3.4 Physics Mechanics
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What is centre of mass/gravity?
Centre of mass is the point where the total mass is considered to act. It is the meeting point of the objects if left due to the influence of gravity alone.
What does a single force through the centre of mass cause?
Pure translation
What will a single force away from the centre of mass cause?
rotation and translation
In a centre of mass question, which mass should you make m1?
The object from which you want to the know the distance to the centre of mass.
In a centre of mass question, which value will always be 0m?
x1
Fill in the gaps:
If __ __________ forces act, if the centre of ____ is stationary, it will ______ __________.
If no unbalanced forces act, if the centre of mass is stationary, it will remain stationary.
Fill in the gaps:
When the centre of mass is __________:
If A (or B) _____ then both objects ____ and meet at the ______ __ ____. This means the ____ massive object will move ______ as it has a _______ distance to travel to reach the centre of mass at the ____ time as the ____ _______ object.
When the centre of mass is stationary:
If A (or B) pulls in then both objects move in and meet at the centre of mass. This means the least massive object will move faster as it has a greater distance to travel to reach the centre of mass at the same time as the more massive object.
Fill in the gaps:
If an object is moving at a ________ ________ it will ________ to move at a ________ velocity.
If an object is moving at a constant velocity it will continue to move at a constant velocity.
Fill in the gaps:
If the centre of mass is ____________ it will ________ ____________.
If the centre of mass is accelerating, it will continue accelerating.
Describe arrow placement for vector addition
Put the two vectors head to tail
Describe arrow placement for vector subtraction
Reverse the vector which is being subtracted
What are the steps for calculating change in momentum using a vector triangle?
Draw Pf, reverse Pi, draw a vector joining the head of Pf with tail of Pi
Fill in the gaps: If momentum is _________, the ______ in momentum of one object must be _____ and ________ to the change of _________ of the other object.
If momentum is conserved, the change in momentum of one object must be equal and opposite to the change of momentum of the other object.
How many forces are involved in banked tracks/ conical pendulums and what are these?
There are only 2 forces: the weight force and the tension/ reaction/ normal force.
What does the missing force in banked track/ conical pendulum mean?
This means that the object cannot be at equilibrium so it is unbalanced. This unbalanced component acts as the centripetal force.
What are the two components of the support/ reaction/ normal froce in banked tracks/ pendulums?
The vertical component, which is equal and opposite to the weight of the object, and the horizontal component which is not cancelled and so provides the centripetal force due to acceleration towards the centre of rotation.
Fill in the gaps:
If the pendulum moves ______ v ________, and therefore __ increases, increasing the ______ component of T, but __ does not change so T has to _______, increasing _____.
If the pendulum moves faster, v increases, and therefore Fc increases, increasing the horizontal component of T, but mg does not change so T has to increase, increasing theta.
Fill in the gaps:
If the car _______ in speed, then the _________ force required to keep it in _______ motion increases. V² = grtan theta, which means that if _ increases then _ must also increase, so the car will slide __ towards the top of the track. If v doubles then r must _______.
If the car increases in speed, then the centripetal force required to keep it in circular motion increases. V² = grtan theta, which means that if v increases then r must also increase, so the car will slide up towards the top of the track. If v doubles then r must quadruple.
At the slowest speed, explain the forces at the top of a loop of motion in a vertical circle:
Fc and mg both act downwards and are equal so the support from the track is 0, so you feel weightless.
At the slowest speed, explain the forces at the bottom of a loop of motion in a vertical circle:
Mg acts downwards whereas Fc acts upwards so the support force must oppose the weight force and provide Fc. This means that support force= mg + mv²/r so feels bigger force pushing up onto you.
State Newton’s law of gravitation:
The force exerted between two objects is directly proportional to their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Explain gravity in space:
There is no reaction force, so anything in space is falling at the same rate and so appears weightless , but gravity is still there.
What is gravitational potential?
The change in potential energy for 1kg that moves from infinity to a point closer than infinity inside a gravitational field.
orbital radius=
radius of planet + orbit height
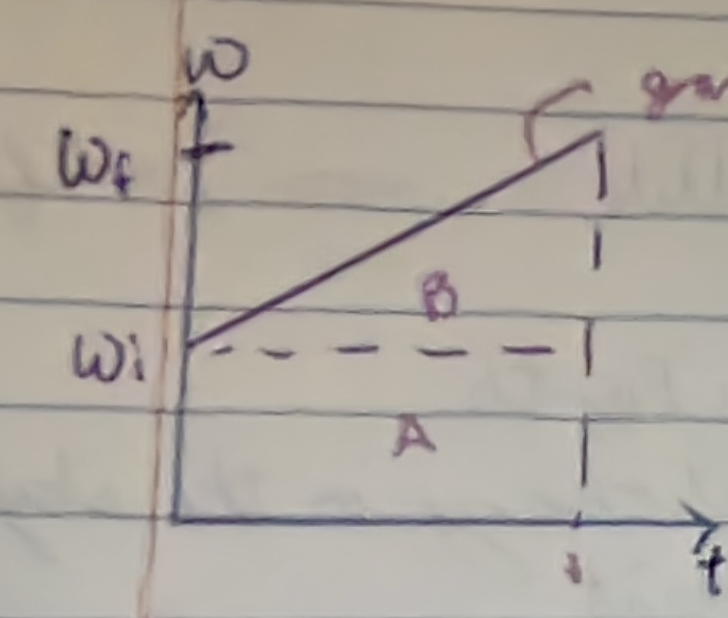
What does the area under this graph represent?
angular displacement, i.e. how far the object has rotated
What is rotational inertia?
