Plate Tectonics
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Plate Tectonics Theory
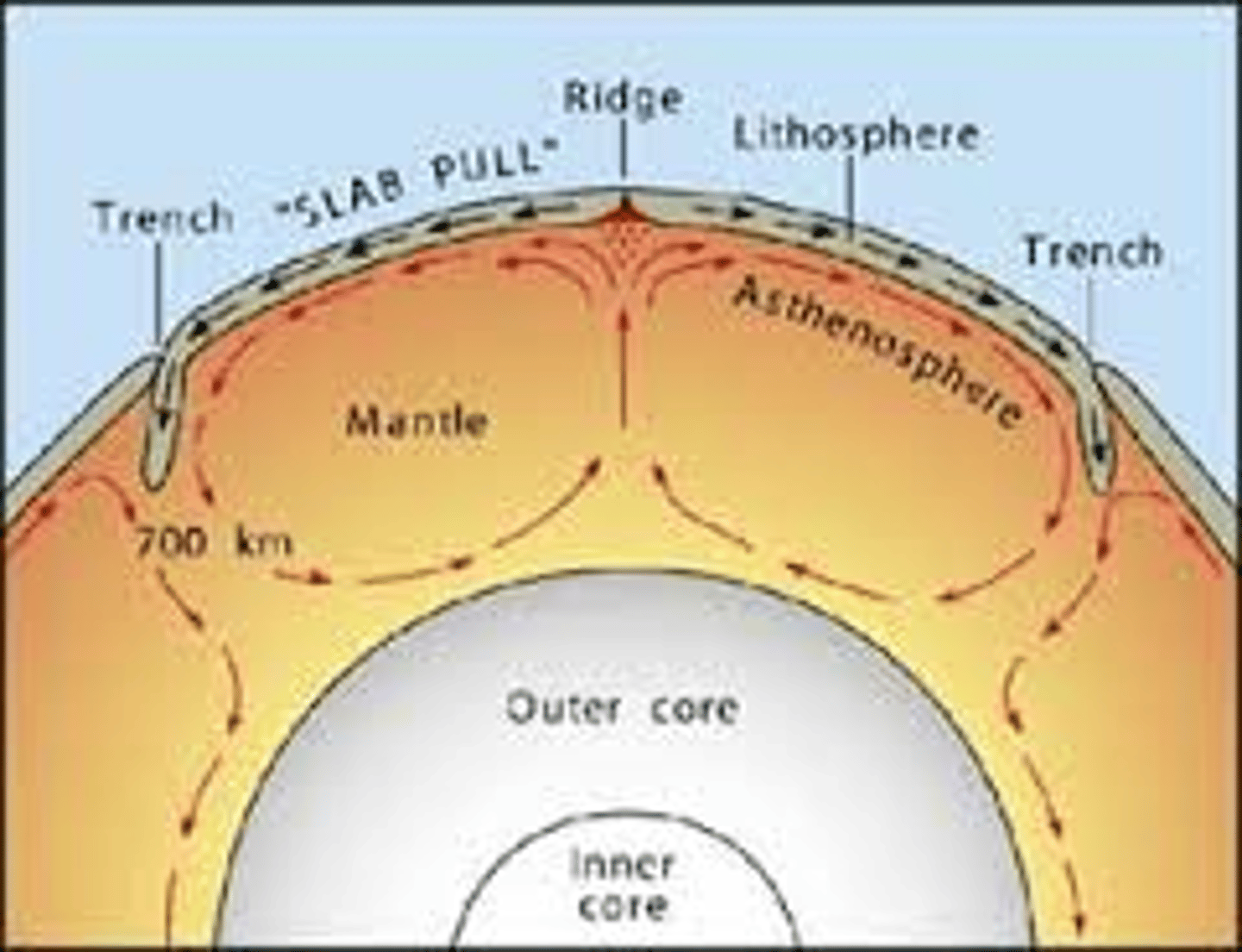
The theory that the earth is broken into plates and are in motion due to convection currents in the asthenosphere (upper mantle)
Alfred Wegener
The man who proposed the continental drift theory in the 1900s

