2.2 Data Transmission
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Data Transmission
Data Transmission is the transfer of data between computers or other electronic devices through a network.
When data is transmitted, it can be sent via a Parallel or Serial link.
Serial Transmission
Serial Transmission is the sending data bit-by-bit along the same data line
Advanatges of Serial Transmission
• It requires only two wires, compared with 8 or 16 in parallel
• serial can travel longer distances than parallel
• It has simpler interface / circuit board
Disavanatges of Serial Transmission
It is much slower than parallel
Parallel Transmission
Parallel Transmission is process of simultaneous sending of all bits in a byte along separate lines
Advantages of Parrallel Transmission
It is much faster than serial transmission
Disadvantages of Parralle Transmission
It cannot be used over a long distance as serial (due to interference along the cable)
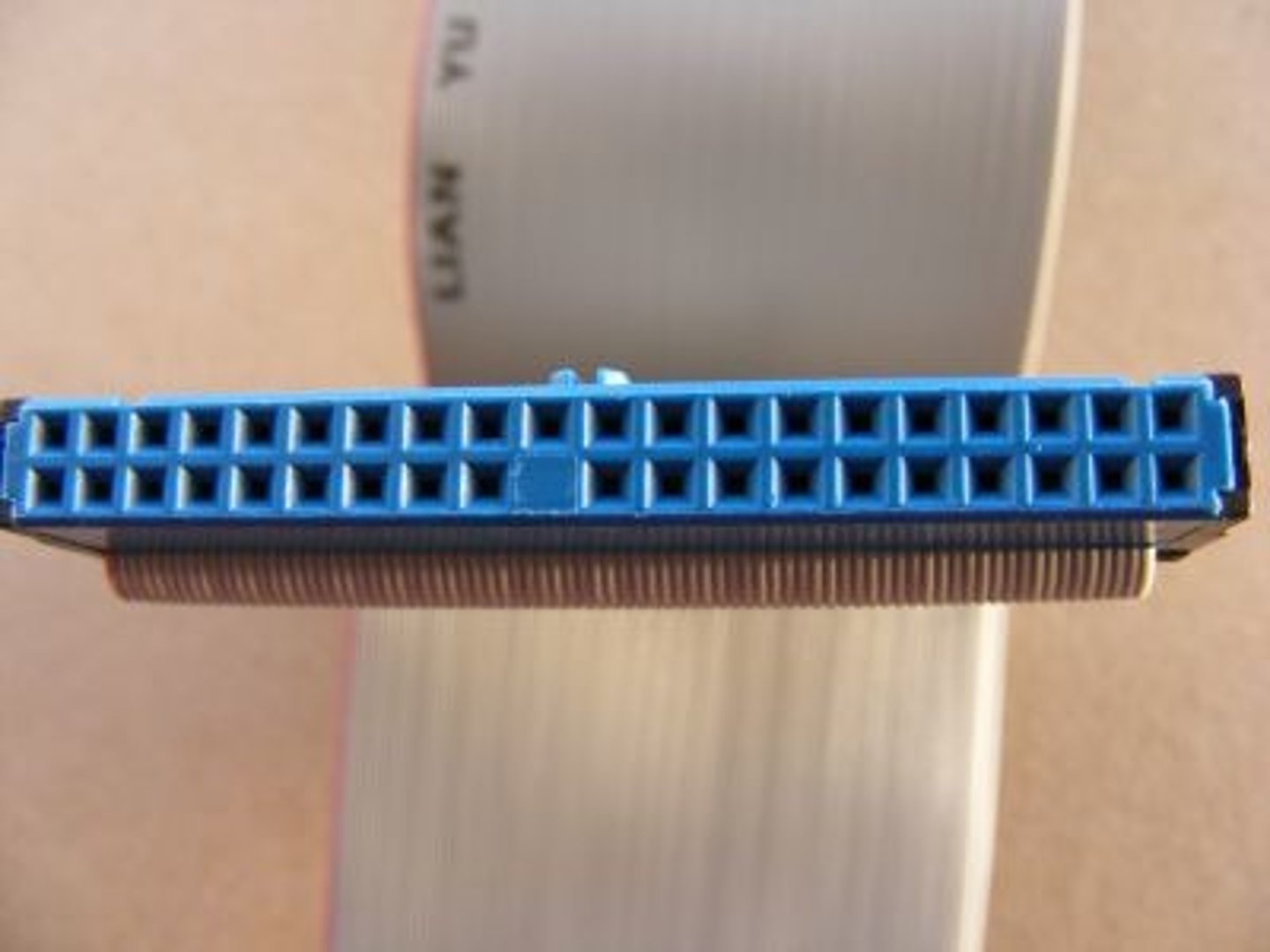
PATA System
Parallel-ATA system uses 40 pins with a maximum bandwidth of 133MB/s

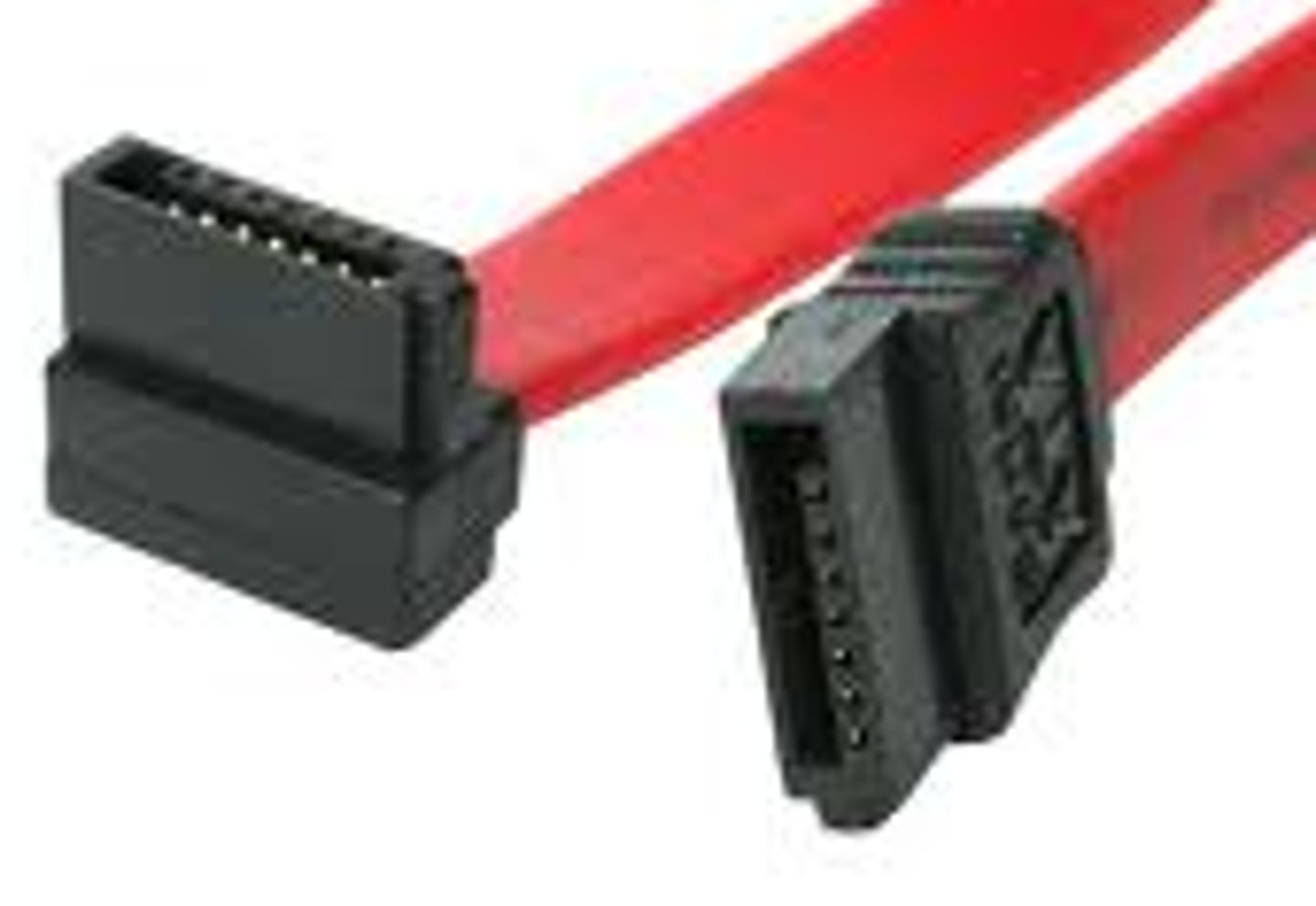
SATA System
Serial-ATA system uses 7 pins with a maximum bandwidth of 600MB/s
Of the 7 pins, 3 are just set to a ground voltage.
