Mechatronic Devices 1: Sensors
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What is the definition of a sensor?
A sensor is a device that detects or measures a physical quantity (such as temperature, position, or pressure) and converts it into a readable signal—often electrical—used for monitoring, control, or automation.
What are the four main criteria used to classify sensors in mechatronics?
1) Power or energy supply requirement (ex: active, passive)
2) Measurement objective
3) Principle of operation (ex: resistive, inductive)
4) Output signal.
What is an active sensor? Give an example.
An active sensor requires an external power source to operate and produces an output signal based on the interaction with a stimulus.
Example: LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), photoconductive cell.
What is a passive sensor? Give an example.
A passive sensor detects and responds to stimuli from the physical environment without requiring an external power supply.
Example: Thermocouple, photodiode in photovoltaic mode.
What is the difference between analog and digital sensors?
Analog sensors produce continuous signals that are proportional to the sensed parameter, while digital sensors output discrete values that can be directly interfaced with digital controllers.
Examples:
Analog sensor: Thermistor, potentiometer
Digital sensor: Rotary encoder, limit switch
What are the key characteristics to consider when choosing a sensor?
Cost
Size
Weight
Type of Output (digital or analog)
Interfacing
Resolution
Sensitivity
Linearity
Range
Response Time
Frequency Response
Reliability
Accuracy
Repeatability
Important: see notes for details
What are position sensors used for?
Position sensors are used to measure displacements (both rotary and linear) and movements. Examples include potentiometers, and rotary encoders.
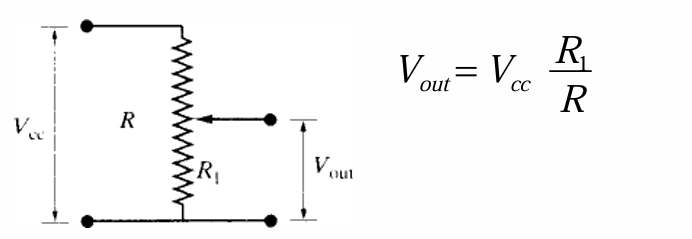
How does a potentiometer work as a position sensor?
A potentiometer works as a position sensor by converting position information into a variable voltage. It acts as a voltage divider, where the output voltage is proportional to the position, and the resistance changes with the position of the wiper. Potentiometers are commonly used as internal feedback sensors to report the position of joints and links, often in combination with other sensors like encoders.
What are the two main types of potentiometers?
Potentiometers can be rotary or linear, measuring rotary or linear motions, respectively.
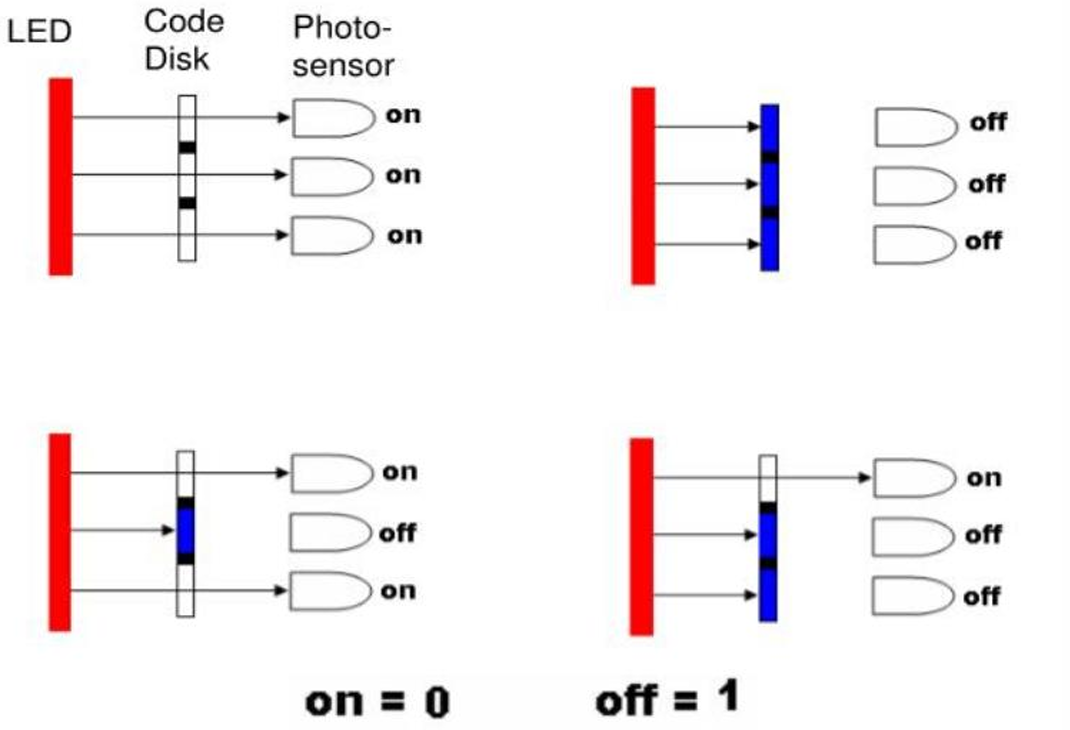
What is an encoder and how does it work? And what are its type?
