L3-introduction to isotopes and radioactive decay
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
what are all the type of radiation
alpha
beta
gamma
explain the feature of alpha particles
they are a positively charged helium nuclei
produced from alpha decay of heavy atoms
in the heavy atoms decay it loses its mass number by 4 and its atomic number by 2
is stopped by only a few cm of air
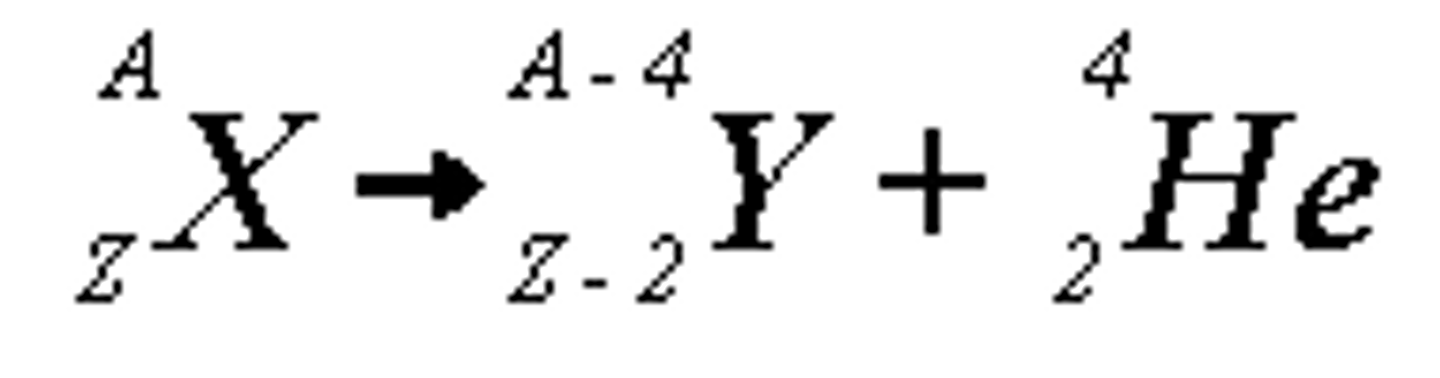
explain the features of beta particles
during beta decay a neutron is transformed into a proton with the emission of an electron and a neutrino ( package of energy )
the mass number remains the same but the atomic number increases by 1
they are negatively charged and can be stopped by an aluminium sheet
Explain features of gamma rays
Gamma rays are usually produced after alpha or beta decay. The daughter nucleus that is formed is typically left in an excited state, and decays to a lower state by emitting a gamma ray photon.
gamma radiation is only stopped by lead
what is half-life
length of time required for half of the radioactive atoms in a sample to decay
what is an equation to show the relationship between the decay constant and half-life
0.693/half-life in minutes

what is an isotope
they are atoms with the same number of protons ( atomic number ) but different number of neutrons so different mass
they have the same chemical properties but different physical properties
explain isotopic stability
having too many or too few neutrons can make it unstable, these unstable isotopes will try and recah lower energy states by nuclear decay
explain the kinetic isotope effect
typically, different isotopes have the same number of electrons so as the chemcial behaviour is determined by this they have identical reactivity
but kinetic isotopes are an exception heavier isotopes tend to react slower than lighter isotopes of the same element - bond energies are affected by the mass of the atoms that form the bond
however the difference in heavier atoms the effect is much more smaller
what is radiolabelling
when a drug or radioactive tracer is labelled with an unstable radionucleotide, the resulting radiation can be used to follow the tracer in the body
example: the use of flourine-18 on a biologically active molecule fludeoxyglucose ( FDG) which emits positrons. its introduced into the body and the emissions can be observed all around the body with varying concentrations
FDG is a good reflection of the glucose uptake by cells in the body