Bacterial Genetics and Recombination
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bacterial recombination and Bacterial genetics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
caused by a type of staphylococcus bacteria that has become resistant to antibiotics used to treat ordinary staph infections
genetic mutation causes drug resistance
non-resistant bacteria exists
bacteria multiply by the billions (a few bacteria will mutate)
some mutations make the bacterium drug resistant (presence of drugs, only drug resistant bacteria can survive)
drug resistant bacteria multiply and thrive
pLW1043 plasmid
trimethoprim resistance
penicillin family resistance
vancomycin resistance
genes to help the plasmid spread
disinfectant resistance
streptomycin family resistance
True
a single plasmid can carry the genes to resist many different antibiotics
genetics
the study of what genes are and how they carry information, how their information is expressed, and how they are replicated and passed to subsequent generations or other organisms
genome
the genetic information in the cell
chromosomes
structures containing DNA that physically carry hereditary information; contains the genes
genes
segments of DNA (except in some viruses which are made of RNA) the code of functional products that are usually proteins (rRNA, tRNA, microRNA)
nucleotides
repeating units consists of a nucleobase, (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine), deoxyribose, and phosphate group
base pairs
adenine - thymine
cytosine - guanine
genetic code
the set of rules that determines how a nucleotide sequence is converted into the amino acid sequence of a protein
central dogma
theory by Francis Crick in 1956
first proposed that the sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein
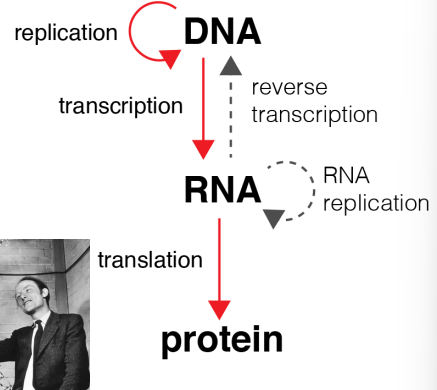
the flow of genetic information
expression
recombination
replication
what happens in the flow of genetic information
DNA is the blueprint of a cell’s proteins, including enzymes
DNA is obtained either from another cell in the same generation or from a parent cell during cell division
DNA can be expressed within a cell or transferred to another cell through recombination and replication
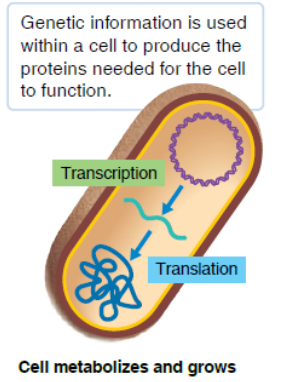
expression
genetic information is used within a cell to produce the proteins needed for the cell to function
the cell metabolize and grows
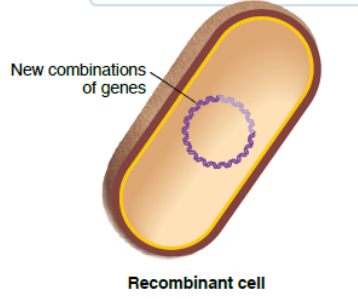
recombination
genetic information can be transferred horizontally between cells of the generation
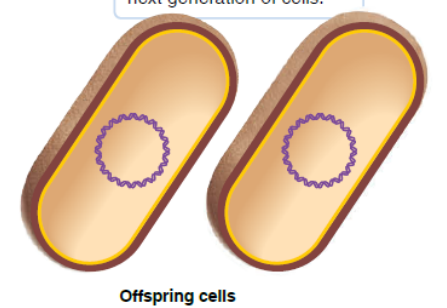
replication
genetic information can be transferred vertically to the next generation of cells
DNA gyrase
relaxes supercoiling ahead of the replication fork
DNA ligase