An encoder converts movement into a digital signal. It uses a wheel or strip divided into sections that are detected by a light source and sensor, generating a signal for each small movement.
Types: incremental, absolute and linear
What is the most popular type of encoder and why?
Optical encoders are the most popular type because they use light and photosensors to produce digital code and can be linear or rotary.
List the main components of an optical encoder.
Light source (LED or IR LED), photodetector (photodiode or phototransistor), and an opaque code disk with slits.
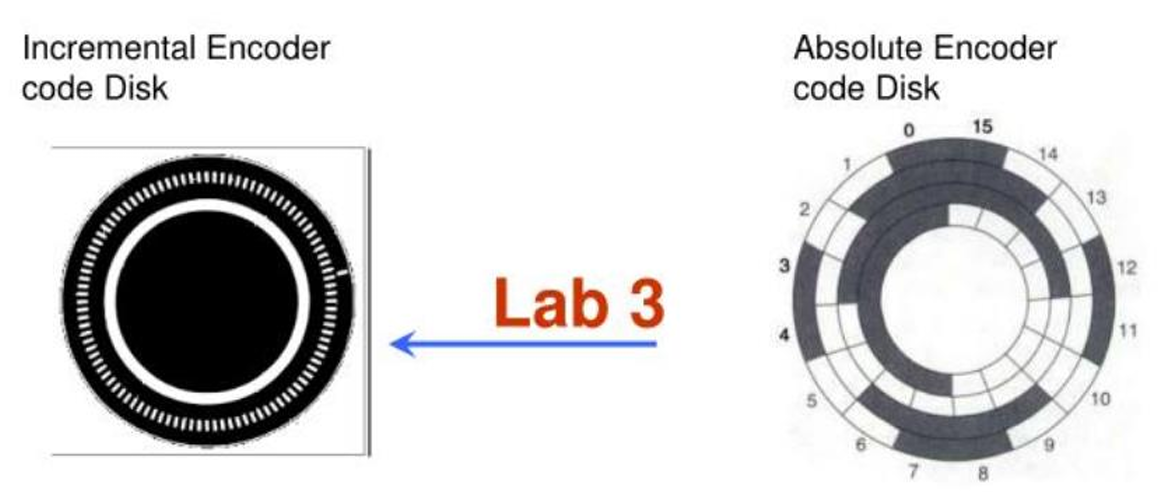
What is the difference between incremental and absolute optical encoders?
Incremental encoders measure motion by counting consecutive "on" and "off" states (pulses), which gives information about the change in position. Absolute encoders provide a unique digital code for each position, so they give precise position information even without needing to count pulses.
