Haemoglobinopathies: Sickle-Cell Anaemia
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
sickle-cell anaemia
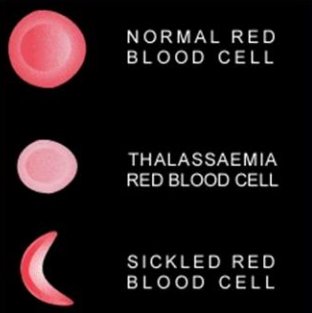
RBCs have an abnormal crescent shape making them sticky and rigid
Get trapped in small vessels and block blood from reaching different parts of the body- can cause pain and tissue damage.
Autosomal recessive condition- can be carrier
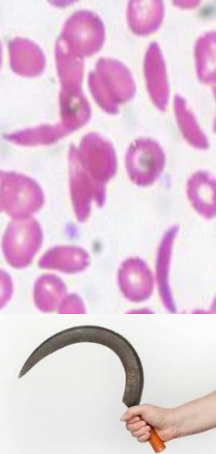
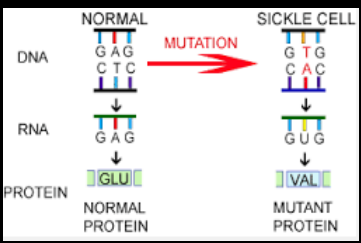
cause of sickle-cell anaemia
point mutation at position 6 on beta chain
A→T
glutamic acid → valine
HbAS- heterozygous (sickle-cell trait/carrier)
HbSS- homozygous (sickle-cell disease)
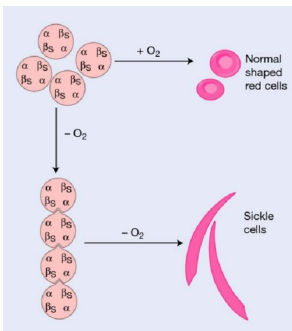
pathogenesis of sickle-cell anaemia
in low oxygen conditions, Hb polymerises
long fibres form crystals
causes rigid “sickle” RBCs
causes obstruction of RBC circulation and anaemia from extravascular haemolysis
sickle cell disease (SCD) symptoms
Symptoms generally occur around 6-months
While there are multiple types of SCD, they all have similar symptoms at different levels of severity. These include:
excessive fatigue or irritability (from anaemia)
fussiness (in babies)
bedwetting (from associated kidney problems)
jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and skin)
swelling and pain in hands and feet (ischemia)
frequent infections (overworked spleen and ischemia)
chest pain (Vaso-occlusive)
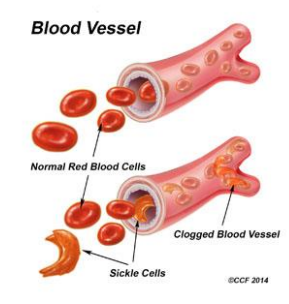
clinical picture of sickle-cell anaemia (acute)
Variable from patient to patient
Mainly systemic: organ and tissue ischaemia.
Episodes of crises:
Vaso-occlusive (VOC- sickle cells block blood vessels)
Visceral sequestration (VOC in spleen, leads to hypervolemic shock)
Aplastic (bone marrow stops making RBCs)
Haemolytic
Chronic haemolytic anaemia
chronic haemolytic anaemia
Sickle cells are destroyed early
Chronic haemolysis sickle cells live for a maximum of 10 to 20 days.
Heart Disease and Chest Syndrome low blood oxygen supply
Enlarged heart and subsequent heart disease.
High blood pressure (hypertension) and stroke may also develop. (7% of patients)
Gallstones caused by the breakdown of RBCs. High levels of bilirubin can lead to gallstones.
Delayed growth children.
