory organs
Sponges (porifera), cnidarians, echinoderms
Osmoregulatory and excretory structures
These phyla have nitrogenous wastes diffuse into the surrounding isosmotic water
Contractile vacuoles
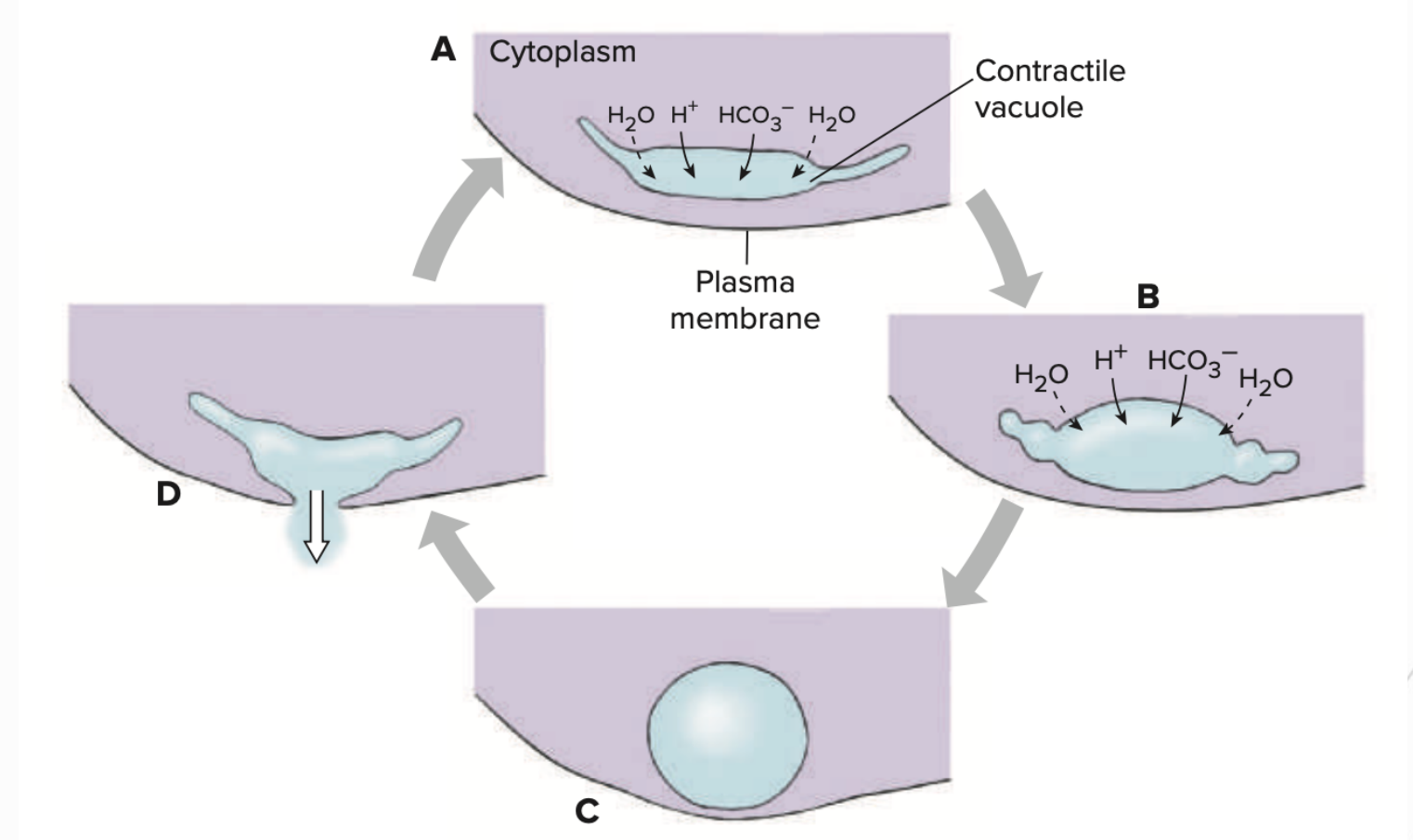
Osmoregulatory and excretory structures
Freshwater sponges and Hydra possess _____________
Contractile vacuoles

Osmoregulatory and excretory structures
Expel excess water gained by osmosis
Nephridia
Most common type of invertebrate excretory organ
Nephridia
Tubular structures designed to maintain appropriate osmotic balance
Protonephridia (sing. Protonephridum)
Metanephridia (sing. Metanephridium)
Nephridia
Two types:
_________________ – closed at the inner end
_________________ – open at both ends
Protonephridia (sing. Protonephridum)
Metanephridia (sing. Metanephridium)
Name the two types of nephridia that reabsorb valuable solutes and remove nitrogenous wastes
Protonephridia
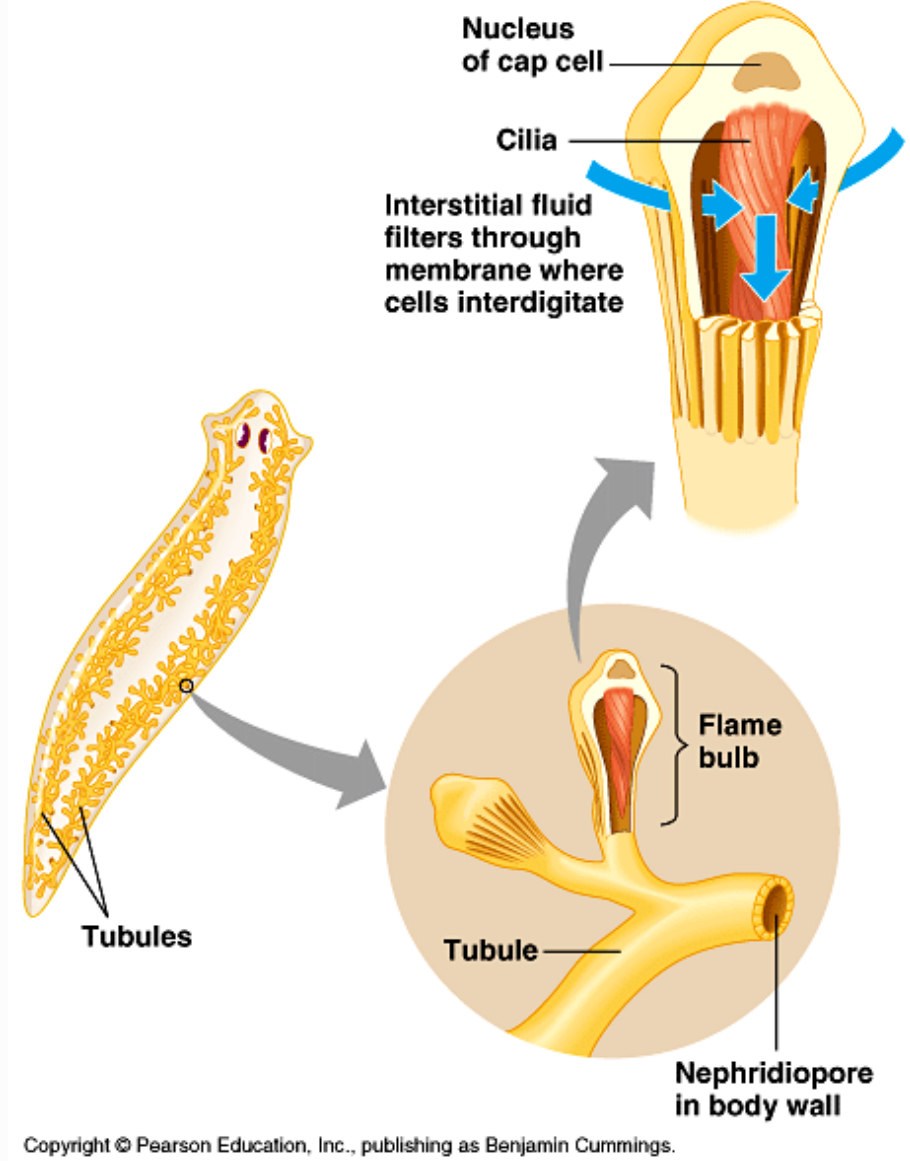
Type of invertebrate excretory organ
Flatworms and rotifers
Protonephridia

Type of invertebrate excretory organ
Each branch terminates in a “flame cell”
Protonephridia

Type of invertebrate excretory organ
Fluid enters the system through the flame cells
Protonephridia

Type of invertebrate excretory organ
Wastes expelled through nephridiopores and diffuse across body surface
Metanephridia
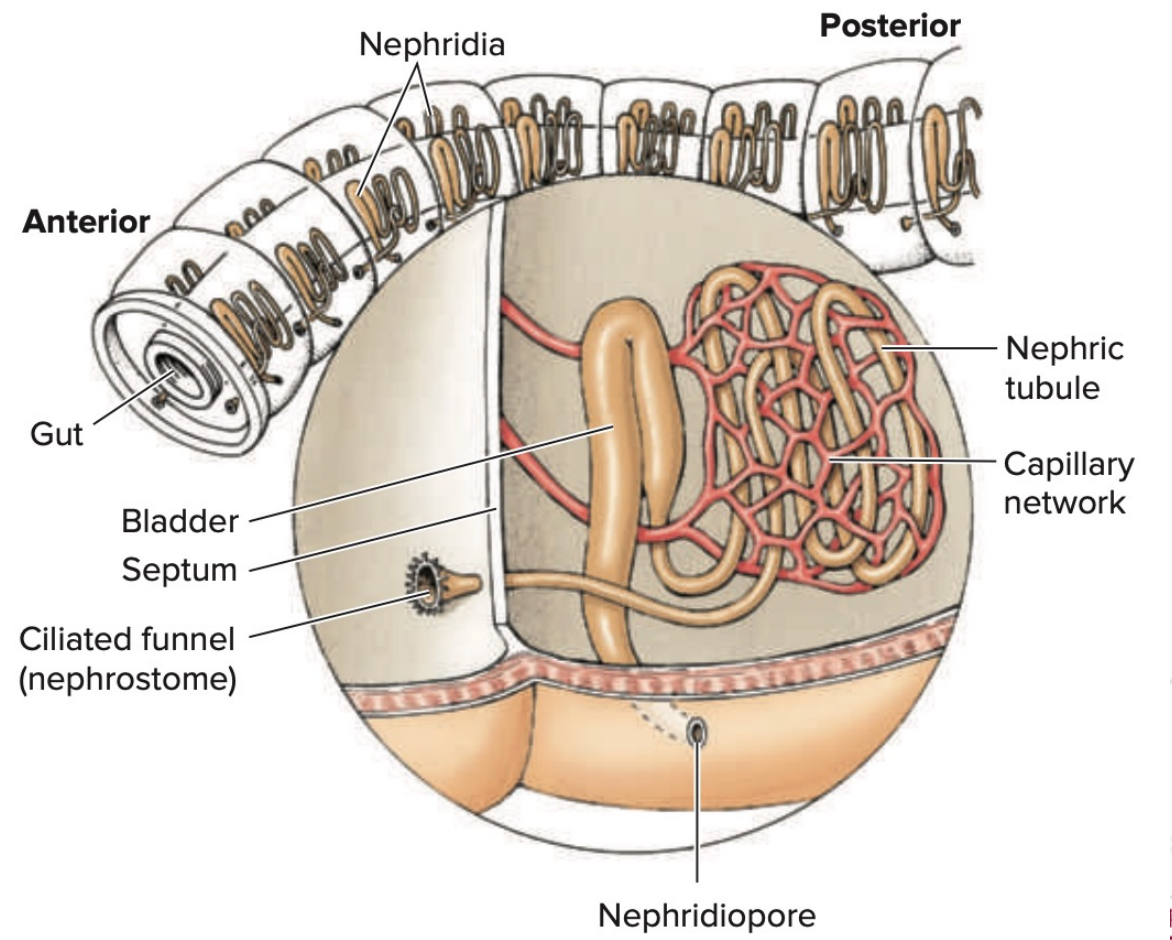
Type of invertebrate excretory organ
Annelids and mollusks
Metanephridia

