Biology B1 - The cardiovascular system
1/144
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Booklet + textbook + research, completed
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
What is the cardiovascular system?
The cardiovascular system is the body's transportation system, that allows the blood to circulate around the body to transport and supply nutrients to organisms so that they can survive
What is the cardiovascular system also known as?
The circulatory system
What is the circulatory system?
Has double circulation.
a network of organs and vessels that includes the heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries), and blood.
Its primary function is to transport oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to cells throughout the body, while also removing waste products like carbon dioxide.
What does the right side pump?
The right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs. Oxygenated blood then returns to the left side of the heart.
What does the left side pump?
The left side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood to the tissues. Deoxygenated blood returns to the right side of the heart.
Why is it called a double circulatory system?
Because the blood flows through the heart twice in each circuit of the body. Once through the right side and once through the left side, during one complete cycle
What is the pulmonary circulation?
This is the 1st loop that transports oxygen and carbon dioxide from the heart to lungs
What is the systemic circulation?
This is the 2nd loop that transports oxygen and carbon dioxide from the heart to the body cells
What is the pulmonary artery?
This is a vessel that carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs for oxygenation
Structure of the pulmonary artery?
Tunica intima, a smooth inner layer.
Tunica media, a middle layer that pushes blood through.
Tunica adventitia, a protective outer layer.
What is the pulmonary veins?
This is a vessel that carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium
What is the left atrium?
This is the upper left chamber that receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle
What is the right atrium?
This is the upper right chamber that receives deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps it into the right ventricle
What is the left ventricle?
This is the lower left chamber that pumps oxygenated blood through the aortic valve into the aorta, sending it to the rest of the body
What is the right ventricle?
This is the lower right chamber that pumps deoxygenated blood through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery, sending it to the lungs
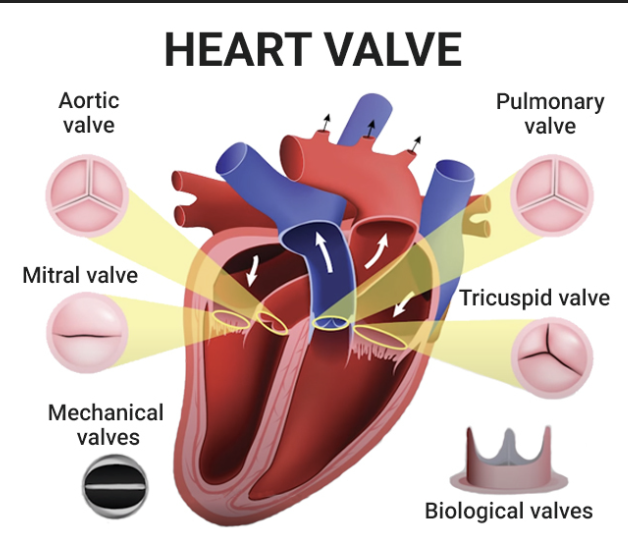
What is the bicuspid valve?
Also known as the mitral valve
This is a valve between the left atrium and left ventricle, and it opens to allow oxygenated blood into the ventricle and closes to prevent backflow when the ventricle contracts
What is the aortic valve?
This is a valve between the left ventricle and the aorta, and its opens to allow oxygenated blood to be pumped to the body and closes to prevent backflow
What is the tricuspid valve?
This is a valve between the right atrium and right ventricle, and it opens to allows deoxygenated blood into ventricle and closes to prevent backflow when the ventricle contracts
Tricuspid valve has 3 flaps
What is the semilunar valve?
Blood does not flow back into the heart because of the semilunar valves
What is the pulmonary valve?
This is a valve between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, and it opens to allow deoxygenated blood to be pumped to the lungs and closes to prevent backflow
What is the superior vena cava?
The superior vena cava receives blood from the head, neck, arms and chest. It transports deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium
What is the inferior vena cava?
The inferior vena cava receives blood from the trunk, legs, feet and organs in the abdomen and pelvis. It transports deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body to the right atrium
What is the aorta?
The largest artery
This is a vessel that carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the rest of the body
What is the septum?
The wall of muscle and tissue that separates the left and right sides of the heart
What is the function of the arteries?
Carry hight pressure oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body
Structure of an artery?
Thick walls with collagen
Small lumen
Smooth endothelium cells which reduces friction
Elastic tissue in the wall and this allows it to expand and recoil
What is an arteriole?