How are haemoglobinopathies diagnosed?
new-born screening
detailed Patient History
appearance of symptoms
lab tests
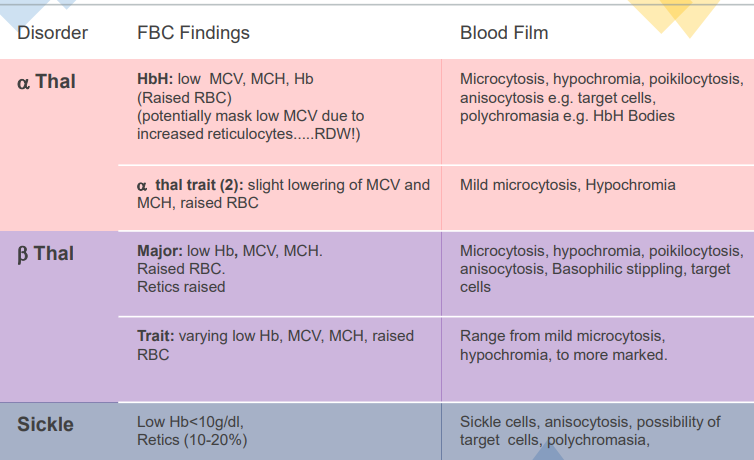
haemoglobinopathies- FBCs and blood films
*polychromasia- multiple colours
Hb H bodies (golf balls)
from alpha thalassaemia
different from reticulocytes
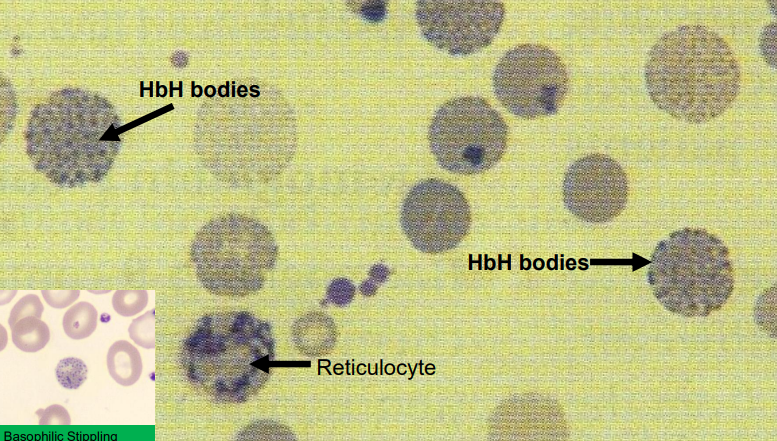
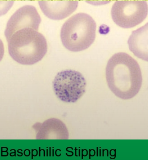
basophilic stippling
beta thalassaemia
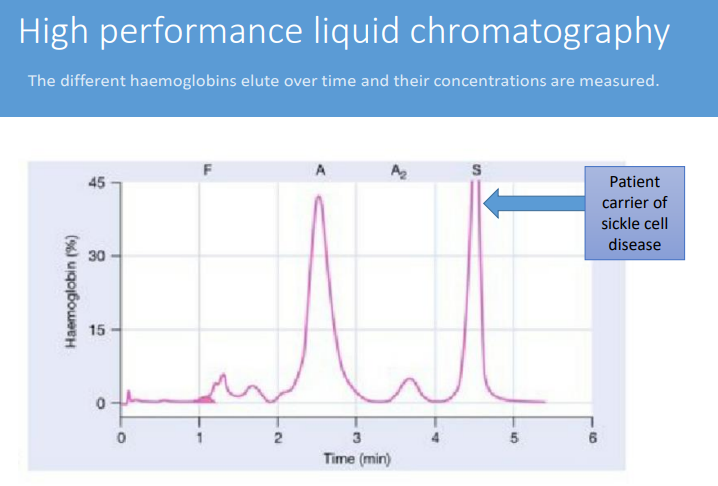
How can haemoglobin variants be detected?