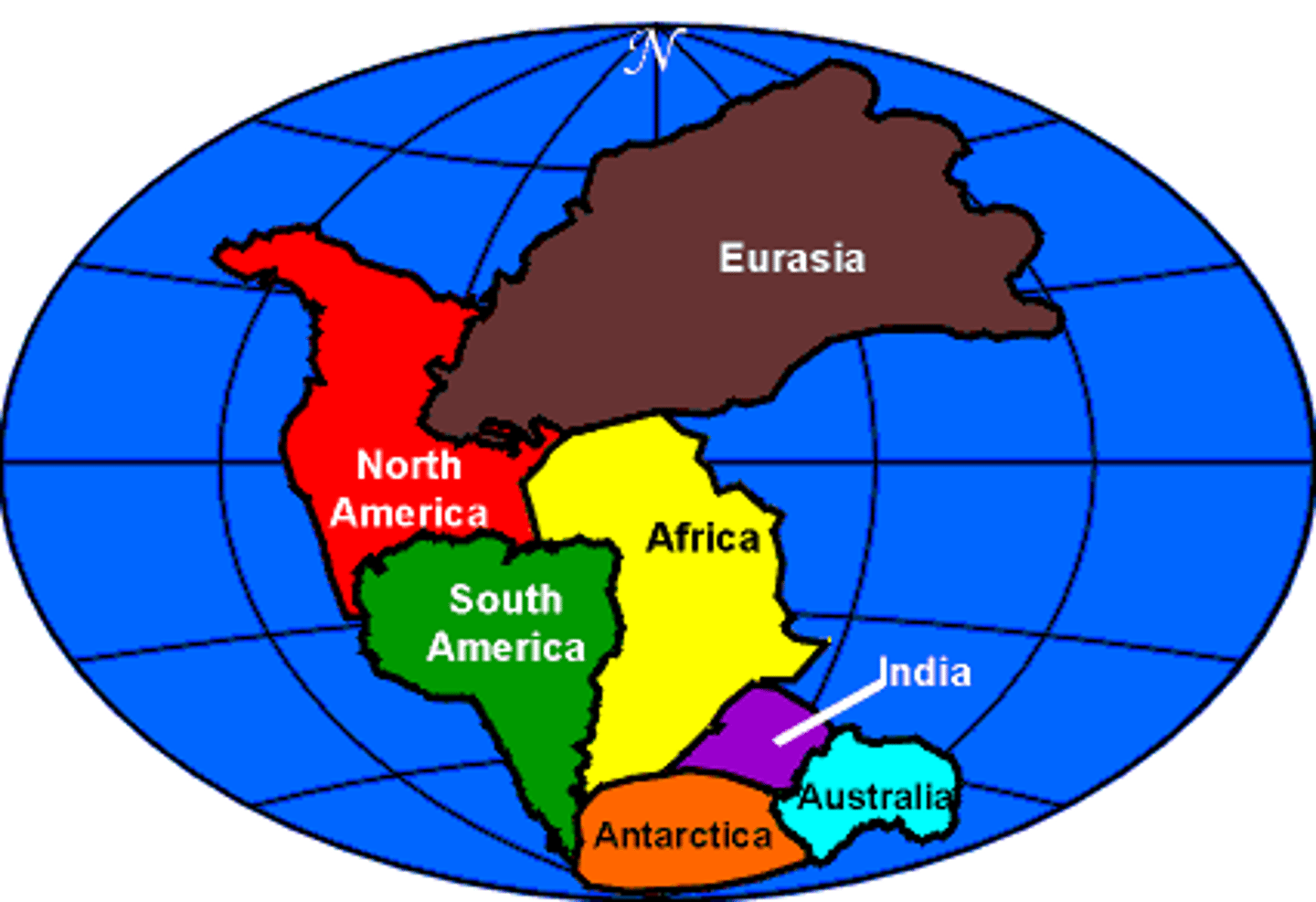
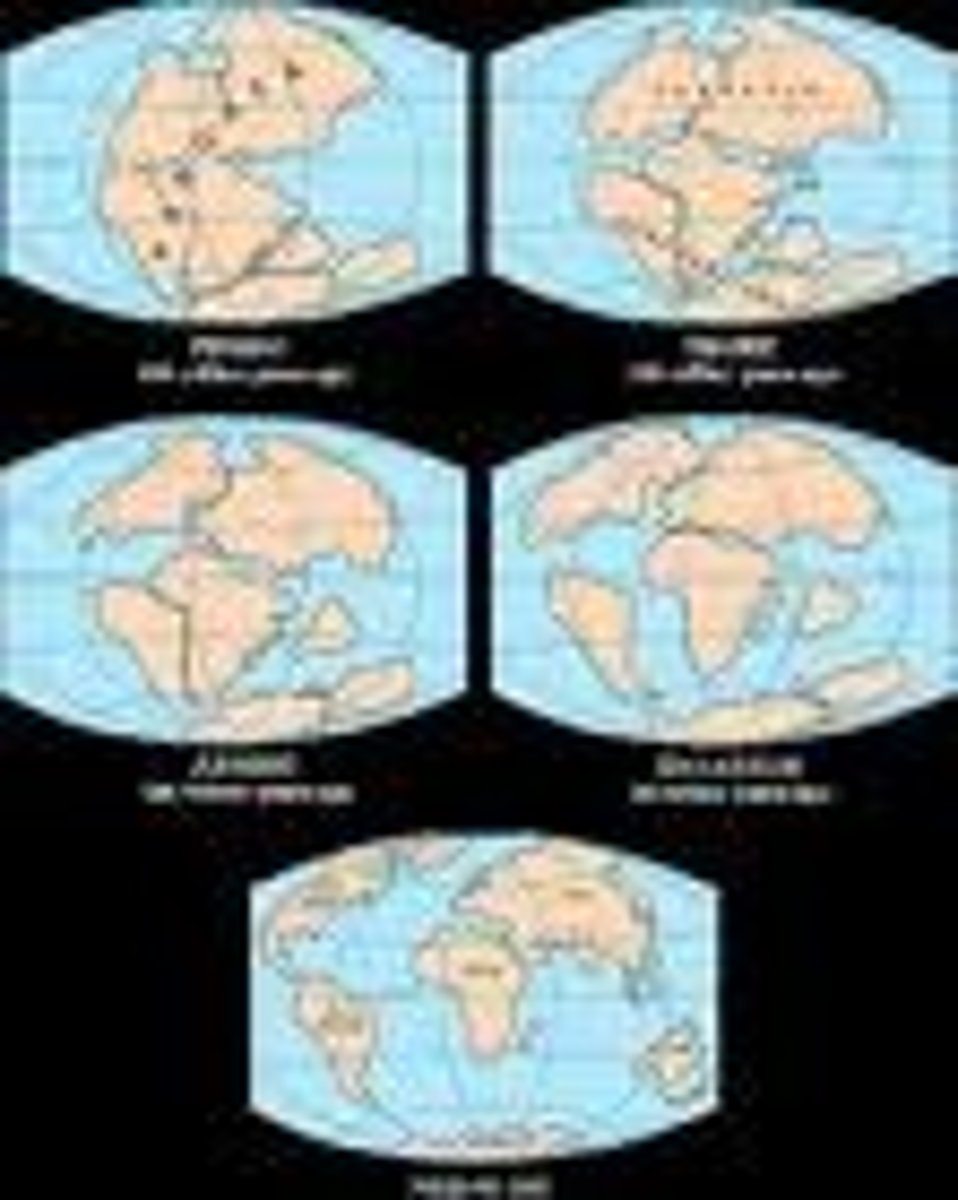
Pangea
The name for the super continent which contained all the continental plates together
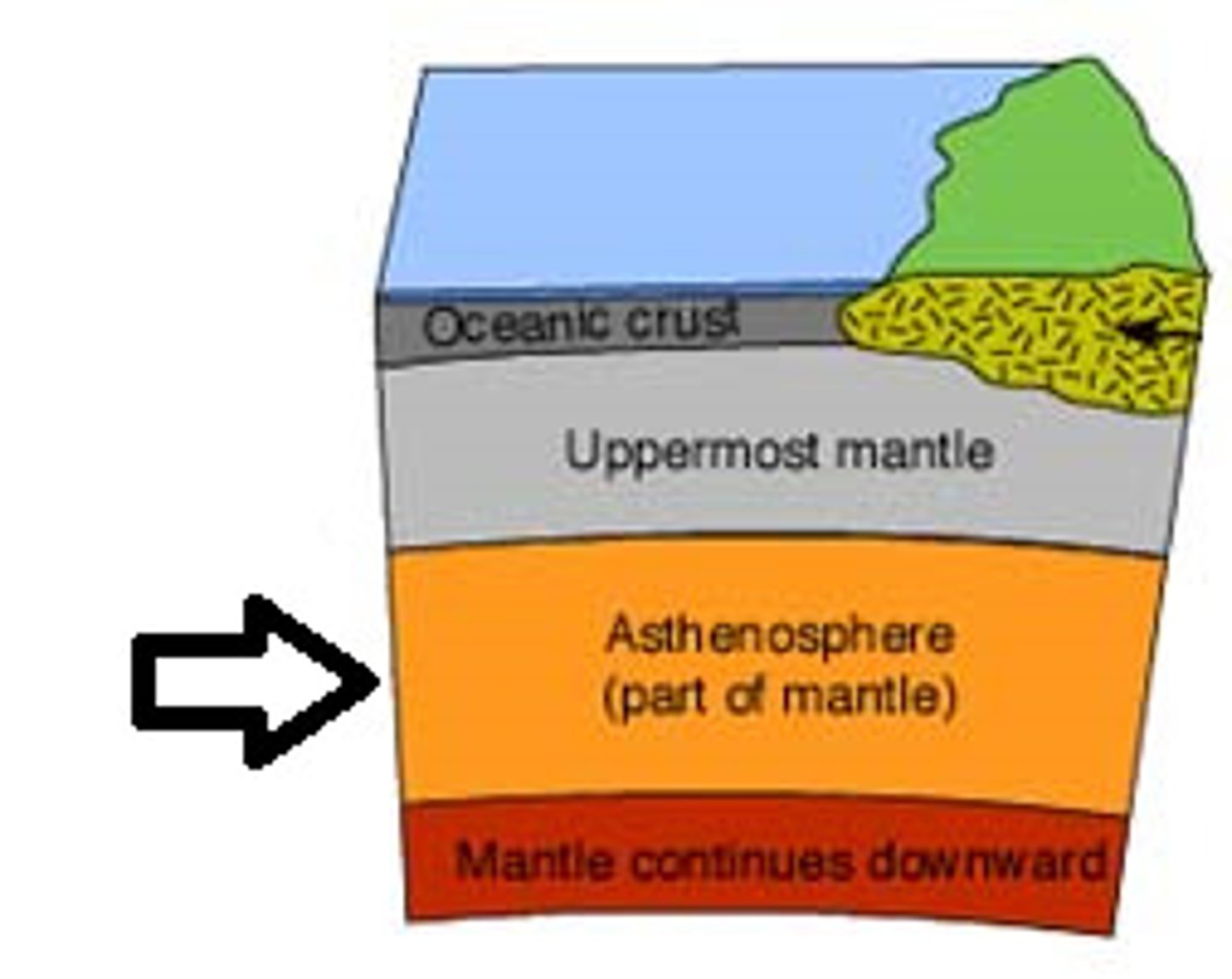
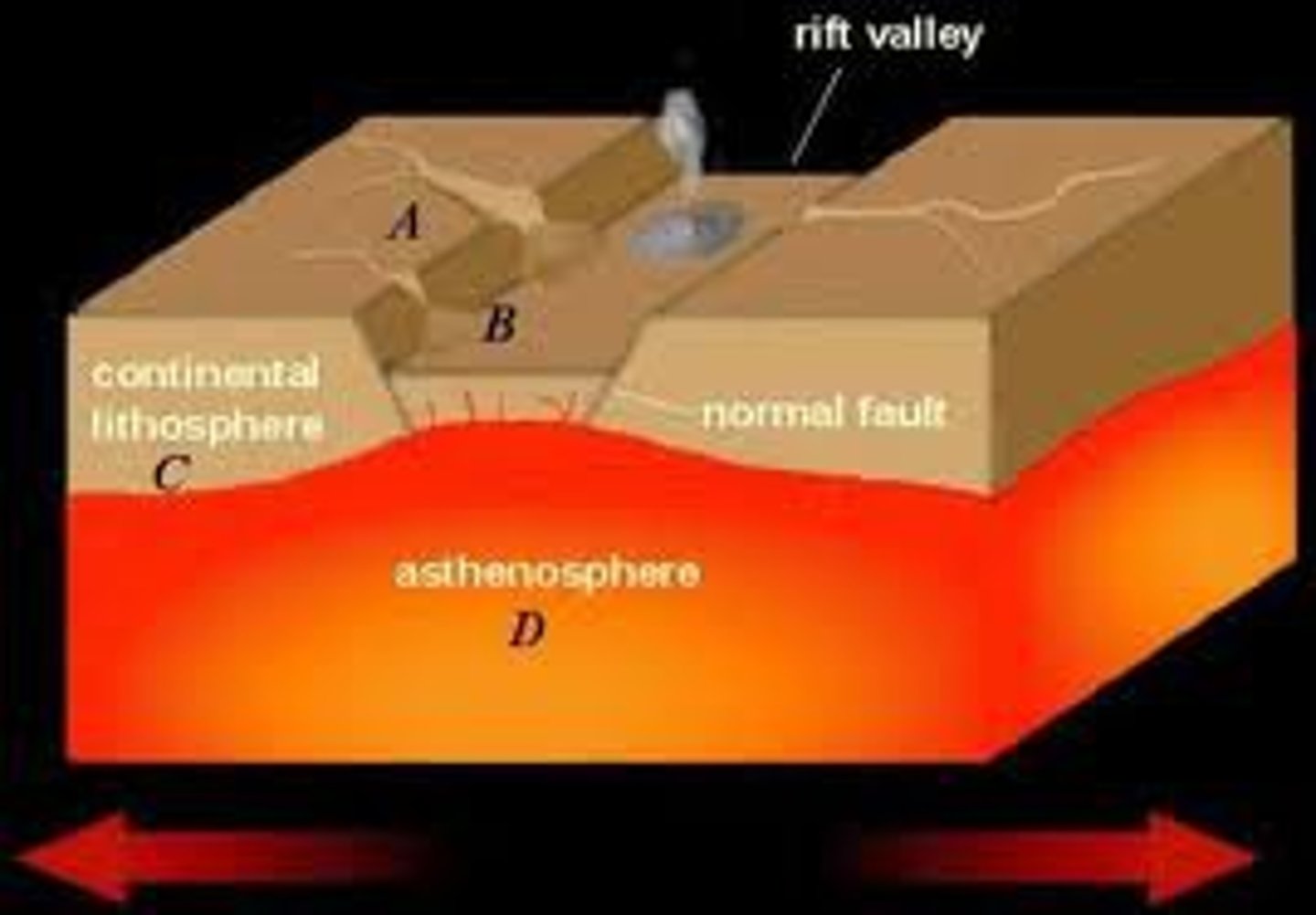
Lithosphere
