Sports Science Semester 1 Exam Practice
1/206
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
207 Terms
Standard Deviation
a spread of scores around the mean
State why standard deviation is useful
Displays the consistency of each sample
t-test
used to determine if two sets of data are significantly different from each other.
Error bars
graphical representation of variability of the data
Specificity
Measuring the skills needed for a sport can see how well the athlete can maintain that skill when repeatedly doing it.
Accuracy
Checking if the instruments you're using in an experiment are working properly
Reliability
if you repeated the test again are you likely to get similar results
Validity
Does the test actually test what is tests
Control group
a bunch of people are put into a group that doesn't get any special treatment for the experiment.
Why is it important to have an control group?
To see if your hypothesis correlates with the data collected and overcoming learning problems
Randomized groups
People of various skill levels are put in different groups by random. This is to ensure that we don't favor one group over another.
Blind experiment
Participants in the experiment don't know which group they are in. If the participants know what they are getting, it will defeat the purpose of the experiment
Double blind experiment
both the participants and the experimenters are unaware of who is in the experimental or control groups. This is to make sure that neither party influences the results.
Placebo
A harmless substance given to the participants in the controlled group. The substance won't affect the person's performance during the experiment.
PAR-Q
a questionnaire that makes sure the participant doesn't have any health issues that will put them in danger in the experiment
Field testing
tests that can be done without expensive equipment and in sports setting
Laboratory testing
experiments that are done in a lab. More accurate than field testing
Maximal
testing for a person's maximum ability. Used for people who are physically fit
Sub-maximal
Not working to exhaustion. For people who are afraid or aren't knowledgeable of pushing their limits. Good for children and the elderly
Body composition
The relation of fat mass to fat free mass (bones, muscles etc)
Cardiovascular fitness
ability to take in, deliver and use oxygen for use of a aerobic activity
Flexibility
ability to move through a full range of movement around a joint
Muscular strength
ability to generate force using muscle(s)
Muscular endurance
ability of a muscle(s) to maintain force or power
Agility
The ability to change direction at speed with control
Balance
stability of body
Coordination
the ability to use different parts of the body together smoothly and efficiently
Reaction time
duration between presentation of a stimulus and associated response
Speed
change of distance with respect to time when movement occurs
Power
rate of doing work?strength and speed
Harvard Step Test
testing the participant on heart rate recovery after performing the task.
Cooper 12 minute run test
Participant run/walk as fast as they can in 12 minutes.
Multi-stage fitness test
AKA the Beep test. Participant runs increasingly faster in 20 meter shuttles until they're exhausted
Sit and reach test
Tests the flexibility of a person in the lower back and hamstring muscles.
Maximum push up test
Participant does as many push ups as they can with no time limit. This measures upper body strength and enduranc
Sit up test
Measure the strength and endurance of your stomach and hip-flexor muscles
Illinois
Tests agility by having you run as quickly as possible through a series of cones placed in a certain way
Hand grip dynamometer
Measures the maximum strength of your hand and forearm using this machine
40 meter sprint test
The person being tested sprints 40 meters as fast as they can. Warm-ups and practice sprints should be done before test
BMI
Equation to calculate the if your is normal, overweight and obese (person's weight divided by their height squared).
Anthropometry
study of measurements and proportions of the human body
Underwater weighting
Measures the mass per unit volume of a person's body using displacement
Standing Stork Stand Test
This test determines a person's balance. To test this the experimenter has the person stand on one foot with hands on their hips
Handball toss
tests hand eye coordination using a ball to throw against the wall and catching it with your opposite hand repeatedly
Drop test
Measures hand eye coordination by dropping an object and having the person catch using their thumb and index finger
Computer simulation
The use of artificial intelligence to measure and test an individual's skills
Standing Broad jump
Measures leg power. To do this test, you jump as far as you can.
Vertical (Sargent) Jump
Using vertical height jumps to test one's leg muscle strength
Warm up
prepares your cardiovascular respiratory system to function more effectively when you are doing exercise. Increases your heart rate, body temperature and breathing rate
Stretching
improves flexibility and lower the risk of injury
Endurance training
Helps resist pain and fatigue when doing any type of exercise you're doing. This will make you perform better during your exercises
Cool down
slowly reduces the cardio-respiratory activity that you were doing.
Flexibility training
Focuses on range of motion and can lower the risk of injury and have better balance.
Resistance training
improves your muscular strength and endurance
Recreational activities
enhances skill while having FUN, improves your health and fitness. Strengthen relationships with friends and family.
specificity
using certain training methods that are relevant and acceptable to the sport in order to be effective for the person you are training
Progression
gradually increase more amounts of exercise over time.
Overload
improve a certain part of your fitness by increasingly placing requirements on the parts you need it most
Reversibility
If the training plan is terminated then fitness improvements will return to pre-training values. The effect of Detraining is much faster with muscle endurance in comparison to strength.
