Grade 11 Pre-AP Biology - Unit 4 Test Review
1/216
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
217 Terms
Homeostasis
process of maintaining a balance in an organism’s internal environment to sustain life
Physiology
study of how living organisms maintain homeostasis
Molecules → Organelles → Cells → Tissues → Systems → Organisms
Molecules → Organelles → Cells → Tissues → Systems → Organisms
Feedback Loop
Stimulus → Receptor → Control Center → Effector
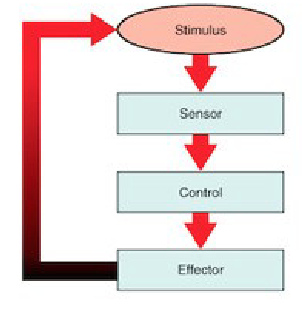
Negative Feedback Loop
response decreases the effect of the stimulus
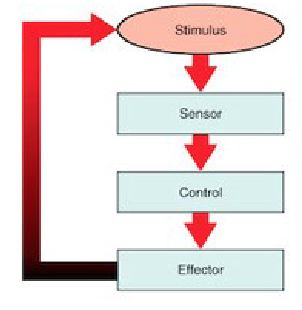
Positive Feedback Loop
response increases the effect of the stimulus
Stimulus
change in the environment
Receptor
part of the organism that detects the stimulus
Control Center
part of the organism that decides what to do about the stimulus
Effector
part of the organism that generates the response
Receptor sends information to the control center through an ________ _______.
afferent pathway (towards CNS)
Control center sends instructions out through an ________ ________.
efferent pathway (away from CNS)
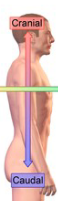
Cranial
towards the head
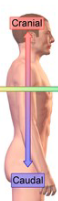
Caudal
away from the head
Superior
higher

Inferior
lower

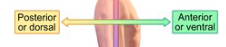
Posterior
back
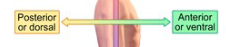
Anterior
front
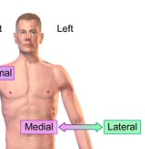
Lateral
closer to the side of the body
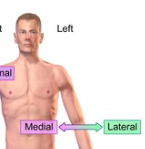
Medial
closer to the center of the body
Proximal
closer to the point of attachment (usually referring to limbs)
Distal
farther from the point of attachment (usually referring to limbs)
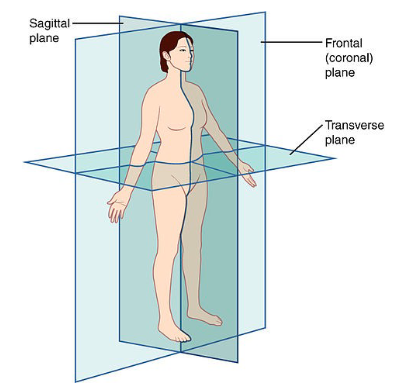
Sagittal Plane
person is cut symmetrically vertically
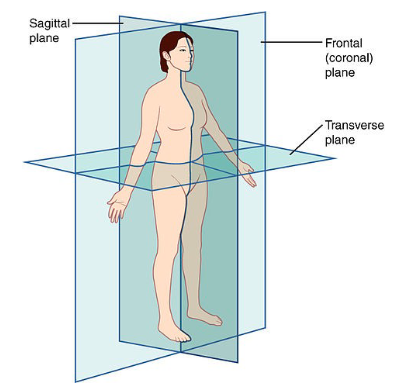
Frontal Plane
person is cut asymmetrically vertically
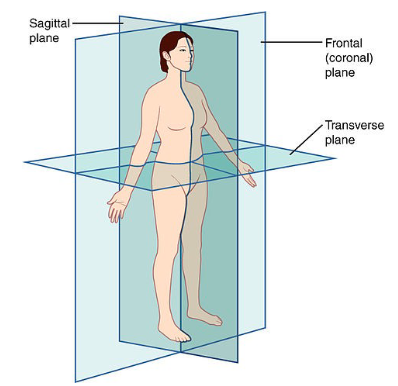
