PUBPOL Prelim 2
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
10/7 - Medicaid Part 1
What does federal vs. state gov establish for Medicaid?
Fed est req for Medcaid (floor)
who’s covered, types of medical services offered, l
States decide whether to exceed
10/9 - Medicaid Part 2
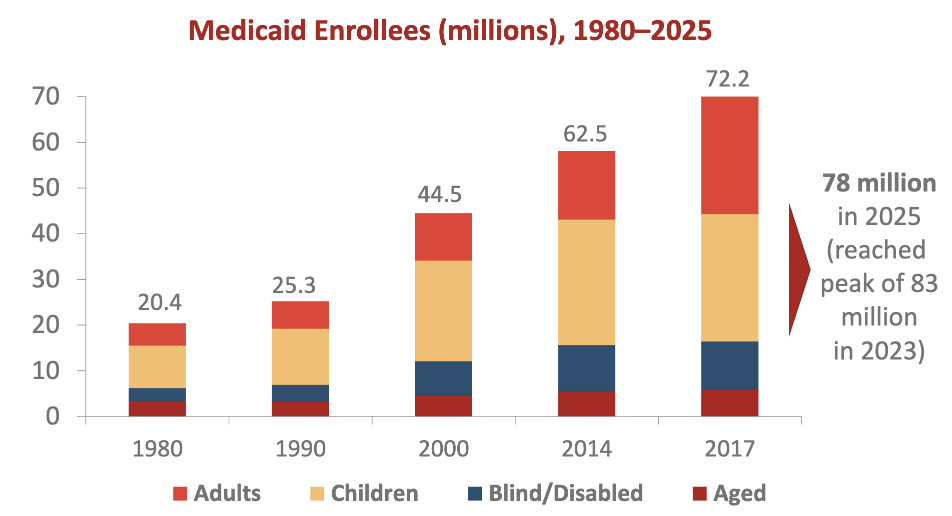
What does this show?
children always largest eligibility group
enrollment quadrupled since 1980
What are mandated benefits in Medicaid which are not covered by Medicare?
hospital, outpatient, & home care, long-term nursing home care, & lab tests
optional = prescription drugs (most states cover them)
Medicaid spending has _ since 1980
increased sharply (9% of medical spending to 18%)
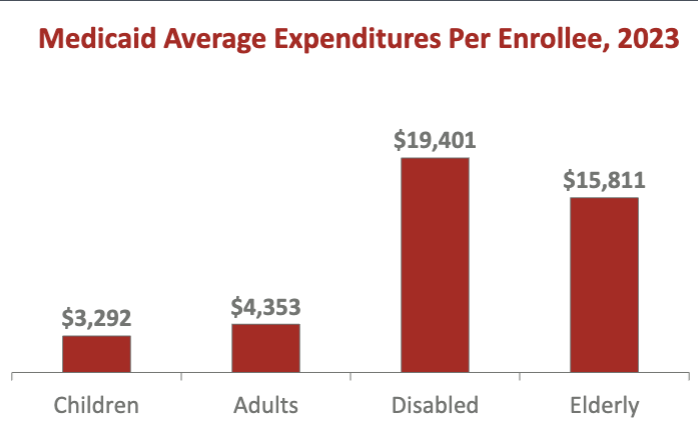
What does this show?
real expensive expenditures are disabled and elderly even though small percentage of total enrollees (children was largesT)
Several studies show Medicaid has…and what was the method
very beneficial long-term health & financial effects & pays for itself (heather at 25-54, complete high school/college, pay more lifetime taxes)
compare children in Medicaid generous state vs children who weren’t
2010 ACA Medicaid Expansion _ low-income mortality rate by 3% (short-term benefit)
reduced
How is Pre-ACA Legacy Medicaid Financed?
costs shared b/t fed & state gov
fed gov share based on state per capita income (cover more if low per capita income i.e. MS or 50/50 for high income)
Fed gov pay about _ of overall Medicaid expenditures nationally
60%
However, state gov spend _ as much on Medicaid as Higher Edu
twice
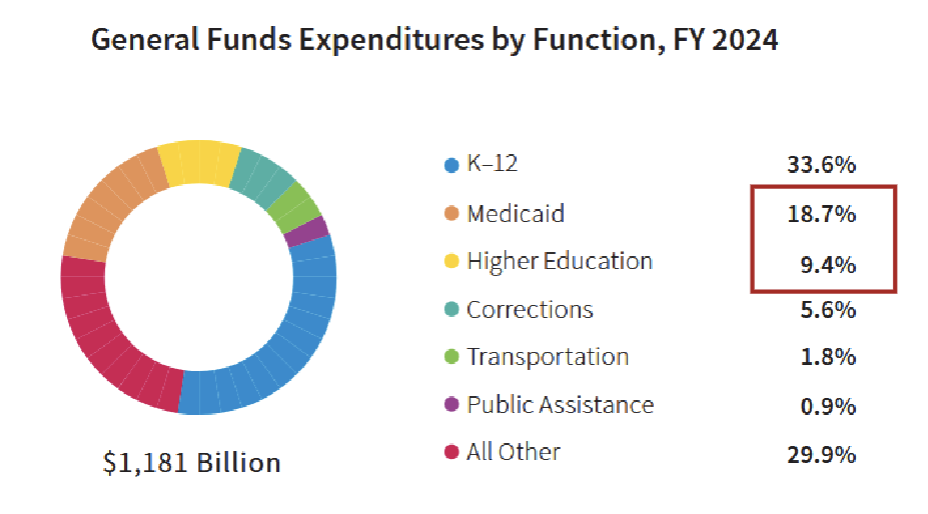
Some restrictive vs. expansive states decide
adults w/o children ineligible
parents eligible only if income <50% of FPL
^both
adults w/o children eligible if income <133% of FPL
How do state govs respond to unfunded federal mandates, high & rising medical costs, & pressure by stat residents to keep other taxes low?
pay Medicaid physicians low fees
On average, ranking how priv health insurers, medicare, & medicaid pay physicians
Priv health insurers pay most generous fee
Medicare pays physicians 25% less & hospitals 50% less
Medicaid pays physicians & hospitals 50% less
*some states Medicaid pays high physician fees but other states Medicaid reimbursement low
Implications of Medicaid paying low fees to physicians
physicians don’t accept new Medicaid patients = fewer services & worse health for them
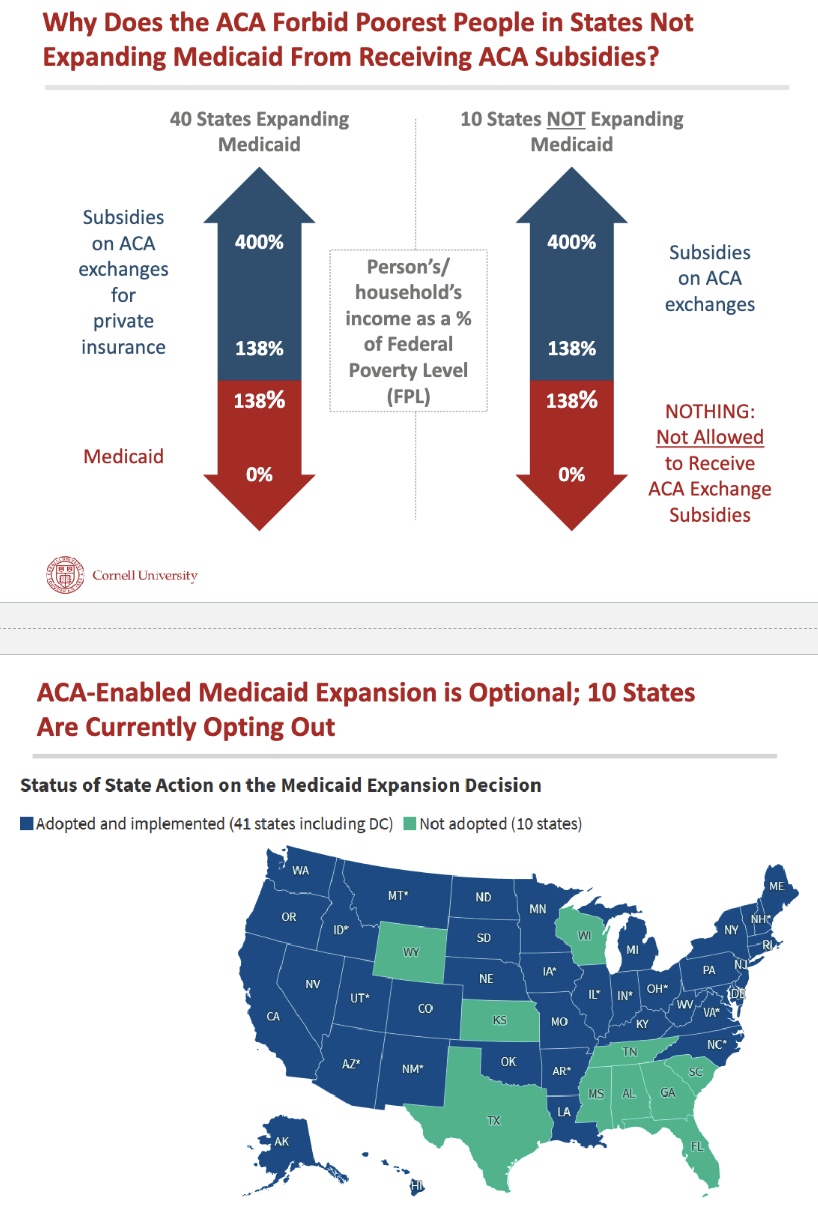
Why coverage gap where some people too rich for Medicaid but too poor for ACA exchange subsidy/tax credit?