makes covalent bonds to join DNA strands; Okazaki fragments, and new segments in excision repair
DNA polymerase
synthesize DNA; proofreads and facilitate repair of DNA
endonucleases
cuts DNA’s backbone in a strand of DNA; facilitate repair and insertions
exonucleases
cut DNA from an exposed end of DNA; facilitate repair
helicase
unwinds double-stranded DNA
methylase
adds methyl group to selected bases in newly-made DNAp
photolyase
uses visible light energy to separate UV-induced pyrimidine dimers
primase
an RNA polymerase that makes RNA primers from a DNA template
ribozyme
RNA enzyme that removes introns and splices exons together
RNA polymerase
copies RNA from a DNA template
snRNP
RNA-protein complex that removes introns and splices exons together
topoisomerase/gyrase
relaxes supercoiling ahead of the replication fork; separates DNA circles at the end of DNA replication
transposase
cuts DNA backbone, leaving single-stranded “sticky ends”
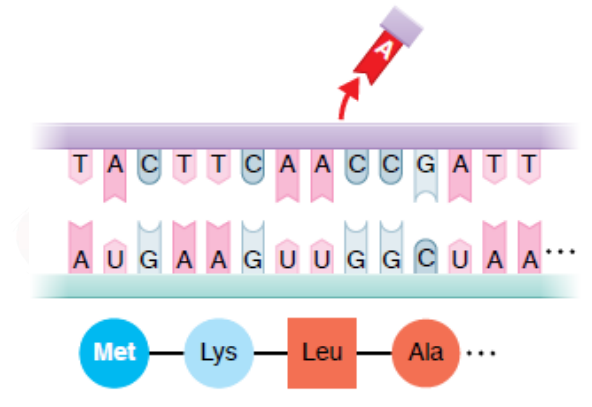
transcription in prokaryotes
the synthesis of a complementary strand of RNA from a DNA template
during transcription, there us the synthesis of strand of mRNA
take note that an adenine in the DNA template dictates a uracil (U) in the mRNA, because RNA contains uracil instead of thymine (T)
the process of transcription requires RNA polymerase
rRNA
integral part of ribosomes; the cellular machinery for protein synthesis
mRNA
carries the coded information for making specific proteins from DNA to ribosomes; where proteins are synthesized
translation
process in which the mRNA serves as the source of information for the synthesis of proteins
the language of mRNA is in the form of codons (group of 3 nucleotides)
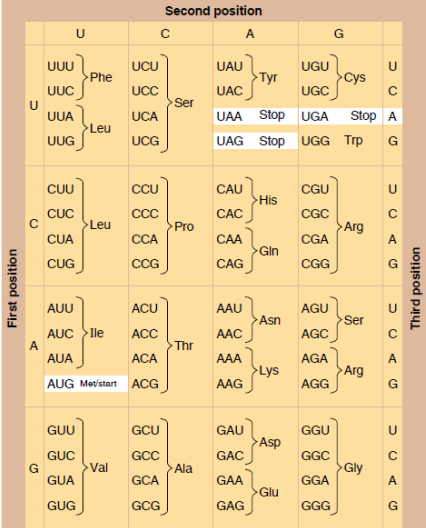
translation process
components needed to begin translation come together
on the assembled ribosome, the tRNA carrying the first amino acid is paired with the start codon on the mRNA.
the place where this first tRNA sits is called the P site.
a tRNA carrying the second amino acid approaches
the second codon of the mRNA pairs with a tRNA carrying the second amino acid at the A site.
the first amino acid joins to the second by a peptide bond
this attaches the polypeptide to the tRNA in the P site
the ribosome moves along the mRNA until the second tRNA is in the P site
the next codon to be translated is brough into the A site.
the first tRNA now occupies the E site
the second amino acid joins the third by another peptide bone, and the first tRNA is released from the E site
the ribosome continues to move along the mRNA, and a new amino acid are added to the polypeptide
when the ribosome reaches a stop codon, the polypeptide is released
finally, the last tRNA is released, and the ribosome comes apart.
