Renal histology (lectures)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
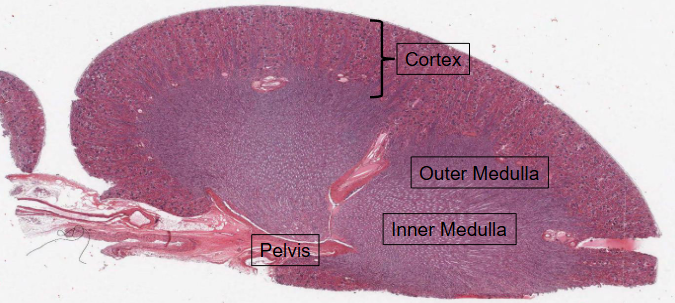
HISTOLOGY → Internal structure of the kidney = Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining.
Boundary between the Cortex (contains the renal corpuscles) and the medulla is very clearly delineated.
Medulla is further divied into:
Outer medulla (adjacent to the cortex)
Innder medulla (adjacent to the pelvis)
Hematoxylin
Has a deep blue-purple colour and stains NUCLEIC ACIDS.
In typical tissue, nuclei are stained blue.
Eosin
Pink and stains proteins nonsepcifically.
The cytoplasm and extracellular matrix have varyding degrees of pink staining.
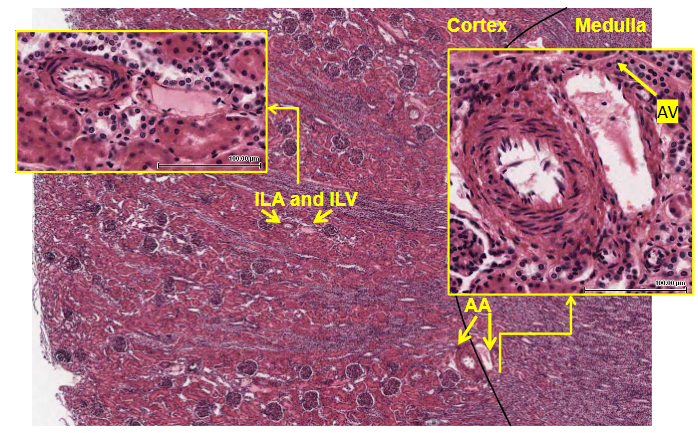
Overview of Vasculature
AA (arcuate arteries) and AV (Acrcuate veins) are loacted at the boundary of the corext and medulla
ILA (Interlobular arteries) and ILV (Interlobular veins) are located in the cortex
NOTE: Veins may often not be easily observed as the collapse due their thin walls. Arteries have a thickened mediial layer e.g. more than one cell thick.
Human Kidney → 2 types of nephron
CORTICAL nephrons have glomeruli in the outer cortex.
JUXTAMEDULLARY nephrons have glomeruli near the cortical-medullary boundary.
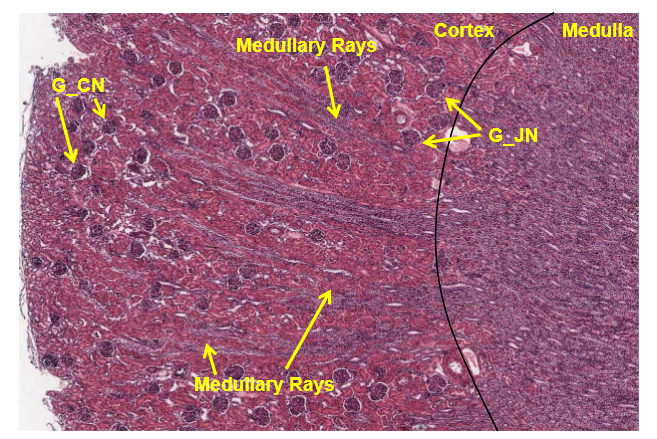
Overview of Cortex-Medulla Boundary
G-CN: Glomerulus-Cortical nephron, G-JN: Glomeruli-Juxtamedullary nephron
Collections of straight tubules form the medullary rays, whcih run up the centre axis of a renal lobule, the region of cortex between the rays called the cortical labyrinth.