ACA thought there would be incredible pressure on states to expand (media) but 10 states still not
Why 10 states still refusing Medicaid expansion if?
they turning down billions of new fund from federal gov
this money would improve health of uninsured
they turning down “free” money from US taxpayers
Predict all states will eventually agree to expand Medicaid b/c
they realize they’re paying for other states = pressure on governors to take federal moeny
States can expand in these 3 creative ways

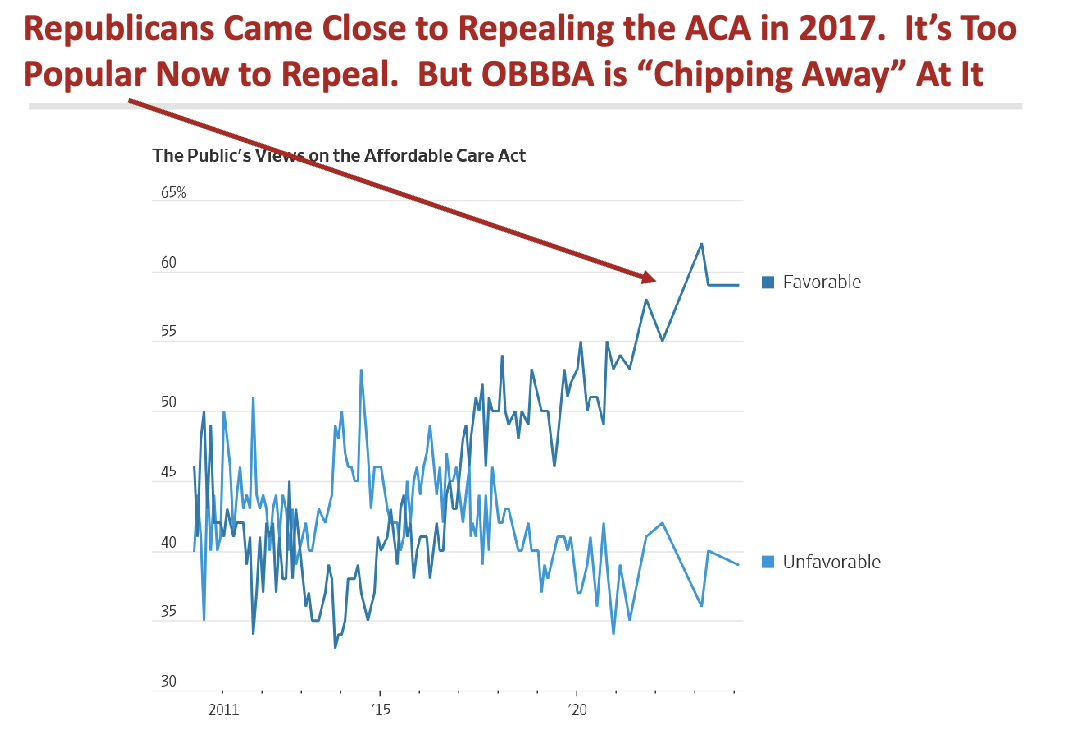
What does this show in 2017?
Republicans very close to repealing ACA but ACA more popular in US now = OBBA try to chip away at ACA
10/16 - Physicians at Work_1
OBBA’s impact
restrict federal Medicaid funding to states by about $90 billion/yr (10% of spending)
How will states respond to reduced Medicaid spending via OBBA?
increase state taxes (not likely)
pay MDs & hospitals less (likely)
vigorously enforce work req (vary across states)
OBBA work reqs?
CBO by 2027
Why OBBA work req expected to cause 5 million to lose Medicaid coverage?
states need to build expensive & complex systems quickly
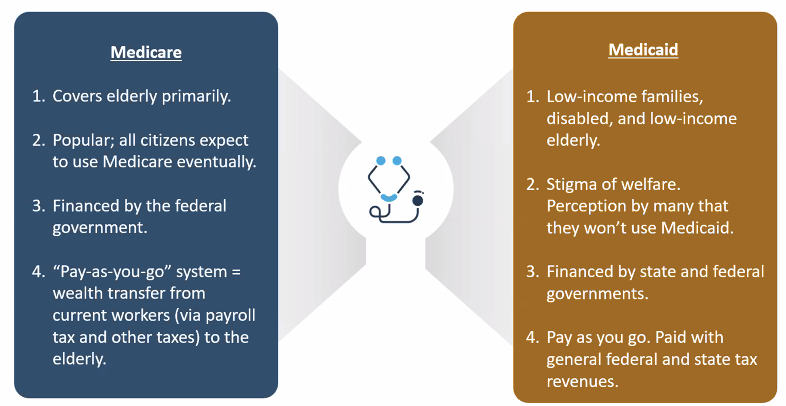
Medicare vs. Medicaid Summary
