EBPP FINAL (MODULE 3)
1/325
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
326 Terms
What are the components of a research paper?
Title
Author's names, credentials, and affiliation
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Results
Discussion
Conclusion
References
Disclosure of conflicting interest
Disclosure of funding source
When analyzing a research paper what info can be gathered from the abstract?
A brief summary of what's going on in the paper
Wterm-1hen analyzing a research paper what info can be gathered from the author's names, credentials, affiliations and conflict of interest?
Allows reader to get a perception of author(s)
When analyzing a research paper what info can be gathered from the funding source?
Potential biases if source has potential benefit
What should you look for when evaluating the purpose of the introduction?
Clear intention
Identifiable investigated variables
Identifiable primary and secondary outcomes
Identifiable population studied
What should you look for when evaluating the hypotheses and research questions of the introduction?
Alignment with intended purpose
Variables Identified
One hypothesis and question per dependent variable
What should you look for when evaluating research design in methods section?
Alignment with purpose
Appropriateness
Use of control or comparison group
Researchers are blind to participants' assignments
Limited extraneous variables
What should you look for when evaluating sample in methods section?
Description of population that sample represents
Appropriate sampling frame
Clear and appropriate inclusion and exclusion criteria
Randomness of participant assignment to treatment vs control/comparison groups
Sufficient sample size
Sample size calculation discussed
Drop-out rate computed into sample size
What should you look for when evaluating research protocol in methods section?
Thorough and detailed description of protocol
Protocol followed appropriately
Study continued long enough
Protocol consistency administered
Steps to control extraneous variables
Ethical protocol approved by Institutional Review Board (IRB)
What should you look for when evaluating data collection in methods section?
Appropriate collection methods
Procedures consistently applied to participants
High level validity and reliability of collection instrument
High level reliability of collectors
What should you look for when evaluating sample in results section?
Similar demographics of intervention and control group or impact by lack thereof
Treatment and control similar at baseline measurement of outcome variable and impact of differences
How participants are accounted for
Comparable discontinuance rate between treatment and control group
What should you look for when evaluating data analysis in results section?
Power analysis indication
Analyzed via on-protocol (per-protocol), intention to treat (ITT), or both
Appropriate statistical analysis for level of data, hypotheses, and answer to research questions
What should you look for when evaluating findings in research section?
Relevance to hypotheses, research question, and variables
Statistically or not statistically significant
When upper and lower limits of confidence levels are enough to implement change
Practical or clinical significance
What should you look for when evaluating the discussion?
Thorough explanation of findings
Logical explanations
Comparison of findings with other studies
Identification and discussion of limitations
Implications for practice
Future recommendations
What should you look for when evaluating conclusions?
Alignment with purpose
Logically follows from findings and interpretation
How to initially assess an article?
Multiple reads
Underline important aspects (purpose, primary outcomes)
Notes for questions needing outside resources (statistics, strengths, limitations)
Reading strategies
Read title and abstract first then read 3 times
How can journal quality be determined when assessing a journal?
If it's found in databases (Pubmed, Cochrane Library, CINAHL)
Directory of Open Access Journal (DOAJ) to determine transparency and best practices in publishing
Why is peer review important when assessing a journal?
Proves that the journal went through the rigorous review process
Refereed publication
What is impact factor based on?
Frequency of articles cited by authors in other journals within the same field of study in a following year
What does a high journal citation report (JCR) signify?
Greater significant within discipline
What information does the Scrimago Journal and Country Rank (SLR) give?