2 are used for sending data
2 are used for receiving data

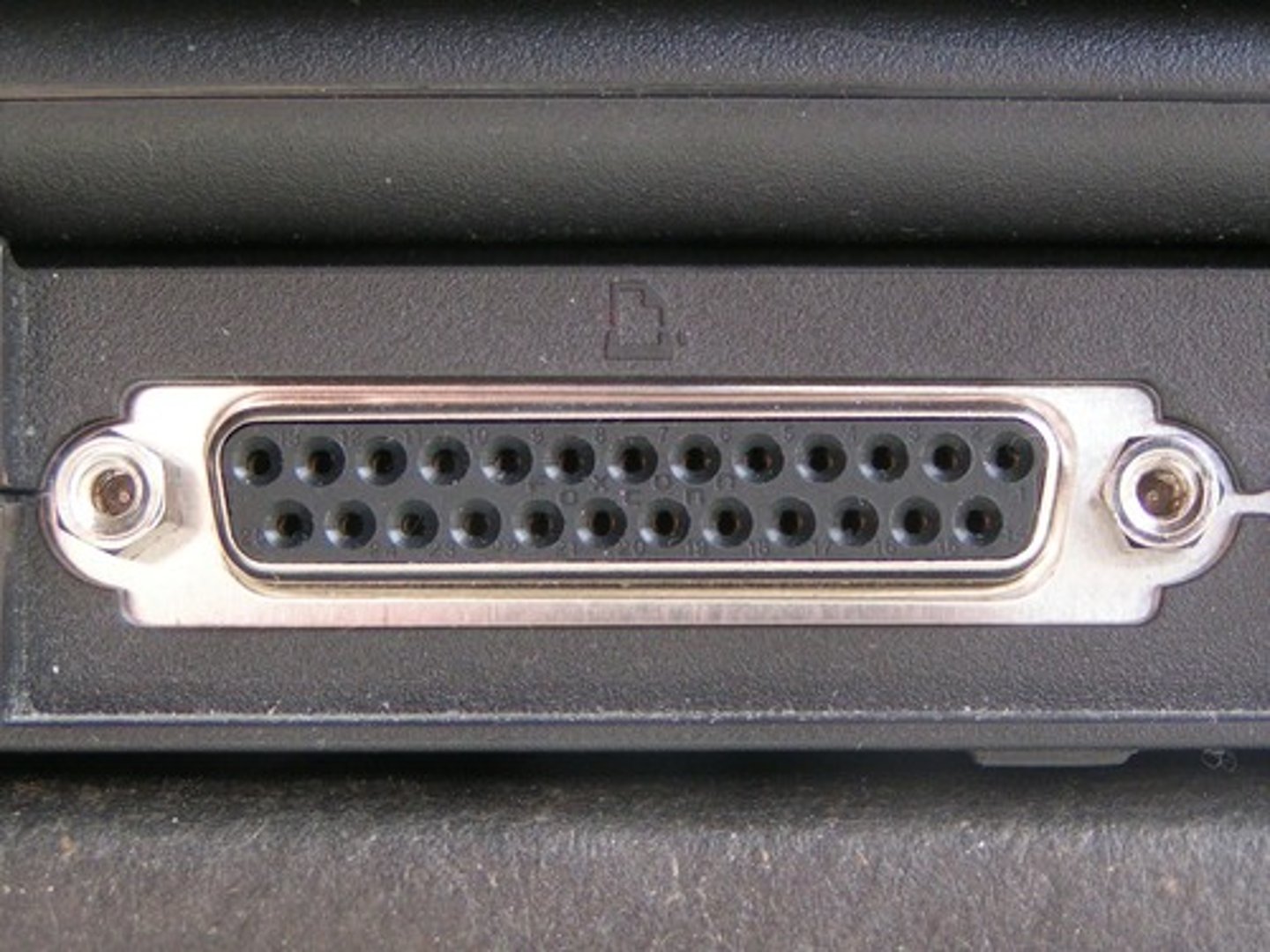
Parallel Port