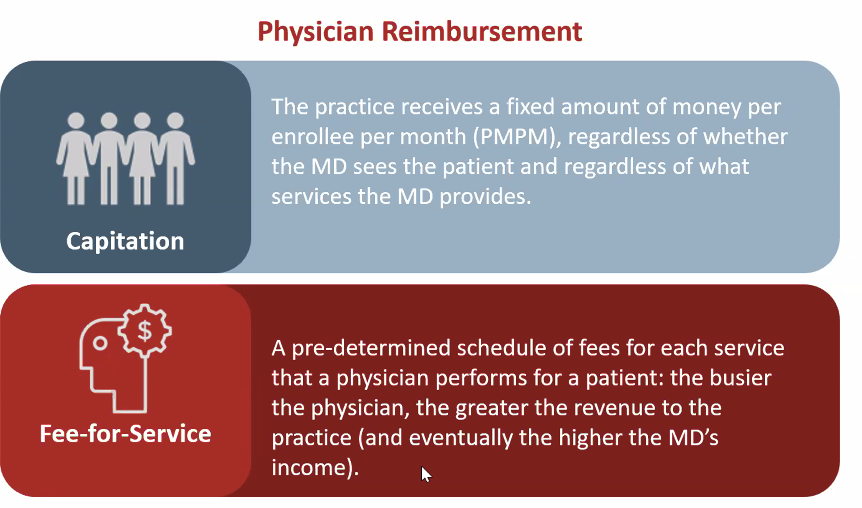
Insurers can pay physicians via
capitation (rare)
fee-for-service
10/21 - Physicians at Work_2
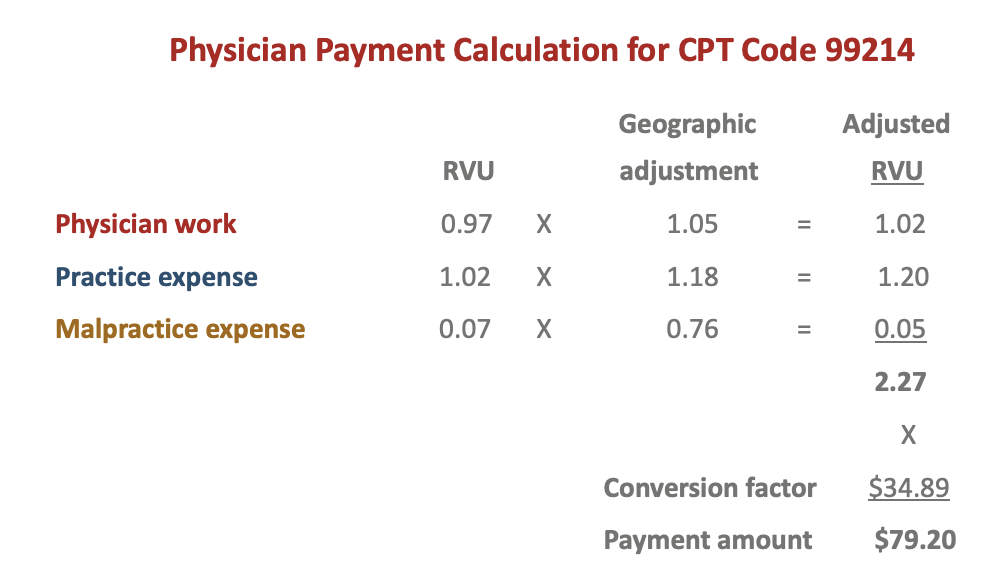
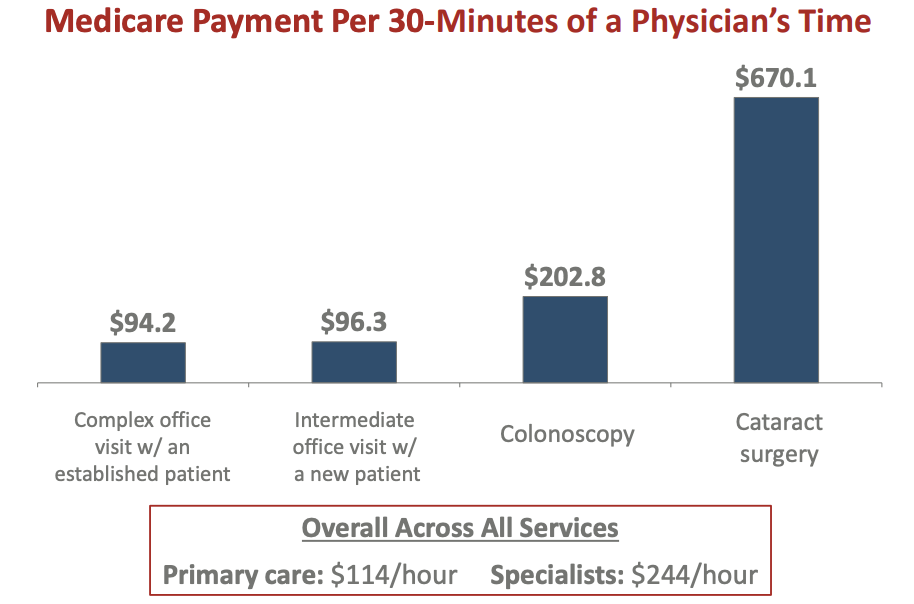
Explain how Medicare set payment to physicians for midlevel office visit?
Medicare’s RBRVS pays specialists or PCPs more across all services?
specialists (who preform procedures)
How private health insurers use medicare method..
private health insurance plans adjust entire Medicare RBRVS schedule but maintain payments b/t CPT codes
private plans pay physicians 40% more than Medicare RBRVS
Why do some health systems/MDs receive higher payments from priv health isnurer?
insurers negotiate w/provider regarding whether they’ll be in-network & how much they’ll be paid
providers valuable to enrollees command higher prices
insurers who are important to providers will pay lower prices
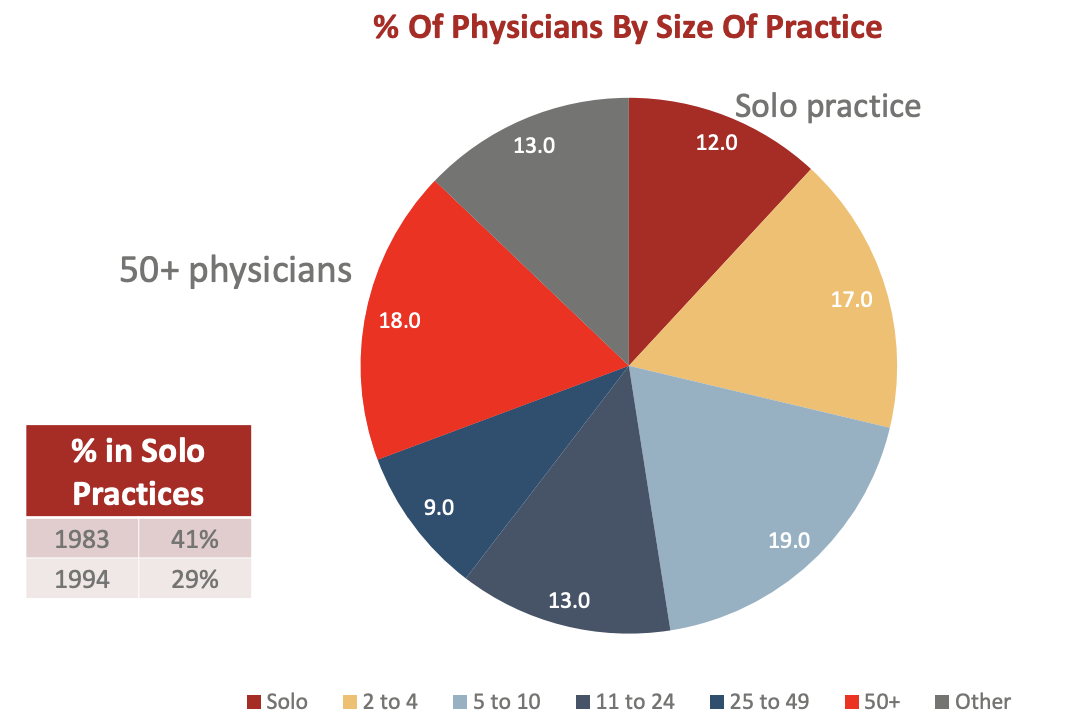
physicians forming larger groups as % in solo practices decreasing but 48% still in practices w/<10 physicians
larger groups have more negotiating power w/ priv insurers
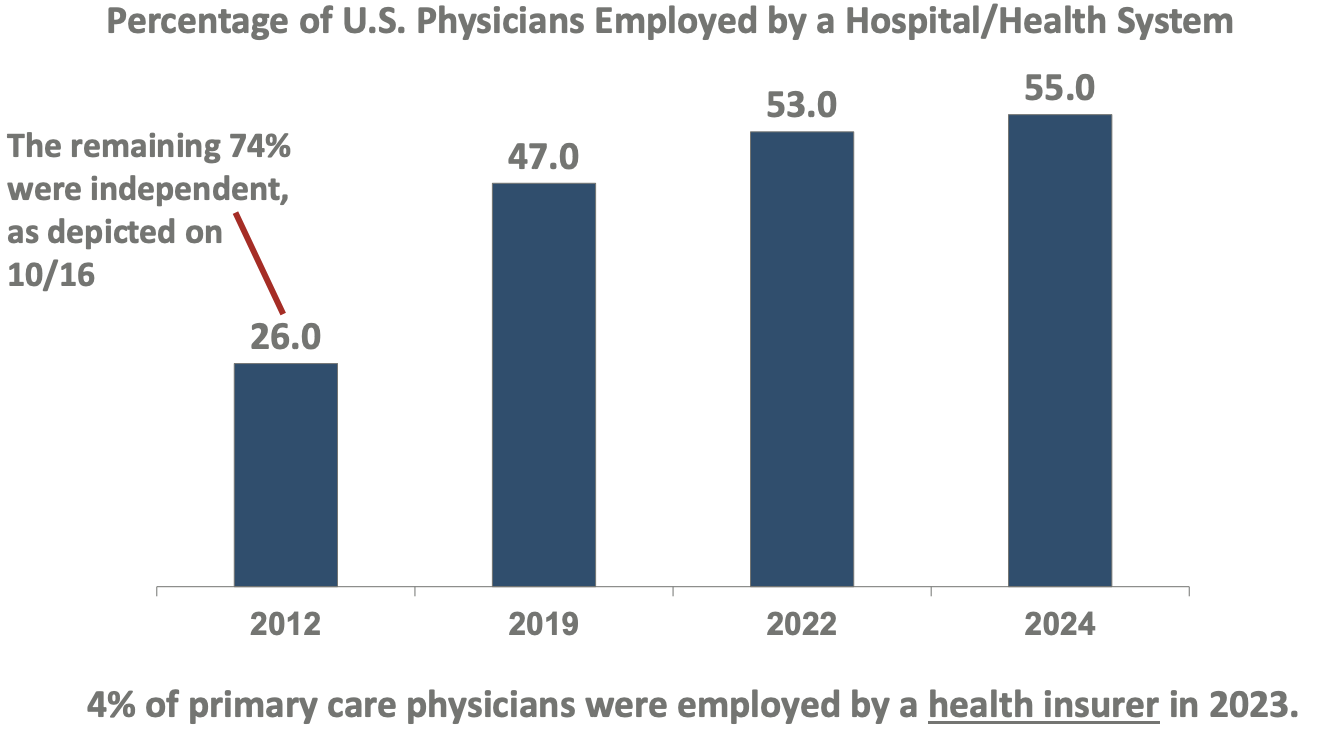
Majority of physicians now employed by?