Transverse Plane
person is cut horizontally
Purpose of the Circulatory System
to move materials from place to place within an organism
Components of the Circulatory System
Fluid
Tubes
Pump
Fluid (Circulatory System)
moves through the system
materials that are being moved are dissolved in the fluid
Tubes (Circulatory System)
network of tubes through which the fluid travels
Pump (Circulatory System)
generates the force to push the fluid through the tubes
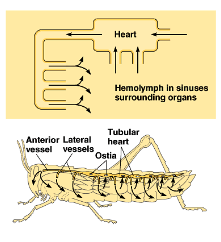
Open Circulatory System
fluid leaves the tubes
pumped onto the tissues of the organism
fluids are recovered using a different set of tubes + recirculated
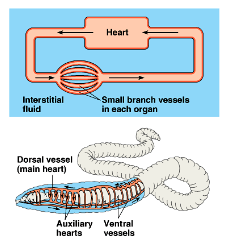
Closed Circulatory System
fluids stay within the tubes at all times
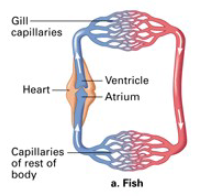
One Circuit System
fluid leaves pump
goes to gills/lungs to pick up oxygen/get rid of CO2
goes directly to the body
after circulating in the body, fluid returns to the pump
Two Circuit System
fluid leaves pump
goes to gills/lungs to pick up oxygen/get rid of CO2
fluid returns to pump
pump pushes fluid out to the rest of the body
after circulating in the body, the fluid returns to the pump
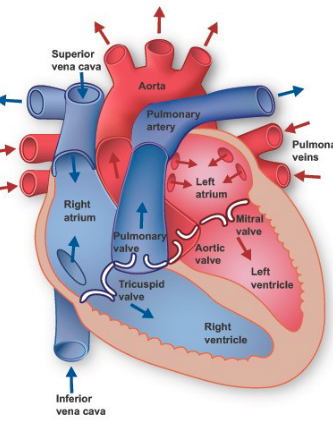
What are the compartments of the heart called?
chambers
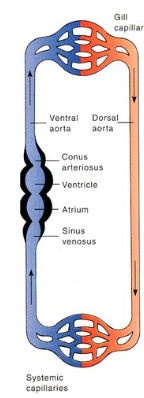
Fish have how many chambers?
2
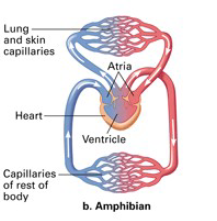
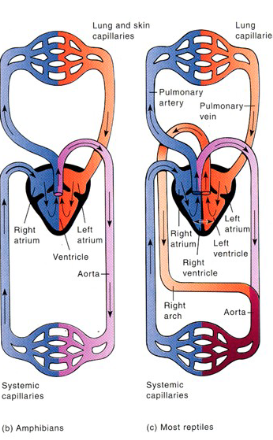
Amphibians + Reptiles have how many chambers?
3
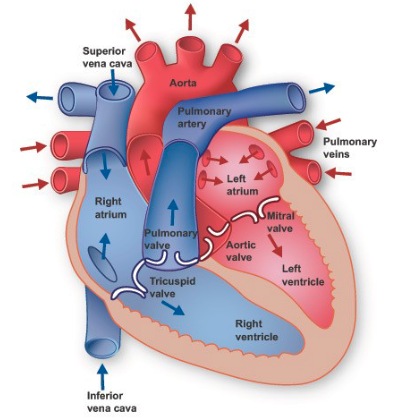
Mammals, Birds + Crocodiles have how many chambers?
4
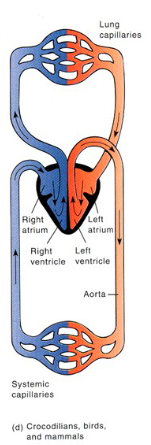
The blood coming back from the body will be __________.
deoxygenated
What is the advantage of a 4-chambered heart?
oxygenated + deoxygenated blood don’t mix

Pulmonary Circuit
blood from heart → lungs and v.v.
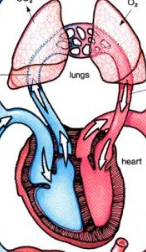
Systemic Circuit
blood from heart → body and v.v.