Parallel Port uses 25 pins with a max bandwidth of 2.5MB/s

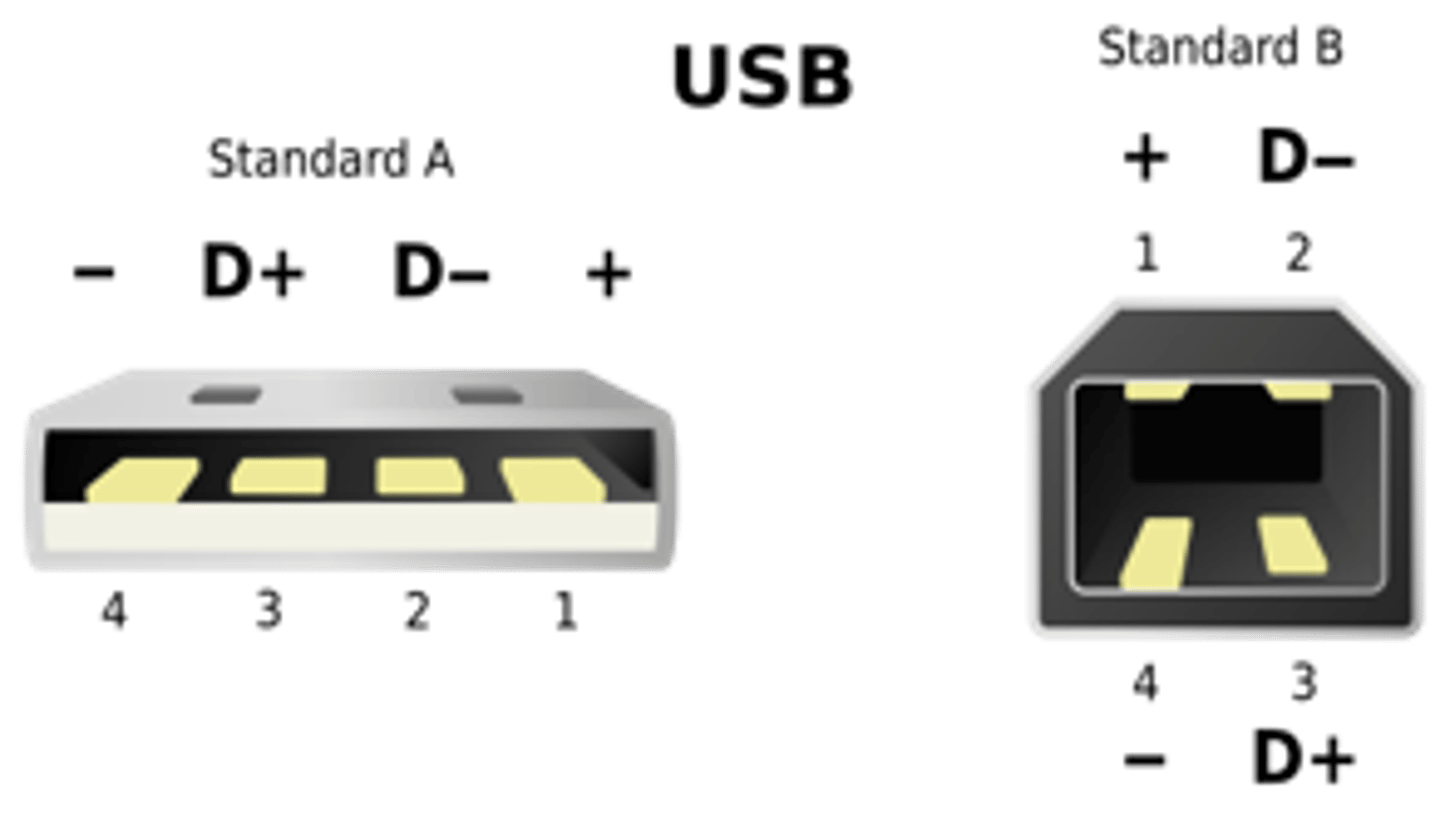
USB Cable/Port
Universal Serial Bus uses 4 pins.