The thin and solid outermost layer of the Earth above the mantle
Asthenosphere
The soft layer of the mantle on which the tectonic plates move
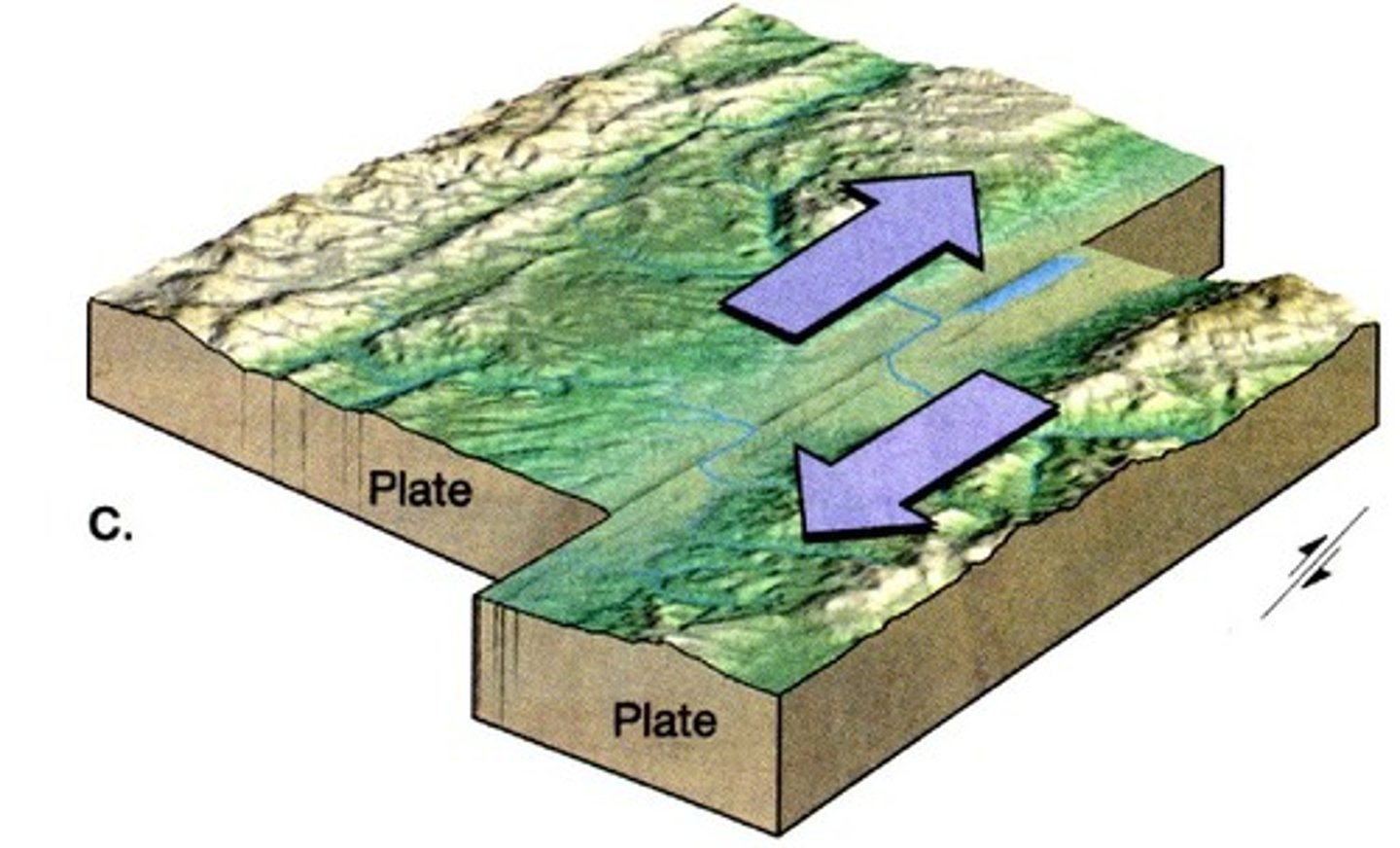
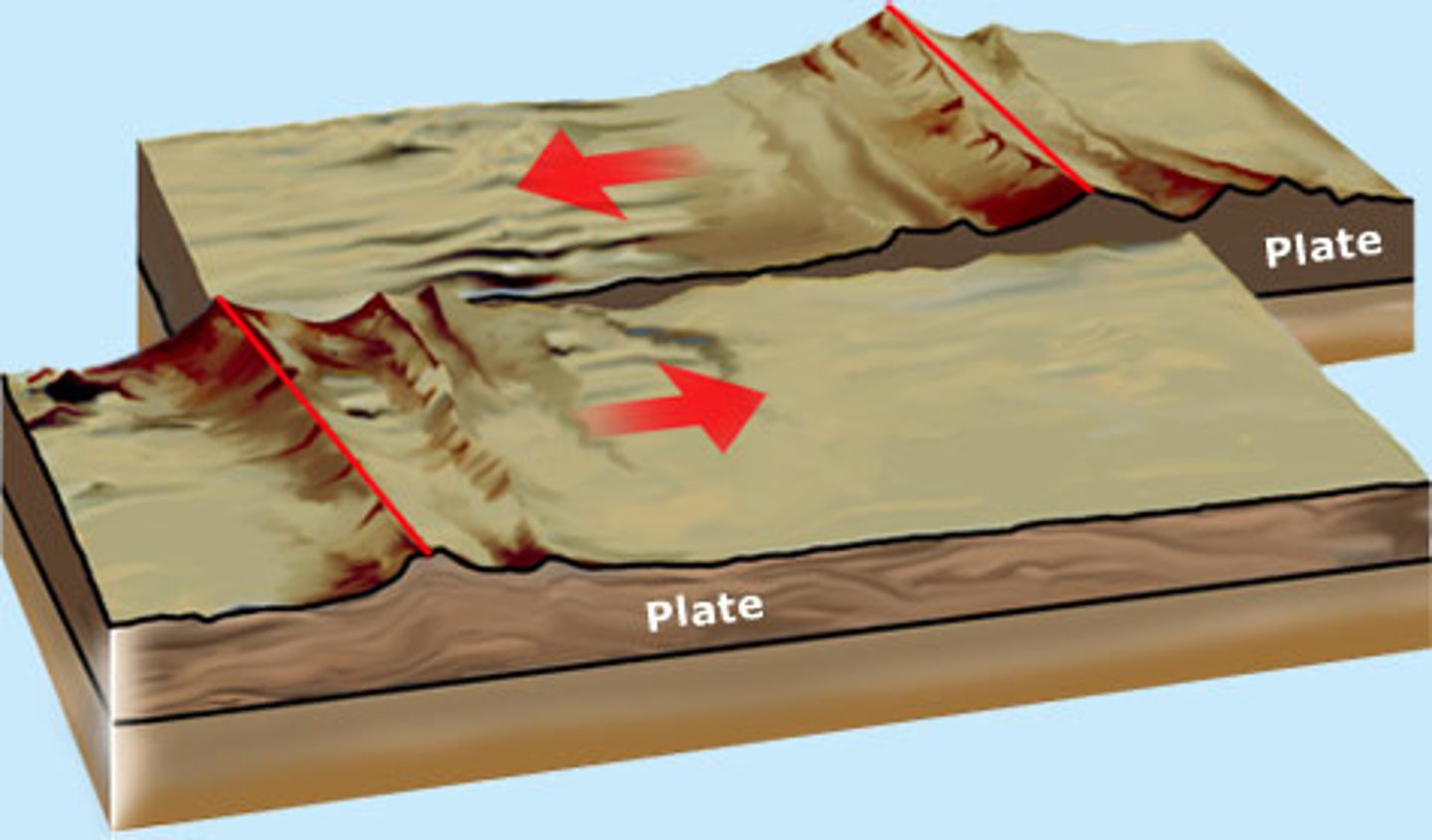
Transform Boundary
The boundary between tectonic plates that are sliding past each other horizontally
