Biology Genetics and mutation pretest
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Phenotype or Genotype:
Freckles dusted across the cheeks and nose
phenotype
Phenotype or Genotype:
The movement of sodium by the sodium/potassium pump
phenotype (a functional process carried out by proteins)
Phenotype or Genotype:
homozygous recessive allele inherited from each parent.
Genotype (describes the allele combination)
Phenotype or Genotype:
True breeding parents in a monohybrid cross
Genotype (true breeding means homozygous alleles
Phenotype or Genotype:
blood clots formed due to a defect in the antithrombin gene
phenotype (the disease effect you observe
In humans brown eye color (B) is dominant to blue eye color (b). A brown- eyed man marries a blue-eyed woman and they have three children, two of whom are brown-eyed and one of whom is blue-eyed.
The brown eyed children are heterozygous (Bb)
blue eyed kid is bb
Which of the following statements are FALSE?
A. An individual who shows a recessive phenotype must have a parent that shows the recessive phenotype
B. If an individual shows a dominant phenotype, at least one parent must show a dominant phenotype
C. Heterozygous individuals always show the dominant phenotype
D. All offspring from crosses of true breeding-parents show the same phenotype
A. An individual who shows a recessive phenotype must have a parent that shows the recessive phenotype
4. Which of the following describes programmed cell death?
A. Metastasis
B. Apoptosis
C. Angiogenesis
D. Necrosis
Apoptosis
5. What is the name given to the specific location of a gene on a chromosome?
A. Allele Site
B. Replication Fork
C. Allosteric Site
D. Locus
D. Locus
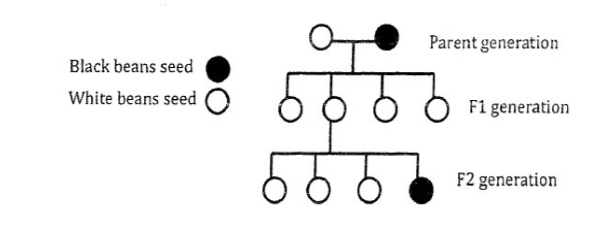
6. Assuming both parents in the following pedigree are true-breeding, why do all of the
individuals in the F1 generation have white phenotypes?
All F1 individuals have white phenotypes because the white allele is dominant, and crossing true-breeding white (WW) with true-breeding black (ww) produces heterozygous (Ww) offspring that express the white trait.
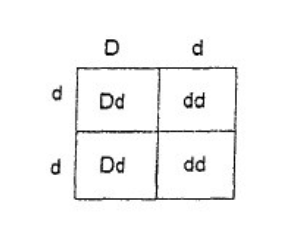
7. The figure to the left is a common way to depict all possible
outcomes of a cross between two individuals.
What is the name of this graphic device?
Does this depict a monohybrid cross or dihybrid cross?
Punnett square
Monohybrid cross
8. A mutation that is due to a dominant allele causes guinea pigs to lose their body hair. A breeder is trying to establish a colony of mutant “hairless” guinea pigs to sell to pet stores. He has a male mutant guinea pig that he wants to use for the breeding. However, due to an error in record keeping, he is uncertain of the mutant male’s genotype. He decides to mate a true- breeding normal guinea pig with the mutant male and notices that 100% of the offspring (F1generation) have the hairless mutant phenotype.
a) The cross that was conducted is often used by breeders to determine the genotype of anindividual that shows the dominant trait. What is the name of this specific cross?
This type of cross is called a test cross.
A dominant-phenotype individual is crossed with a true-breeding recessive individual to determine the unknown genotype.
8. A mutation that is due to a dominant allele causes guinea pigs to lose their body hair. A breeder is trying to establish a colony of mutant “hairless” guinea pigs to sell to pet stores. He has a male mutant guinea pig that he wants to use for the breeding. However, due to an error in record keeping, he is uncertain of the mutant male’s genotype. He decides to mate a true- breeding normal guinea pig with the mutant male and notices that 100% of the offspring (F1generation) have the hairless mutant phenotype.
b) The hairless mutation is dominant and it occurs because there was a deletion of the 3 bases that are bolded in the coding sequence of the gene – 5’ CATTGGTA 3’. The
deletion or removal of the bases is a mistake or error that occurs during which phase of
the cell cycle?
b)
The deletion of bases occurs during the S phase (DNA synthesis phase) of the cell cycle.
This is when DNA is replicated, and copying errors like deletions can happen.
8. A mutation that is due to a dominant allele causes guinea pigs to lose their body hair. A breeder is trying to establish a colony of mutant “hairless” guinea pigs to sell to pet stores. He has a male mutant guinea pig that he wants to use for the breeding. However, due to an error in record keeping, he is uncertain of the mutant male’s genotype. He decides to mate a true- breeding normal guinea pig with the mutant male and notices that 100% of the offspring (F1generation) have the hairless mutant phenotype.
c) The mutation in the above coding sequence causes the protein that is responsible for hair follicle stimulation in guinea pigs to be non-functional. This protein is made and secreted by skin or epidermal cells. What organelle would produce this protein
c)
The protein would be produced by the rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER).