Initially it had a max bandwidth of 1.5MB/s
USB 2.0 increased this to: 60MB/s
USB 3.0 goes up to: 625MB/s
USB 3.1 goes up to: 1250MB/s
USB 4.0 goes up to: 5000MB/s
Note: USB 3.0 upwards use more than 4 pins/wires
Three types of Data Transmission processes
• Simplex
• Half-Duplex
• Full-Duplex
Simplex
In simplex transmission, Data transmission is possible in one direction only
Half-Duplex
In half-dublex, Data transmission is possible in both directions, but only in one direction at a time.
Full-Duplex
Data transimission is possible in both directions simultaneously
Why transmit data digitally
• Digital transmission is preferred as it is less likely to suffer corruption / degradation / interference
• It is possible to error-check data
• Can compress data and therefore transfer time is quicker
Multiplexing
• A multiplexor allows multiple messages to be combined, so that they can be sent over a data link simultaneously, then separated again at the end of the link.
• Time division multiplexing allocates small time slices alternately for data from each of the input message streams.
• Frequency division multiplexing sends the different messages simultaneously, but using different transmission frequencies.
• On a mainframe (multi-user) computer, a multiplexor allows input to the system from different terminals, then routes system output to the correct terminal.
• On a wide-area network (e.g., the Internet), multiplexing may be used to combine messages for transmission over the very fast, high-capacity backbone of the network.
Switching
Switching prevents all data being sent to all parts of a network and makes efficient use of the data lines
Types of Switching
- Circuit Switching
- Packet Switching
Circuit Switching
Circuit switching is where a path is set up between the sender and receiver before the start of transmission and is kept open until the end of transmission.
All data follows the same path, in order. The path cannot be used by any other data.
Packet Switching
Packet switching is where the data is split into packets before transmission.
Each packet may be transmitted by different routes through network.
They may arrive out of order and are re-assembled on arrival.
In addition to the actual data, the packet will contain the order number of the packet, source and destination addresses, control signals etc
What does each packet carries?
Each packet carries
• the actual data
• the order number of the packet
• source and destination addresses
• control signals
• error control bits
Why is packet switching preferable?
Packet switching is preferred because:
• It results in better security as it is very difficult to intercept and reconstruct the packets.
• Packet switching also promotes the more efficient use of data lines as there is no waiting during gaps.
• It is also less likely to be affected by network failure because multiple paths are used.
A Switch (Hardware)
• A switch is used to connect computers in a local area network.
• The switch is programmed and maintains a table with the IP addresses and machine addresses of connected devices, so it can send data to the required device.
• When a packet of data is received by the switch, it is checked to determine the destination address.
A Router (Hardware)
• A router is used to forward data packets between networks.
• Routers control traffic on wide area networks such as the Internet.
• The router determines the destination of a data packet from the IP address in the packet protocol, then selects an appropriate route for onwards transmission.
• Routers may hold information about current transmission speeds to adjacent nodes, so that the fastest path for onward transmission can be selected.
A modem
A modem connects a computer to a telephone line or cable
Network Protocols
Network protocols are necessary to enable devices to communicate with each other.
The protocol will specify the format in which the data is transmitted.
eg: using ftp / http / smtp / voip / pop3 to transfer data between devices
Data Collision
Data collision occurs when two sets of data are detected on the network simultaneously
The network detects the error.
