Biological Systems - Fungi Module
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary and concepts related to fungi, including their characteristics, reproductive strategies, ecological roles, and significance to humans.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Fungi
Eukaryotic organisms that primarily have a cell wall made of chitin and absorb nutrients through their environment.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that cannot make their own food and must absorb nutrients from their environment.
Mycelium
A mass of hyphae that forms the main body of a fungus.
Hyphae
Filamentous structures that make up the body of a fungus, which are involved in nutrient absorption and reproduction.
Spores
Reproductive cells produced by fungi, which can be dispersed and germinate into new fungal individuals.
Plasmogamy
The fusion of cytoplasm from two fungal cells, leading to a dikaryotic stage in fungal reproduction.
Karyogamy
The fusion of nuclei from two cells after plasmogamy, resulting in a diploid cell.
Ascomycota
Phylum of fungi known as sac fungi, characterized by having spores produced in sac-like structures called asci.
Basidiomycota
Phylum of fungi known as club fungi, characterized by having a basidium for spore production.
Mycorrhizae
Symbiotic associations between fungi and plant roots that enhance nutrient and water uptake for plants.
Lichens
Symbiotic associations between fungi and algae or cyanobacteria, which create a new organism that thrives in harsh environments.
Zygomycota
Phylum of fungi characterized by their production of zygosporangium and high diversity in life histories.
Chytridiomycota
Phylum of fungi known as chytrids, characterized by their flagellated spores called zoospores.
Decomposers
Organisms, including fungi, that break down organic material, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Ectomycorrhizae
A type of mycorrhizal association where fungal hyphae encircle but do not penetrate plant root cells.
Endomycorrhizae
A type of mycorrhizal association where fungal hyphae penetrate the plant cell walls.
Mutualism
A symbiotic relationship where both organisms benefit from the association.
Pathogens
Organisms that cause disease; in the context of fungi, these include species that infect plants or animals.
Diversity food sources related to diversity of ecological roles
Decomposers, parasites, predators, mutalists
Decomposers
Absorb nutrients from dead organic material
Parasites
Absorb nutrients from the cells of living hosts
Predators
Trap animals and digest them
Mutualists
Absorb nutrients from a host, but reciprocate with actions that benefit the host
Predatory fungi
Fungi that obtain nutrients by trapping and digesting organisms, including insects and nematodes.
Fungi reproduce by…
Producing spores that can develop into new organisms.
Fungi can produce spores…
Sexually or asexually
Asexual - Pores
Spores produced by mitosis
Phylogen
Spores produced by meiosis
Phylum chrytridiomycota
Chytrids have flagellated spores called zoospores but are true fungi
Phylum zygomycota
This phylum includes fungi that reproduce sexually through zygospores and typically have a coenocytic hyphal structure.
Phylum glomeromycota
This phylum consists of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi that form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, facilitating nutrient exchange.
Mycorrhiza
Fungal hyphae colonise plant roots
Arbuscular mycorrhiza
Hyphae reach inside the plant cell
Phylum ascomycota
This phylum includes fungi that produce spores in sac-like structures called asci, including yeast and truffles.
Varied clade
Variety of habitats
Unicellular yeasts to complex multicellular fungi
Phylum basidiomycota
This phylum includes fungi that produce spores on club-shaped structures called basidia, including mushrooms and puffballs.
