Physics: Unit 12 Heat Transfers
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is conduction?
The transfer of heat energy through a solid.
How does conduction work?
Vibrating particles bump into neighbours, transferring energy along the bar
Where does heat energy travel?
From hot to cold.
Why are metals very good conductors?
Their (delocalised) electrons can move freely and transfer energy,
What medium can convection happen in?
Fluids (gas and liquid)
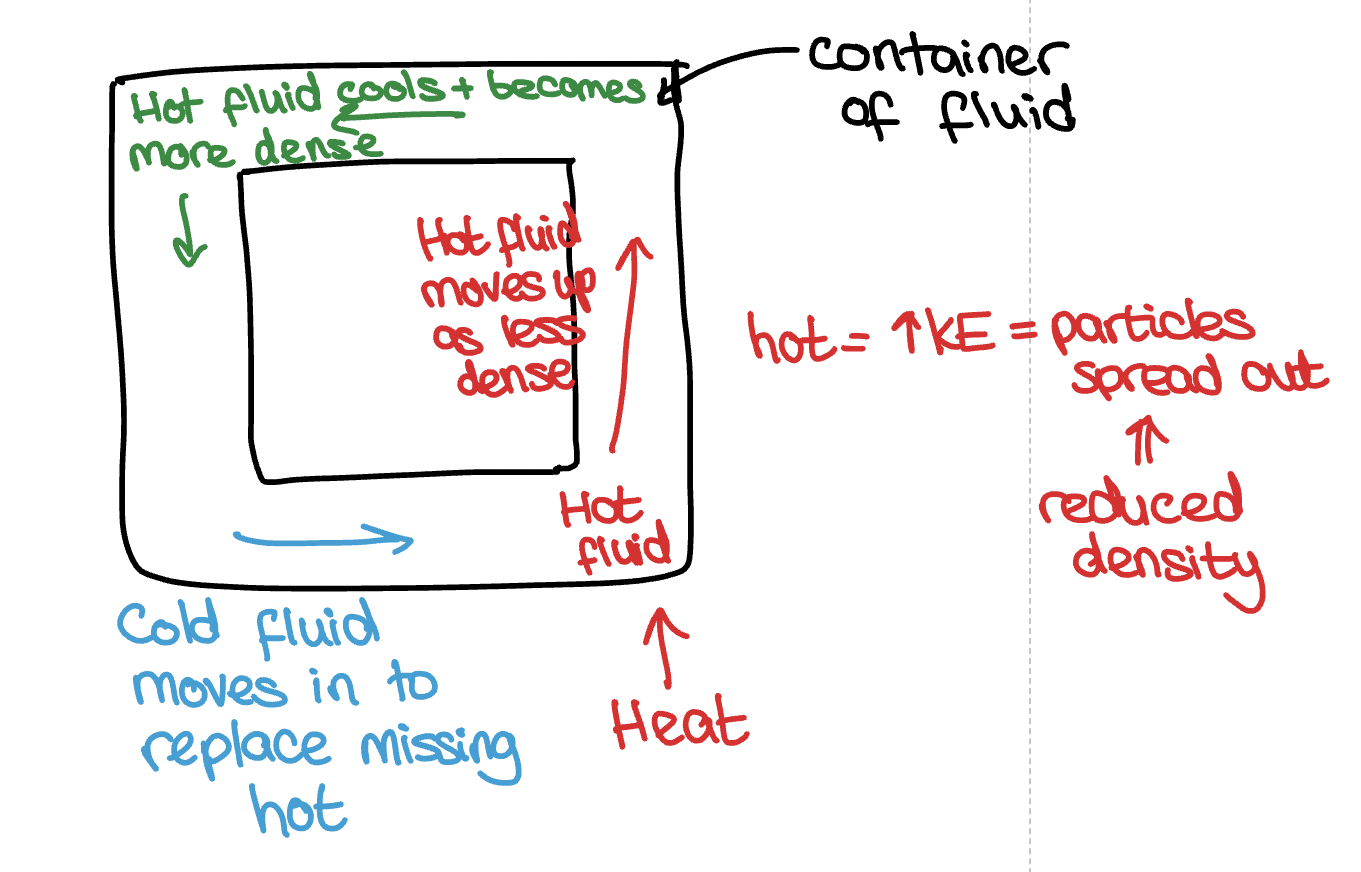
What is a convection current?
When particles heat they gain energy and spread apart due to reduced density
The hot fluid rises as they are less dense.
They start to cool as they move away from the heat source, increasing density and sinking.
Cold fluid moves in the replace the missing hot.
This creates the convection current.
Why is air the worst conductor for heat?
Because particles are very spread out so collisions are less likely.
Why. do birds fluff their feathers?
To trap a layer of air inside the feathers, and since air is a bad conductor, it stops transfer.
What is radiation?
A form of heat transfer by infrared waves. Infrared ration can be reflected, emitted and absorbed.
What surfaces are good emitters/absorbers of radiation but bad reflectors?
Dark, matte surfaces
What surfaces are bad emitters/absorbers of radiation but good reflectors?
Lighter, Shinier surfaces.
Can radiation happen in a vaccum?
Yes as it does not need particles.
What is insulation used for?
It is used to stop unwanted heat transfers.
What are some examples of insulating materials?
double glazing, reflective surfaces/blankets, foam insulation, and fibreglass loft.
How does double glazing insulate?
Air between 2 pieces of glass and air reduces conduction as is a bad conductor.
How does foil blanket insulate?
Shinier surface is more reflective, so radiation cannot escape.
How does a vacuum flask insulate?
Lid stops convection in air above bottle, vacuum stops conduction and convection.