Each computer waits for a short / random time, then sends the data again
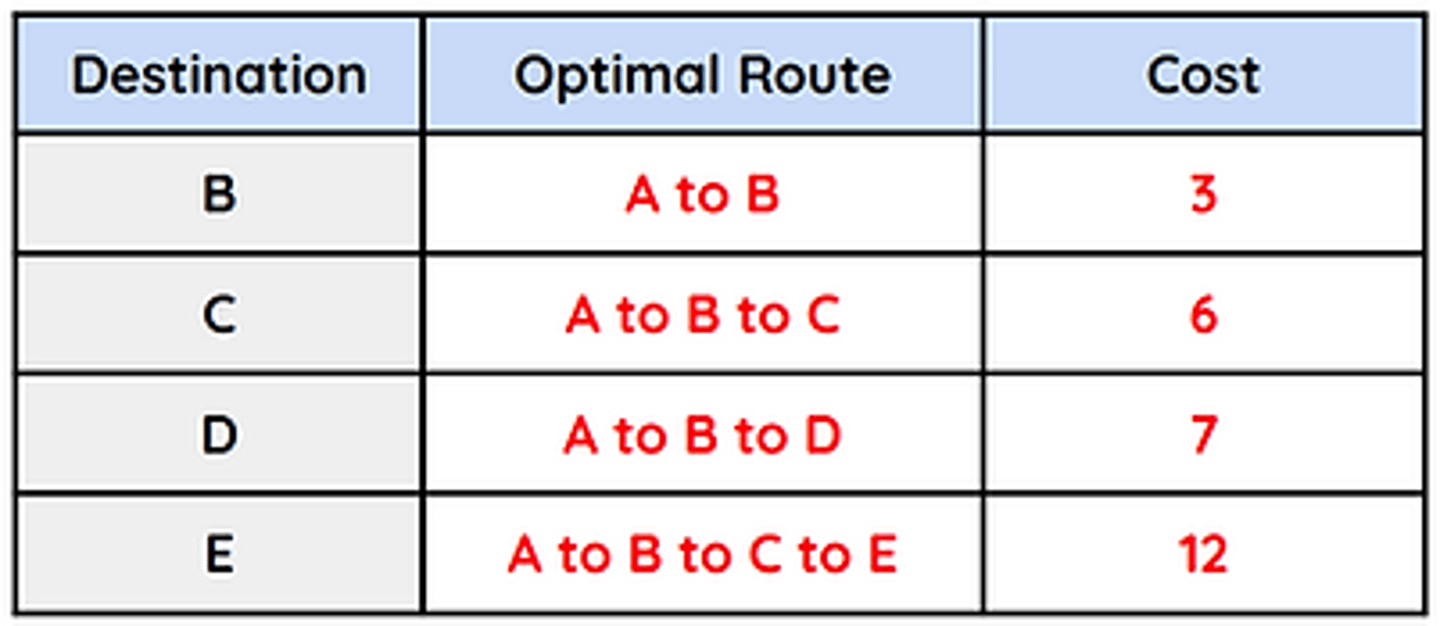
Routing Costs
In order to make the best use of network resources, the path chosen when routing needs to consider the lowest cost route.