Visibility of Jornals in Scopus Database
T/F: An article analyzed by the intention to treat analysis will use a method to input the data for participants that drop out early
True
1 multiple choice option
Aspects of background and overview
Study citation
purpose/background
study objective
Historical context
Study citation
Cite article with proper format
Purpose/Background
Brief description of importance study and background
Study objective
Clearly state the objective, study aim, or goal and copy directly to not change the meaning
Historical context
Other related trials prior to this study
Aspects of methods
Study design
Funding
Population
Interventions or study procedures
Outcomes
Statistical analysis
Things to consider in study design
Retrospective vs. prospective
Randomization
Blinding
Case control vs. RCT vs. meta-analysis
Superiority vs. non-inferiority
Multicenter vs. single site
etc
Funding
Disclose funding and consider potential conflicts of interest
Aspects of population in methods section
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria
List the major inclusion criteria
Exclusion criteria
List the major exclusion criteria
Consider appropriateness
Reason not needed but should be a point of discussion
Interventions or study procedures considerations
Was it active-controlled
Dose
How often it was administered
Washout period
Enrollment period to determine adherence
Randomization
Duration of intervention period
Median follow-up frame time-frame
Similar follow-up between groups
Outcomes
Primary and secondary outcomes/endpoints
Statistical analysis
Statistical tests used for eat data set
If there's a sample size calculation
Evaluation of appropriateness of statistical tests to discussion
Aspects of results
Study sample
Results
Summary
Aspects of study sample
Sample size
Baseline characteristics
Sample size
Amount of participants
Baseline characteristics
Well matched between treatment groups
Noteworthy characteristics of the sample
Results
Tables/bullet points to describe and summarize main results
Amount of dropouts and why
Results of primary and secondary outcomes
Statistical significance
Number needed to treat (NNT)
Number needed to harm (NNH)
Noteworthy adverse event rates
Summary
Key takeaways form trial
No interpretations
Aspects of Discussion and Conclusion
Evaluation of study quality
Author's discussion and conclusion
Personal discussion and conclusion
Application to patient care
Aspects of evaluation of study quality
Strengths of the study
Limitation of the study
Strengths of the study
List strengths
Examples of strengths of a study
large sample size, external validity, etc
Limitations of the study
What could be improved
what weakened overall impact
Examples of limitations of a study
internal/external validity, statistical vs. clinical significance, inclusion/exclusion criteria appropriateness
Author's discussion and conclusion
Summary of conclusion
Personal discussion and conclusion
List conclusions
Reference other articles and how their findings play a role in interpretation
Application to patient care
How information will be used in practice
Potential Background and Overview Questions
1. What are the current guideline recommendations for this particular disease state or topic?
2. If applicable, how do we stratify the severity of disease being studied (i.e. A1C for patients with diabetes, CKD stages, COPD GOLD classifications, etc.)?
3. If this is a new therapy, what is the biological rationale for why it might be useful for a particular disease state?
Potential Methods Questions
1. How do the inclusion/exclusion criteria limit the population you can apply the results to?
2. Were the patients appropriately randomized to their treatment groups? Was there stratification in the process?
3. Did the authors include a power analysis? Did enrollment achieve desired power?
4. Was everyone (patients, physicians, study personnel, etc.) blinded to treatments?
5. Was this an active controlled trial? If yes, does the active control depict the standard of care? Was it appropriately dosed?
6. Was the method used to study the primary outcome appropriate? For example, if a study is assessing agitation, was the chosen behavioral scale appropriate and validated? Have other studies assessing similar outcomes used it?
Potential Results Questions
1. How do the baseline characteristics of the population in the study compare to the disease state being studied? Did exclusion criteria eliminate outliers and patients who may be at increased harm?
2. For statistically significant results, how does the NNH compare to the NNT? Are they similar, or are the two significantly different from each other? Are these results clinically significant?
3. Was the trial long enough to detect a difference?
4. Are the potential treatment benefits worth the potential harm and costs?
Potential Discussion Questions
1. For your personal conclusions, would you change guideline recommendations based on the study? If so,how? Will this study change how you practice?
2. Would it be feasible/appropriate to apply the study to your specific institution?
3. What additional limitations would you note besides the limitations described in the study?
4. Is the population in the study similar to patients in your practice?
5. Was there any bias present in the study? Who funded the study and what was the sponsor's role in the study?
6. How would you apply this to your practice?
Descriptive statistics
statistics used to summarize the data and tables or graphs that display and communicate the observations
Scale of measurement
the precision with which a characteristic is measured
What determines the statistical methods for analyzing the data
scale of measurement
Used for the simplest level of measurement when data values fit into categories.
Nominal scales
In a mortality study, patients who die may be labeled with a 1 while those that live may be labeled with a 0. This is an example of?
dichotomous or binary observations
Dichotomous or binary
Outcome can take on only one of two values (yes or no)
Data evaluated on a nominal scale are sometimes called ___
Qualitative or categorical observations
Nominal or qualitative data are generally described in terms of ___
percentages or proportions
What is often used to display nominal data?
Contingency tables and bar charts
What section are contingency tables and bar charts found?
"Tables and Graphs for Nominal and Ordinal Data."
When should observation be measured on an ordinal scale?
When an inherent order occurs among the categories (more/greater than observations)
What type of ordered scale has observations that are ranked from highest to lowest (or vice versa)?
rank-order scale
What statistical measure may be used for an entire set of data on an ordinal scale?
median
Observations for which the differences between numbers have meaning on a numerical scale
quantitative observations
What are the two types of numerical scales?
Continuous and discrete
Which numerical scale has values on a continuum (e.g., age)?
Continuous
Which numerical scale has values equal to integers (e.g., number of fractures)?
Discrete
What are the three measures of central tendency used in medicine and epidemiology?