Smaller arteries that contain smooth muscle cells wrapped around the endothelium cell
Structure of an arteriole
The intima (endothelium)
The tunica media (smooth muscle)
The adventitia (collagen)
What are capillaries?
tiny vessels with very thin walls consisting of only one layer of endothelium cells
Function of capillaries?
allows exchange of material between the body’s cell via tissue fluid
Structure of capillaries?
One cell thick and thin walls
Site of diffusion
Narrow lumen which helps the RBC release oxygen
What are venules?
A group of a larger capillaries that can join to form veins
Function of veins?
Carry blood to the heart
Structure of veins?
Large lumen
Have valves
Thin walls, low pressure
What is the pathway of the pulmonary circulation?
Right ventricle →pulmonary artery → lungs (CO2 exchange for O2) → pulmonary veins → left atrium
From the heart to lungs, the right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood into pulmonary artery, branches to each lung. In the lungs, blood flows through capillaries surrounding the air sacs (alveoli), exchange carbon dioxide for oxygen. From the lungs to heart, oxygenated blood then travels through pulmonary veins to the left atrium of the heart
What is the pathway of the systemic circulation?
Left ventricle → aorta → arteries → capillaries (capillary exchange) → veins → vena cava → right atrium
Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to aorta. The aorta branches into smaller arteries. Arteries branch into arterioles, then into network of capillaries which supply all tissues and organs. In capillaries, oxygen and nutrients are delivered to body cells, C02 and other waste products are picked by blood. Deoxygenated blood then flows from the capillaries into venules, merges into larger veins. Veins carry blood back towards the heart, leading into the superior and inferior vena cava. The vena cava empty deoxygenated blood into right atrium of the heart.
This completes the systemic loop and starts the pulmonary circulation to get more oxygen
What is the structure of the heart?
The heart is a muscular organ with 4 chambers, 2 atria and 2 ventricles, and contains valves to keep blood flowing in one direction.
The 2 atria are the upper chambers and the 2 ventricles are the lower chambers.
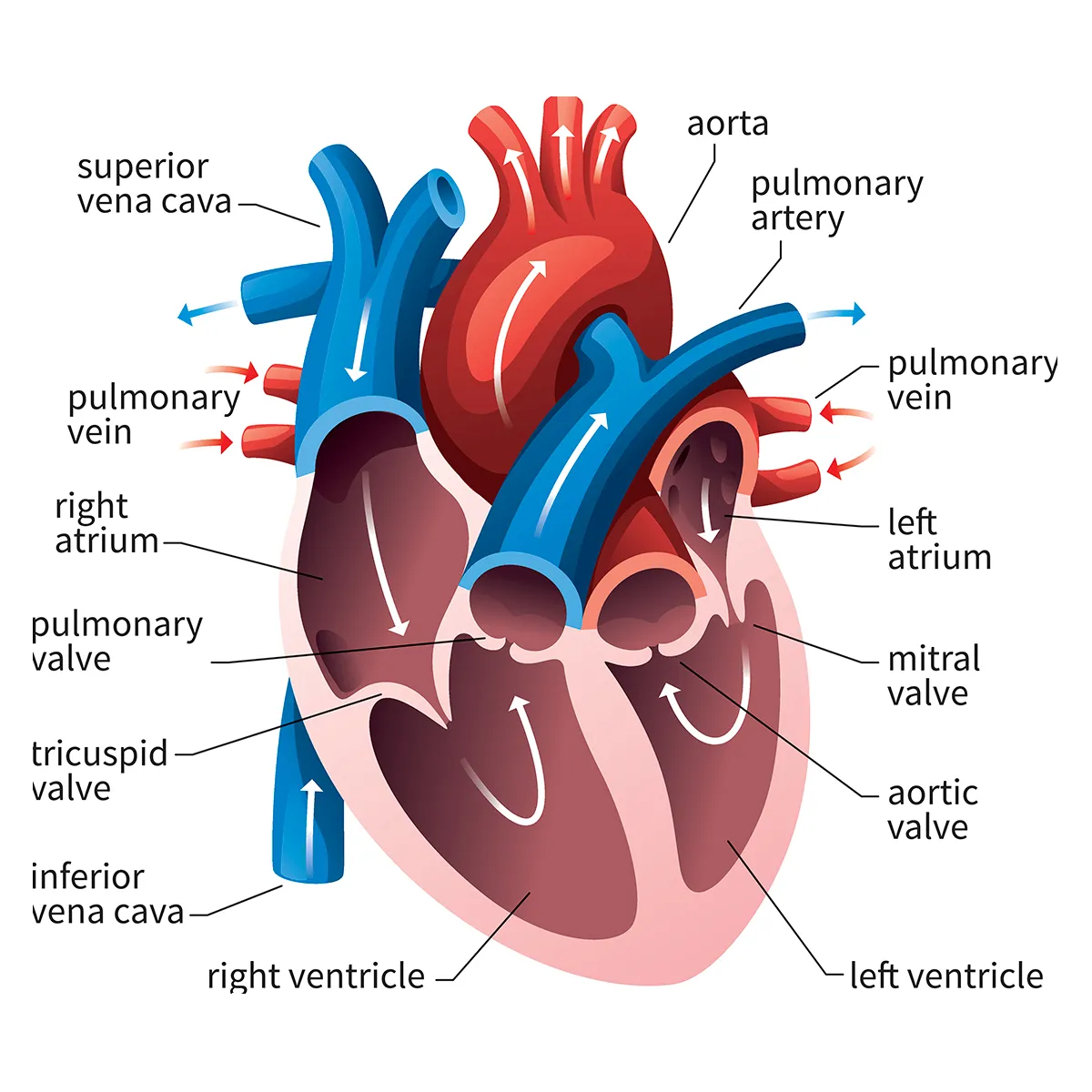
What is the function of the heart?
The heart pumps blood through the double circulatory system, which sends blood to the lungs for oxygen and then to the rest of the body to deliver oxygen and nutrients.
What does the coronary arteries take to the heart muscles?
Coronary arteries takes oxygen and food to the heart muscles
What does the right atrium and ventricle connect through?
The tricuspid valve
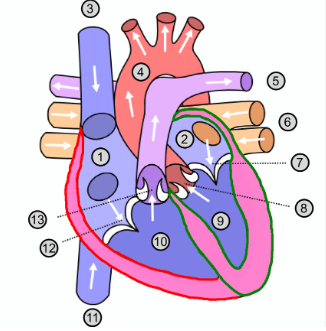
What is number 1?
Right atrium
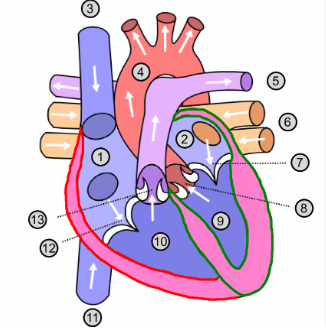
What is number 2?
Left atrium
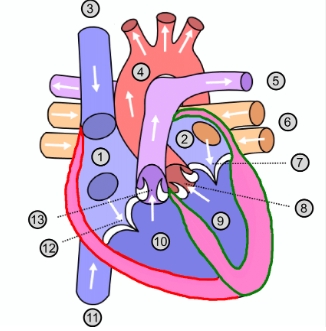
What is number 3?
Superior vena cava
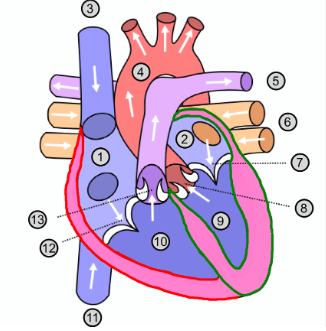
What is number 4?
Aorta
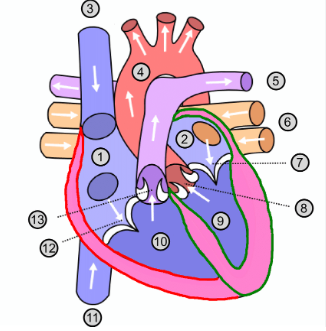
What is number 5?
Pulmonary artery
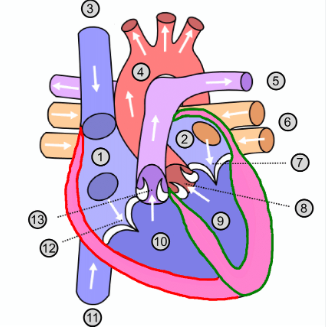
What is number 6?