Type of invertebrate excretory organ
Fluid swept into the tubule through a ciliated funnel-like opening, the nephrostome.
nephrostome

In the Metanephridia Fluid is swept into the tubule through a ciliated funnel-like opening, the _________.
Metanephridia

Type of invertebrate excretory organ
Surrounded by a network of blood vessels that assist in reabsorption of water and valuable materials such as salts, sugars, and amino acids
Arthropod excretory organs
Antennal, maxillary, and coxal glands
Arthropod excretory organs
probably originated from nephridia and are homologous with each other
Arthropod excretory organs
lack an open nephrostome and function by filtration through a closed filtration membrane
Arthropod excretory organs
Hemolymph pressure forces fluids, ions, and small molecules through the filtration membrane and into the tubule system
Antennal glands
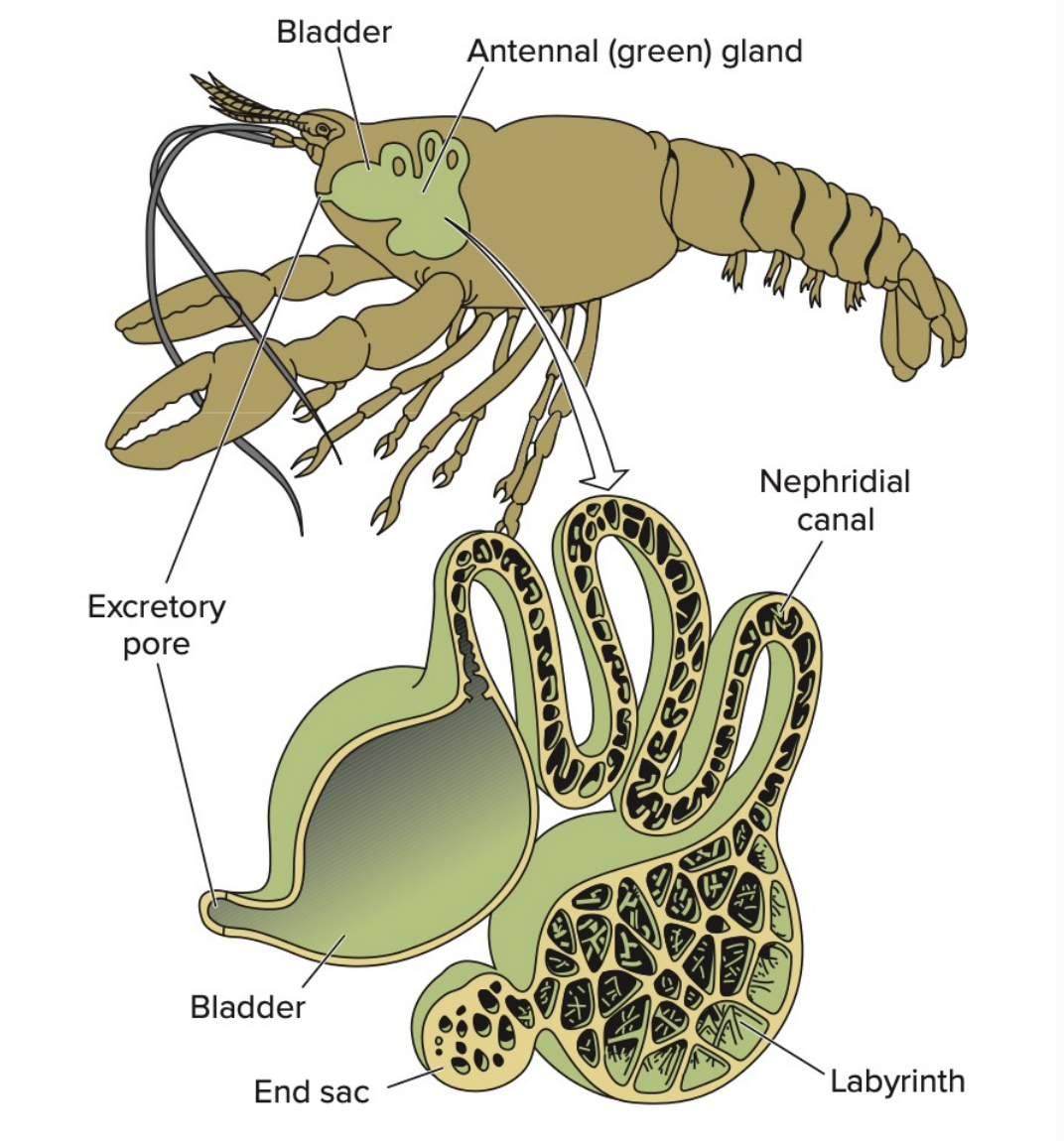
Aquatic crustaceans excrete ammonia through this gland in their gills
Antennal glands

_________________ gland removes excess water and reabsorbs ions while discharging other nitrogenous wastes
Antennal glands

Also known as green glands in arthropods
Coxal glands
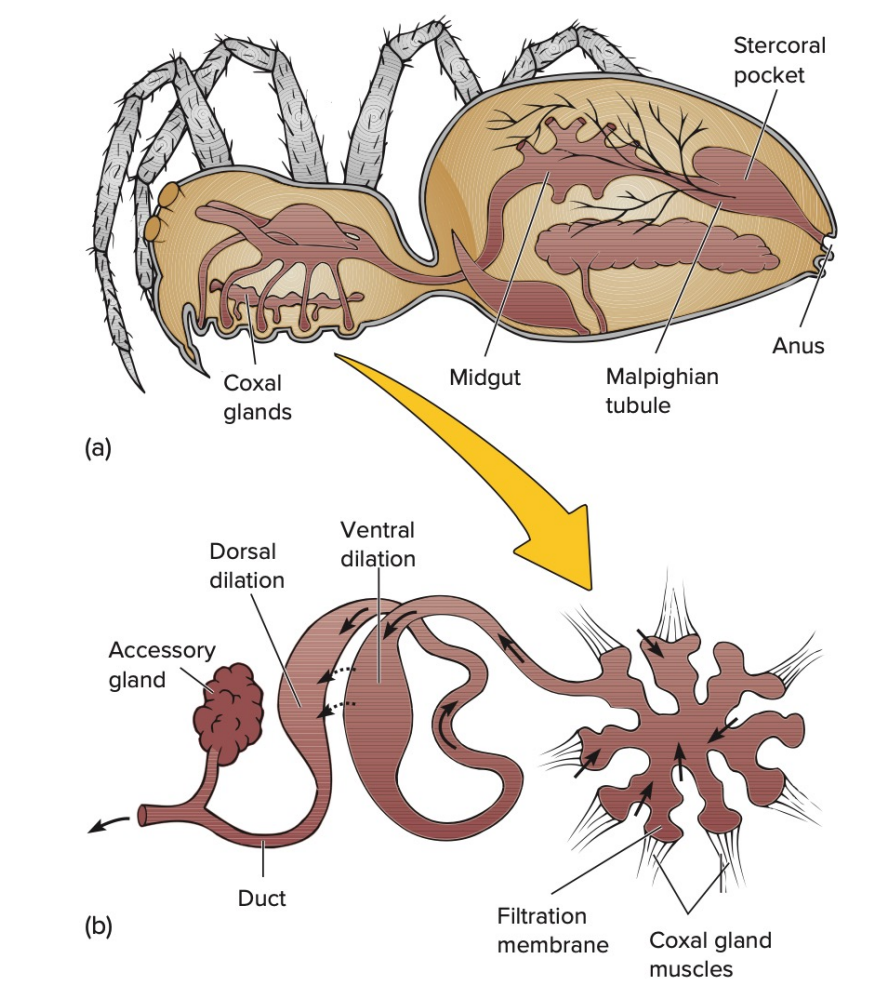
Gland common among arachnids (spiders, scorpions, ticks, and mites)
Coxal glands

Wastes are discharged through pores on one to several pairs of appendages near the proximal segment (coxa) of the leg
Malpighian tubules
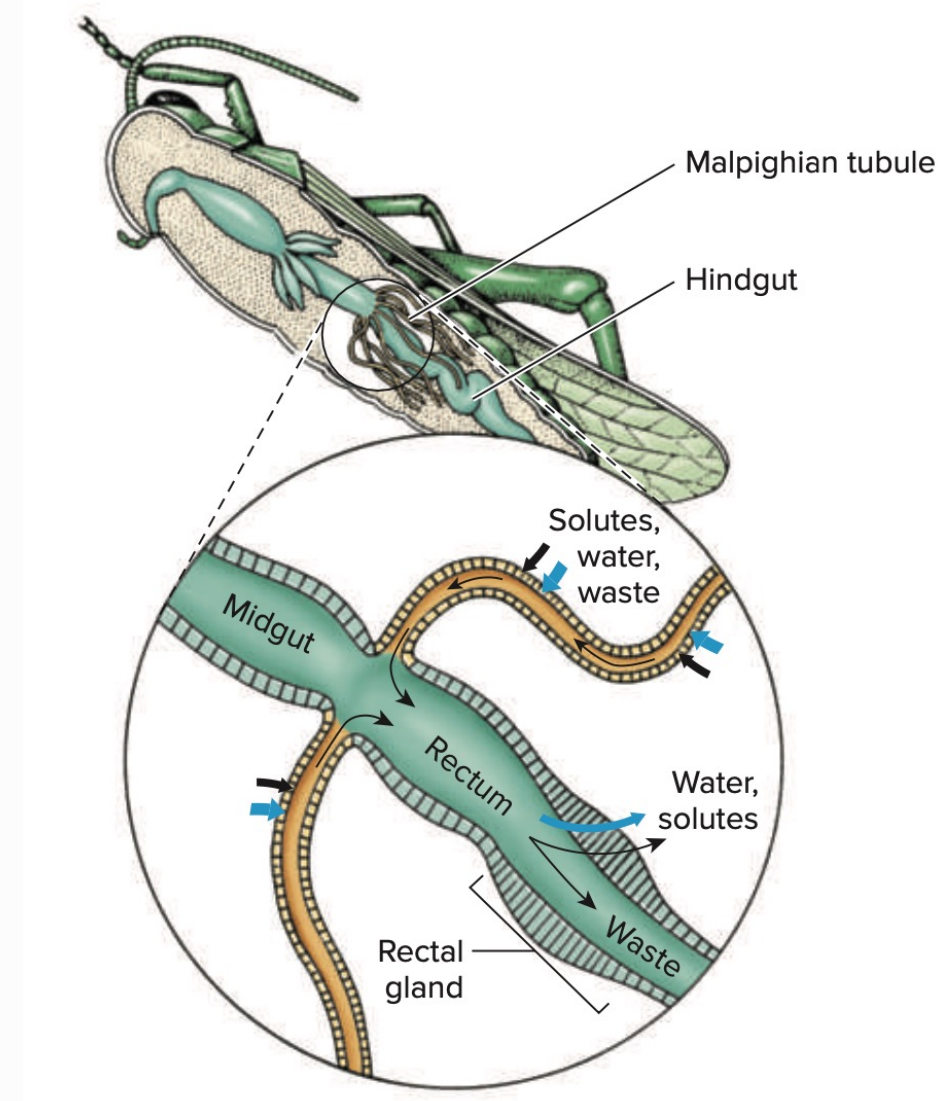
Excretory (network of) organs Found in insects and myriapods
Malpighian tubules

Not nephridial in origin; derived from the gut
Malpighian tubules

Involves the active transport of potassium ions into the tubules from surrounding hemolymph
Malpighian tubules

