2.1C Properties of Ionic Compounds
1/8
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Tell me about the structure of Ionic Compounds
exist as three-dimensional lattice structures. The structure is based areound a repeating unit (the formula unit/empirical formula)
The coordination number is used to express the number of ions that surround a given ion in the lattice
What is lattice enthalpy?
a measure of the strength of the forces between ions in an ionic solid
The physical properties of ionic compounds reflect their lattice structure
What does lattice enthalpy depend on?
ionic radius (smaller radius, stronger attraction)
charge of ion (higher charge, stronger attraction)
Tell me about melting and boiling points in relation to ionic compounds
ionic compounds tend to have high melting and boiling points due to the strength of the electrostatic attraction between the ions in the lattice
The melting and boiling points are generally higher when the charge on the ions is greater
What is Volatility? Tell me about it.
a term used to describe the tendency of a substance to vapourize
Substances with high volatility are more likely to exist as a vapour
Ionic bonds are very strong, require large amounts of energy to overcome
At room temperature, ions do not have enough to break away
ionic compounds have no odor
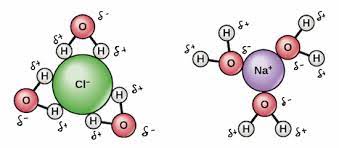
What is Solubility? Tell me about it.
the ease with which a solid (the solute) becomes dispersed through a liquid (the solvent to form a solution
Dissolving in water involves the attraction fo polar water molecules to the oppositely-charged ions in the ionic lattice, and the hydration of the separated ions
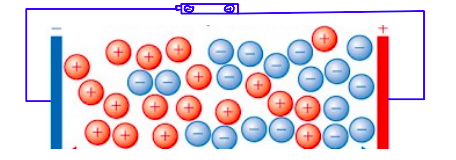
What two conditions are needed for Electrical Conductivity?
Presence of charged particles
Charged particles must be free to move
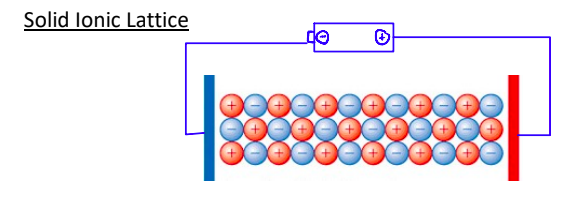
Why can Solid Ions Lattice not conduct electricity?
because there are no freely moving charged particles and ions are locked into position
Why can Molten Ions Compounds/Solutions conduct electricity?
since ions are separated from each other, they are free to move allowing for electrons to flow