Proteins that are made for secretion are synthesized by ribosomes attached to the rough ER.
9. A purebred plant that produces yellow seeds is crossed with a purebred plant
that produces green seeds.
The F1 plants have yellow seeds.Why do all the individuals in the F1 generation have yellow phenotypes?
All F1 plants are yellow because the yellow allele is dominant over the green allele.
10. A zookeeper crossed two tigers that were both heterozygous for two traits. The
tigers produced a litter of 16 pups!
How many of these offspring would you expect to be recessive for both traits?
1 offspring — in a dihybrid heterozygous cross, 1 out of 16 is recessive for both traits.
11. In watermelons, solid green color (G) is dominant to stripes (g), and round
shape (R) is dominant to an oblong shape (r). If you cross a watermelon that is
homozygous dominant for color and heterozygous for shape with a watermelon
that is heterozygous for both traits ...
What percentage of the offspring will be solid green and oblong?
25% of the offspring will be solid green and oblong.
12.Two brothers are born of the same parents. One of the boys has sickle cell
disease while the other brother is healthy. Neither parent exhibits symptoms of
sickle cell. The parents want to have another child but are afraid this child will also
be affected.
What would genetic counselors say is the probability that the next child will have
the disease?
25% chance the next child will have sickle cell disease.
13. Achondroplasia is a form of dwarfism caused by a dominant allele. The
homozygous dominant genotype causes death, so individuals who have this
condition are all heterozygotes. If a person with achondroplasia mates with a
person who does not have achondroplasia...
What percentage of their children would be expected to have achondroplasia?
50% of their children would be expected to have achondroplasia.
What is meiosis?
A type of cell division that makes sex cells (gametes).
🧠 Trick: Meiosis = makes “me” (sex cells)
How many divisions occur in meiosis?
Two — Meiosis I and Meiosis II.
🧠 Trick: Meiosis = double division
Why is meiosis called a reduction division?
It reduces chromosome number by half.
🧠 Trick: Reduce = half
What happens in Meiosis I?
Homologous chromosomes pair up and separate.
🧠 Trick: I = “Identify pairs”
What happens in Meiosis II?
sister chromatids separate.
🧠 Trick: II = “Split sisters”
Why are sex cells haploid?
So fertilization restores the diploid number.
🧠 Trick: Half + half = whole
During which phase does synapsis occur?
Prophase I.
🧠 Trick: Prophase I = pairing time
How does meiosis create genetic variation?
Through crossing over and independent assortment.
🧠 Trick: Mix & match genes
How is meiosis similar to mitosis?
Both involve cell division stages.
How is meiosis different from mitosis?
Meiosis makes 4 haploid cells; mitosis makes 2 diploid cells.
🧠 Trick: Mitosis = make more body cells
Are germ cells somatic cells?
No.
Do germ cells divide by mitosis, meiosis, or both?
both
Gametes
Sex cells (sperm or egg).
Zygote
A fertilized egg.
Germ Cell
A cell that produces gametes.
Somatic Cell
A body cell (not sex cells).
Synapsis
Pairing of homologous chromosomes.
🧠 Trick: Synapsis = sync up
What is genetics?
The study of inheritance.
: Who is the Father of Genetics?
Gregor Mendel.
🧠 Trick: Mendel = Mendelian genetics
What organism did Mendel study?
: Pea plants.
🧠 Trick: Peas are peaceful science plants
: What is a Punnett square used for?
A: To predict offspring genotypes and phenotypes.
: P Generation
A: Parent generation.
F1 Generation
First offspring generation.
F2 Generation
Offspring of F1 parents.
Monohybrid cross
Cross involving one trait.
: Dihybrid cross
Cross involving two traits.
Phenotypic ratio of heterozygous monohybrid cross
A: 3:1.
🧠 Trick: 3 dominant, 1 recessive
Phenotypic ratio of heterozygous dihybrid cross
: 9:3:3:1.
🧠 Trick: Classic Mendel ratio
What causes genetic variation?
Synapsis and crossing over.
What is a test cross?
Crossing with a homozygous recessive to find genotype.
Homozygous dominant
Two dominant alleles (AA).
Homozygous recessive
Two recessive alleles (aa).
Heterozygous
One dominant, one recessive (Aa).
True/Pure breeder
Always produces same trait.
Genotype
Genetic makeup.
🧠 Trick: Geno = genes
Phenotype
Physical appearance.
🧠 Trick: Pheno = physical
Who is a carrier?
A heterozygous person with no symptoms.
Wild type
Normal, most common gene.
Q: Mutant
A changed gene.
: What is cystic fibrosis?
Recessive disease causing thick mucus.
What is sickle cell disease?
Recessive disease causing misshaped red blood cells.
How is cancer related to cell division?
Cancer is uncontrolled cell division.
What is virotherapy?
Using viruses to kill cancer cells.
🧠 Trick: Virus vs cancer