Animal Digestion
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
intercellular digestion
inside the cell - used by single celled organisms (protists) & sponges
food is ingested in a food vacuole using phagocytosis
extracellular digestion
outside the cell - used by hydra, flatworms like planaria
incomplete digestive systems
gastrovascular cavity
alimentary canal
oral cavity
pharynx
esophagus
stomach
small intestine
large intestine
accessory organ
salivary glands
pancreas
liver
gall bladder
salivary amylase
breaks down sugars
esophagus (peristalsis)
process where food breaks down esophagus
stomach (pepsin)
breaks down protein
pyloric sphincter
a muscular valve that opens to allow food to pass from the stomach to the top of the small intestine
small intestine
major organ for digestion & absorption
pancreas
produces digestive enzymes & an alkaline solution that changes the pH of the digestive contents in the duodenum
pancreatic amylase
breaks down starch
proteins
trypsin & chymotrypsin
nucleic acids
nucleases break down DNA & RNA
absorption of nutrients
the longer your intestines are, the more nutrients you will absorb
digestive circulation
food travels to small intestine, then to the liver
large intestines
stores water & wastes
major function - reabsorbs water that was not absorbed by the small intestines, producing feces
intestinal bacteria inhabit the colon-producing vitamins K & B
ruminant
a large group of herbivores with a four-chambered stomach
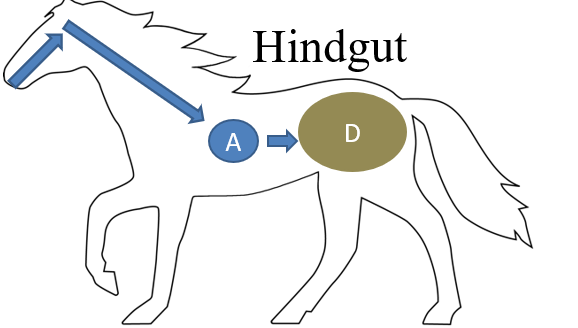
hindgut
the part of the vertebrate digestive tract comprising the colon and rectum
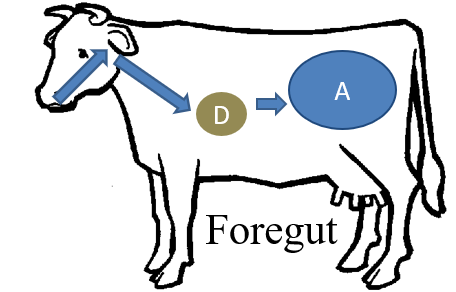
foregut
the anterior part of the digestive tract of a vertebrate embryo that develops into the pharynx, esophagus, stomach, and extreme anterior part of the intestine
coprophagia
the practice of eating stool (feces)