hospital/health system (26% → 55%)
What happens when physicians agree to sell practice to be part of hospital B?
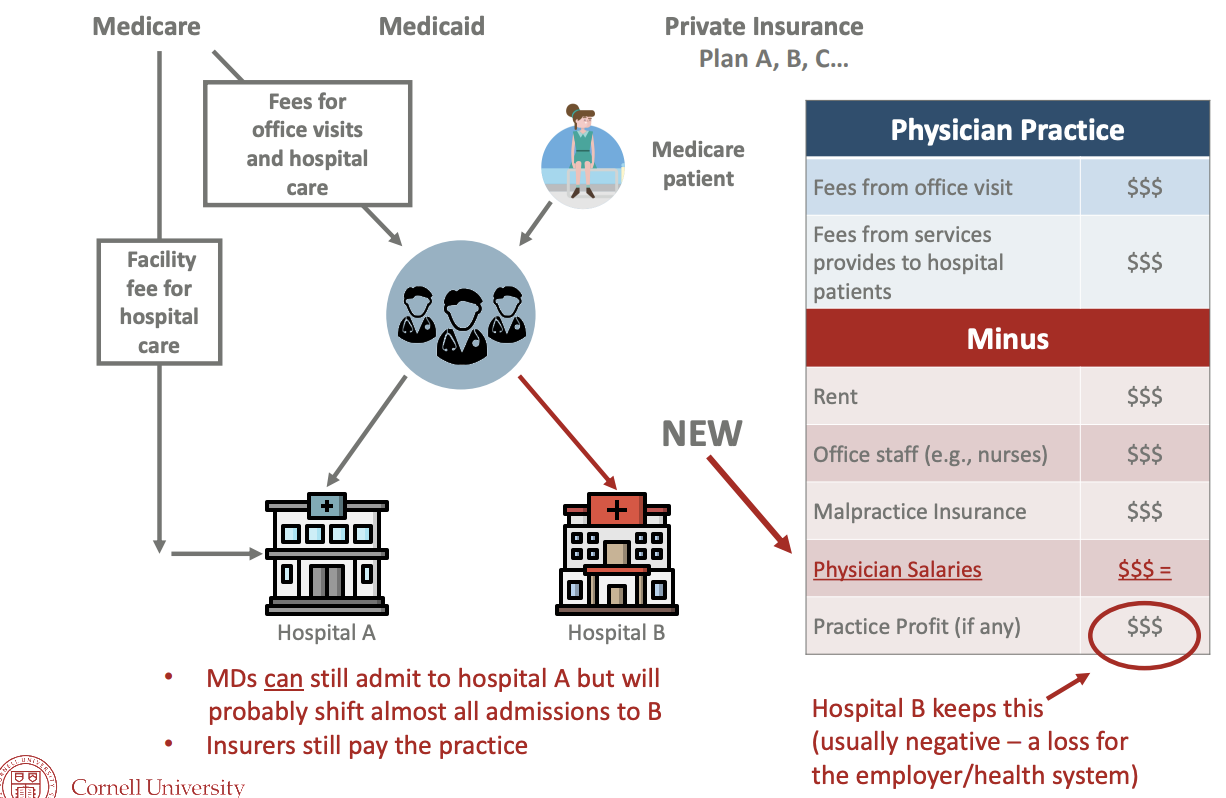
Why are physicians increasingly becoming hospital employees?
hospitals can negotiate higher payment w/insurers
hospitals increase access to costly resources (i.e. electronic medical records)
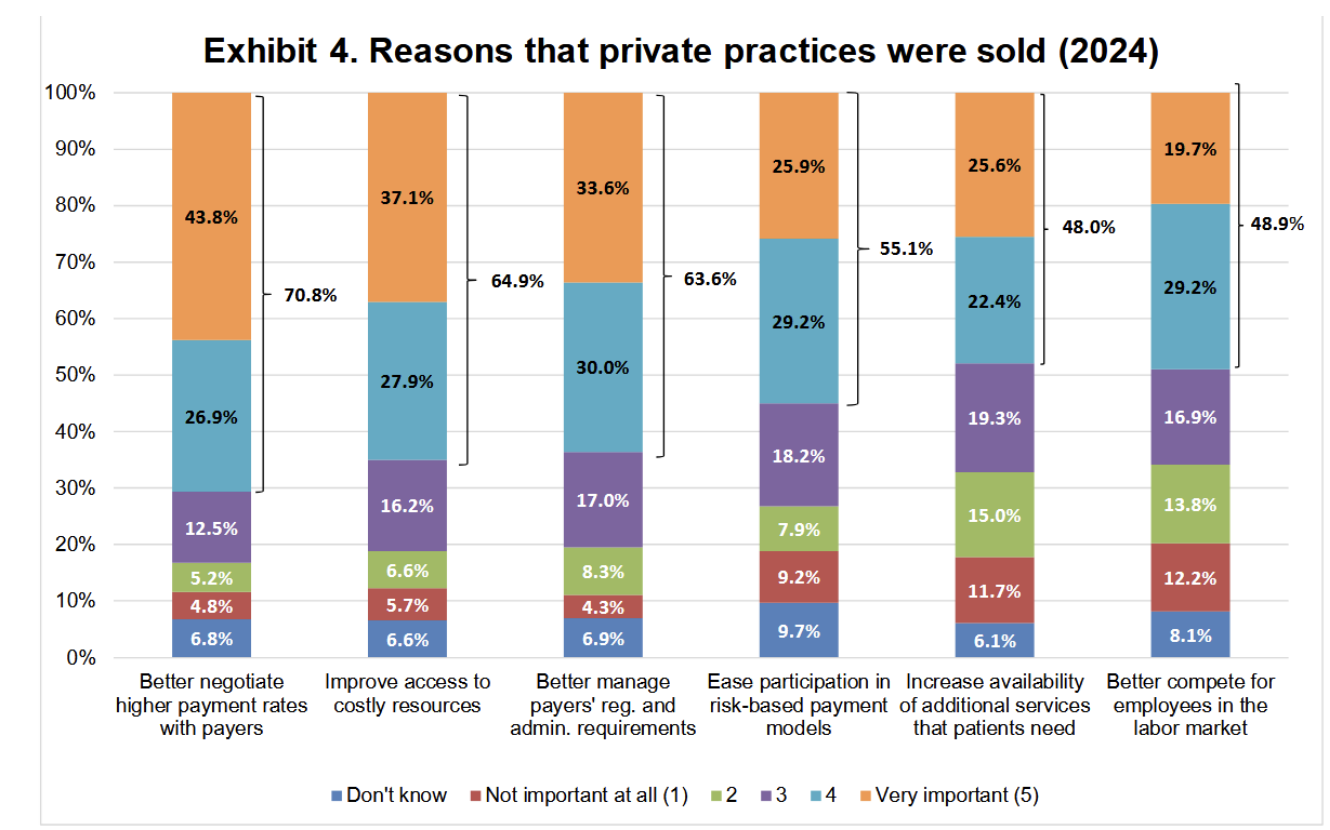
Why is operating a solo practice more expensive, complicated, & risky?