Continental Drift
The hypothesis that states that the continents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and drifted to their present locations
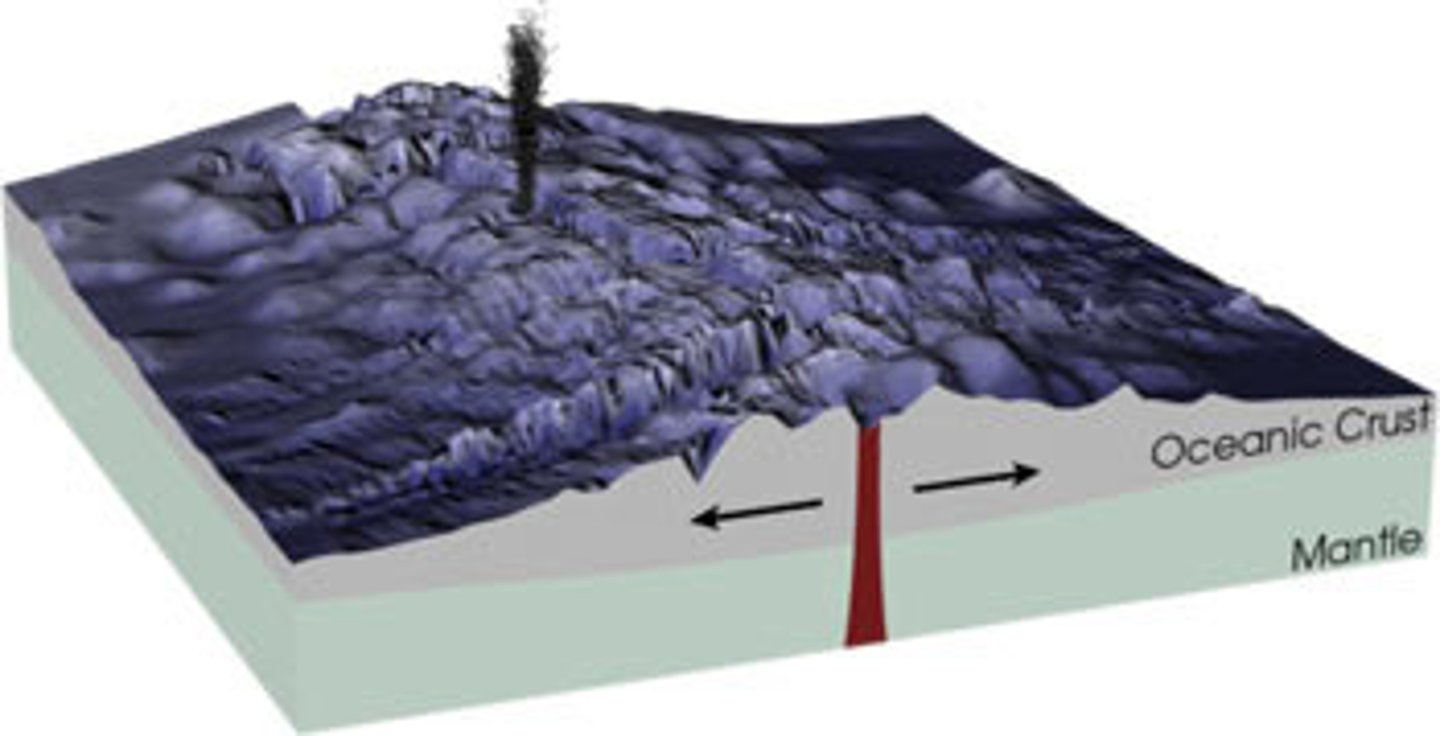
Sea-floor spreading
The process by which new oceanic crust forms as magma rises towards the surface and solidifies