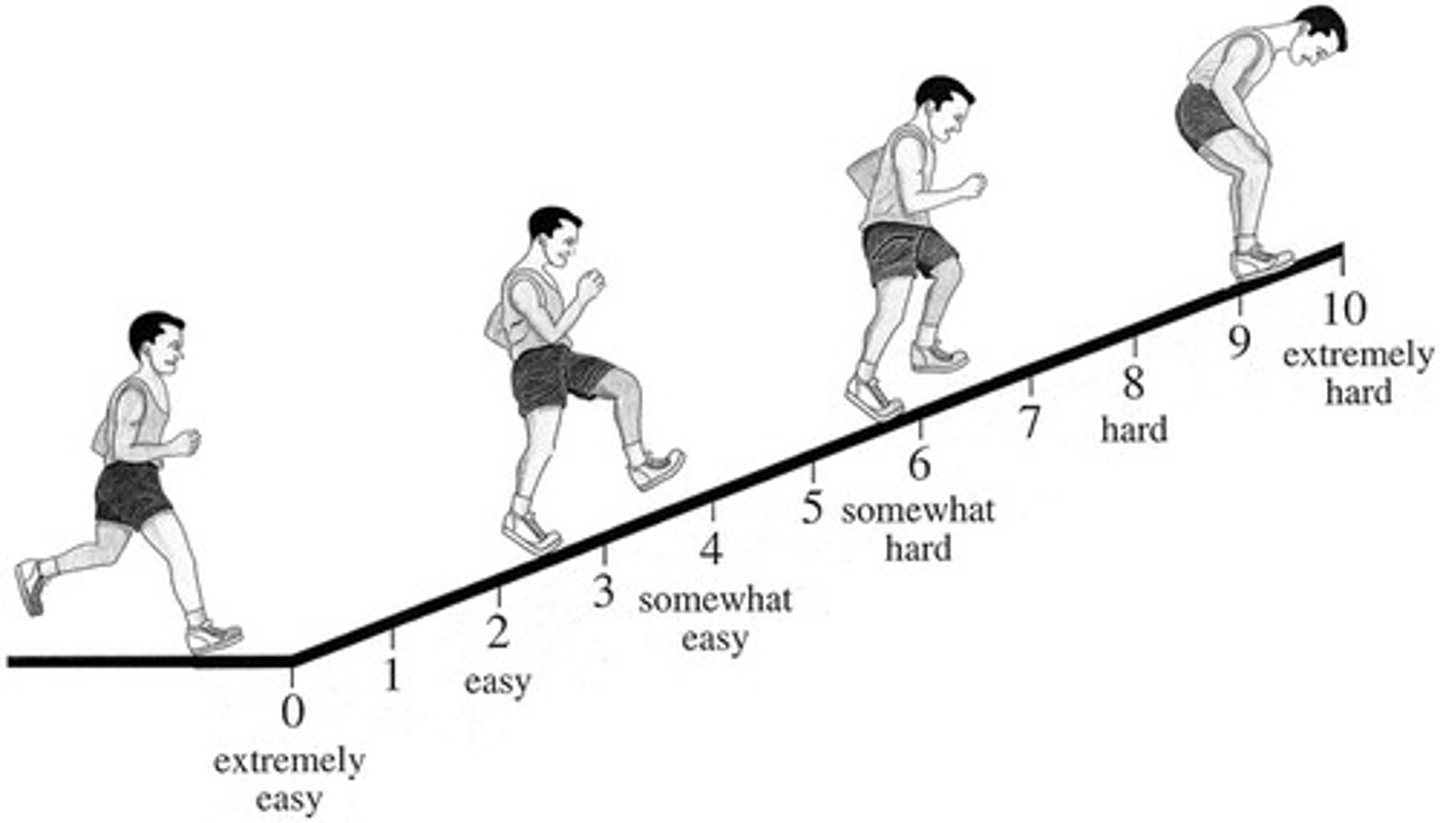
CERT/ OMNI scale
scale used for children for rating of perceived exertion
coefficient of variance
The ratio of the standard deviation to the mean expressed as a percentage.
VO2 max
the maximum amount of oxygen the body can take in and use during exercise
Borg Scale
A quantitative rating system of perceived exertion. (Adults)
Elements of Training Program
Warm up, Cool down, Recreation/Sports
Principles of a Training Program
Progression, Overload, Specificity, Reversibility, Variety, Periodization
Myofibril
One of the slender threads of a muscle fiber, composed of numerous myofilaments
Myofilament
Myofibrils are made up of even smaller threadlike structures
Actin Filament and Myosin Filament
Two protein sites responsible for movement
Sarcomere
Is the basic unit of a muscle and is the part of the muscle that contracts
H Zone
The region of the sarcomere that contains only thick myofilaments
I Band
From the end of the Myosin to the Z Line
A Band
The band of the sarcomere that extends the full length of the thick filament
Z Line
Separates one sarcomere from the next and is where actin filaments attach
Tropomyosin
An actin-binding protein which regulates muscle contraction. Active sites of actin are blocked by this
Troponin
The protein that acts as a calcium receptor in skeletal muscle
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Organelle of the muscle fiber that stores calcium. (Ca+)
Calcium Ions
Serves as the actual "trigger" for muscle contraction by removing the inhibition of the troponin molecules
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
The main energy source that cells use for most of their work
Movement types
Flexion, Extension, Adduction, Abduction, Rotation, Circumduction, Plantar, Dorsi, Supination, Pronation, Inversion, Eversion, Depression, Elevation
Muscle contraction
Shortening/lengthening of sarcomere. Z Lines move closer, I Band, H Zone decrease
Straited (striped) Muscle
Another name for skeletal muscle
Motor Unit
A motor neuron and all the muscle cells it stimulates
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons. Acetylcholine
Nueron
Nerve cell that carries messages throughout the body as electrical signals
Fast twitch muscle fibres
Rapid contraction speed but tire easily
Slow twitch muscle fibres
Continuous low intensity exercise over a long duration (aerobic). High mitochondria, myoglobin, capillary
Flexion
Decreases the angle of the joint
Extension
Straightening at a joint
Rotation
Moving a bone around its own axis, with no other movement
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
Medial
Towards the midline
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body
Concentric
Where the muscle shortens as the fibres contract
Isometric
When a muscle contracts with no resulting movement
Isokinetic
A muscle contraction with constant speed
Isotonic
Force remains constant during the movement
Eccentric
Muscle lengthens under tension
Agonist
Prime mover - contracts to cause movement
Antagonist
Relaxes to allow movement. The triceps brachii when you flex your guns!