Uric acid and water move into tubules via osmosis
Water and ions reabsorbed in the rectum
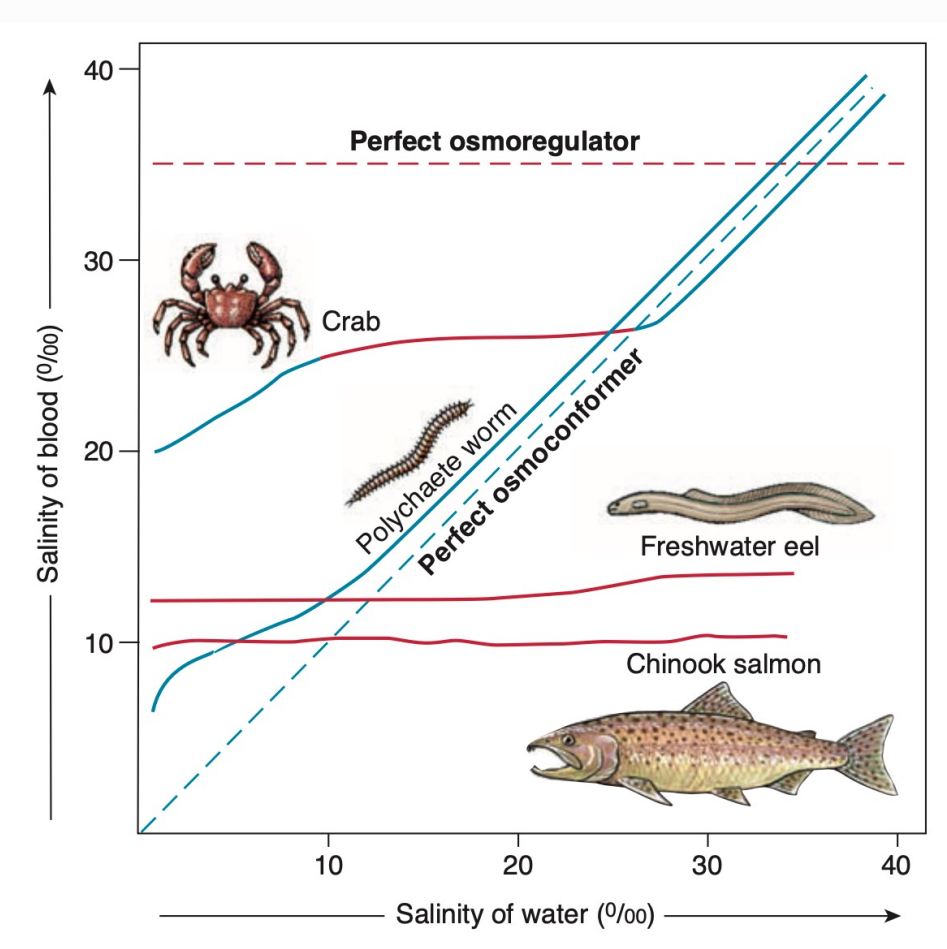
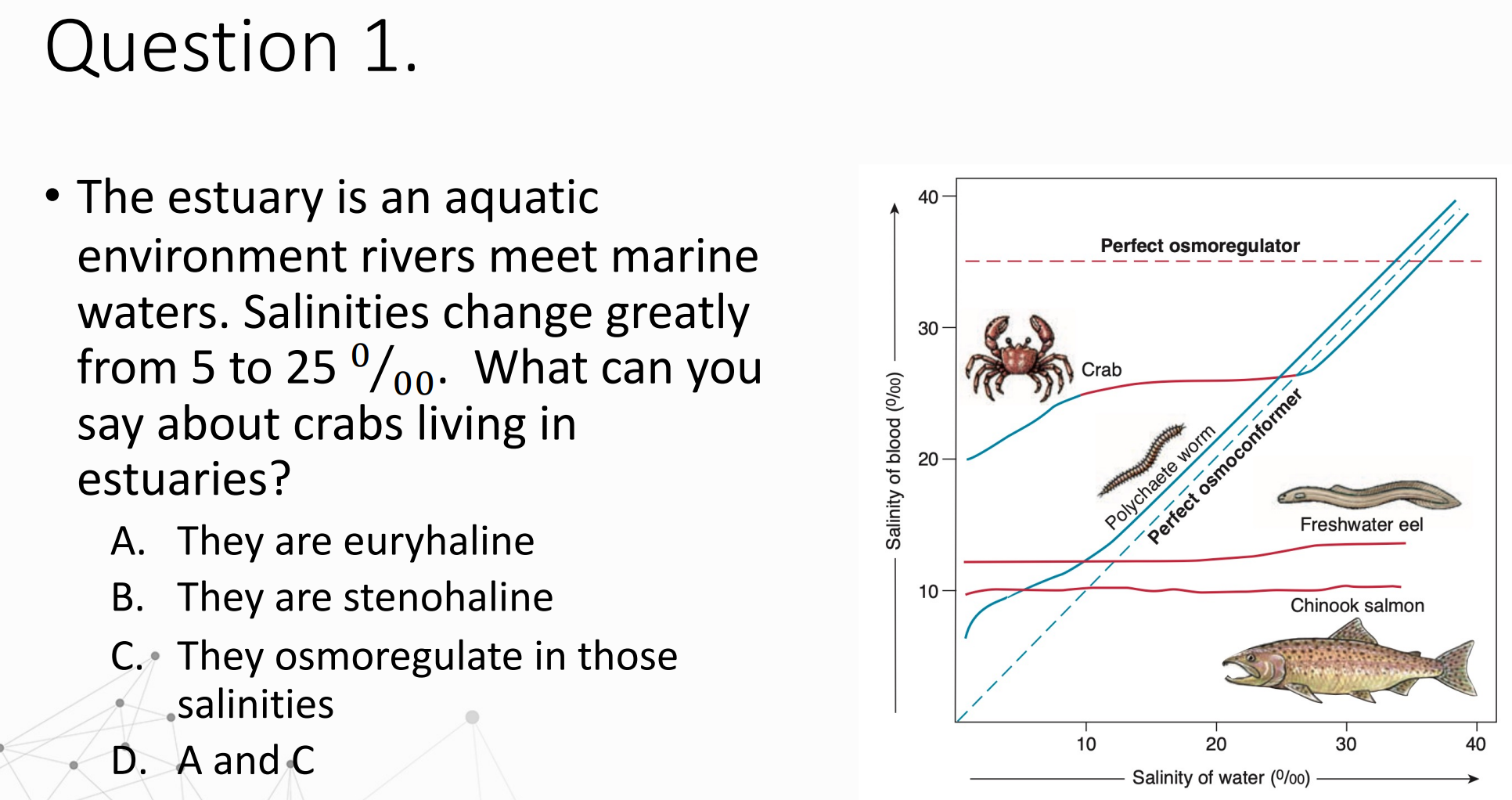
From the graph, the crab keeps its internal (blood) salinity relatively constant even as the external water salinity changes → this means it osmoregulates.
Because estuaries fluctuate widely in salinity (5–25 ‰) and the crab tolerates this wide range, it is euryhaline.
So the correct interpretation is:
A — They are euryhaline ✔
C — They osmoregulate in those salinities ✔
Therefore D (A and C) is correct.
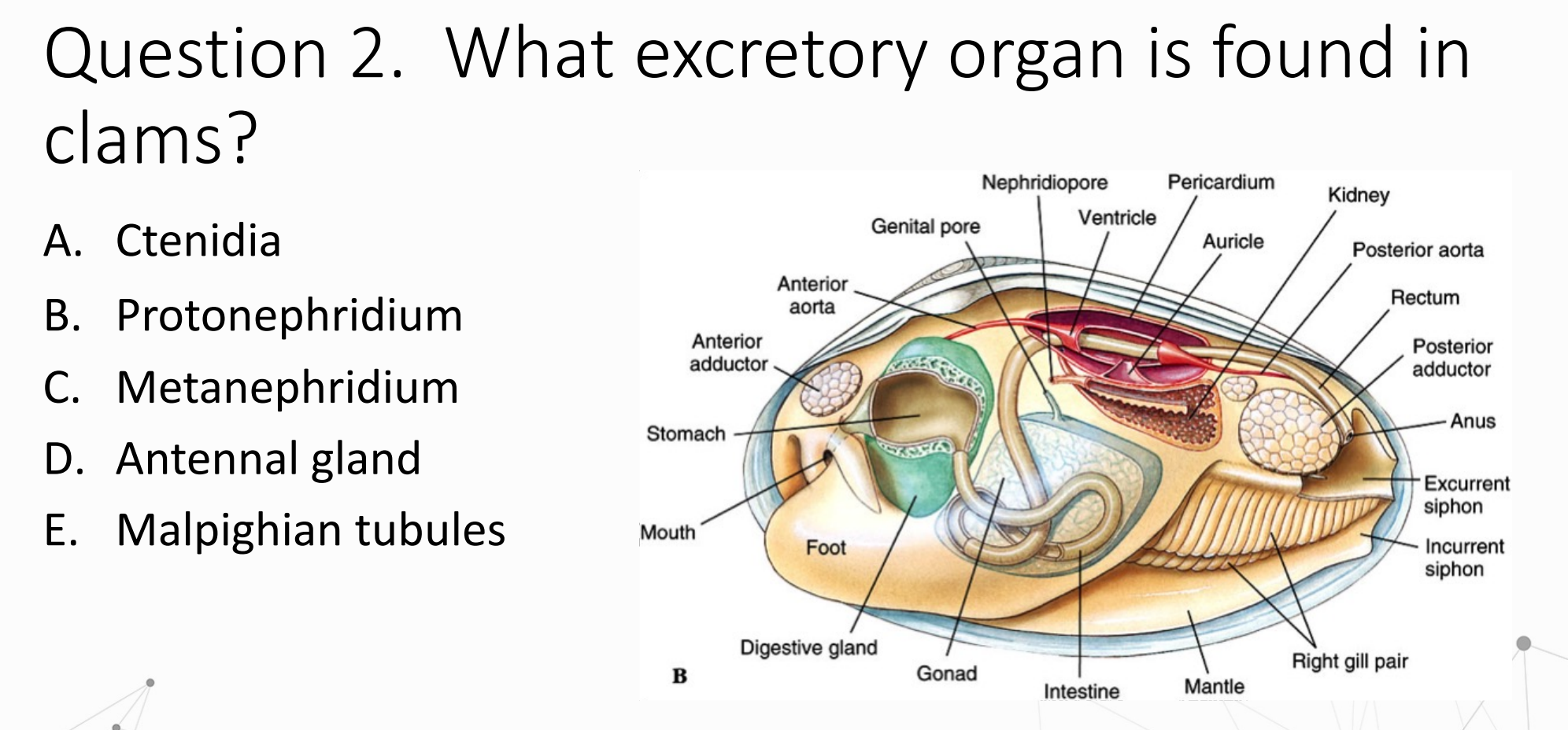
Correct answer: C. Metanephridium
Clams (bivalves) possess metanephridia, also called kidneys in mollusks.
You can even see it labeled as “Kidney” in the diagram.
Here’s why the other options are incorrect:
A. Ctenidia → These are gills, not excretory organs.
B. Protonephridium → Found in flatworms/larvae, not adult mollusks.
D. Antennal gland → Found in crustaceans.
E. Malpighian tubules → Found in insects and some arachnids.
So the excretory organ in clams = Metanephridium.
Correct answer: A. Marine sharks tend to gain water
Because:
Marine sharks are slightly hyperosmotic to seawater (due to high urea + TMAO).
Water moves from lower osmolarity → higher osmolarity.
So seawater is slightly hypoosmotic relative to the shark’s internal fluids.
➡ Water naturally enters the shark’s body by osmosis.
This is why:
Sharks do not drink seawater like bony fish.
They produce very dilute urine to get rid of the excess water.
So the correct answer is A.