health systems negotiate higher fees
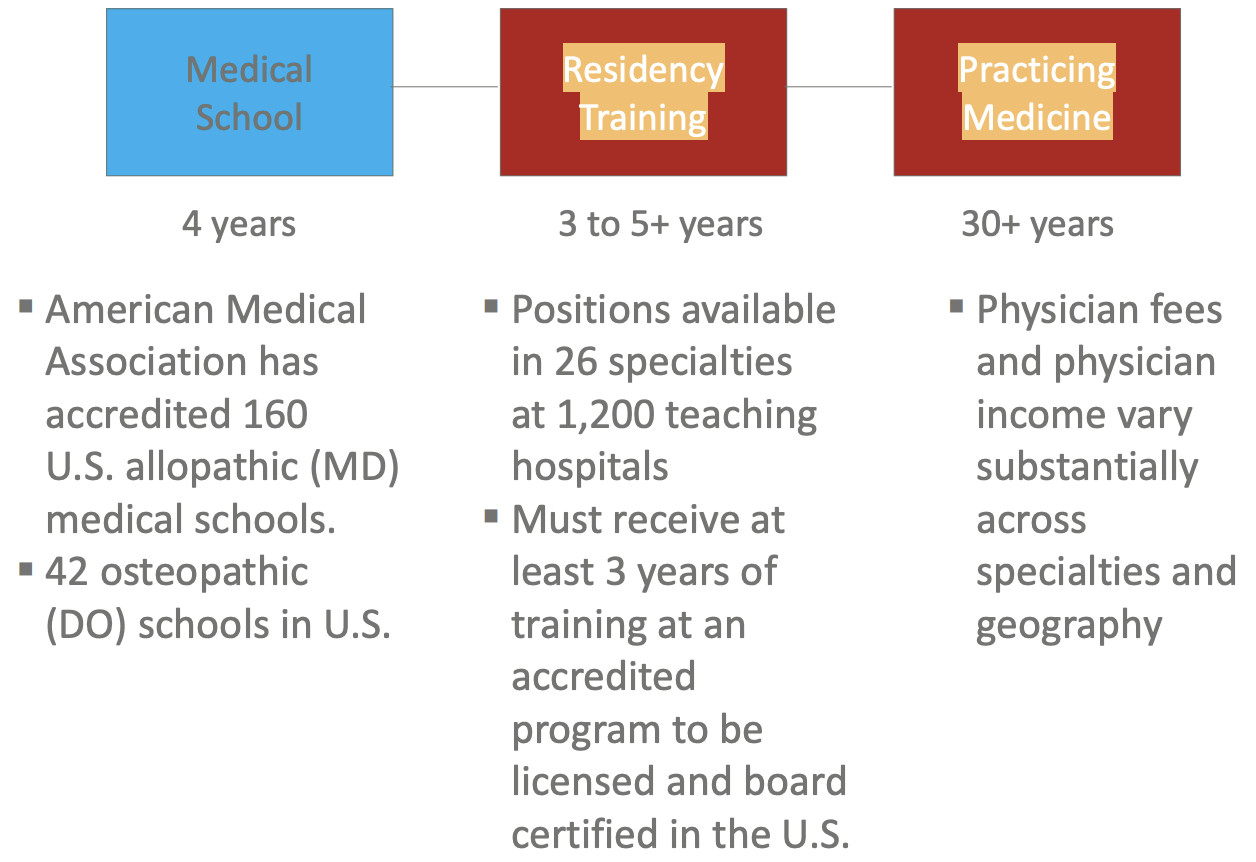
Overview of Physician’s Career
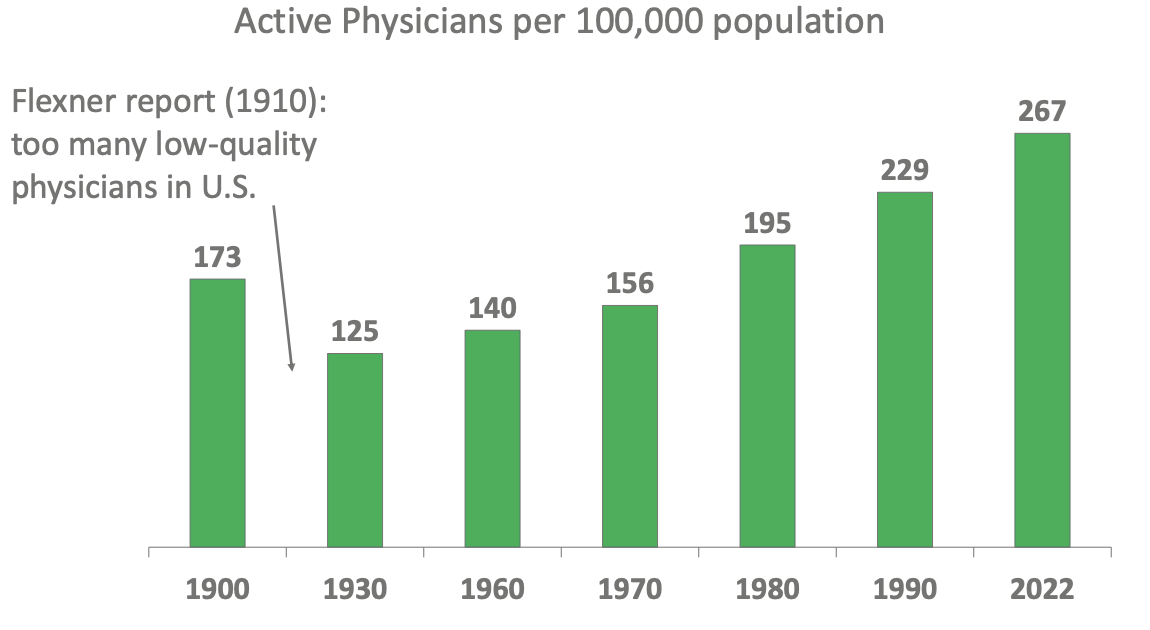
Why is there dip between 1900 and 1930 with number of physicians in US?
Flexner study where he reported too many low-quality physicians = close some med schools???
