manufacturing class notes
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Single crystals
Polycrystalline structure
Most common atomic arrangements (lattice structures) in crystalline materials
FCC
BCC
HCP
UNIT
Material deformations
slip plans or twinning - permanent deformation
Line defects - dislocations
Point defects - impurities, vacancies, interstitial
Permanent deformation
Slipping and twinning
Line defects
Dislocations
Point defects
vacancy
Interstitial/impurity
Larger grain size causes
rougher surface
Increases ductility
High creep resistance
Lower strength
Microporosity increases
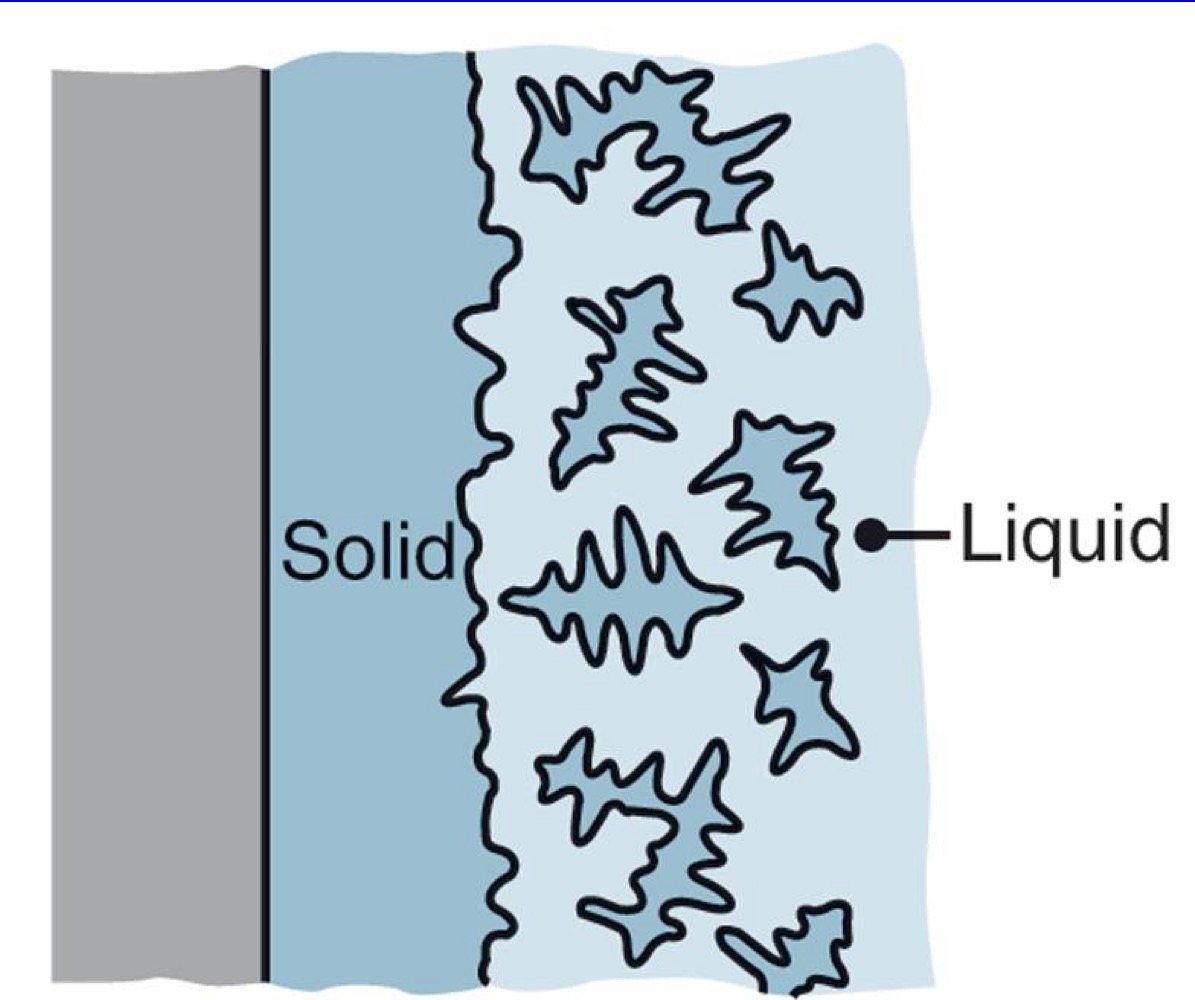
Equiaxed dendritic growth
Dendrites grow freely often with a shape with all equal dimensions
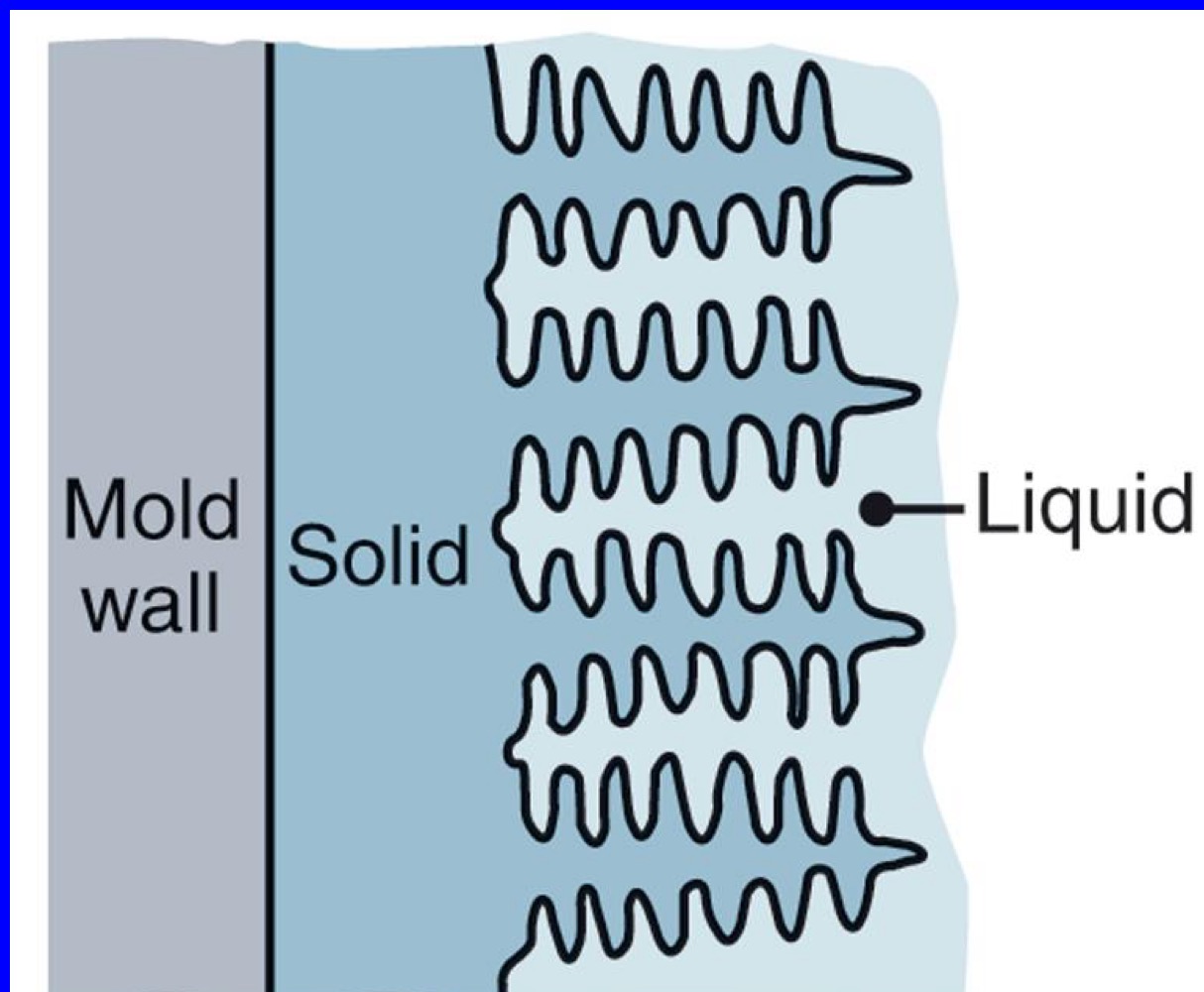
Columnar dendritic growth
Dendrites growth in long columns with direction of temp gradient
Cold working
Plastic deformation at room temp
Smaller grain size causes
increases strength
Microporosity decreases
Ductility decreases
Hot working
Deformation occurs above recrystallization temp
Dislocations make plastic deformation easier true/false
True
Dislocation movement is impeded by __?