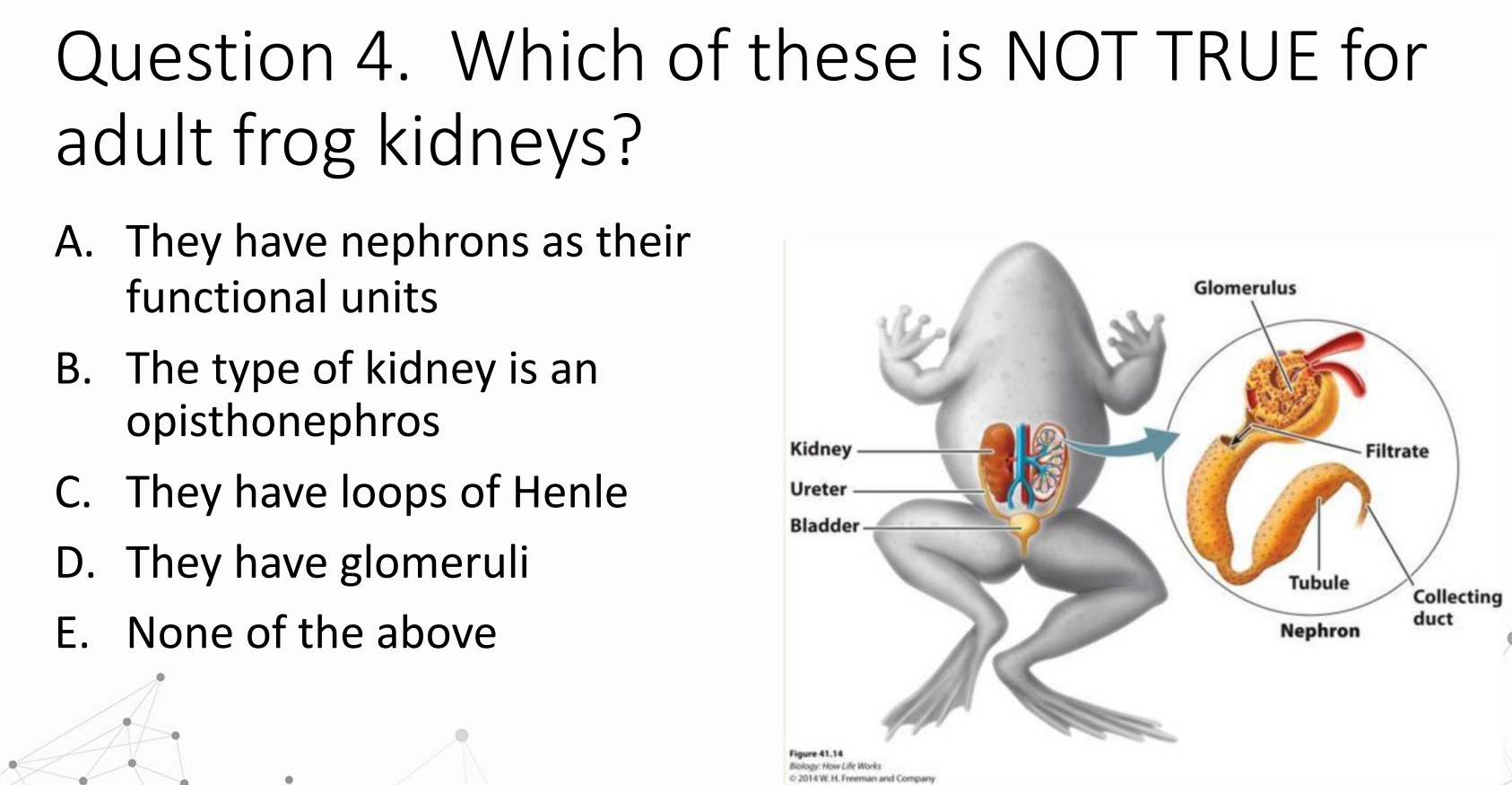
The statement that is NOT TRUE for adult frog kidneys is:
C. They have loops of Henle
Explanation:
Adult frogs (amphibians) have opisthonephric kidneys → so B is true.
Their kidneys are made of nephrons → A is true.
Their nephrons contain glomeruli → D is true.
BUT amphibians do not have loops of Henle; only mammals have them.
Frogs cannot produce hyperosmotic urine for this reason.
✅ Correct answer: C
The correct answer is:
E. B and C
Why?
Alcohol is a diuretic, meaning it inhibits ADH (antidiuretic hormone).
Less ADH → kidneys reabsorb less water → more urine is produced.
So:
B is true: You produce more urine.
C is true: Excess water loss → risk of dehydration.
Therefore, the correct combination is:
✅ E. B and C



Lose water through:
evaporation
urine
feces
Gain water via:
food
metabolic
Water Balance in Terrestrial Vertebrates
Terrestrial vertebrates evolved physiological mechanisms to avoid desiccation
Lose water through:
_________ from the respiratory and body surfaces
excretion in ________
elimination in _______
Gain water via:
Consuming water in _______
drinking water when available
retaining __________ water
Mucus
Integument as an osmotic barrier
an extracellular secretion of mucopolysaccharides, lipids, and proteins
Mucus
Integument as an osmotic barrier
Hydrophobic barrier
Mucus
Integument as an osmotic barrier
Lines vertebrate lungs and amphibian skin to reduce water loss
Stratum corneum in skin
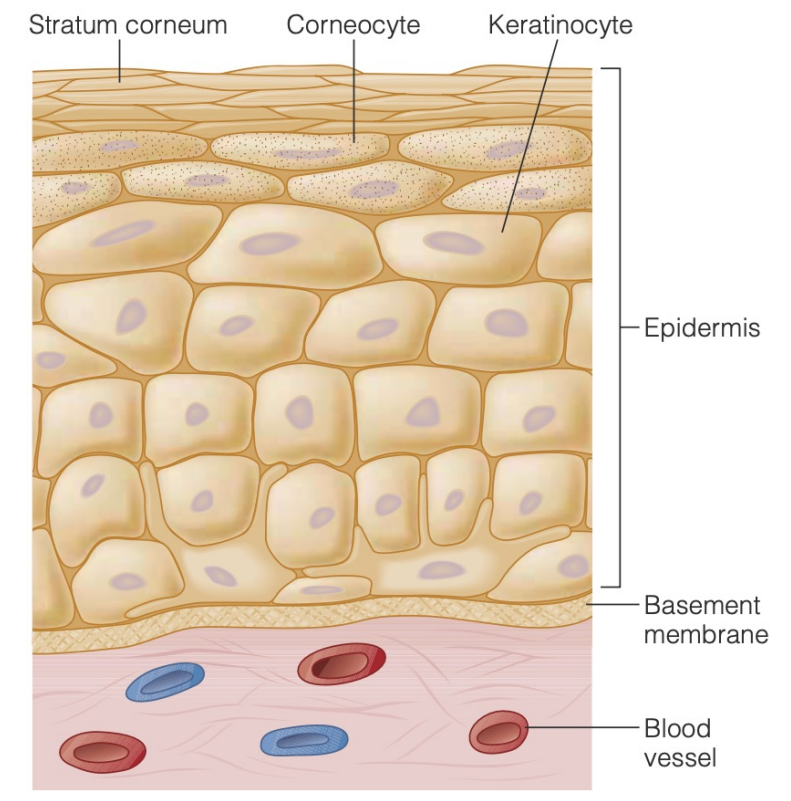
Integument as an osmotic barrier
Keratinized to minimize desiccation
skin; kidneys
Salt and water balance in frogs
Water enters the highly permeable _____ and excess is excreted by __________.
salt; salt; skin
Salt and water balance in frogs
Must compensate for _______ loss by actively absorbing ________ from the water through their _______
urinary bladder
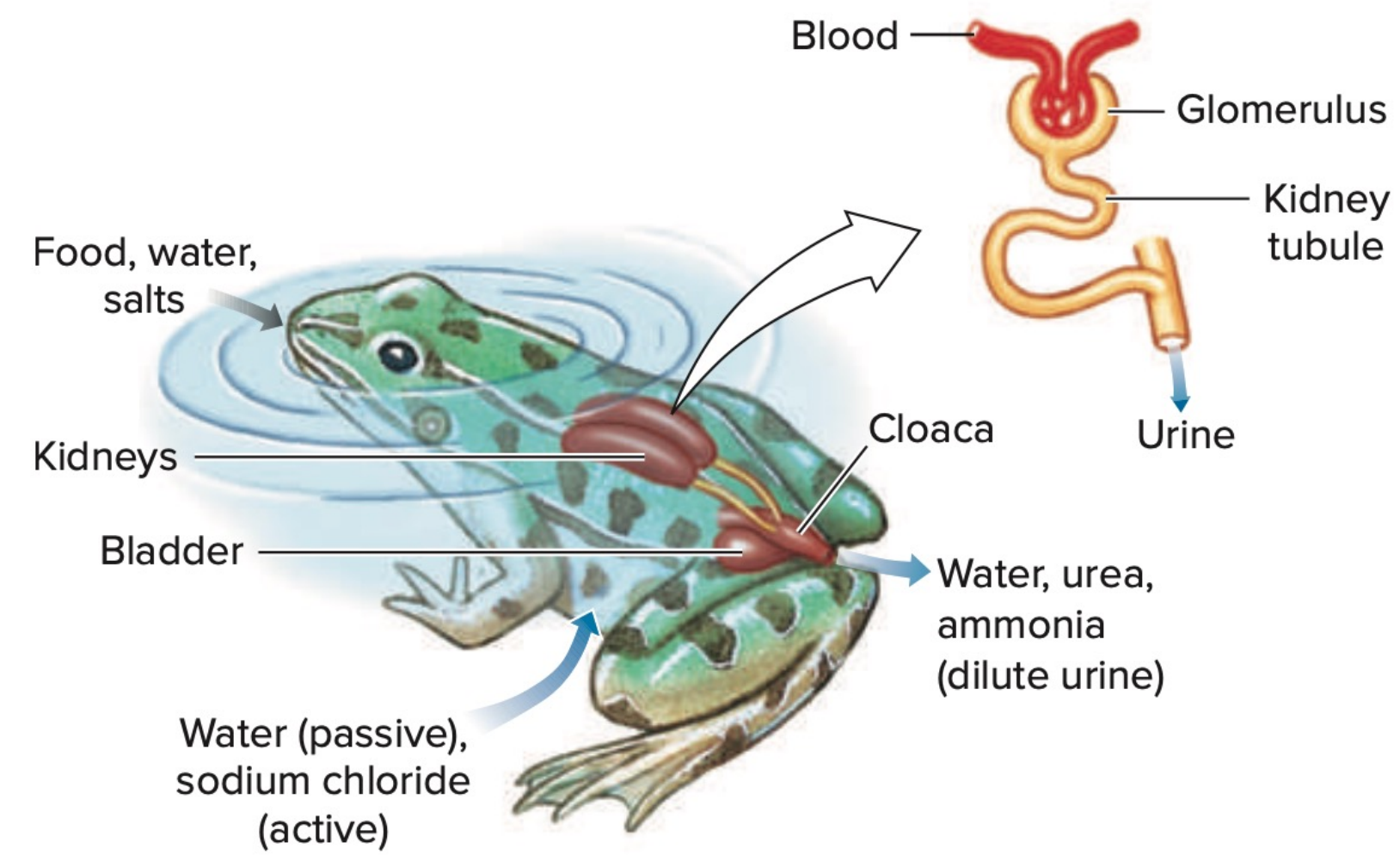
Salt and water balance in frogs
Urine flows into the ___________ where salts are reabsorbed
Desert animals
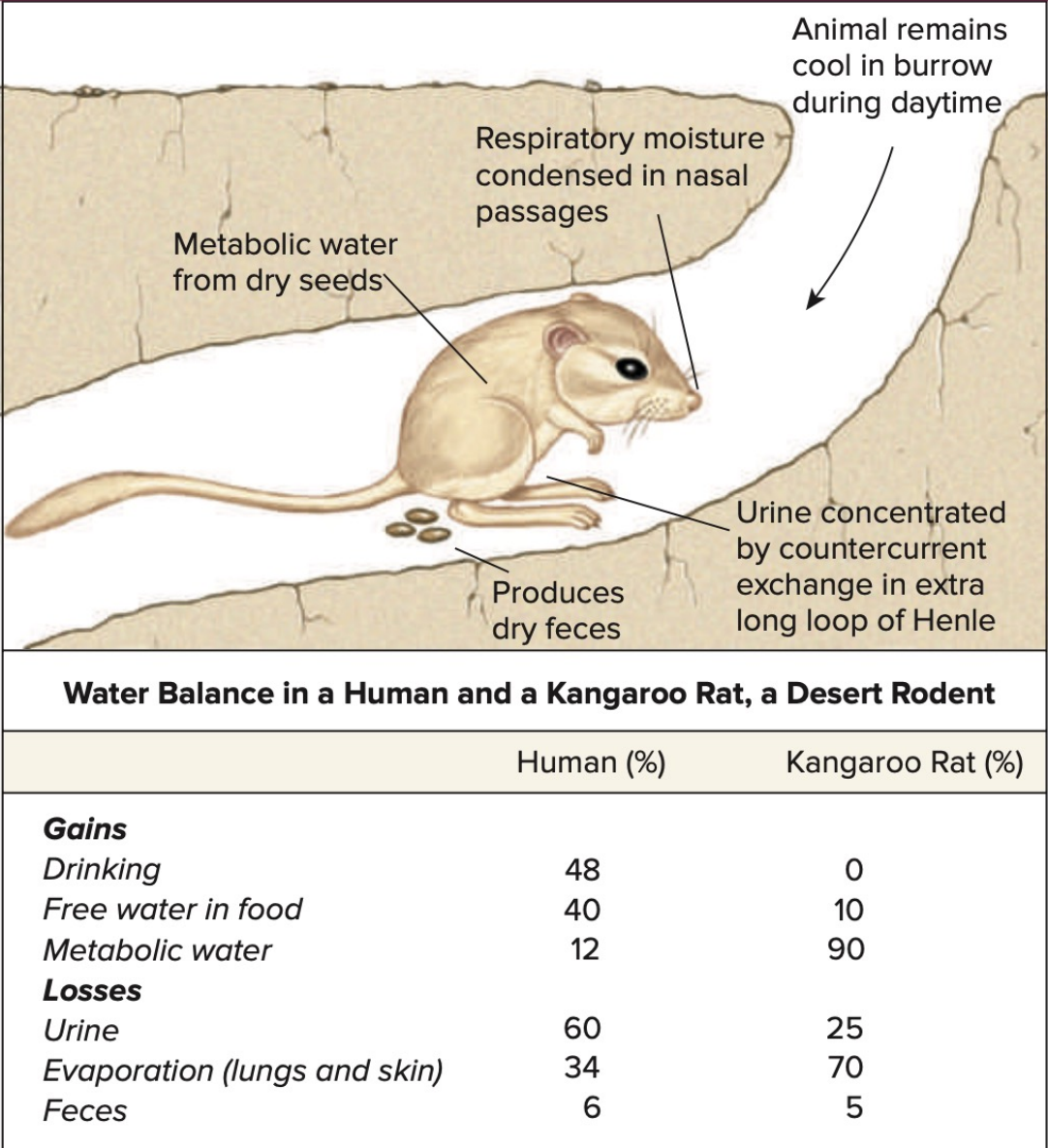
At risk of dehydration
Conserve water by excreting highly concentrated urine and minimizing evaporation from lungs and skin
Desert animals