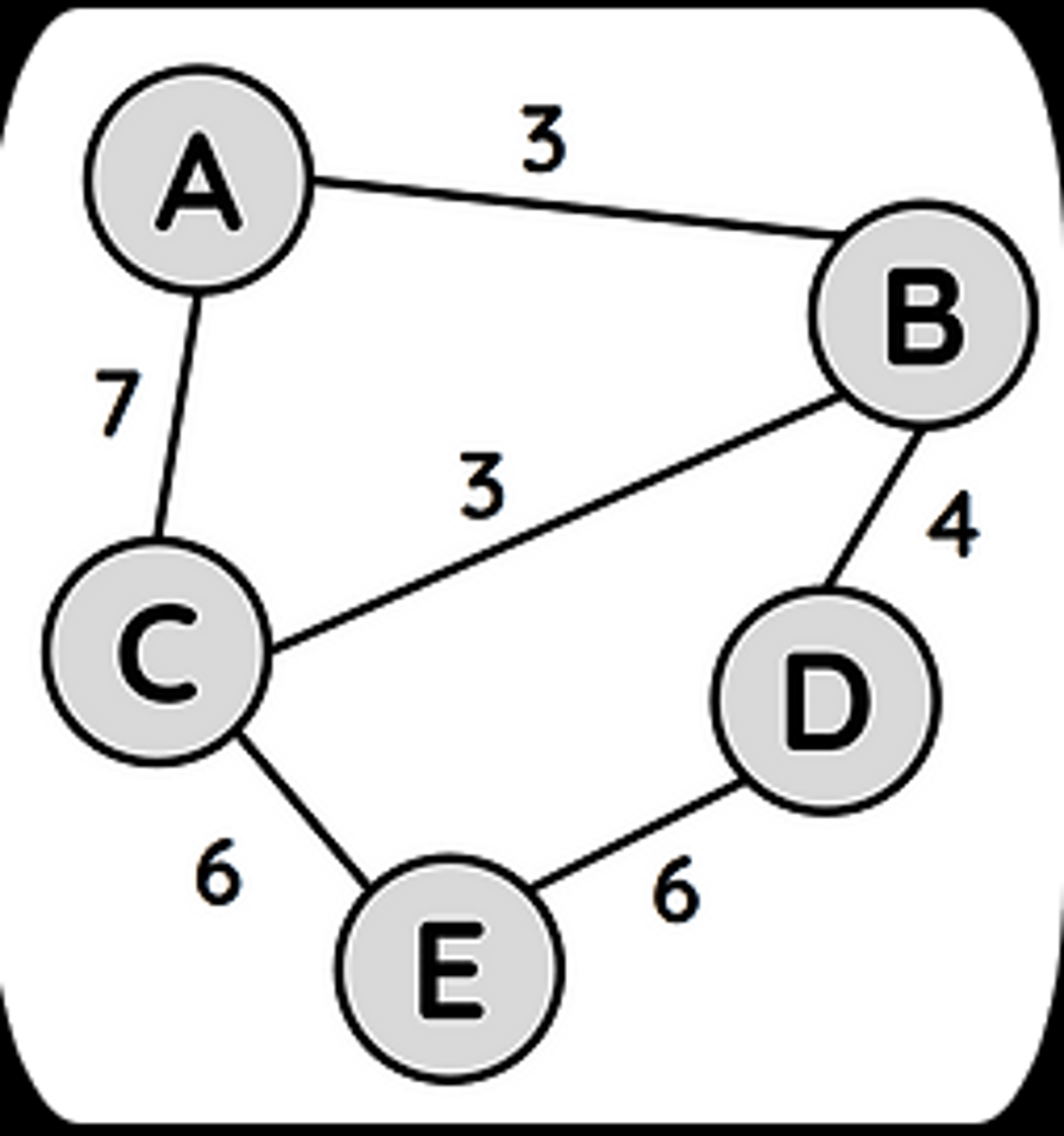
Routing Table
Network devices make use of a routing table to keep track of the lowest cost routes between key points.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is not a measure of speed, but a measure of how much data can be fitted onto a cable at any point in time.
Bitrate
Bitrate is the amount of data per second that changes with a faster connection, but the data still travels at the speed of the electrical signals in the cable.
Bandwidth is frequently known as bitrate.
Examples:
A 1Mbit/s connection means that every second, 1Mb can be passed down the cable.
A 10Mbit/s connection sounds like it is ten times faster but the data actually travels at the same speed.
The Internet
The internet is a world-wide communications infrastructure of interconnected packet-switched networks.
These networks use the standard internet protocol, TCP/IP, and are linked together using wired, wireless and fibre-optic technologies.
They consist of a number of specialist hardware components, such as routers, gateways, bridges and switches, and a system of software layers.
The internet provides the infrastructure to access a range of information resources and services via the World Wide Web.
The World Wide Web is not the Internet - it is a feature of it.