Rotational inertia is a measure of an object’s resistance to angular acceleration, i.e. how easy it is to start or stop something rotating.
Fill in the gaps:
Rotational ______ depends on the ____ of an object, its _____ and where the mass is ________, i.e. how ___ from the _____ of rotation it is.
Rotational inertia depends on the mass of an object, its shape and where the mass is located, i.e. how far from the centre of rotation it is
What can rotational inertia be viewed as?
It can be viewed as the weight equivalent of an object
What does L stand for and what is it measured in?
Angular momentum
kgm2s-1
What does the principle of conservation of angular momentum state?
Provided no unbalanced external torque forces act, the angular momentum of a system is constant.
What does ω stand for and what is it measured in?
Angular velocity
rad s-1
What does I stand for and what is it measured in?
Rotational inertia
kgm²
I is proportional to:
mr2
Ek is proportional to:
ω2
Fill in the gaps for ice skater question:
Angular _________ is conserved unless external unbalanced ______ act. Ice is ___________ so there are no ________ torques. Lbefore= _____, Iiωi= ____. If Wf is bigger than __ then If must be _______ than Ii. I is proportional to ____ and her mass _______ change but by moving her arms __ towards her shoulders, her radius is ___________. Ekrot = ½Iω2 so as __ decreases and ω increases and Ek is proportional to ___, then the increase in ω2 is ______ than the drop in I so Ekrot therefore ________.
Angular momentum is conserved unless external unbalanced torques act. Ice is frictionless so there are no external torques. Lbefore= Lafter, Iiωi= Ifωf. If Wf is bigger than Wi then If must be smaller than Ii. I is proportional to mr2 and her mass doesn’t change but by moving her arms in towards her shoulders, her radius is decreased. Ekrot = ½Iω2 so as I decreases and ω increases and Ek is proportional to ω2, then the increase in ω2 is larger than the drop in I so Ekrot therefore increases.
When working out the velocity of dog on roundabout what inertia value do you use for the final L=Iω equation?
Use the total inertia = inertia of dog + inertia of roundabout
For an object rolling down a ramp, what is energy conversion and what is the formed equation to represent this?
GPE → linear Ek and rotational Ek
Ep= Ek + Ekrot
Circumference=
2πr
If something rolls down a slope slower what does this mean?
This means it has a smaller angular acceleration so a greater rotational inertia.
Explain change in energy for a flywheel
The GPE of the weight is converted into Ekrot of the flywheel and Eklinear of masses
T= (something)
something between 0 and W
Equation for flywheel W=
W=mg
What are the conditions for simple harmonic motion?
An object is undergoing simple harmonic motion if
Its acceleration (or restoring force) is directly proportional to its displacement and
Its acceleration (or restoring force) is directed towards the equilibrium position
When a bouncing spring is heading upwards is x negative or positive?
positive
When a bouncing spring is heading downwards is x negative or positive?
negative
Fill in the gaps:
Pendulums are only in ______ ________ motion for _____ angles so that the points ______ the __________ position.
Pendulums are only in simple harmonic motion for small angles so that the FN points towards the equilibrium position.
On the far left of a swing of pendulum in SHM what are the x, v and a values?
x= -A
v= 0
a= +max
In the middle of a swing of pendulum in SHM what are the x, v and a values?
x= 0
v= maximum
a= 0
On the far right of a swing of pendulum in SHM what are the x, v and a values?
x= +A
v= 0
a= -max
What is considered to be the length (l) of a swinging pendulum?
The distance from the pivot to the centre of mass of the bob.
What is the equation for calculate Fc for banked tracks/ conical pendulums?
Fc= mgtantheta
If you know the time period, what equation can you use to calculate the velocity of circular motion?
v= 2pir/T
Explain damping, including any energy conversions:
Damping is the gradual decrease in amplitude of an oscillation due to energy loss (without time period being affected). Some of the mechanical energy of the system is lost due to friction or air resistance. This reduces the amplitude of oscillations over time. So mechanical energy -> heat or sound energy
Briefly explain resonance:
The amplitude of oscillations increases significantly when the driver frequency is equal to the natural frequency (the frequency the system would oscillate at without the driver).
Fill in the gaps to explain resonance for a chord example:
By _______ the chord at the ________ frequency, the _________ of oscillation will ________. This is because a _____ amount of ______ is added at the right moment and ________ with the energy of the ______, i.e. the shaking energy is ___________ into __ and __ of the ball.
By shaking the chord at the resonant frequency, the amplitude of oscillation will increase. This is because a small amount of energy is added at the right moment and combines with the energy of the system, i.e. the shaking energy is transferred into Ek and Ep of the ball.
What is the formula for velocity of a satellite?
v=2pir/T