Gain water from food but mostly from metabolic water
salt glands
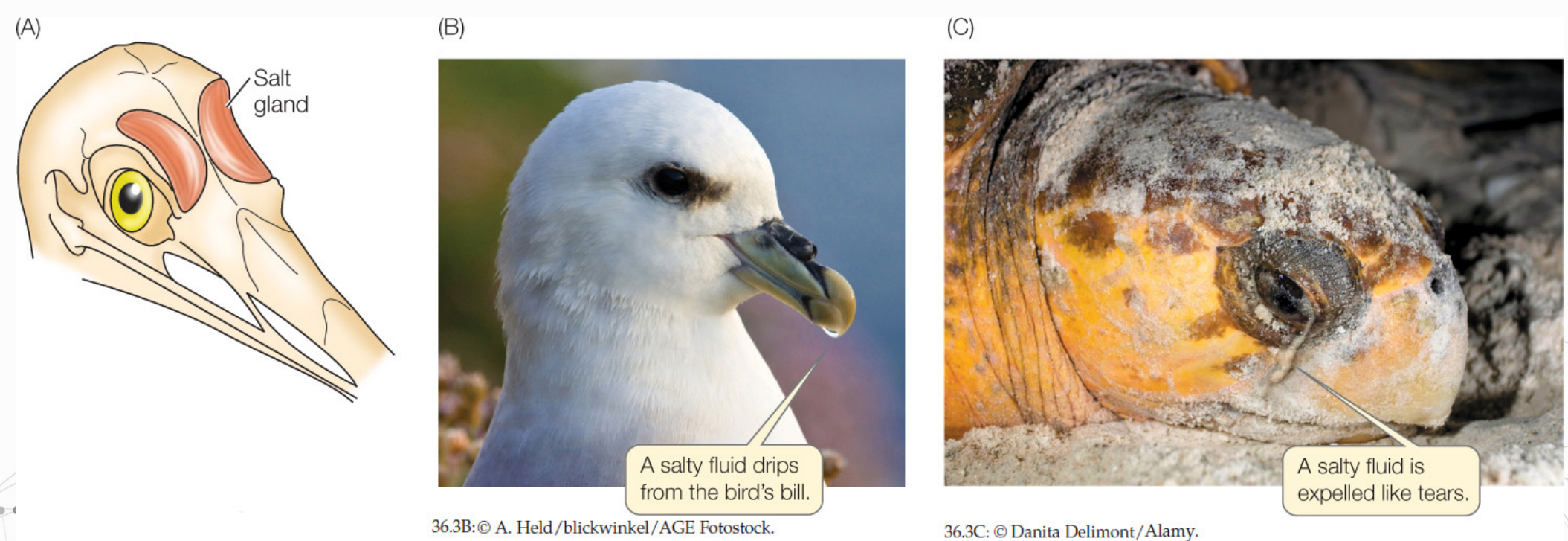
Marine birds and reptiles
Have __________ to pump excess salt
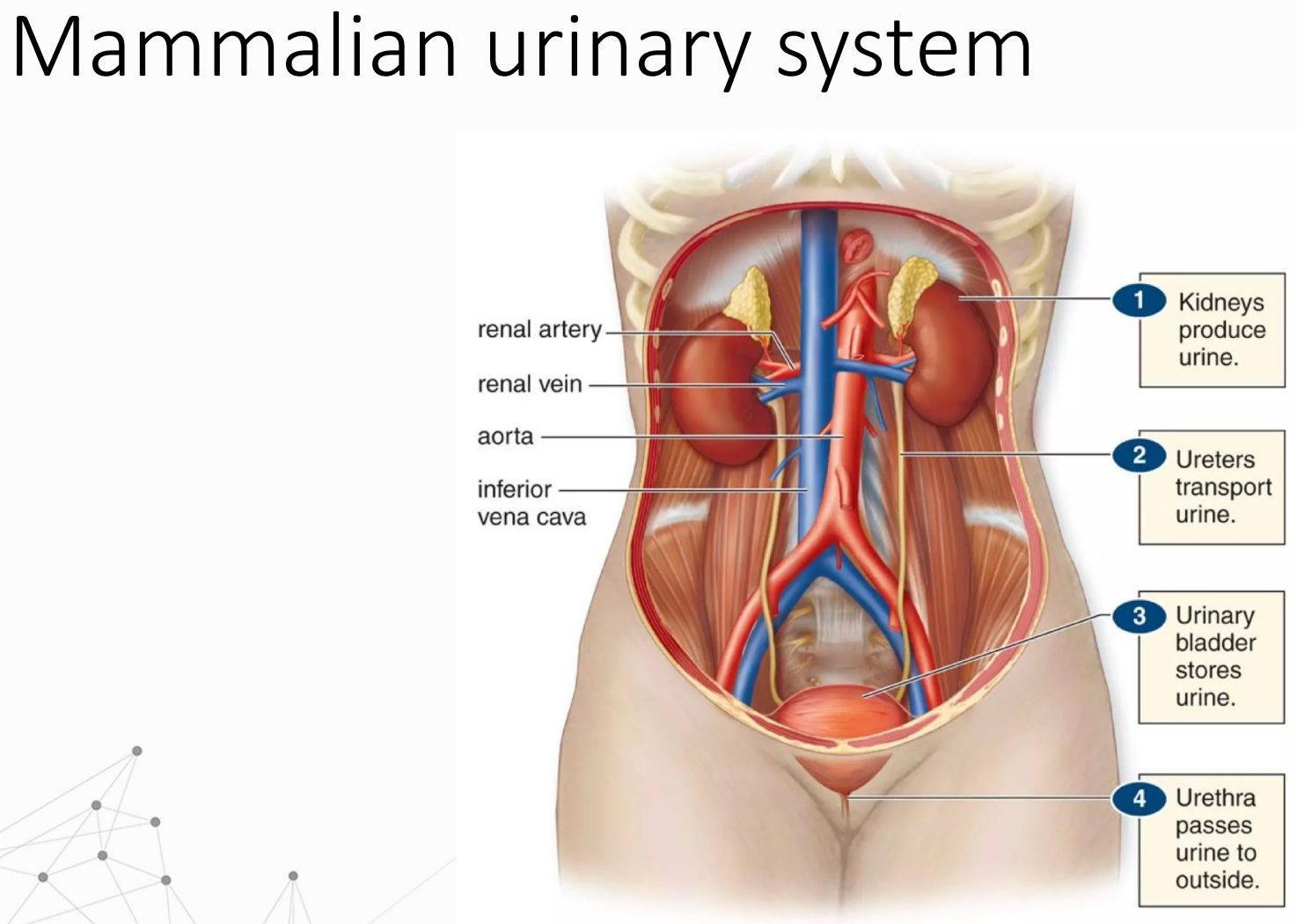
Vertebrate kidneys
Osmoregulatory and excretory organ of vertebrates
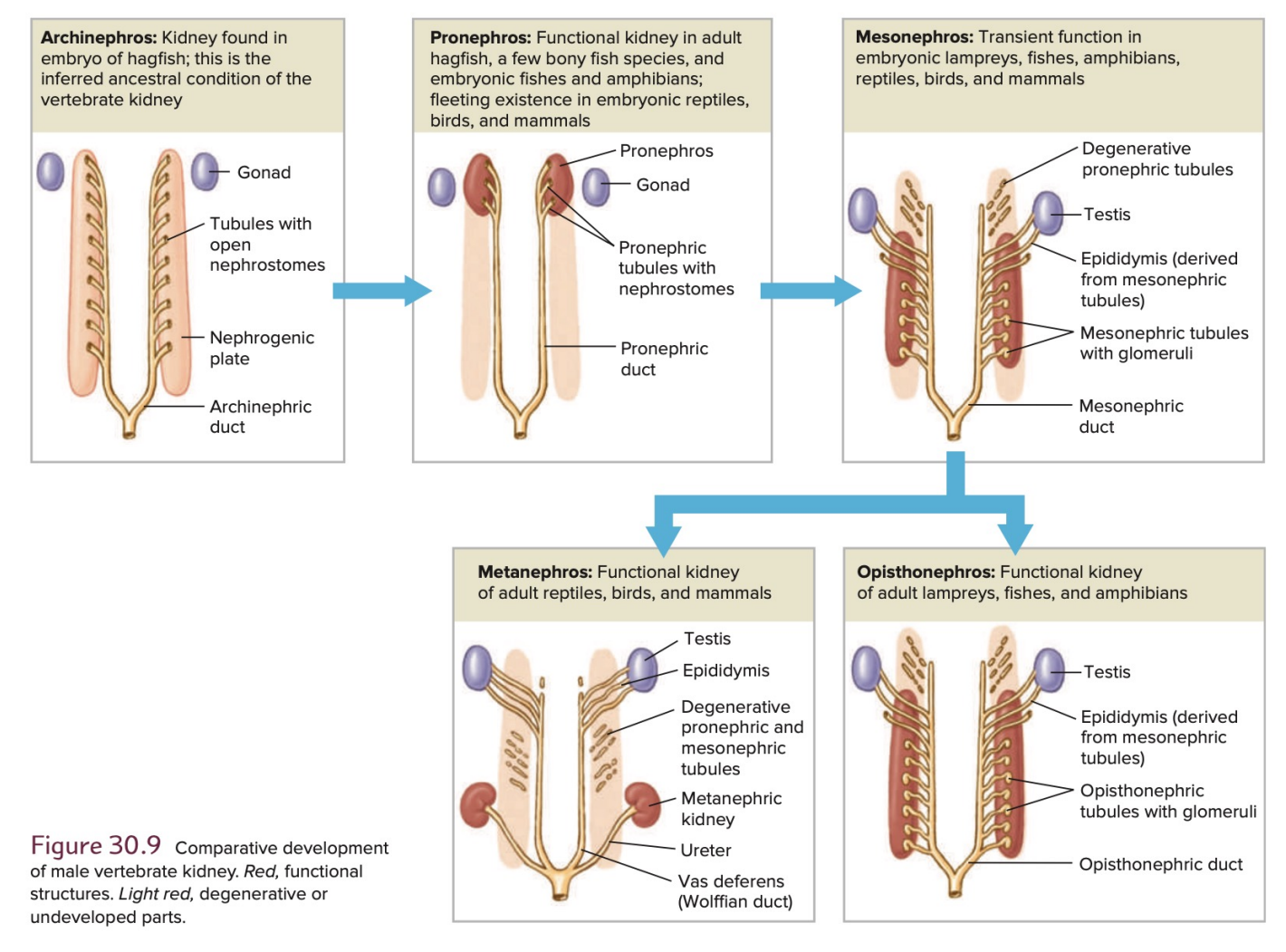
Archinephros
Kidneys form embryologically from tissue that extends the length of the body cavity
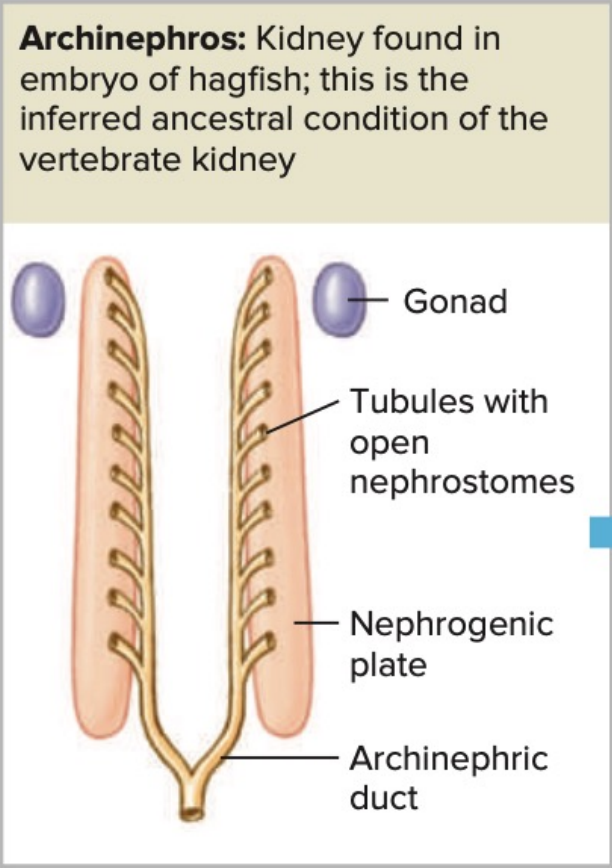
_______________: Kidney found in embryo of hagfish; this is the inferred ancestral condition of the vertebrate kidney
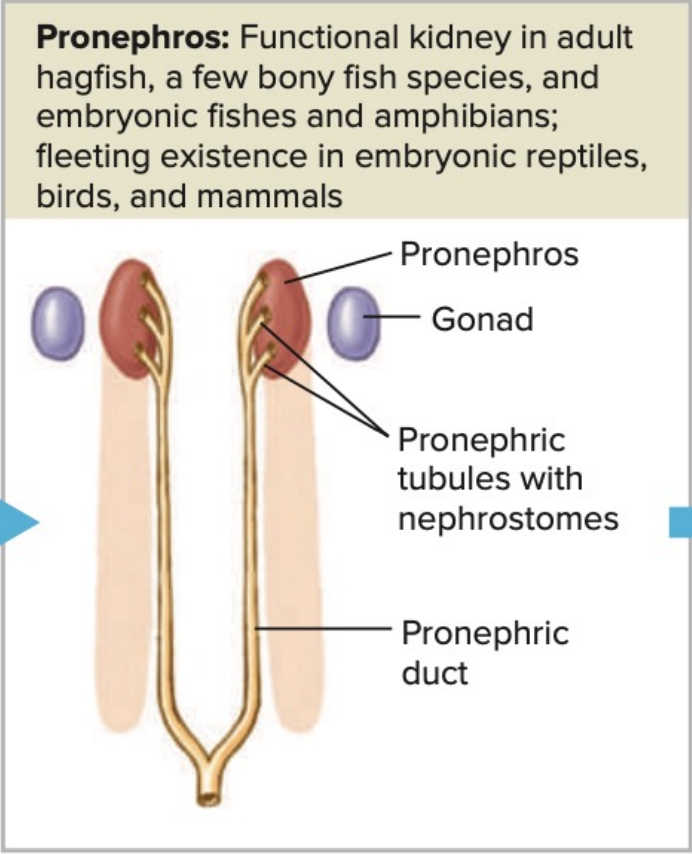
_______________: Functional kidney in adult hagfish, a few bony fish species, and embryonic fishes and amphibians; fleeting existence in embryonic reptiles, birds, and mammals