Pulmonary vein
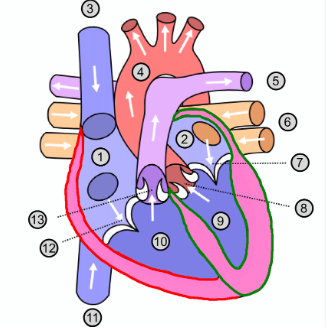
What is number 7?
Mitral valve
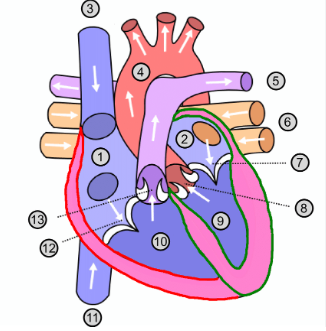
What is number 8?
Aortic valve
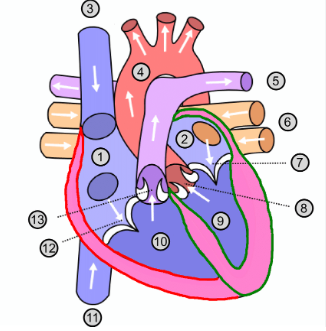
What is number 9?
Left ventricle
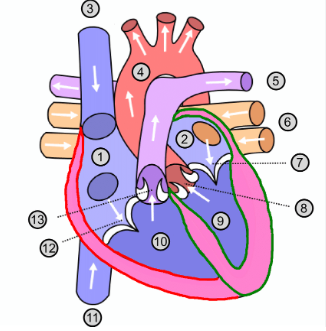
What is number 10?
Right ventricle
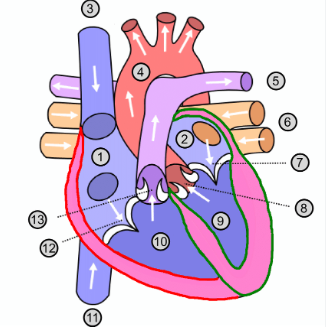
What is number 11?
Inferior vena cava
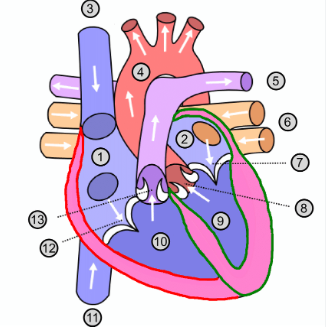
What is number 12?
Tricuspid valve
What is number 13?
Pulmonary valve
What is the atrioventricular valve?
Crucial heart structure that regulates blood flow between the atria and ventricles, specifically the tricuspid and mitral valves
Where is atrioventricular valve found?
Between the atrial and ventricular chambers of the heart
What is the function of atrioventricular valve?
To prevent backflow of the blood between the atria and the ventricle chambers of the heart
What is atrioventricular valve also know as?
Mitral (bicuspid) or tricuspid valve
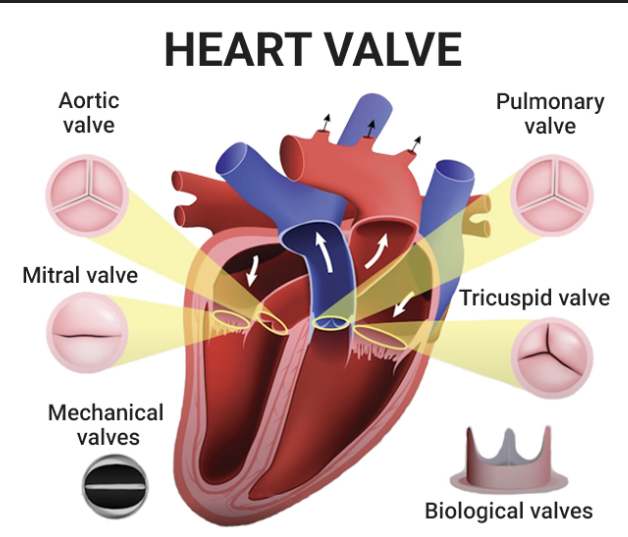
What is the semi-lunar valves?
Two pocket-like structures in the heart that prevent backflow of blood from the arteries into the ventricles
Where are the semi-lunar valves found?
At the base of the aorta and the pulmonary artery, specifically between the ventricles and the outflow vessels
What is the function of the semi-lunar valves?
Allow blood to flow from the ventricles into the arteries during ventricular systole while preventing backflow of blood into the ventricles during diastole
What does the semi-lunar valve do?
Prevents backflow of blood between the aorta and the pulmonary artery
How many semi-lunar valves are there?