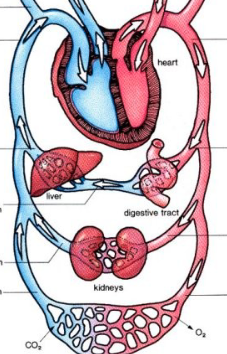
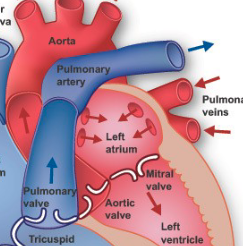
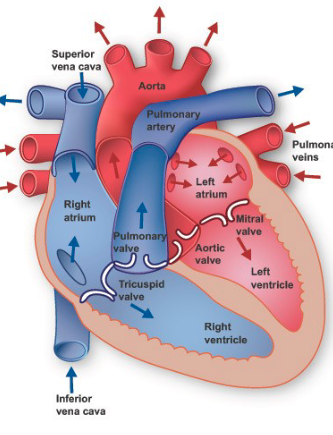
Path of Blood
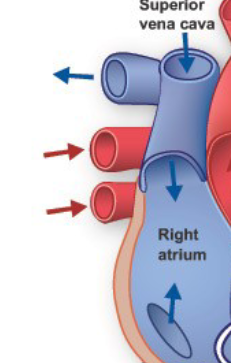
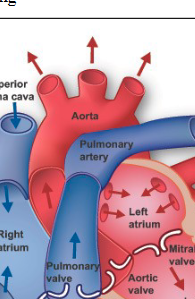
Deoxygenated blood returns to the heart through the vena cava
Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium → then goes to right ventricle
Deoxygenated blood is pumped by right ventricle → lungs to receive oxygen and get rid of CO2
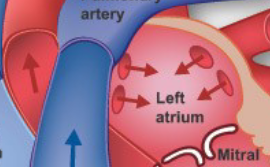
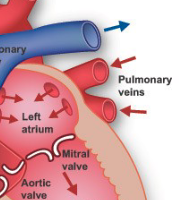
Oxygenated blood returns to the heart via the pulmonary vein → left atrium
Oxygenated blood → left ventricle which pumps the blood out to the body via the aorta
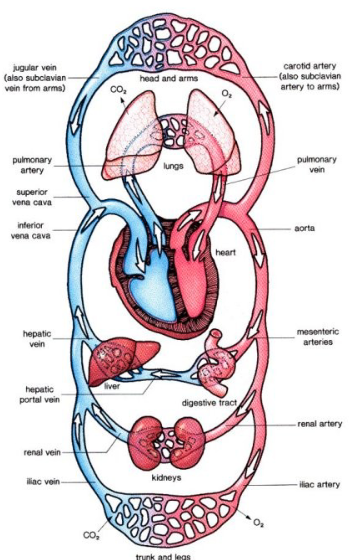
Vena Cava
vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the body back to the right atrium
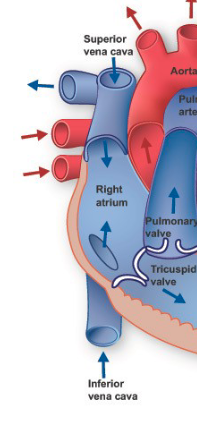
Right Atrium
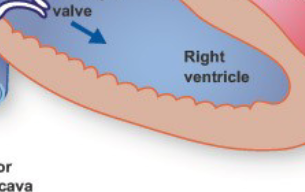
Right Ventricle
Left Atrium
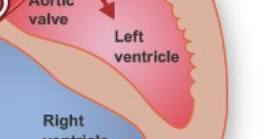
Left Ventricle
Pulmonary Artery
artery from heart to lungs
Pulmonary Vein
vein from lungs to heart
Aorta
artery that carries blood from heart to rest of body
Septum
wall that divides the heart into two sides
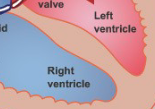
Valves in Order
TPMA
Tricuspid
Pulmonary
Mitral
Aortic
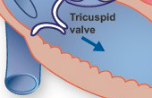
Tricuspid Valve
blood from right atrium → right ventricle
Pulmonary Valve
blood from right ventricle → lungs

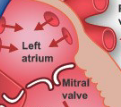
Mitral Valve
blood from left atrium → left ventricle
Aortic Valve
blood from left ventricle → aorta (→ rest of body)
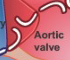
Atrioventricular Valves
(tricuspid + mitral)
allow blood to flow only in atrium-to-ventricle direction
Semilunar Valves
(pulmonary + aortic)
prevent blood from flowing back into the heart after it leaves the ventricles
Diastole
filling of the heart
Systole
emptying of the heart as the ventricles pump
Neurogenic
needing the nervous system to tell it what to do and when to do it
Myogenic Muscle
special type of muscle that the heart is made out of
heart muscle is able to generate its own signal within the heart itself
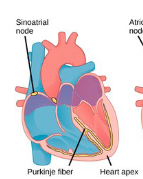
Sinoatrial Node (SA)
cluster of cells that generate a small electrical pulse
causes atria to contract
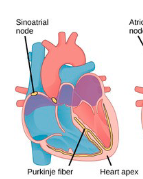
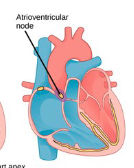
Atrioventricular Node (AV)
2nd node that receives the SA’s electrical pulse
Pukinje Fibers
nerve fibers that run down the ventricles casing them to contract
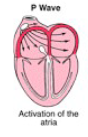
P Wave
initial signal from SA causing atria to contract
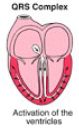
QRS Complex
signal travels through Pukinje fibers to cause the ventricles to contract
T Wave
signal used to allow the heart to rest to prepare for the next beat
Heart Sound
“lub-dub”
“lub” → atrioventricular valves closing after blood has been pumped through
“dub” → semilunar valves closing after blood has been pumped through
Artery
blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart
Vein
blood vessel that carries blood towards the heart
Arteries will ____ when the heart beats/pressure is ____. Arteries will ______ in between heartbeats.