Number of physicians per capita has _ since 1930 but _
doubled but US has fewer physicians than most high-income countries
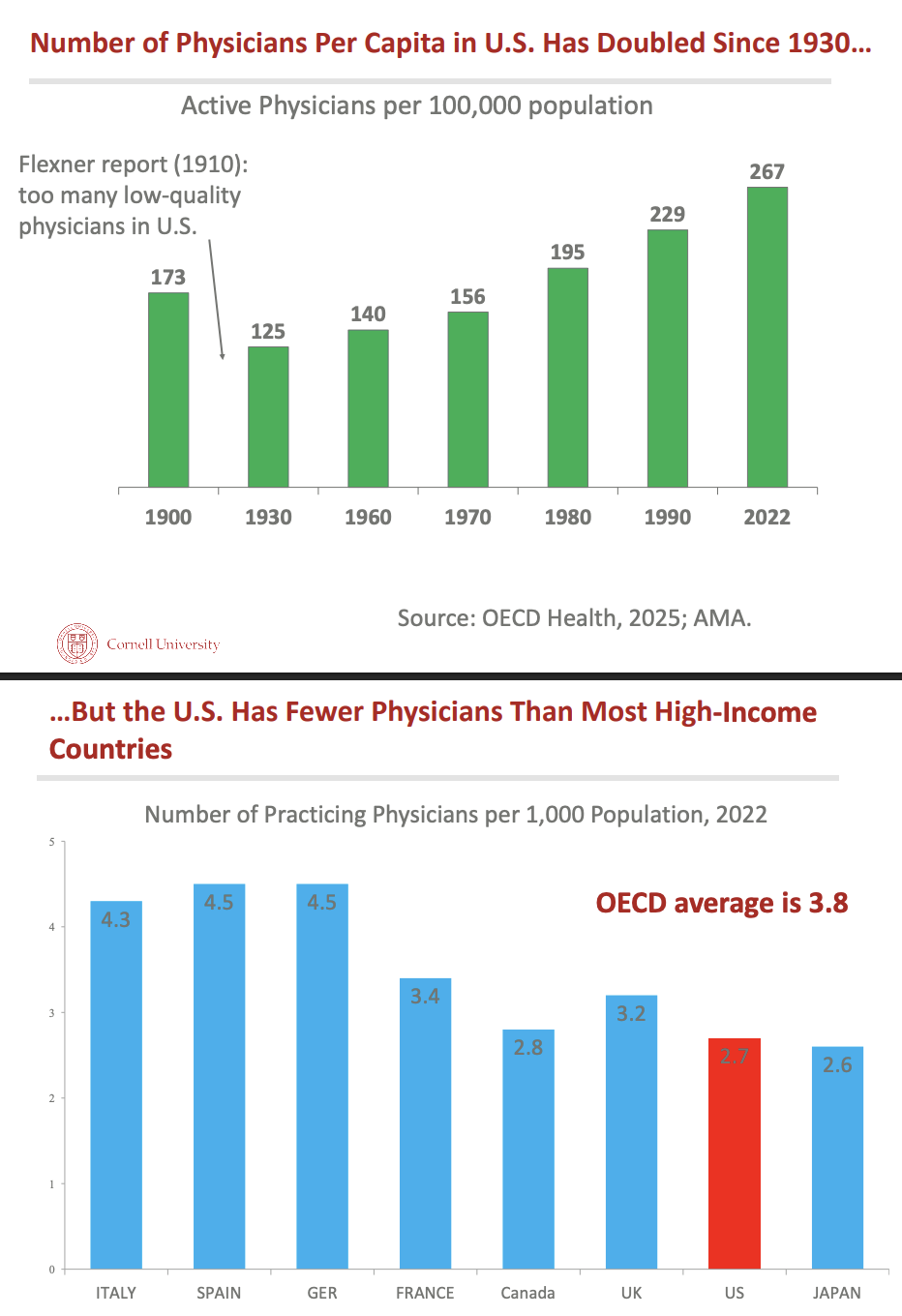
What created physician shortage in US?
_ times more applicants to US allopathic (MD) med schools than available positions and % female matriculated _
2-3x, increased
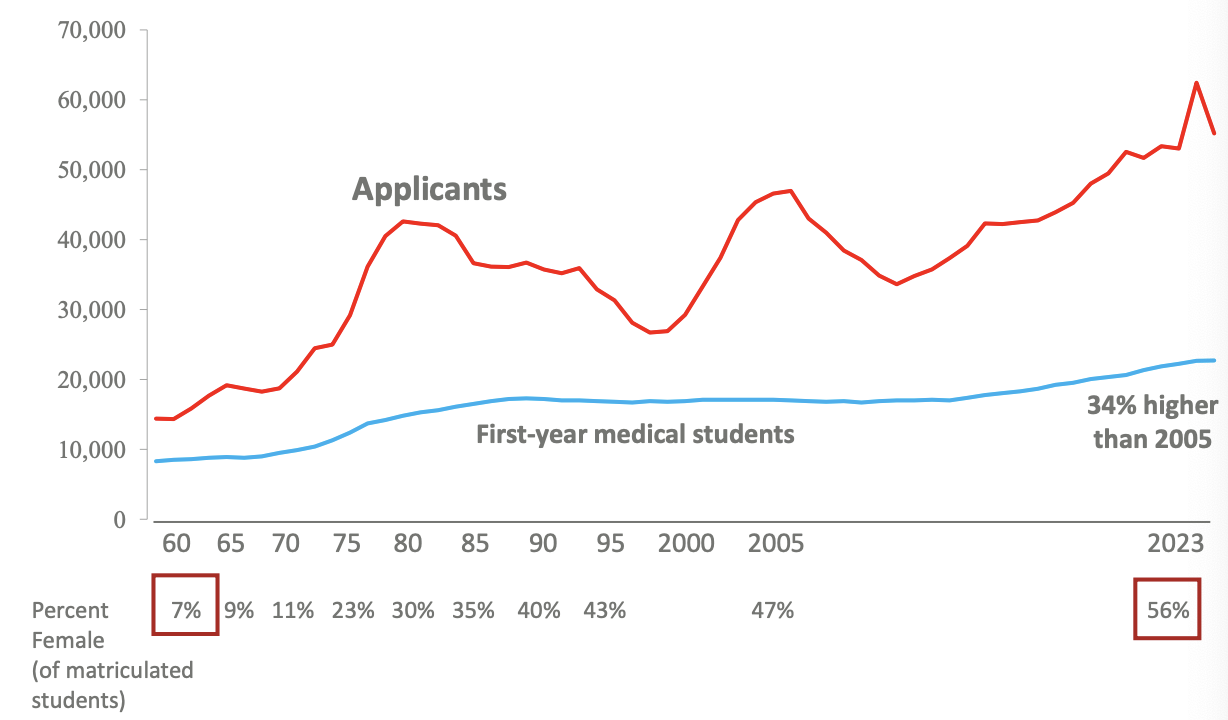
What is evidence that we are in a physician shortage?
longer time to get appointment (21-31 → days) & worse in certain areas and non-primary care specialities
mid-level practitioners (CRNA, PA, nurse practitioner) are taking on greater responsibilities
What is ameliorating primary care MD shortage?