2
What are the semi-lunar valves called?
Aortic valve and pulmonary valve
Where is the aortic valve located?
Between the left ventricle and the aorta
Where is the pulmonary valve located?
Between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery
What is the sinoatrial node (SAN)?
Heart’s natural pacemaker
Why is it called the hearts natural pacemaker?
Continuously generates electrical impulses and sets a healthy rhythm and pace
Where is the SAN found?
Right atrium
What does the SAN do?
Responsible for initiating electrical impulses that regulate the heartbeat
What is the atrioventricular node (AVN)?
Crucial component of the heart’s electrical conduction system
Where is the AVN found?
Top of the septum
What does the AVN do?
Picks up the wave of excitation from the atria and delays it so the atria has time to complete the contraction
What does the AVN stimulate?
Bundle of His
What is the Bundle of His?
a collection of the heart muscle cells specialised for electrical conduction
What is the conducting tissue of the bundle of His made from?
Purkinje fibres
What is purkinje fibres?
specialised conducting fibres found in the heart
What is the function of Purkinje fibres?
Conduct electrical impulses to the ventricles, so it can coordinate the contraction to pump blood efficiently
Where is purkinje fibres found?
Walls of the ventricles
What is cardiac diastole?
The phase of the cardiac cycle where the heart muscles relaxes and the chambers fill with blood, preparing for the next contraction
What happens during cardiac diastole?
Blood flows into the atria from the vena cava and pulmonary vein. Elastic recoil of the atrial walls generates low pressure in the atria, helping to draw blood into the heart
What is atrial systole?
The phase of the cardiac cycle where the atria contract, pushing blood into the ventricles and contributing significantly to the hearts overall efficiency
What happens during atrial systole?
As atria fills with blood, the pressure in the atria increases, the atrioventricular valves are pushed open and blood flows into the relaxing ventricles. The 2 atria contract simultaneously, forcing the remaining blood into the ventricles
What is ventricular systole?
The phase of the cardiac cycles during which the ventricles contract to pump blood out of the heart into the pulmonary and systemic circulations
What happens during ventricular systole?
After a slight delay, the ventricles contract. This increases the pressure in the ventricles so the atrioventricular valves close. This causes the first heart sound ‘lub'.
Blood is forced into the aorta and pulmonary artery.
The semilunar valves close.
Blood begins to flow into the relaxing atrium
What protects the heart?
Pericardium
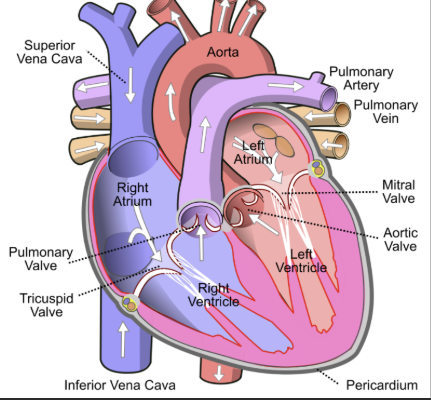
What is pericardium?
A fibrous membrane that surrounds and protects the heart
What is the middle and thickest layer of the heart wall called?
Myocardium
What is myocardium also known as?
Cardiac muscle
What is cardiac muscle?
Specialised type of involuntary muscle thats found only in the heart
What is the cardiac muscle responsible for?
Pumping blood throughout the body
What does myogenic mean?
It can contract and relax without nervous stimulation
What is coronary arteries?
Major blood vessel that supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle
What is the function of the coronary arteries?
To supply the cardiac muscle with its own oxygen supply
What are the 2 main coronary arteries?
The left and right coronary arteries, further branch into smaller arteries to ensure that all parts of the heart receives adequate blood supply
What is cardiac output?
The total volume of blood the heart pumps to the body’s circulatory system in one minute
How do you calculate cardiac output?
Multiplying the heart rate (bpm) by stroke volume
What is the stroke volume?
Blood pumped per beat
What is the 1st step of the cardiac cycle?
Both atria relax and fill with blood from the pulmonary vein and vena cava (atrial diastole)
What is the 2nd step of the cardiac cycle?
The atria contract and force the AV valves open. Blood flows into the ventricles and they fill up (ventricular diastole)
What is the 3rd step of the cardiac cycle?
The AV valves close when the pressure in the ventricles rises above the pressure in the atria to prevent the backflow of blood into the atria