the released polypeptide forms a new protein
mutations
a permanent change in the base sequence of DNA
such change can cause a change in the product encoded by the gene
types of mutation
base substitution/point mutation
silent mutation
spontaneous mutations
induced mutations
base substitution/point mutation
most common type of mutation involving single base pairs
a single base at one point in the DNA sequence is replaces with a different base
normal DNA molecule
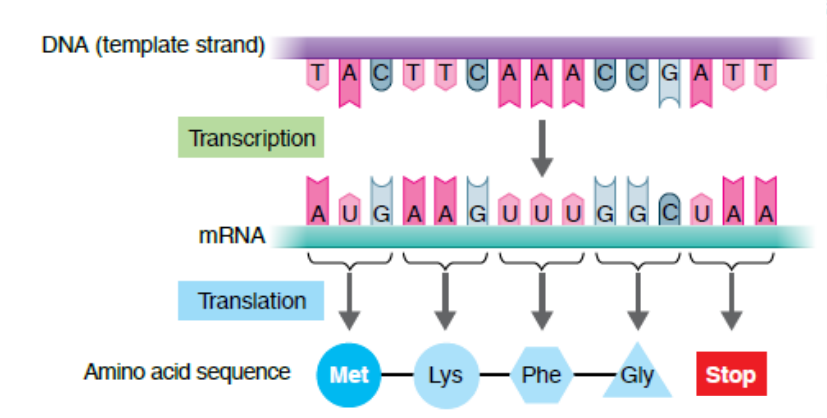
missense mutation
when the change of a single base pair causes the substitution of a different amino acid in the resulting protein
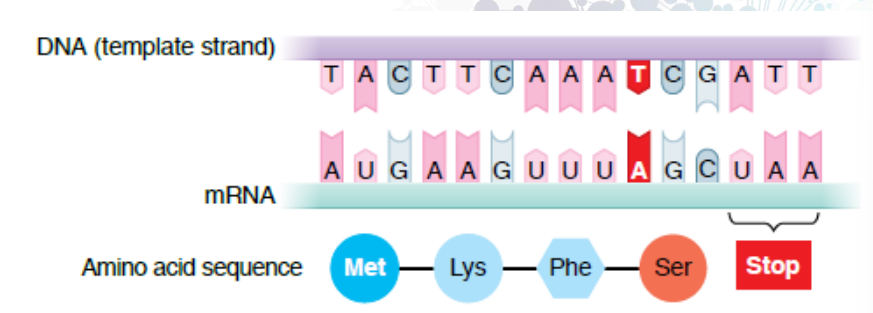
nonsense mutation
base substitutions that create a stop (nonsense) codon that prevents the synthesis of a complete functional protein
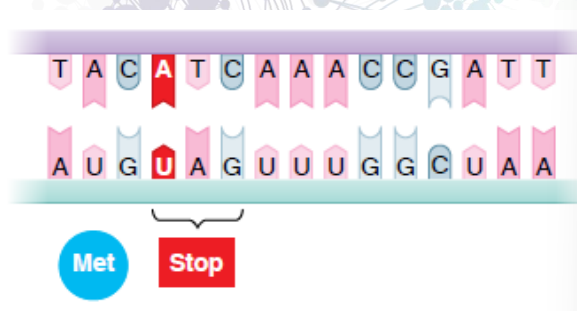
frameshift mutation
one or a few nucleotide pairs are deleted or inserted in the DNA
this can shift the translation reading time
silent mutation
occurs when one nucleotide is substituted for another in the DNA which results to new codon that might still code for the same amino acid
if the amino acid is changed, the function of the protein may not change if the amino acid is in a nonvital portion of the protein
spontaneous mutations
mutations that arise in the absence of known mutagens
induced mutations
mutations that occur following treatment with a mutagen
mutagenesis
the process by which a mutation is produced
mutagens
agents that increase the frequency of mutation
nitrous acid
action:
converts the base adenine to a form that pairs with cytosine instead of the usual thymine
result: base substitution
nucleoside analog
action: they are randomly incorporated in DNA
result:
causes mistakes in base pairing during DNA replication
subsequently, base-pair substitutions in the progeny cells
intercalating agents
action: inserts between base pairs
result: addition of base pairs
x-rays and gamma rays
action:
forms of radiation that are potent mutagens
ionize atoms and molecules
penetrating rays cause electrons to pop out of their usual shells which will cause more damage and some ions oxidizes bases in the DNA
result:
errors in DNA replication —> mutations
breakage of covalent bonds
ultraviolet (UV)
action:
formation of harmful covalent bonds between pyrimidine bases
thymine dimer formation
result:
thymine dimers causes problem in transcription or replication of the DNA
genetic recombination
refers to exchange of genes between two DNA molecules to form new combinations of genes on a chromosome
vertical gene trasnfer
occurs when genes are passed from an organism to its offspring
horizontal gene trasnfer
pass their genes laterally to other microbes
between normal microbiota and pathogens in spread of antibiotic resistance
donor and recipient cell
donor cell
gives a portion of its total DNA
recombinant
the recipient cell that incorporated donor DNA into its own DNA
transformation
process where in genes are transferred from one bacterium to another as “naked'“ DNA in solution
conjugation
required direct cell-to-cell contact
conjugating cells must generally be of opposite mating type
sex pili
gram negative
sticky surfaced molecules
gram positive
trasnduction
bacterial DNA is transferred from a donor cell to recipient inside a virus that infects bacteria called bacteriophage or phages