Convergent Boundary
The boundary formed by the collision of two plates moving towards each other
Divergent Boundary
The boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other
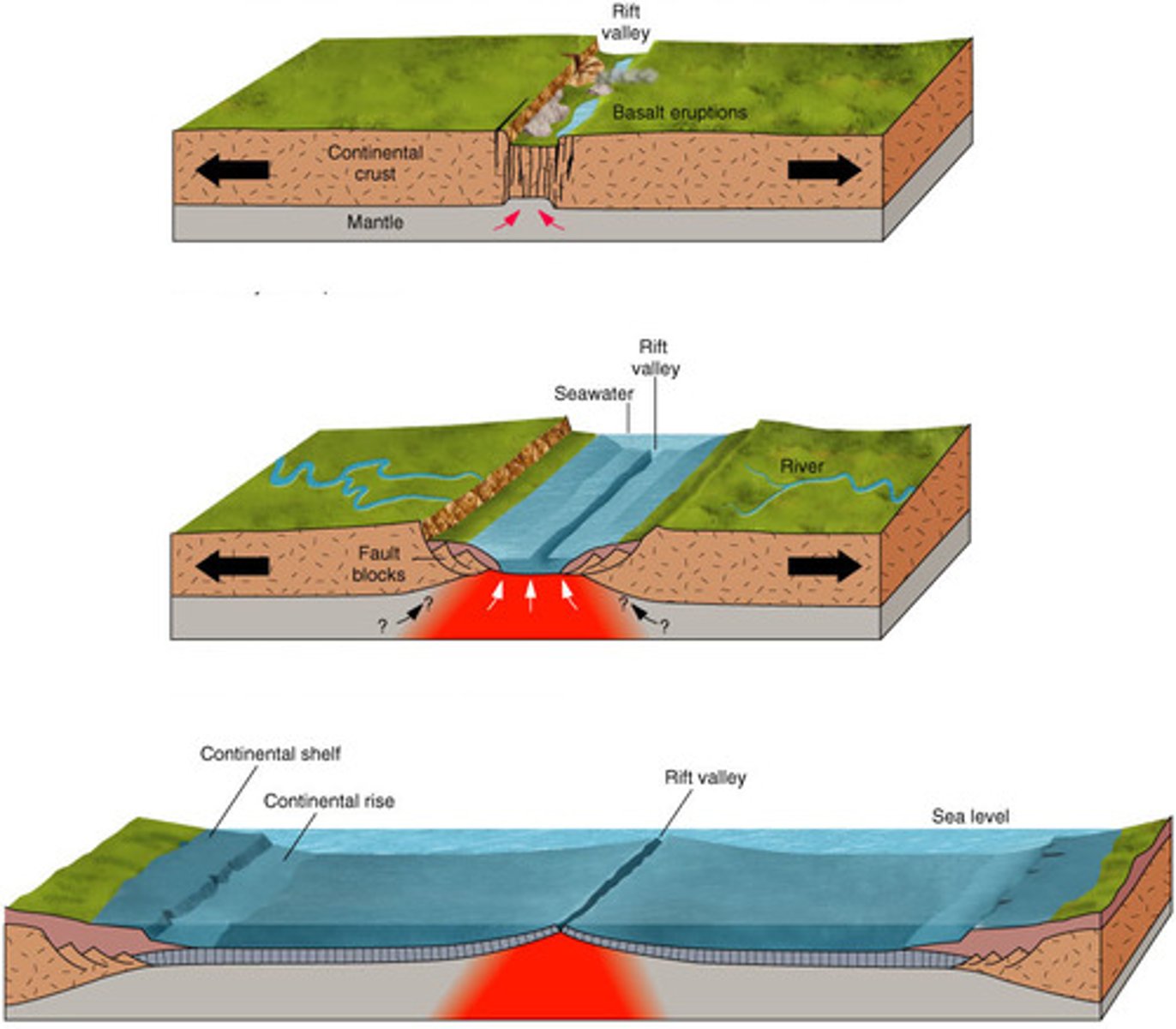
Rift valley
A long, narrow depression formed at divergent boundaries on land