Grain boundaries
FCC
12 slip planes
Shear stress required for slip is low
Moderate strength
Good ductility
BCC
48 slip systems
High shear stress required for slip
Good strength
Moderate ductility
HCP
3 slip planes
Low probability of a slip
Brittle at room temp
Forging
metal working using compression, often with heat
Rolling
Metal working with rotating cylindrical rollers to reduce thickness of metal and enhance mechanical properties
Extrusion
Material pushed through die with a specific shape to create continuous product
Drawing
Uses tensile forces to stretch and shape materials by pulling through die
Increasing temperature effects on stress strain curves
Ductility and toughness increase
Yield stress and the modulus of elasticity decrease
Yield stress
Max stress a material can withstand before plastic deformation (permanent)
Elastic vs plastic deformation
Elastic the material cans go back to its OG shape
Plastic the material permanently deforms
Ultimate tensile strength
Max stress a material can withstand before it fractures
Residual stresses
Stresses that remain within a part after it has been formed and all forces removed
Hardness
Resistance to indentation
Strain hardening
Material becomes harder and stronger from plastic deformation
True strain at the onset of necking
E=n
True strain
Measure of deformation that considers the changing length during deformation
true stress
Measures stress and considers the change in cross sectional area during deformation
Engineering stress
Force applied without considering change in cross sectional area but rather uses the PG area
Engineering strain
measure of deformation without considering change in length during deformation but rather uses the end and OG
Alloy
Composition of two or more chemical elements at least one is a metal
Phase
Chemically and structurally homogenous area (solid, liquid, gas)
Solution
Homogenous mixture where solute dissolved in solvent
Pure metals have a wide range of properties true/false
False
Alloying metals produces a wide/narrow range of material properties?
WIDE
Solid solutions of alloys
interstitial
Substitutional
Interstitial solid solution
Impurities are located in spaces between the solvent atoms
Substitutional
Impurities are located in sites normally occupied by solvent atoms
Intermetallic compounds
Substances combine in definite properties
strong
Hard
Brittle
good high temp strength
Provide oxidation resistance
Crystal structures differ than constituents
Binary alloys
Mixture of two different metallic elements to Create materials with improved material properties
Iron has what lattice structure?
BCC
Ferrite
Max solid solubility of carbon
soft
Ductile
Austenite
Iron structure changes BCC to FCC
FCC has more interstitial positions
Cementite
Iron carbide (Fe3C)
intermetallic compound
Hard and brittle
Can include other alloying elements
What determines the microstructure?