First kidney to appear in all vertebrate embryos
Located anteriorly in the body
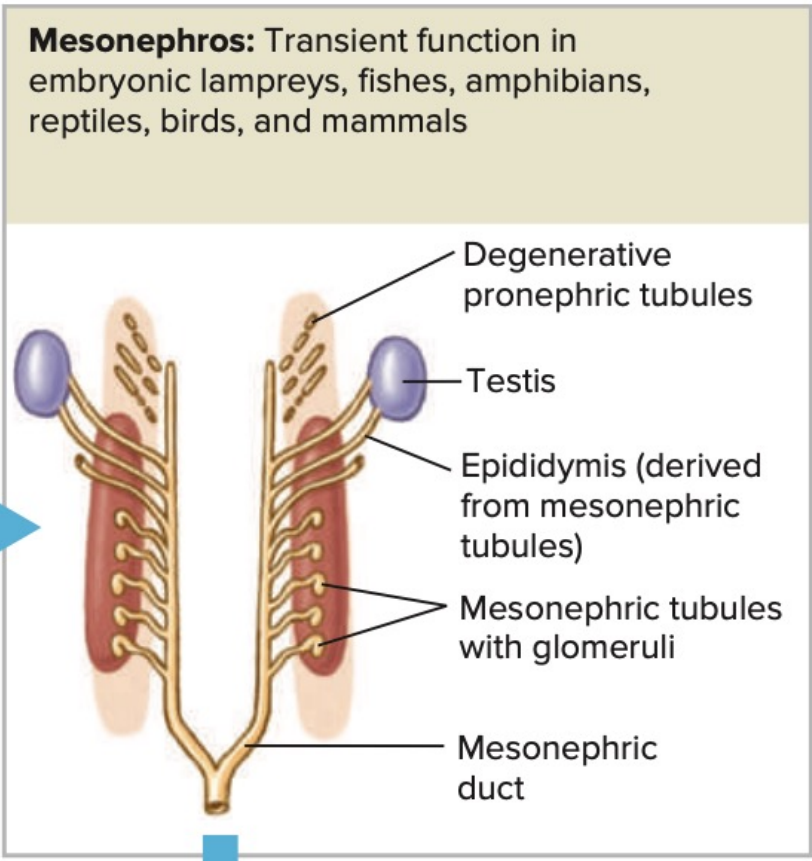
_______________: Transient function in embryonic lampreys, fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals
functional kidney of embryonic amniotes (reptiles, birds and mammals)

kidney made up of an increased number of nephrons, usually dozens to hundreds

Kidney that Allowed vertebrates to face the rigorous osmoregulatory and excretory demands of freshwater and terrestrial environments
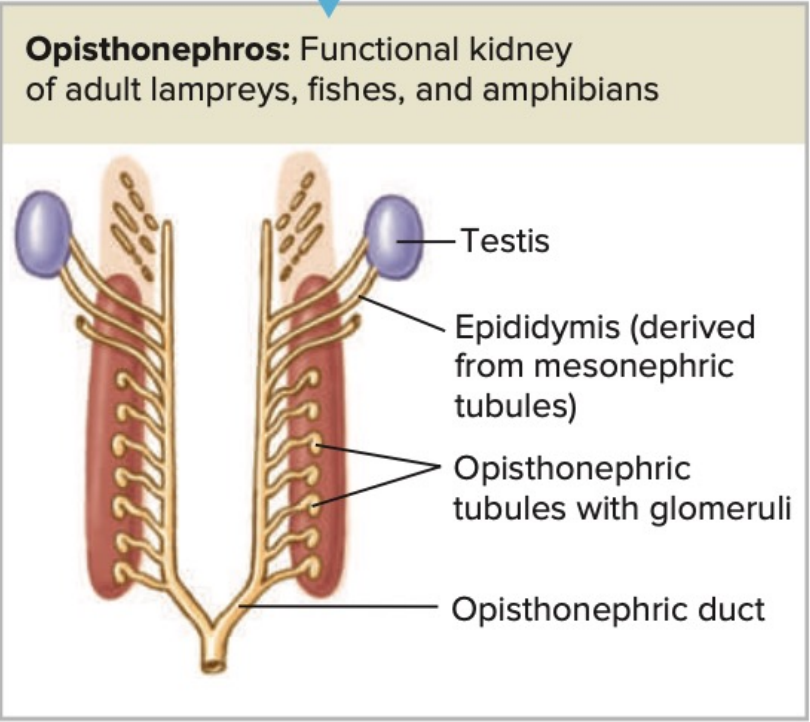
_______________: Functional kidney of adult lampreys, fishes, and amphibians

Kidney Comprised of mesonephros and metanephros
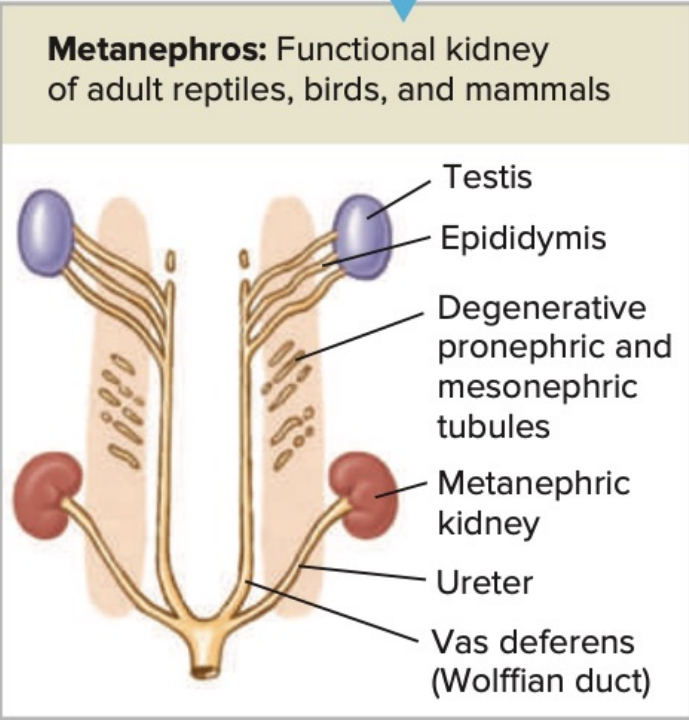
_______________: Functional adult kidney of amniotes (reptiles, birds, and mammals)