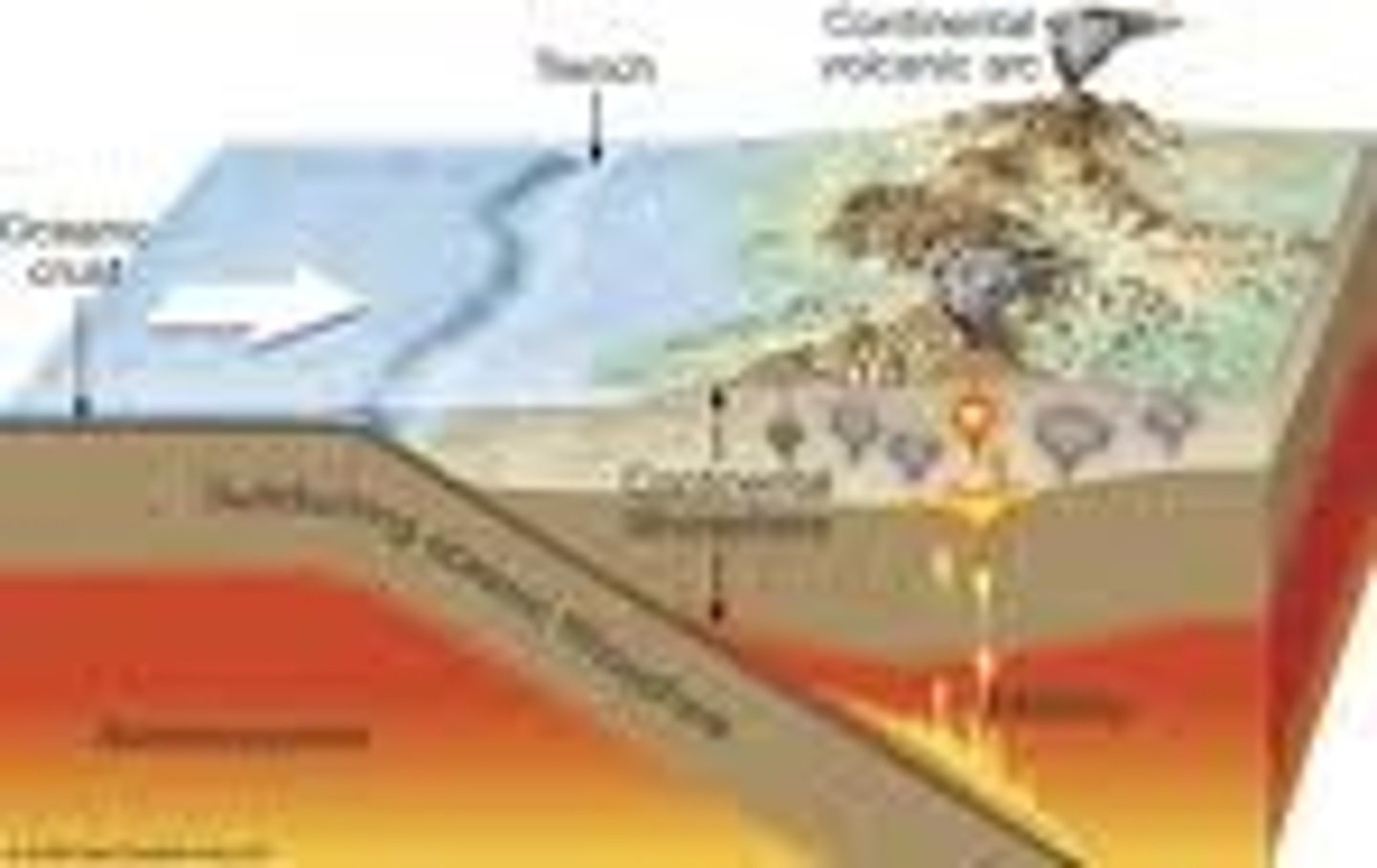
Subduction
Process in which two plates collide and the denser ocean plate sinks below the other

Convection current
This flow of material in a fluid caused by movement of heat, and is believed to drive motion of the plates
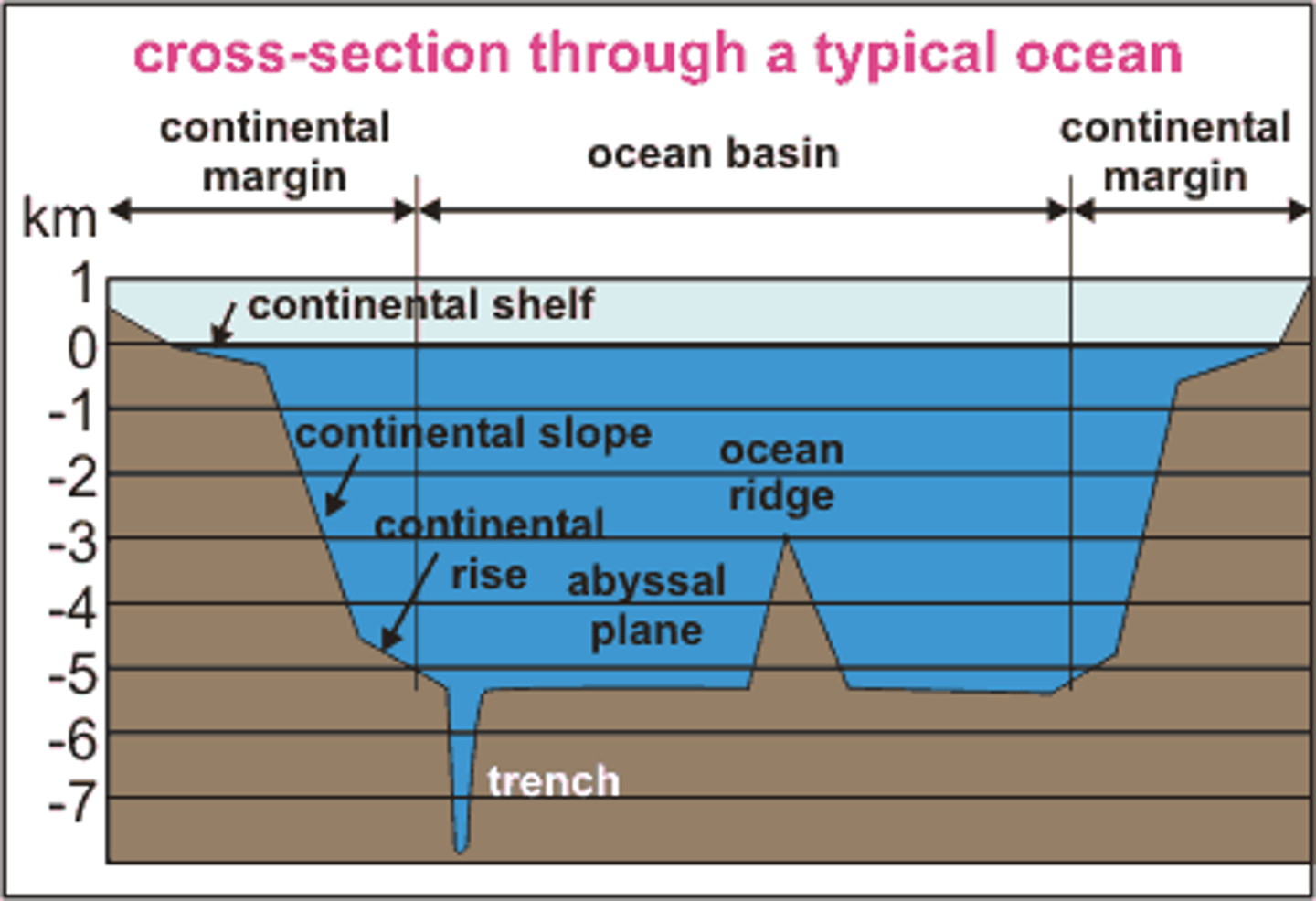
Trench