Cross section through the renal cortex
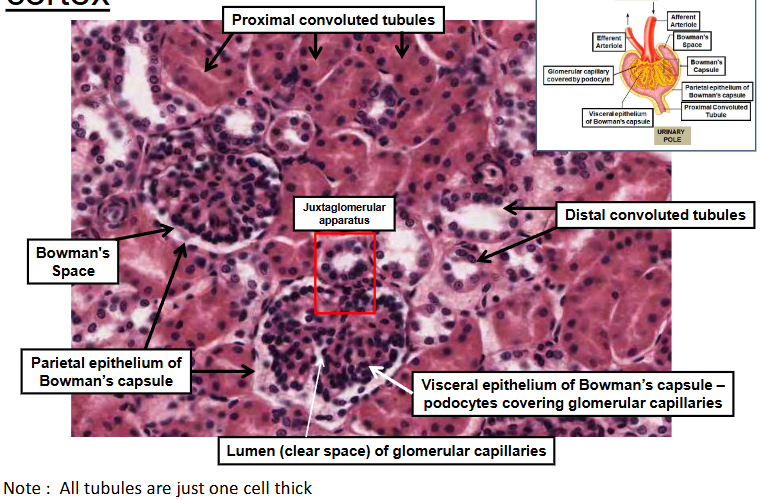
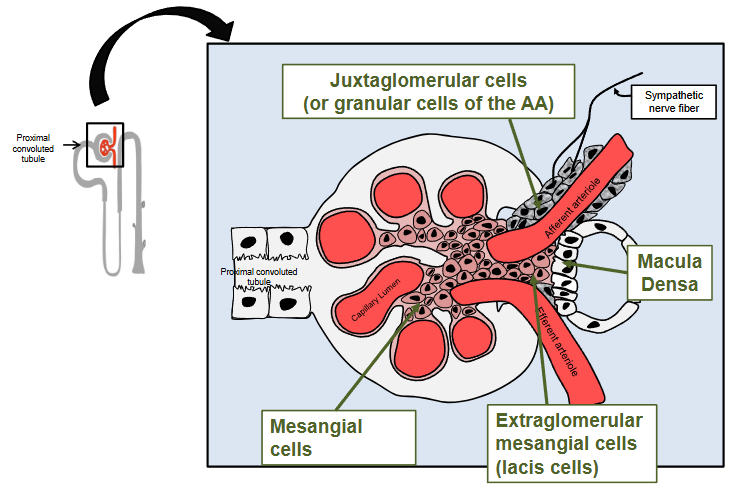
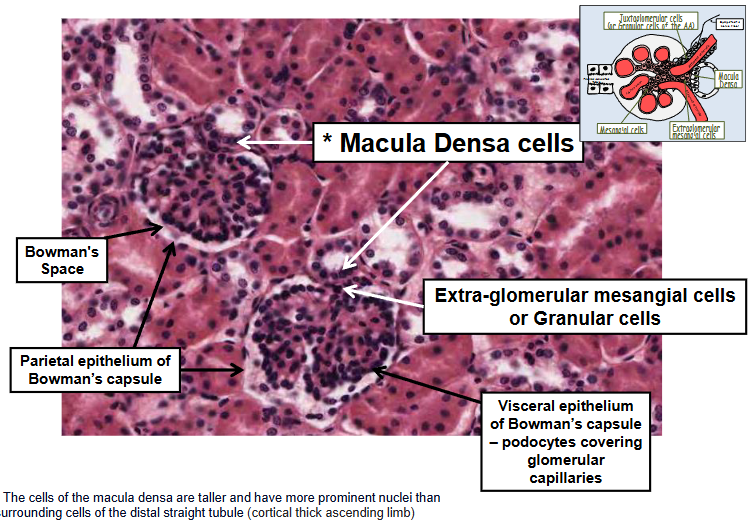
Juxtaglomerular apparatus
Structure that make up the Juxtaglomerular apparatus include:
The macula densa of the thick ascending limb
columnar epithelial cells that act as sal sensors
Extraglomerular mesangial cells (also known as lacis cells or Polkissen cells)
specialised smooth muscle cells that regulate blood flow
Granular cells of the afferent arteriole
Specialised smooth muscle cells that manugacturer, store and release the hormone renin
Renal corpusle and juxtaglomerular apparatus
Cross section through the renal cortex
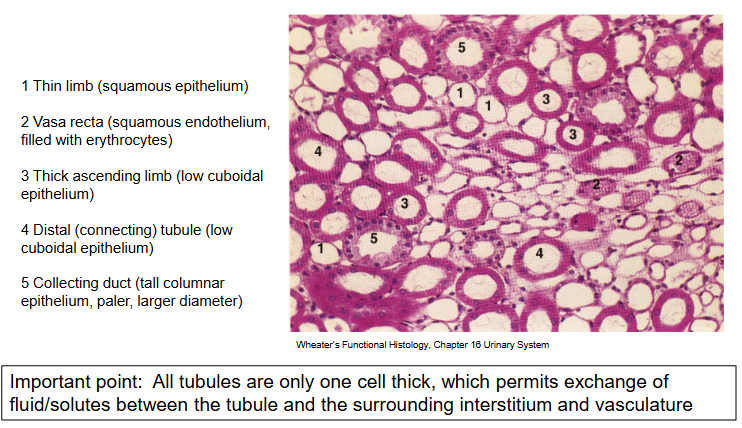
Epithelial cells of the renal tubule
All tubes are a single layer of epithelial cells
Proximal tubule:
Simple cuboidal epithelial cells with extended brush border
Thi descending and ascending limbs:
Squamous (flattened) epithelium
Thick ascending limb and the distal tubule:
Cuboidual epithelium with invaginated basolateral membranes
Collecting duct cells:
Columnar epithelium, two main cell types
Principal cells (NaCl reabsorption and K+ secretion) and intercalated cells (acid-base balance).
Cross section through the renal medulla
Key concepts from lectureS
Six key functions of the kidneys
Each functional renal unit is composed of a filtering component (glomerulus) and a transporting tubular component (the nephron and collecting duct).
There are 2 different categories of nephrons (and their associated vasculature) that have important functional differences.
The cortex receives an enormous volume of blood (glomerular and peritubular capillaries) whereas the vasa recta are the only blood supply to the mdeulla.
The tubule is made up of a single layer of epithelial cells which differ in structure and function along the length of the tubule.