The mean, the median, and, to a lesser extent, the mode
T/F: All measures of central tendency used for numerical data
True
1 multiple choice option
What is the arithmetic average of the observations that is symbolized by X-bar?
Mean
What is formed by multiplying each data value by the number of observations that have that value, adding the products, and dividing the sum by the number of observations?
weighted average
What is the middle observation symbolized by M or Md?
Median
What is the value that occurs most frequently?
Mode
For frequency tables or a small number of observations, what is the mode estimated by?
modal class
What is another measure of central tendency not used as often as the arithmetic mean or the median?
geometric mean
When outliers are noticed in one direction this is known as?
Skewed distribution
What is it called when the distribution the same shape on both sides of the mean?
Symmetric distribution
mean = median
symmetric
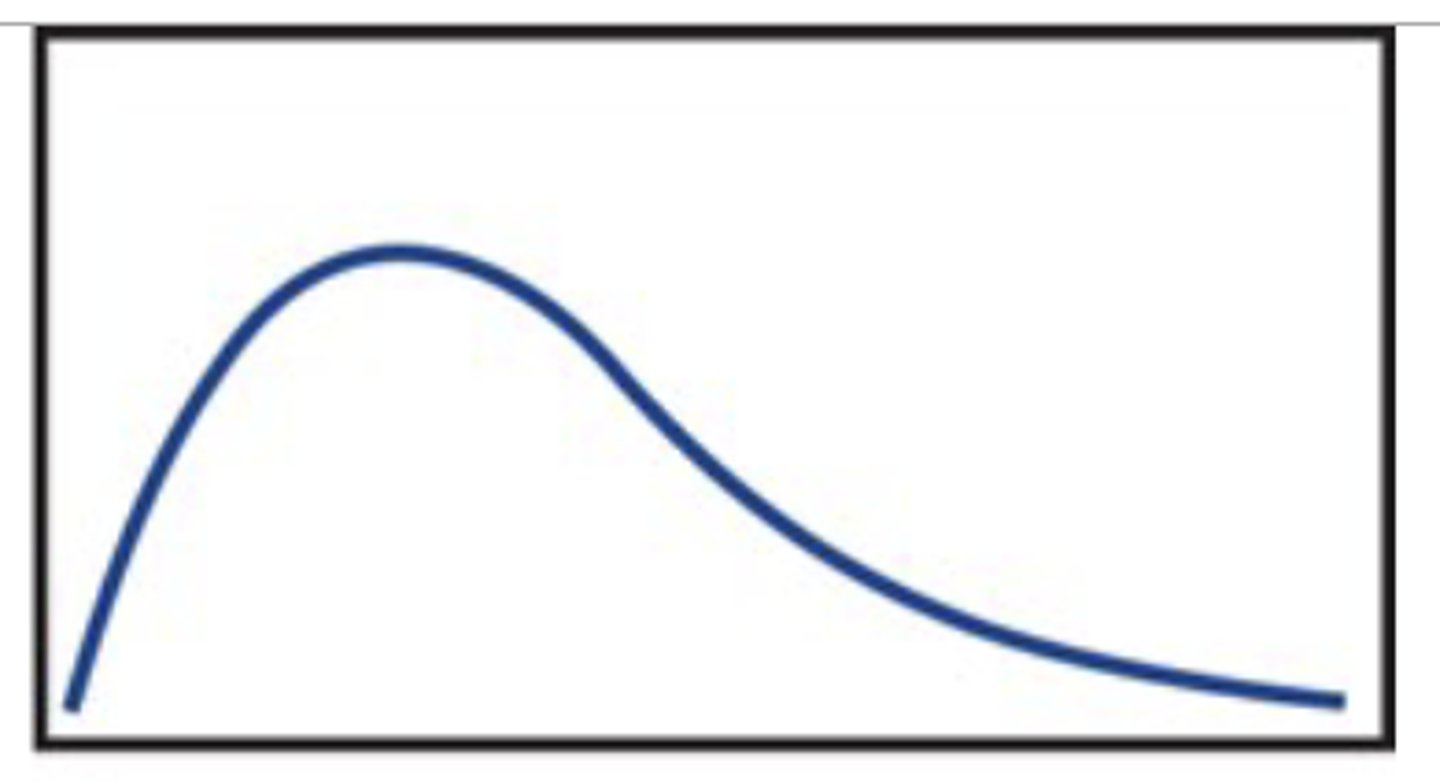
mean > median
skewed right
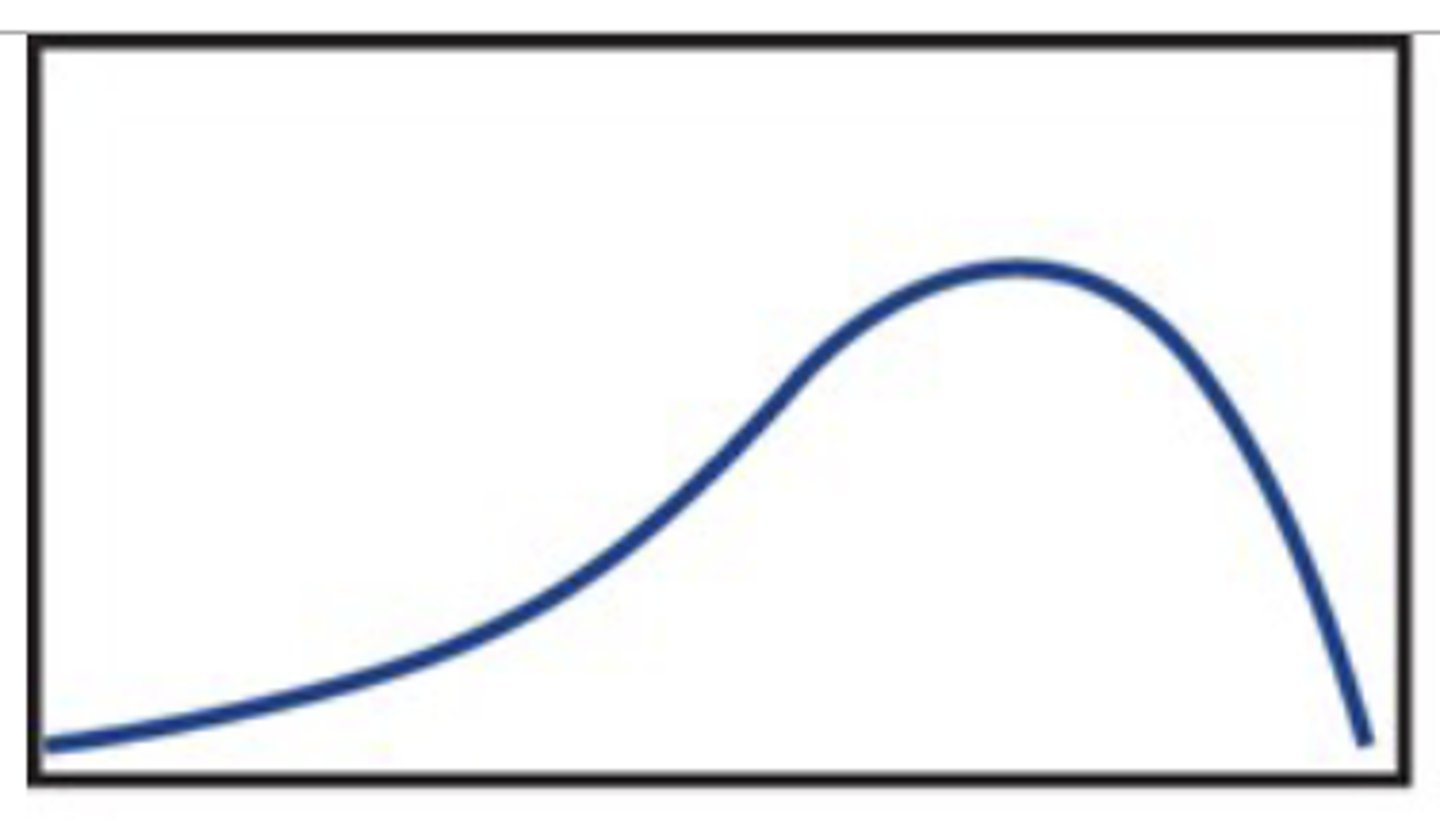
mean < median
skewed left

What is used for numerical data and for symmetric distributions?
Mean
What is used for ordinal data or for numerical data if the distribution is heavily skewed?
Median
What is used primarily for ordinal data and bimodal numeric distributions?
Mode
What is generally used for observations measured on a logarithmic scale or data with moderate skewness?
Geometric mean
What is the difference between the largest and the smallest observation
Range
What is a measure of the spread of data about their mean
standard deviation
What ignores the sign of the number and is denoted by vertical bars oneach side of the number
Absolute value of a number
The name of the statistic before the square root is taken
Variance
More can be said about the percentage of observations that lay between the mean and ±2 standard deviations when the distribution is what shape?
Bell-shaped
What is the standard deviation divided by the mean times 100% known as?
Coefficient of variation
What is the percentage of a distribution that is equal to or below a particular number?
Percentile
What is a measure of variation that makes use of percentiles?
Interquartile range
What is the difference between the 25th and 75th percentiles?
first and third quartiles
What is useful to compare an individual observation with a norm?
Percentiles