widen, high, narrow
Vasodilation
muscles relax to widen the arteriole
Vasoconstriction
muscles contract to narrow the arteriole
occurs in areas of the body that are not currently being used + to conserve body heat in the extremities
Capillaries
arterioles branch off into smaller blood vessels called capillaries

Cells give co2 and get oxygen at the _______.
capillaries
True or False: RBCs travel almost single file through capillaries
True
True or False: cells in the body can be more than two cells away from a capillary
False; all cells are no more than two cells away from a capillary
The walls of the capillaries are ___ cell thick
one
Veins and Venules
heading back to the heart, capillaries merge together to form venules, and the venules merge together to form veins
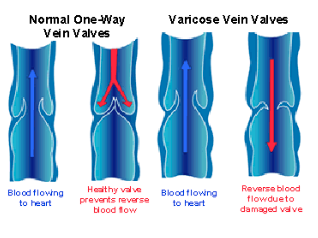
Special Valves in Venules & Veins
have special valves that prevent blood from flowing backwards
flexing of nearby muscles helps push the blood in the right direction
if valves wear out, blood can build up in areas causing varicose veins
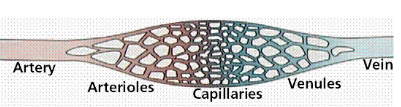
Arteries (Area, Velocity, BP)
↓ Area
↑ Velocity
↑ BP
Venules/Veins (Area, Velocity, BP)
↓ Area
↑ Velocity
↓ BP
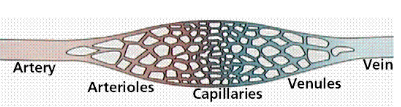
Capillaries (Area, Velocity, BP)
↑ Area
↓ Velocity
↓ BP

Proper circulation requires a clear pathway through the blood vessels. Excess fats and cholesterol can cling to the inside of the blood vessels. If this builds up it creates a ______ which ↑ __ and makes it harder for the heart to maintain _________.
blockage, BP, circulation
Sclerosis
condition where normally flexible tissue hardens + loses function
Atherosclerosis
condition where a blood vessel hardens because of the layer of fat accumulated inside it
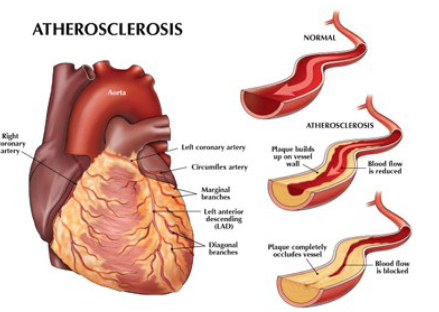
If a blockage occurs in one of the coronary vessels that supply the heart itself, a ______ ______ may be necessary to ensure continued circulation to the heart. Blood vessels are removed from another part of the body and grafted to the aorta and the heart.
bypass surgery
Normally a little more fluid exists in the capillaries than is returned to the venules. This extra fluid accumulates in the spaces in between tissues and is called ________ _____.
interstitial fluid
Lymphatic System (DONT NEED TO KNOW FOR TEST)
open circulatory system
in charge of interstitial fluid/lymph
has no pump + relies on movement/flexing of muscles to move lymph into ducts where fluid is delivered back to the main closed circulatory system
filters fluids
Lymph Nodes (DONT NEED TO KNOW FOR TEST)
areas where cells in your immune system are stored when not fighting infection
BP is measured in
mm Hg
Normal Diastolic BP
70-90 mm Hg
Normal Systolic BP
110-140 mm Hg
Ideal BP (Systolic/Diastolic)
120/80 mm Hg
Hypotension
Low BP
not a problem unless causing fainting/weakness
can be caused by sudden loss of blood/dehydration
Hypertension
High BP
can cause serious problems like heart attacks, heart failure, or stroke
can be caused by poor diet, lack of exercise, or diabetes
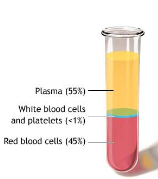
Blood is composed of…
RBCs (45%)
WBCs + Platelets (<1%)
Plasma (55%)
Red Blood Cells are also called
erythrocytes