cellulose acetate electrophoresis
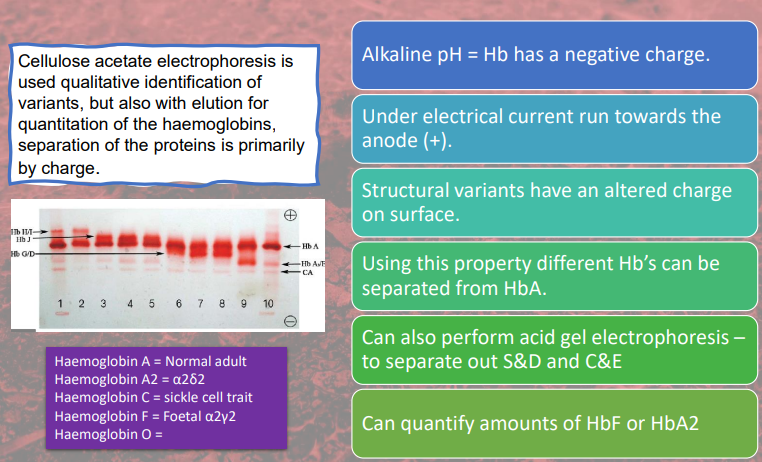
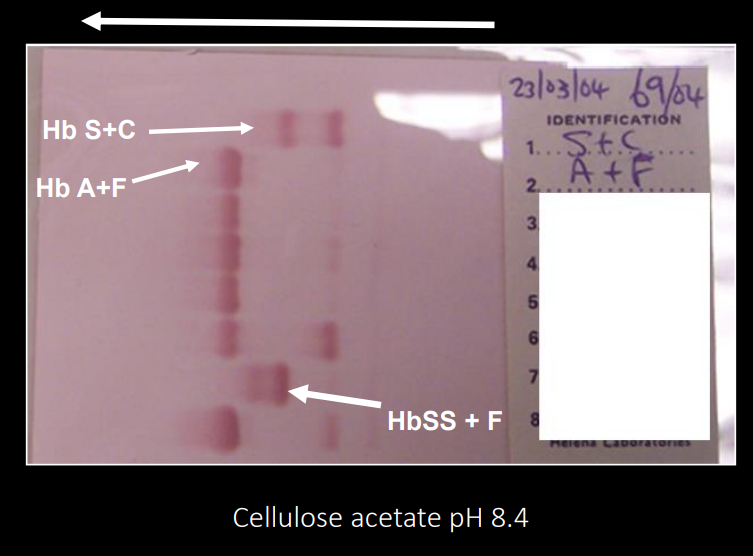
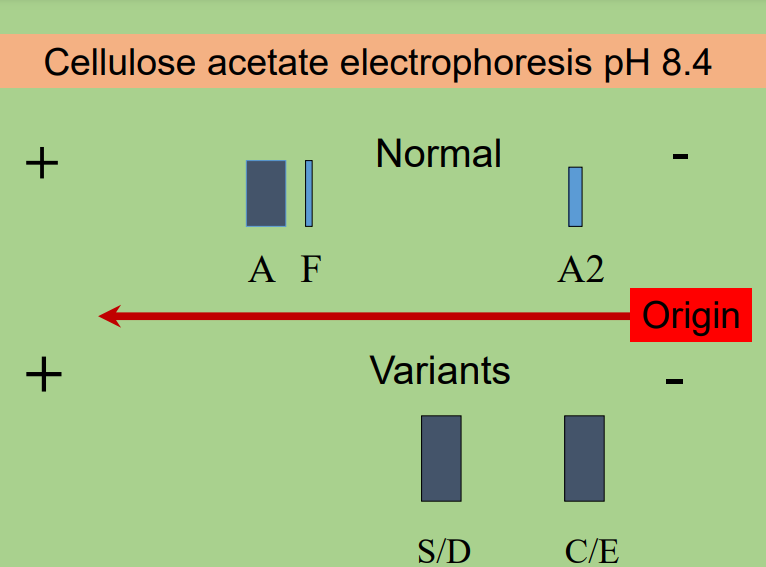
cellulose acetate electrophoresis
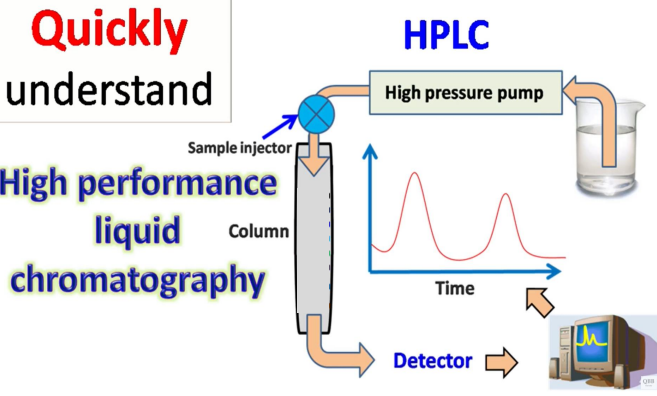
another way to test the variant is to use
HPLC chromatography
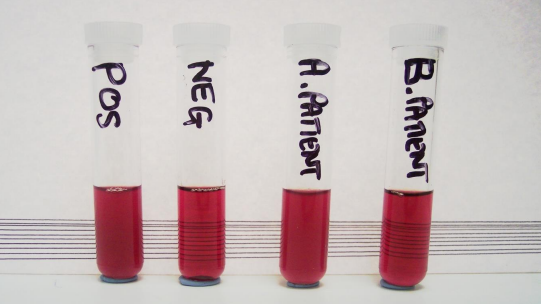
POCT test for HbS
rapid solubility test
cloudy = positive result (sickle-cell)
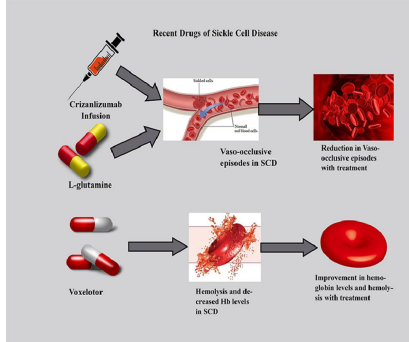
sickle-cell disease treatment
depends on type and severity of disease involved
Blood transfusions and chelation therapy
Bone marrow transplant in children
