Earth Science (EARTH-1141) - Streams/Groundwater Vocab
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Last updated 12:16 AM on 4/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
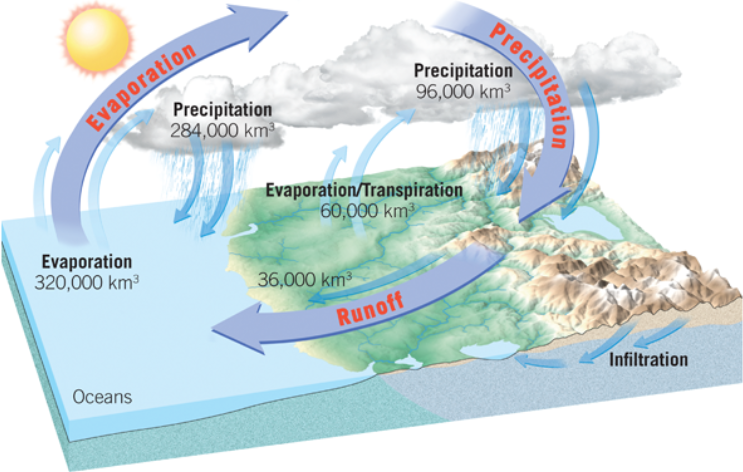
hydrologic cycle
the unending circulation of Earth’s water supply. The cycle is powered by energy from the sun and is characterized by continuous exchanges of water among the oceans, the atmosphere, and the continents
2
New cards
evaporation
the process of converting a liquid to a gas; how water enters the atmosphere from the ocean
3
New cards
infiltration
movement of surface water into rock or soil through cracks and pore spaces
4
New cards
runoff
water that flows over the land rather than infiltrating into the ground; the rate of rainfall exceeds the ground’s ability to absorb it
5
New cards
transpiration
the release of water vapor to the atmosphere by plants
6
New cards
evapotranspiration
the combined effect of **evaporation** and **transpiration**
7
New cards
drainage basin
the land area that contributes water to a stream; aka watershed
8
New cards
divide
imaginary line that separates the drainage of two streams; often found along a ridge
9
New cards
headward erosion
the extension upslope of the head f a valley due to erosion
10
New cards
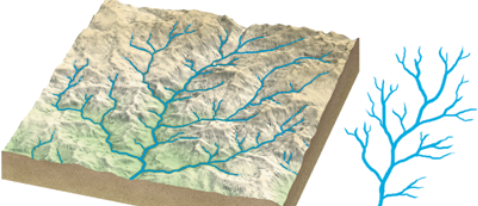
dendritic pattern
stream system that resembles the pattern of a branching tree; relatively uniform underlying material means that the pattern is determined by slope direction of land
11
New cards
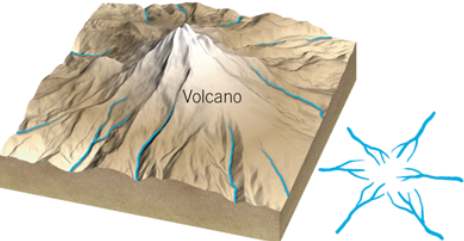
radial pattern
stream system running in all directions away from a central elevated structure such as a volcano
12
New cards
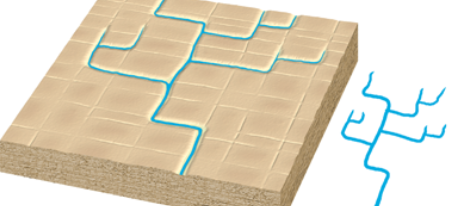
rectangular pattern
drainage pattern characterized by numerous right-angle bends that develops on jointed or fractured bedrock
13
New cards
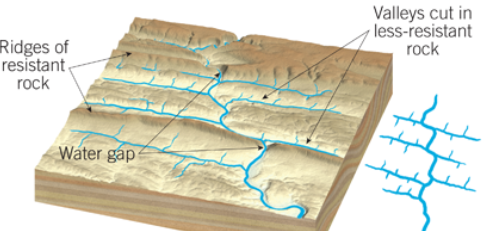
trellis pattern
system of streams in which nearly parallel tributaries occupy valley scut in folded strata
14
New cards
laminar flow
the movement of water particles in straight-line paths that are parallel to the channel. The water particles move downstream, without mixing
15
New cards
turbulent flow
movement of water in an erratic fashion, often characterized by swirling, whirpool-like eddies. Most streamflow is of this type
16
New cards
gradient
the slope of a stream; generally measured in feet per mile
17
New cards
discharge
the quantity of water in a stream that passes a given point in a period of time
18
New cards
longitudinal profile
cross section of a stream channel along its descending course from the head to the mouth
19
New cards
pothole
circular depression in a bedrock stream channel created by the abrasive “drill-like” action of particles swirling in fast-moving eddies
20
New cards
dissolved load
the portion of a stream’s load that is carried in solution
21
New cards
suspended load
the fine sediment carried within the body of flowing water
22
New cards
bed load
sediment that is carried y a stream along the bottom of its channel
23
New cards
settling velocity
the speed at which a particle falls through a still fluid. the size, shape, and specific gravity of particles influence settling velocity
24
New cards
saltation
transportation of sediment through a series of leaps or bounces
25
New cards
capacity
the total amount of sediment a stream is able to transport
26
New cards
competence
measure of the largest particle a stream can transport; a factor that is dependent on velocity
27
New cards
sorting
the process by which solid particles of various sizes are separated by moving water or wind
28
New cards
alluvium
unconsolidated sediment deposited by a stream