Kidney More caudally located and more compact
increased number of nephrons, (thousands to millions)

Kidneye Drained by a new duct, the ureter,
Old archinephric duct was relinquished to the male reproductive system for sperm transport
ureter

In the metanephros, the kidney is drained by a new duct, called the ________,

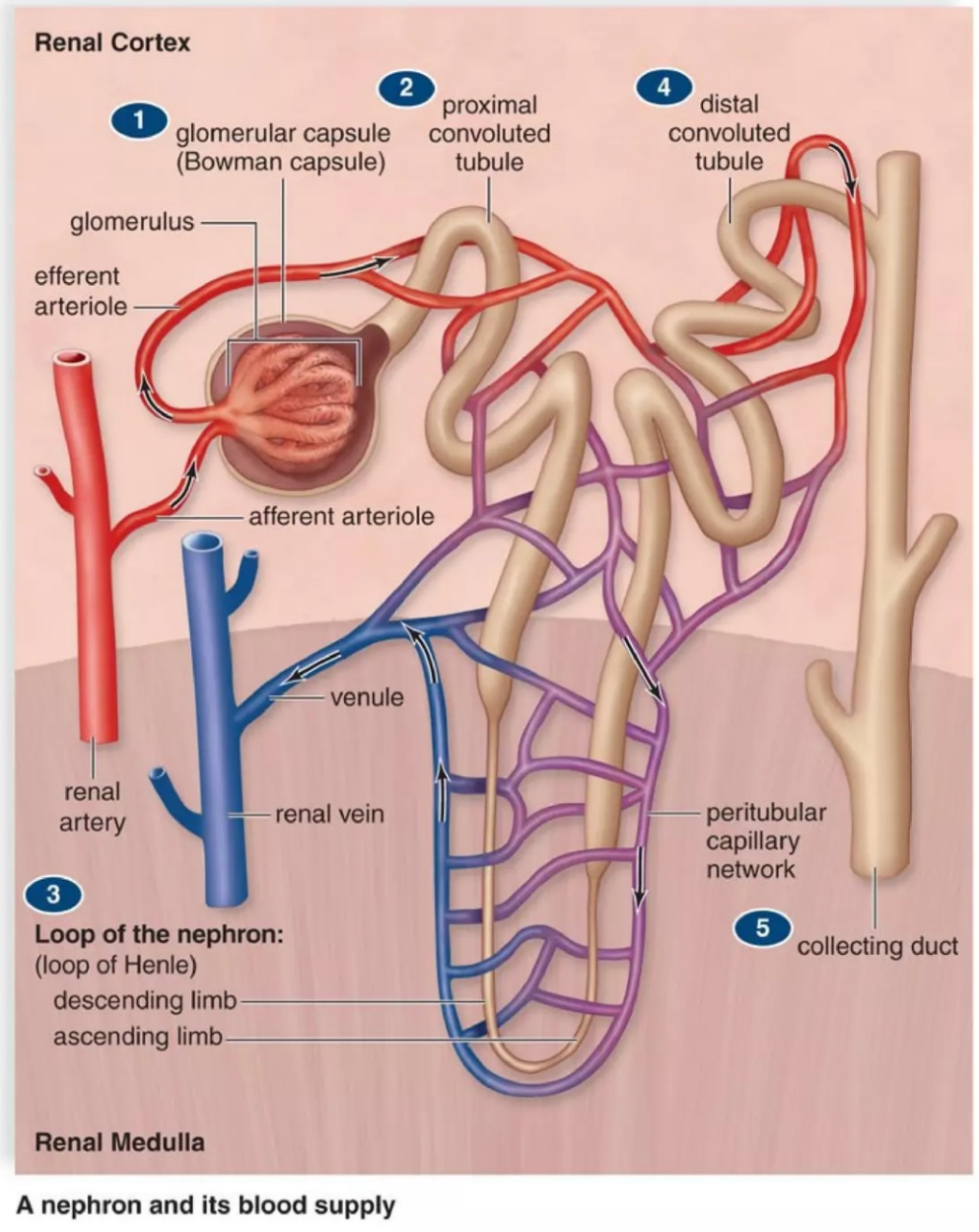
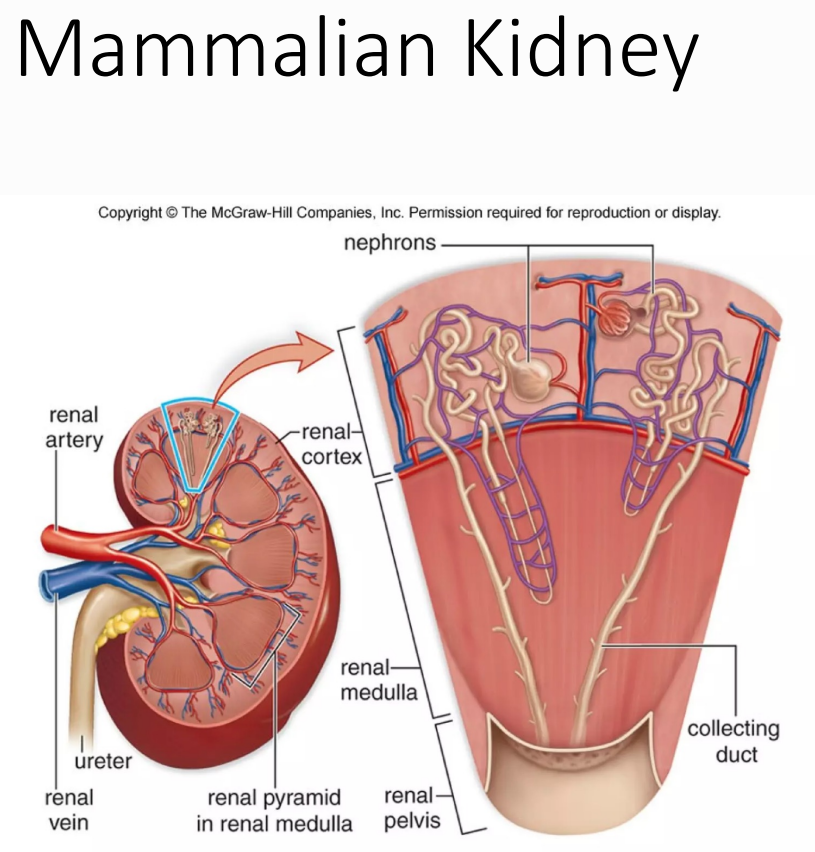
Nephron
Functional unit of vertebrate kidneys
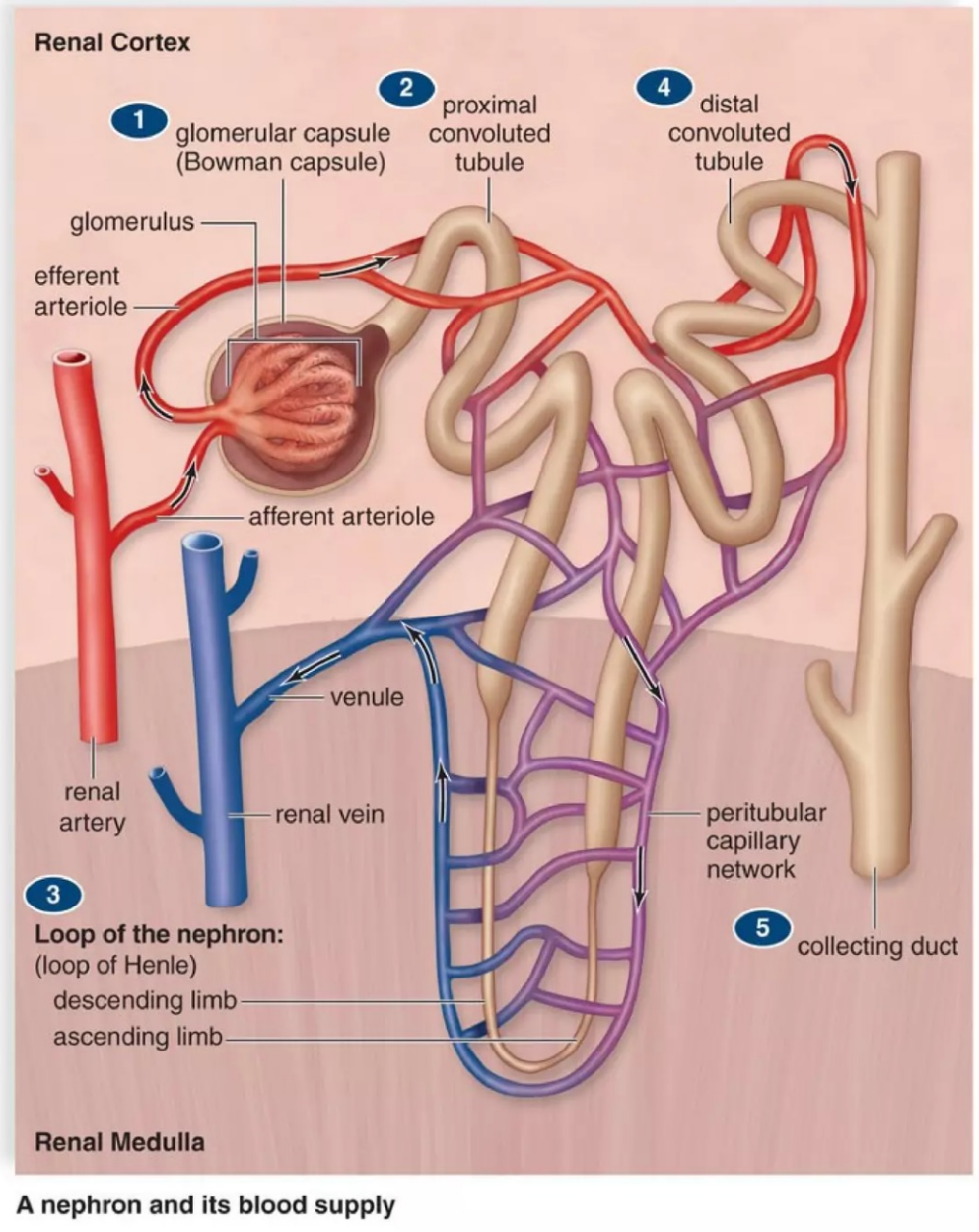
Renal cortex
Outer portion of kidney
Renal cortex

Contains the renal corpuscles and tubules (glomerular filtration)
Renal medulla

Split into renal pyramids
Renal medulla

Contains the loop of Henle and collecting ducts (maintain salt and water balance in blood)
Renal pelvis