Combination of different iron carbon solid phases
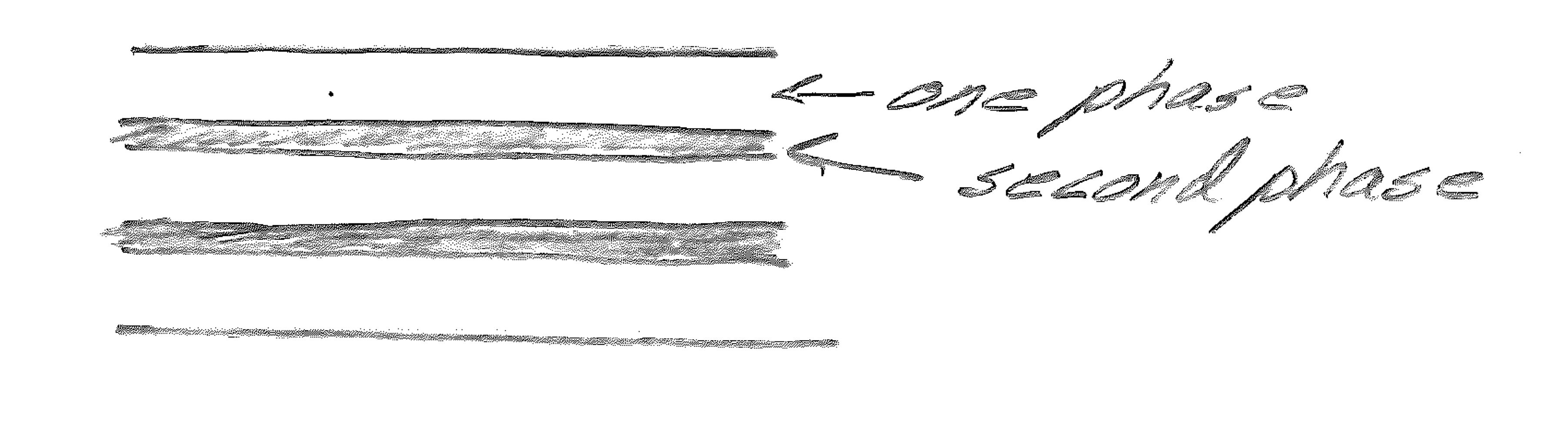
Lamellar structure
Heat treatment modifies
Microstructure
strength
Hardness
Ductility
Toughness
Heat treatment controlled by
Heating and cooling at different rates
Pearlite
From Austenite
ferrite/cementite lamellae structure
Sphearoidite
From Pearlite
cementite becomes spherical
Has ferrite and cementite
Bainite
Similar to Pearlite with different shapes
ferrite cementite
Feathery needle shape
Martensite
From quenching Austenite rapidly
fcc structure transforms to BCC
Super solid solution of carbon iron
Time temperature transformation (TTT) diagrams
provide information required to design heat treatment schedules to obtain desired microstructures
Heat treatment of ferrous alloys
Controlled cooling and heating of alloys Induces solid phase transformation and changes the microstructure
Affects:
strength
Hardness
Ductility
Toughness
Wear
Thermal conditions
temp
Time
Cooling/heating rate
Quenching
cooling at rapid rate
Important properties for quenching
specific heat
Thermal conductivity
Annealing
Heat to specific heat T (usually in furnace)
hold at T for specific time
Cool at specific rate in gas (air) - usually occurs at slow rate
Usually reduced hardness
USED TO INCREASE DUCTILITY
Tempering
Controlled heating used to reduce brittleness and increase toughness
High strength low alloy steels (HSLA) designations
BH bake hardenable
DP -dual phase
TRIP - transformation induced plasticity
TWIP - twinning induced plasticity
CP - complex phase - mixed ferrite/martensite structure
Ferrous alloys exs
carbon steels
Alloy steels
Stainless steels
Tool steels
Die steels
Casting process
creating a pattern
Creating a mold
Pouring molten metal into mold
Allowing to solidify (cool)
Removing part from the mold
Must consider what for casting
Molten metal reached all regions on the mold
Cooling of the mold - conduction, convection, radiation
Type of solidification - dendritic, single crystal or polycrystalline, amorphous (no crystal structure)
Causes of porosity in casting
shrinkage
Dissolved gas
Characteristics of molten metal that influence fluidity
surface tension
Viscosity
Inclusions
Solidification pattern of the alloys
Mold design
Mold material
Degree of superheat
Rate of pouring
Heat transfer
Turbulent vs laminar flow
laminar is smooth ordered fluid motion
Turbulent is chaotic and irregular
Fluidity
The ability to flow into the mold cavities
Pure metals have the best fluidity true/false
True
Alloys are supplied at what temps?
Superheated temps
Solidification rate is controlled by what?
Rate that heat can be absorbed by the mold
From an energy balance, Heat transfer for an arbitrary shape is related to what?
Volume/area
SMAW shielded metal arc
Consumable
GTAW gas tungsten arc
Nonconsumable
GMAW gas metal arc
Consumable
SAW submerged arc
Consumable
PAW plasma arc
Nonconsmable
DCEN weld shape (negative)
Shallow wide
DCEP weld shape (positive)
Deep narrow
AC weld shape
Not too deep not too wide