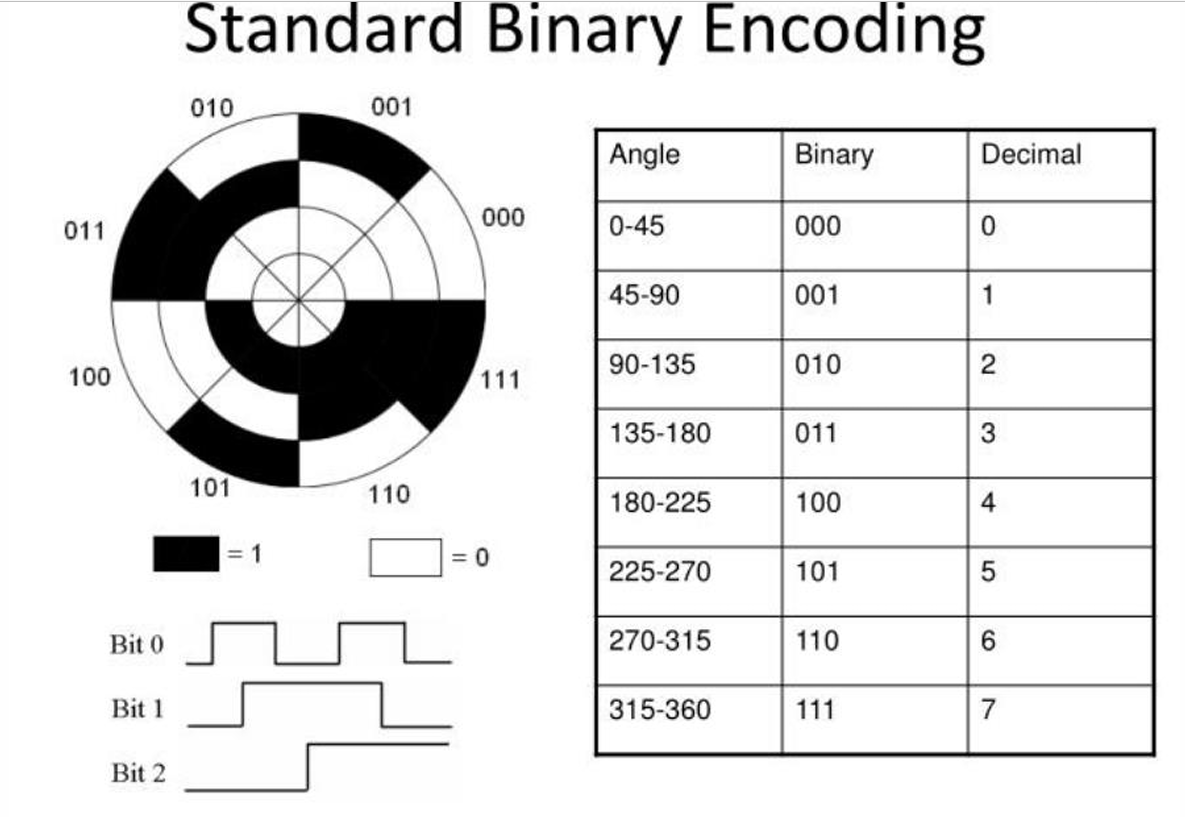
How does standard binary encoding work in optical encoders?
In standard binary encoding, binary numbers are assigned to the segments of the code disk. Each segment represents a specific angle range, allowing the encoder to produce a binary code that corresponds to the position.
What is quadrature in the context of encoders?
Quadrature refers to two signals that are 90° out of phase with each other. These signals are used to determine the direction of rotation in encoders.
How can direction of rotation be determined using a quadrature encoder?
The direction is determined by the sequence in which the two quadrature signals (A and B) change state. If signal A leads signal B, the direction is one way; if signal B leads signal A, the direction is the opposite.
How is the resolution of an absolute optical encoder calculated?
Resolution = 360º/(2ⁿ), where n is the number of encoder bits.
How is the resolution of an incremental optical encoder calculated?
Resolution = 360/N, where N is the number of windows on the code disk. Using quadrature, Δθ = 360/4N.
List some applications of encoders.
Encoders are used in motors (for velocity and position monitoring), robotics, conveyor belts, locomotives, and tachometers.
What is the main difference between linear and rotary optical encoders?
The main difference is the type of motion measured: linear encoders measure linear displacement, while rotary encoders measure angular displacement.
What is a force-sensing resistor (FSR) and how does it work?
An FSR is a polymer thick-film device whose resistance decreases as the force applied to its surface increases.
What is the resistance range of a typical FSR for forces between 10 and 10,000 grams?
The resistance changes from about 500 KΩ to about 1 KΩ.
block diagram?
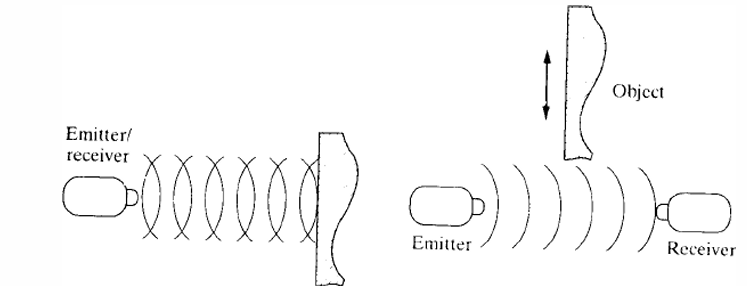
How does an ultrasonic proximity sensor work?
It emits bursts of high-frequency sound waves (~200 kHz). There are two modes:
In opposed mode, a receiver is placed opposite the emitter and detects the sound directly.
In echo mode, the receiver (next to or integrated into the emitter) detects reflected sound from nearby surfaces.
If the wave is received, a signal is produced; otherwise, there’s no signal. These sensors have a blind zone near the emitter and don't work well with soft surfaces like rubber or foam that absorb sound instead of reflecting it.