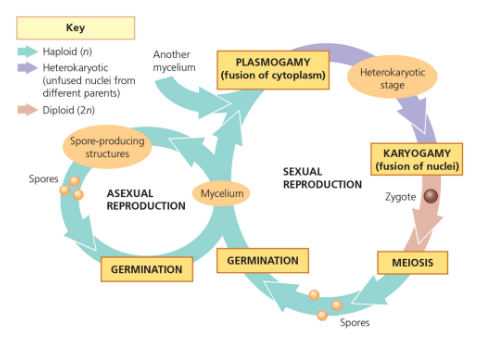
Name
Generalised life cycle
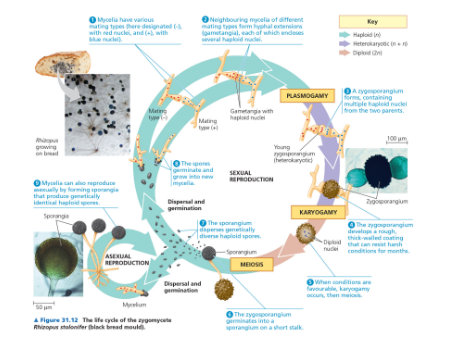
Name
Life cycle of bread mold
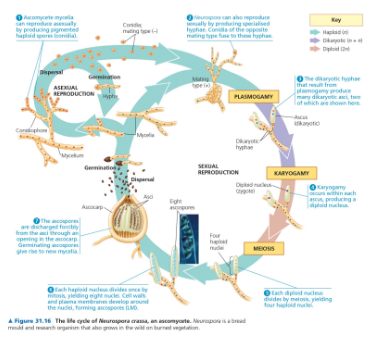
Name
Life cycle of an ascomycete
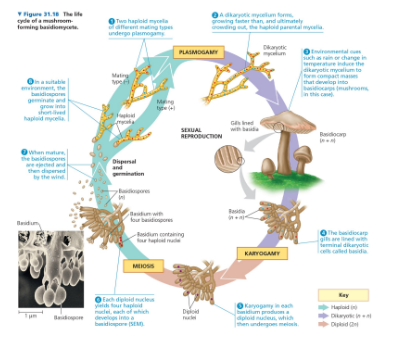
Name
Life cycle of a basidiomycete
Five fungi phyla
Chytridiomycota, zygomycota, glomeromycota, ascomycota, basidiomycota.
Chytridiomycota
A phylum of fungi characterized by the formation of zygospores during sexual reproduction, typically including molds like Rhizopus.
Zygmycota
A phylum of fungi known for their asexual reproduction through the production of spores in sporangia, which includes species like Rhizopus.
Glomeromycota
A phylum of fungi that form mutualistic associations with the roots of plants, known as arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, which enhance nutrient uptake for the plants.
Ascomycota
A phylum of fungi characterized by the production of ascospores in sac-like structures called asci, which includes yeasts and molds like Penicillium.
Basidiomycota
A phylum of fungi known for producing basidiospores on club-shaped structures called basidia, which includes mushrooms, puffballs, and shelf fungi.
Roles fungi play in nutrient cycling
Decomposers, mutualists, pathogens
Decomposers - fungi role
Fungi that break down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Pathogens - fungi role
Fungi that cause diseases in plants, animals, or humans, often leading to detrimental effects on health and agriculture.
Mutualists - fungi role
Fungi that form beneficial relationships with other organisms, such as plants, aiding in nutrient absorption and enhancing growth.
Fungi secrete…
Enzymes that can break down almost any carbon-containing substrate
Without decomposers…
Life as we know it would go for one last round and then would cease to exist
Myccorhizae
Symbiosis between plant and fungi that dramatically increases water and nutrient supply for plant in exchange for sugars from plant for fungiE
Ectomycorrhizae
Outside root cellsE
Endomycorrhizae
Inside root cells
Some fungi share…
Digestive services with animals, helping break down plant material in the guts of cows and other grazing mammals
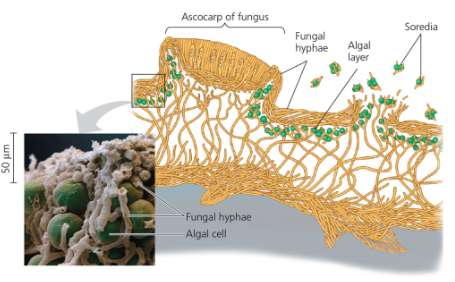
Lichen
Highly integrated symbiotic association of algal with fungal hyphae
What does protist provide
C and N compoundsWHa
What does fungus provide
Moise environment and minerals
Name
Lichen life cycle
About 30% of known fungal species are…
Parasites or pathogens, mostly on or in plants
Mycosis
Infection by fungal parasite
Beneficial human use of fungi
Medicine, research and bioremediation