rapid growth of osteopaths (77%) & mid-level practitioners (122%)
27 states expand nurse practitioner practice
number of nurse practitioners providing primary care same as PCPs = PC appointment times haven’t lengthened as much
10/23 - Physicians at Work_3
Overview of National Resident Matching Program
in 4th year of med school apply to residency programs & rank them
computer algorithm assign students to residency positions & obliged to attend the one they matched
students who didn’t match can scramble for unfilled spot
Even though you can’t suggest ranking depending on other party’s level interest,
35% of family programs indicate that hearing a student will rank the program high improve applicant ranking
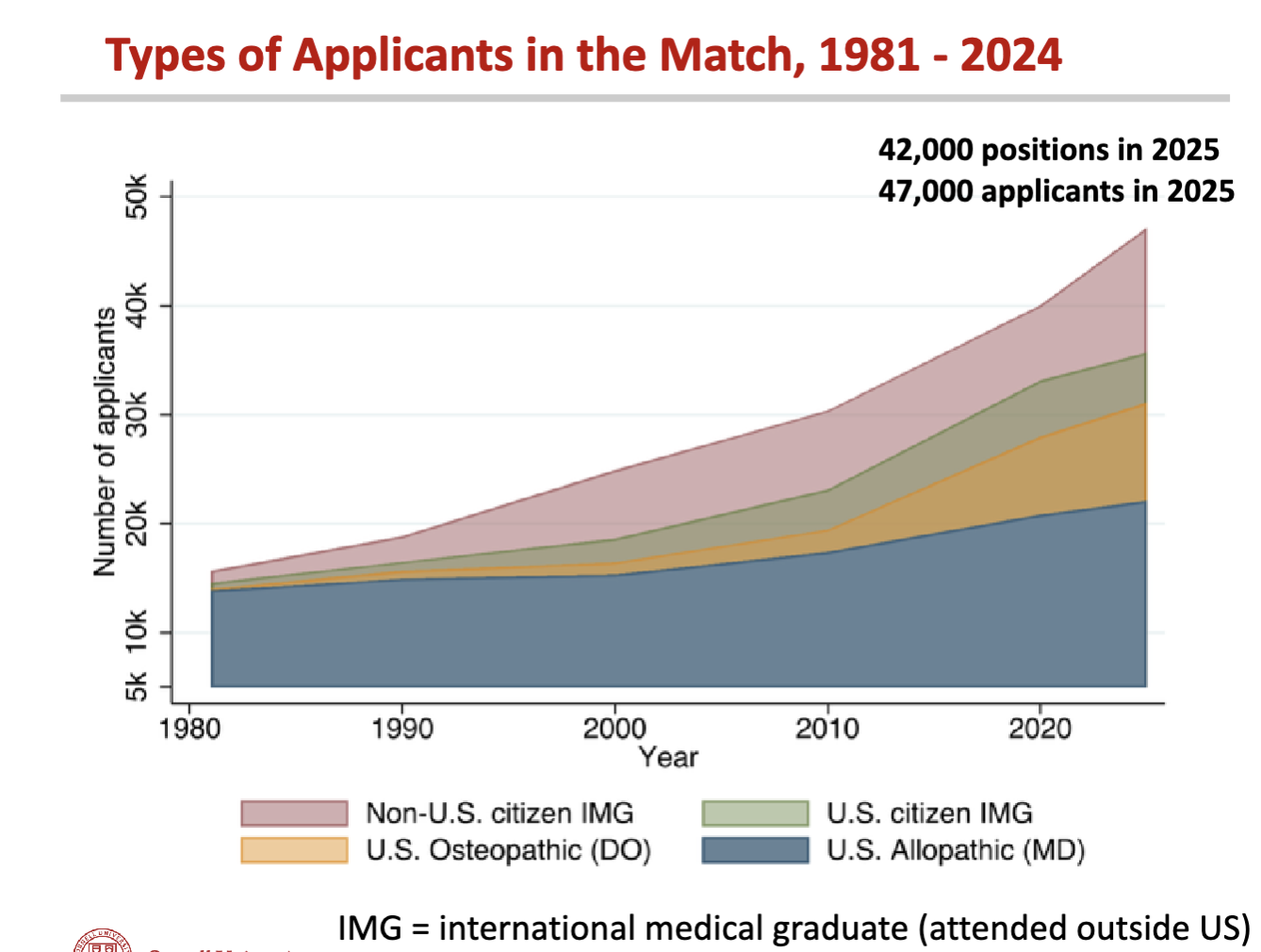
What does this show?
growth of applicants (both non-US citizens and US citizens) & from ?
What is bottleneck for alleviating current/future physician shortage?
increasing residency positions
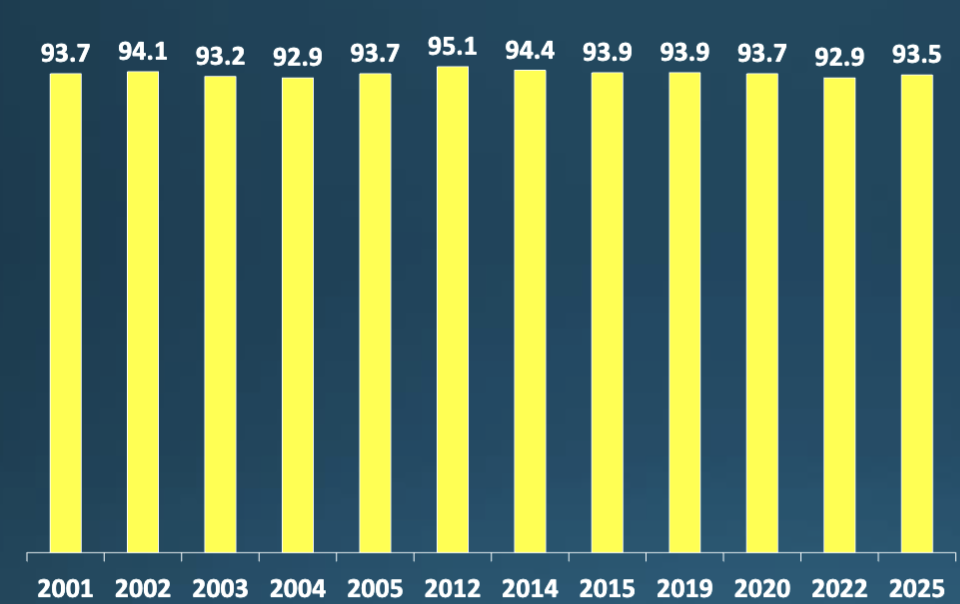
What does this show?
95% usually get matched & this trend stable for
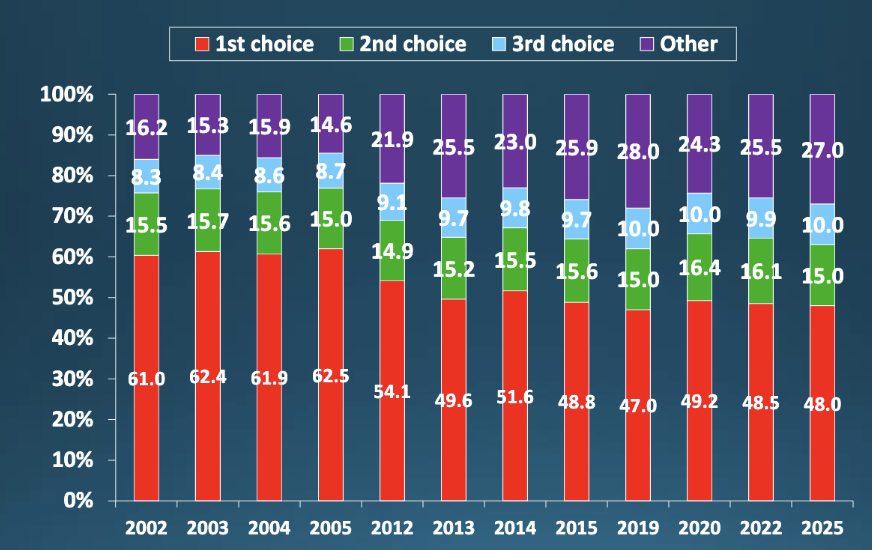
What does this show?