Medications and supplements (not iron if blood transfusions)
Surgery to remove the spleen or gallbladder
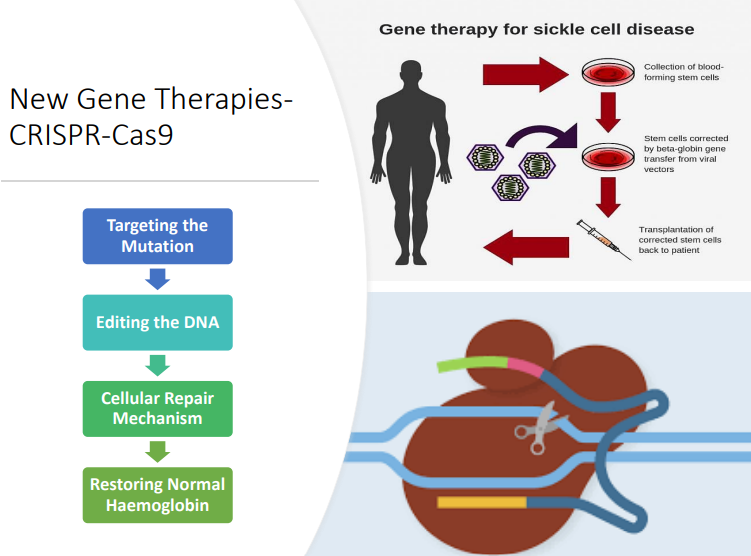
Gene therapy??
Taking care of yourself: Altitude • Pregnancy • Operations • Exposure to cold • Exercise • Infections- treated quickly with antibiotics • Immunisations
new gene therapies- CRISPR-Cas9
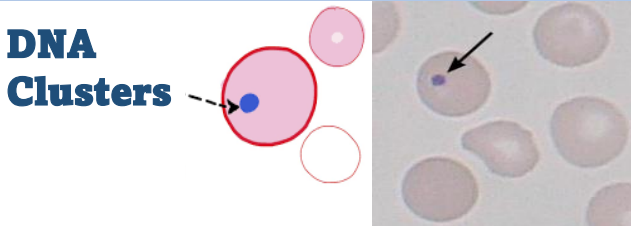
What type of cells may be observed after a splenectomy?
Howell-Jolly bodies
The presence of Howell–Jolly bodies usually signifies a damaged or absent spleen, because a healthy spleen would normally filter such erythrocytes
haemochromatosis
build up of iron in tissues