Dilated portion of the ureter
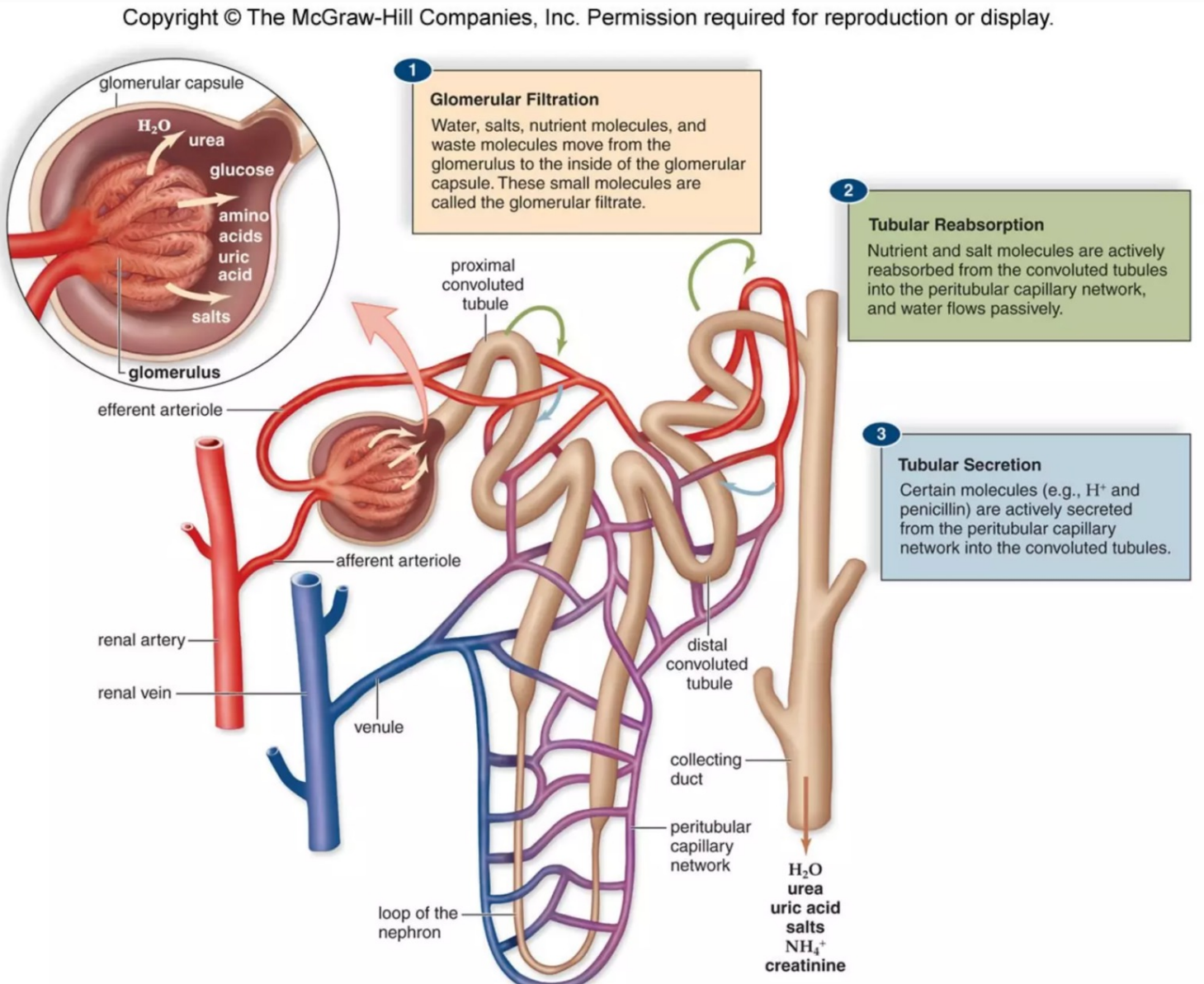
Urine Formation
Filtration
Small molecules move across glomerular wall because of blood pressure
Filtrate is protein-free, otherwise same composition as blood plasma
Reabsorption
Salts and nutrients actively reabsorbed from convoluted tubules
Secretion
Removes ammonia, uric acid, hydrogen ions, creatinine and penicillin which are secreted into convoluted tubules
Urine Formation
____________
Small molecules move across ____________ because of blood pressure
Filtrate is protein-free, otherwise same composition as blood plasma
____________
Salts and nutrients are actively reabsorbed from ____________
____________
Removes ammonia, uric acid, hydrogen ions, creatinine, and penicillin which are secreted into ____________
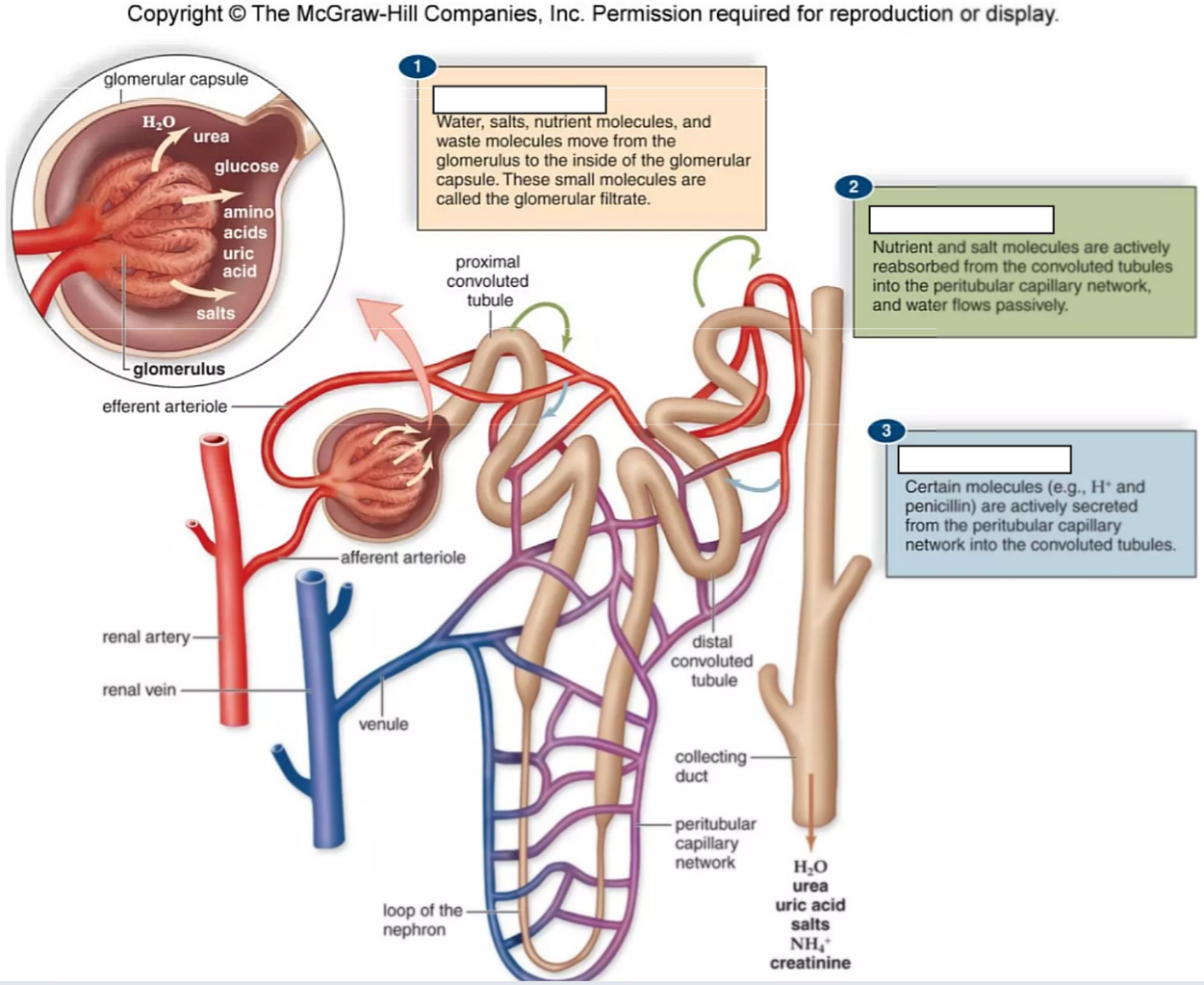
permeable
impermeable; permeable
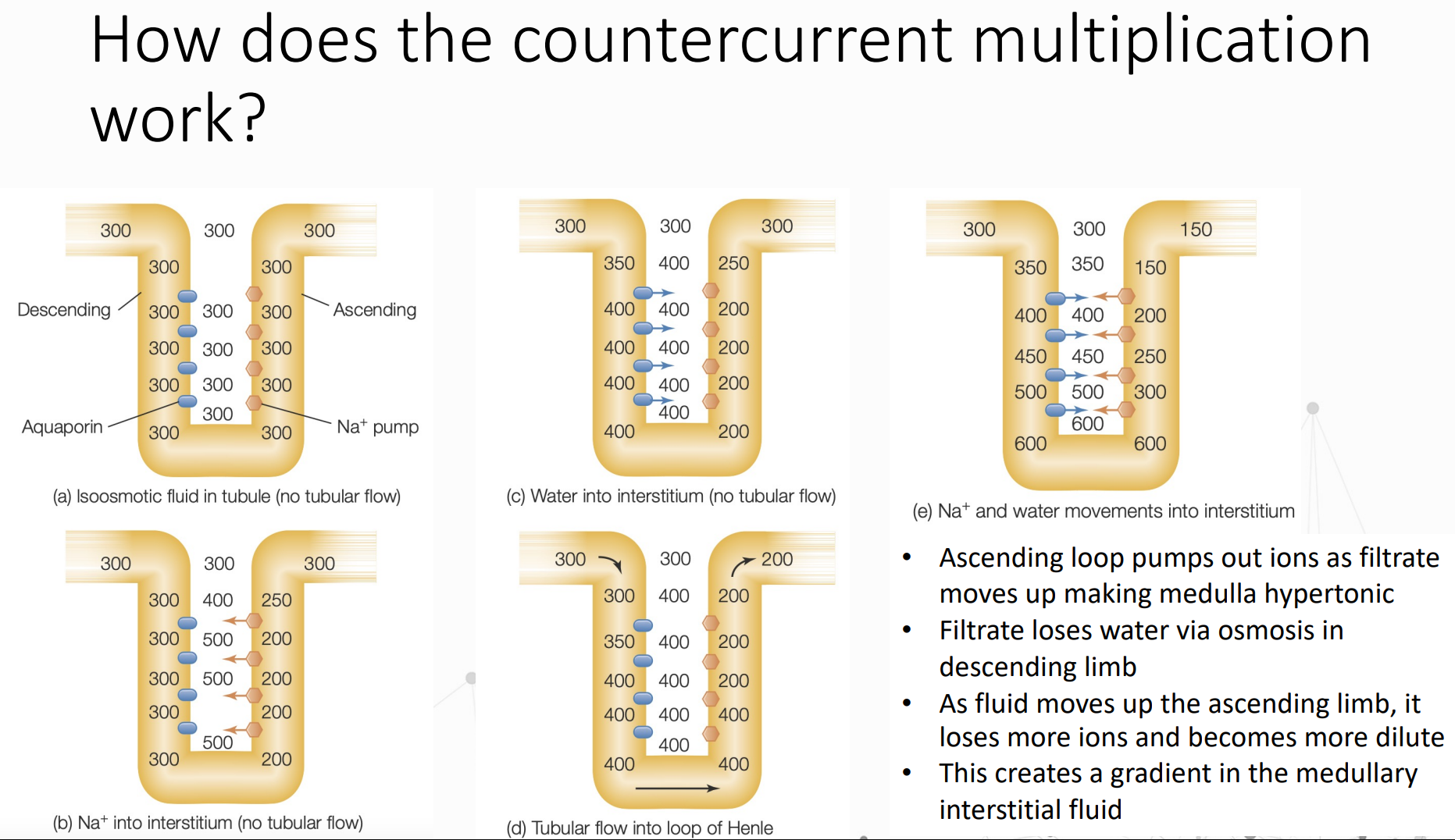
Kidneys concentrate urine to maintain salt-water balance
Loop of Henle has a descending and ascending limb
Descending limb – _________ to water
Ascending limb – _________ to water, __________ to salt ions
countercurrent multiplication
Kidneys concentrate urine to maintain salt-water balance
Solute concentration increases near the inner renal medulla because of _________________
anti-diuretic hormone (ADH)
Kidneys concentrate urine to maintain salt-water balance
Collecting duct can be made more porous to reabsorb water by the ______________ hormone
Make urine concentrated