Even though most people get matched, not all allopathic graduates receive their top choice
Why don’t all US allopathic medical school graduates receive match/match to top-ranked program?
speciality
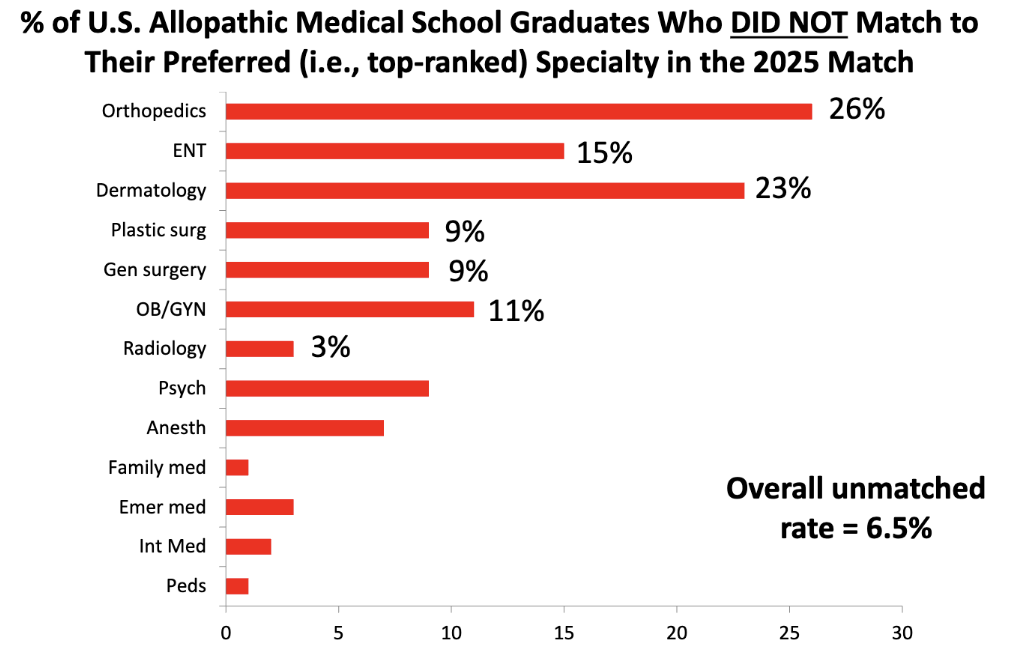
What does this show?
speciality matters amongst the allopathic graduates who did not match (ppl who didn’t match ranked dermatology/orthopedics speciality first)
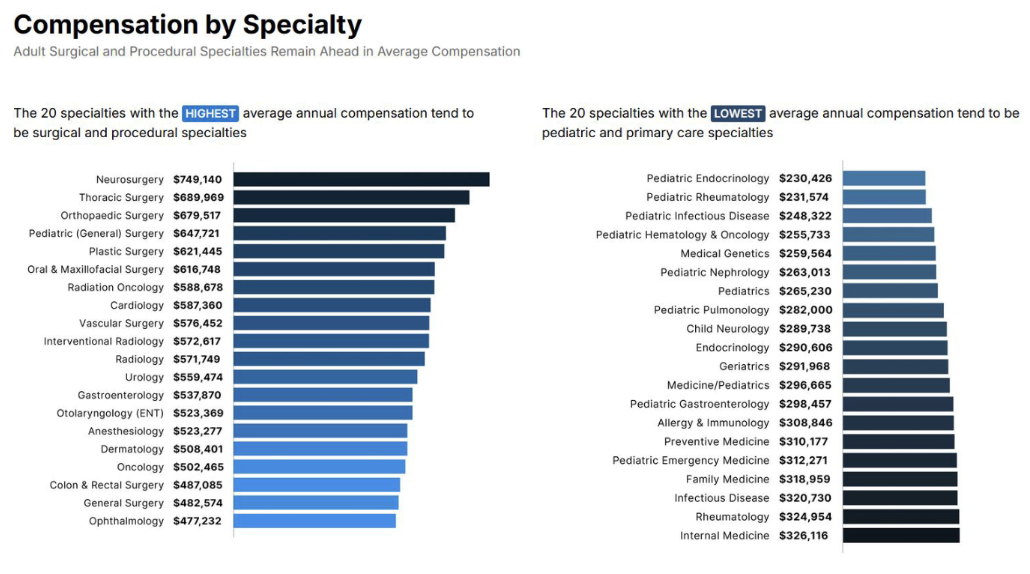
Unmatched rates are generally _ in high-paying specialities
higher
Why don’t residency programs in high-income/competitive specialities expand to accept more medical students?
restricted entry / “cartel” behavior where physician-run orgs need to approve program expansion
competitive specialities run “tournament” to see which med students are “worthy
3 Aspects of this “Tournament”
higher test score = more competitive but now exams past/fail
average research output (most competitive have more publications)
higher grades in med school = inducted into AOA (Med School Honor Society) = more accepted to competitive resident programs
Private med school debt _ then public med school
greater
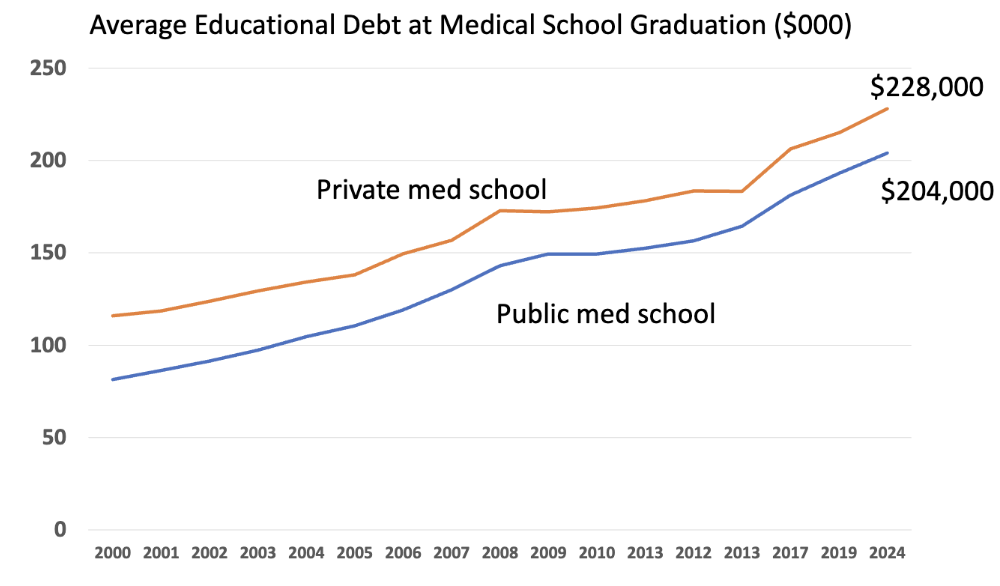
Can med students w/edu debt afford relatively low-paying speciality?
yes but higher income = easier to pay
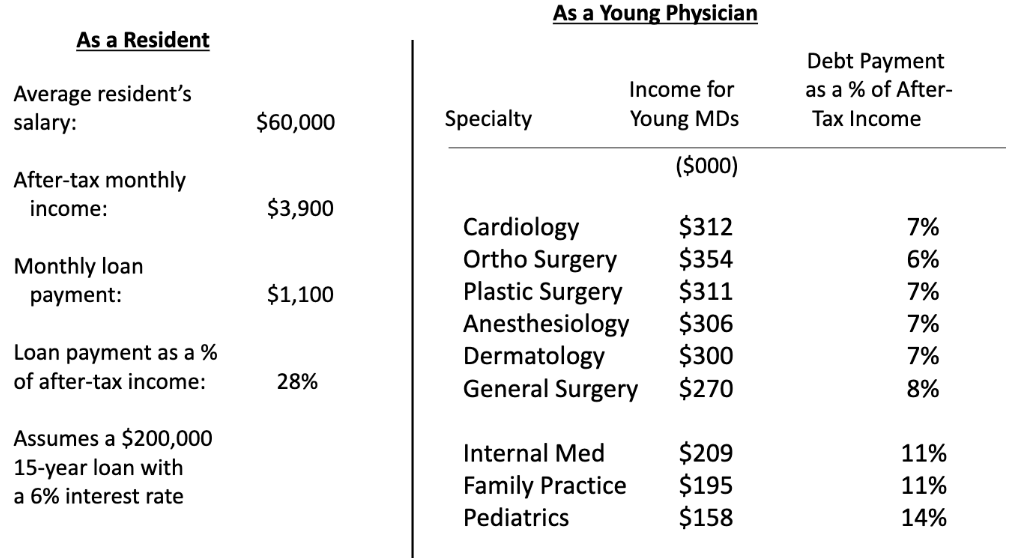
Evidence that Edu Debt doesn’t affect med student speciality choice
some med schools charge no tuition = no debt
program goal for graduates to choose speciality based on passion/aptitude not financial obligation
After controlling for observed factors, male physicians earn _ than female physicians
25% more
b/c gender bias, structural sexism, compensation models favoring male MD practice styles, & diff in bargaining power