Extremely deep areas in the ocean that are created by a subducting plate
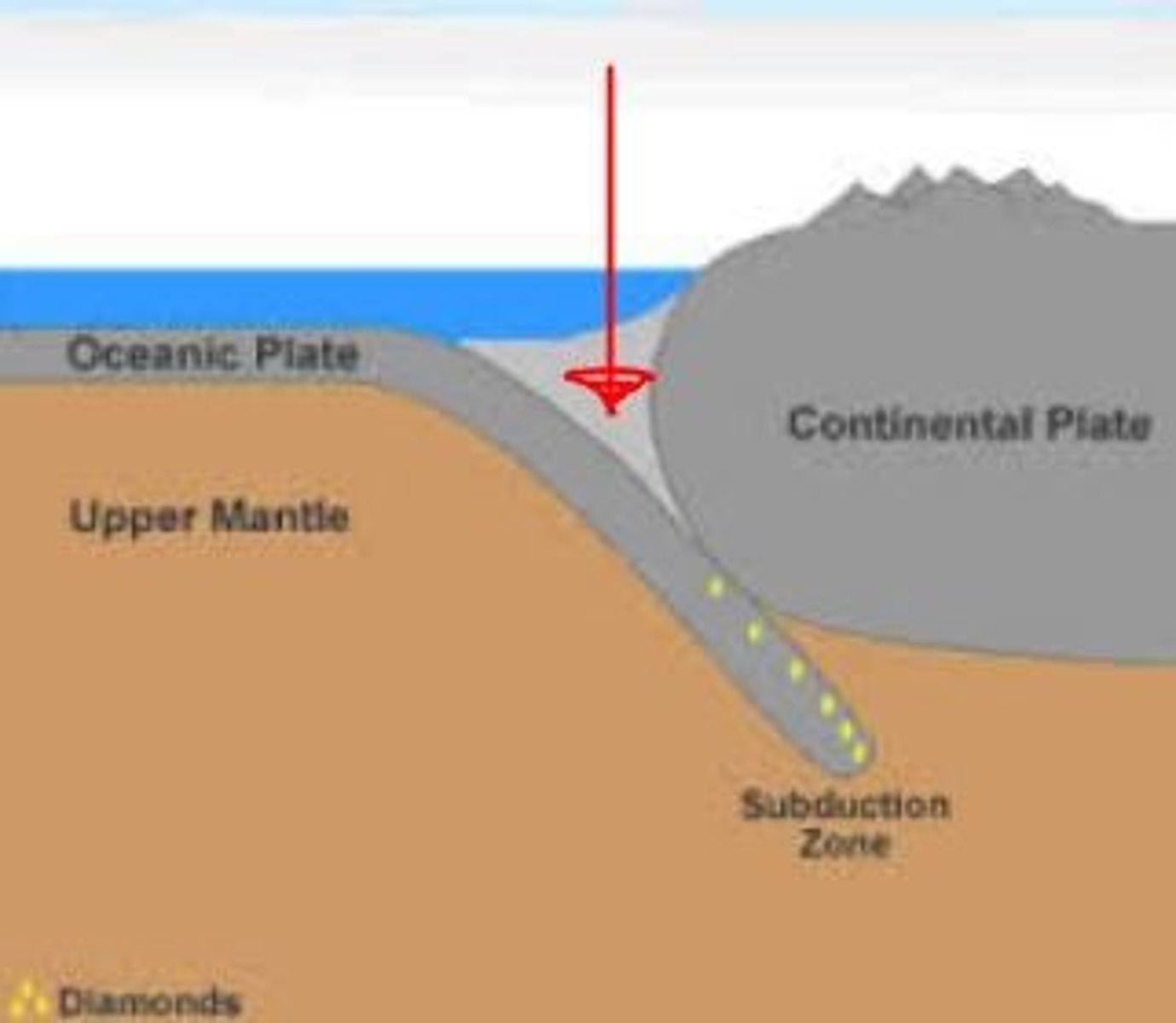
Ocean basin
Areas that are below sea level and typically filled with deep water
Dormant volcano
Inactive or "sleeping" volcano that is not erupting

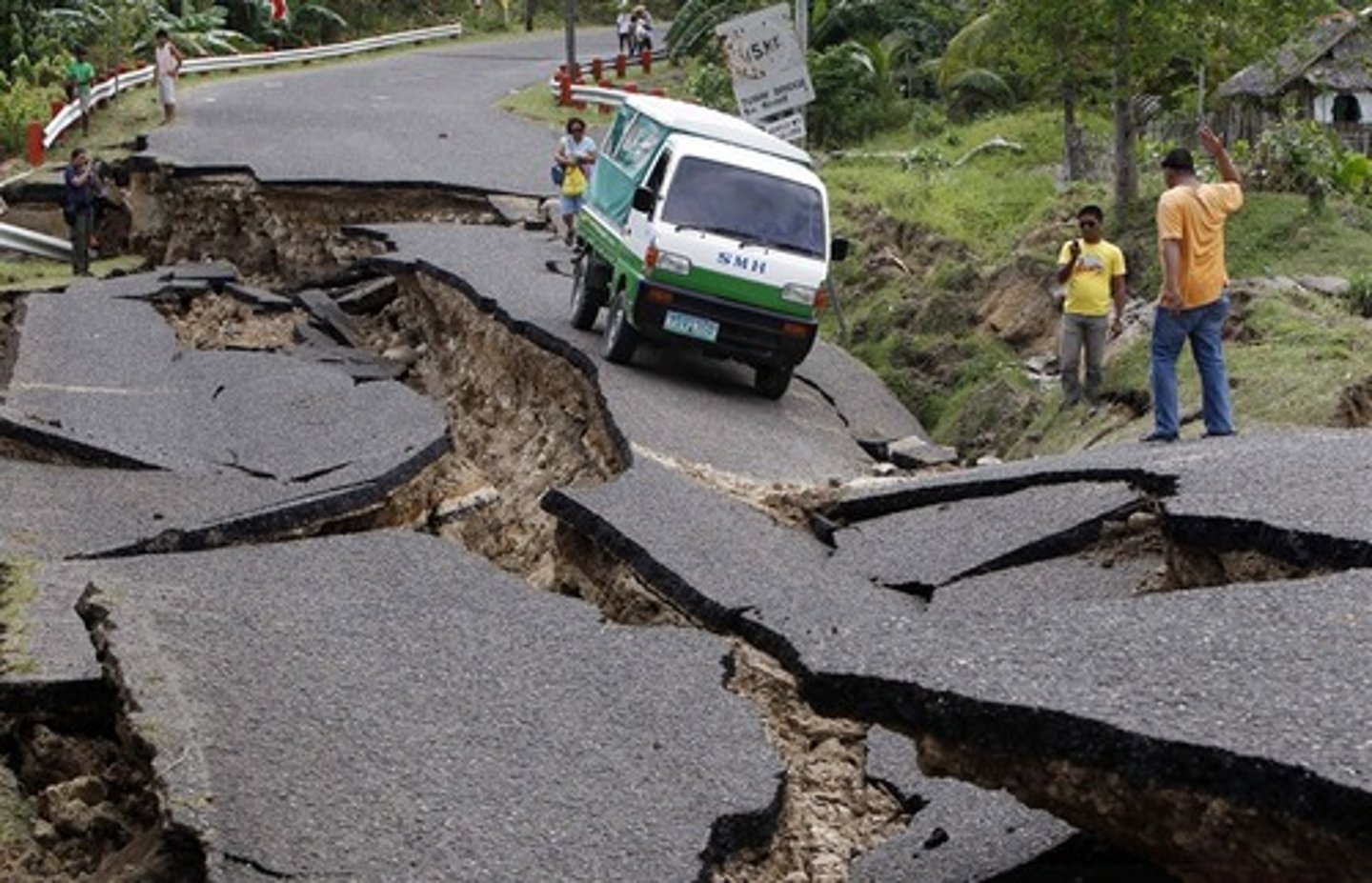
Earthquake
A shaking or sliding of the ground. It is caused by the sudden movement of masses of rock along a fault or by changes in the size and shape of masses of rock far beneath the earth's surface.

Magma
Molten rock beneath the earth's surface
Convergent
Continental - Continental
Features: mountain ranges, mountains
Example: Himalayas
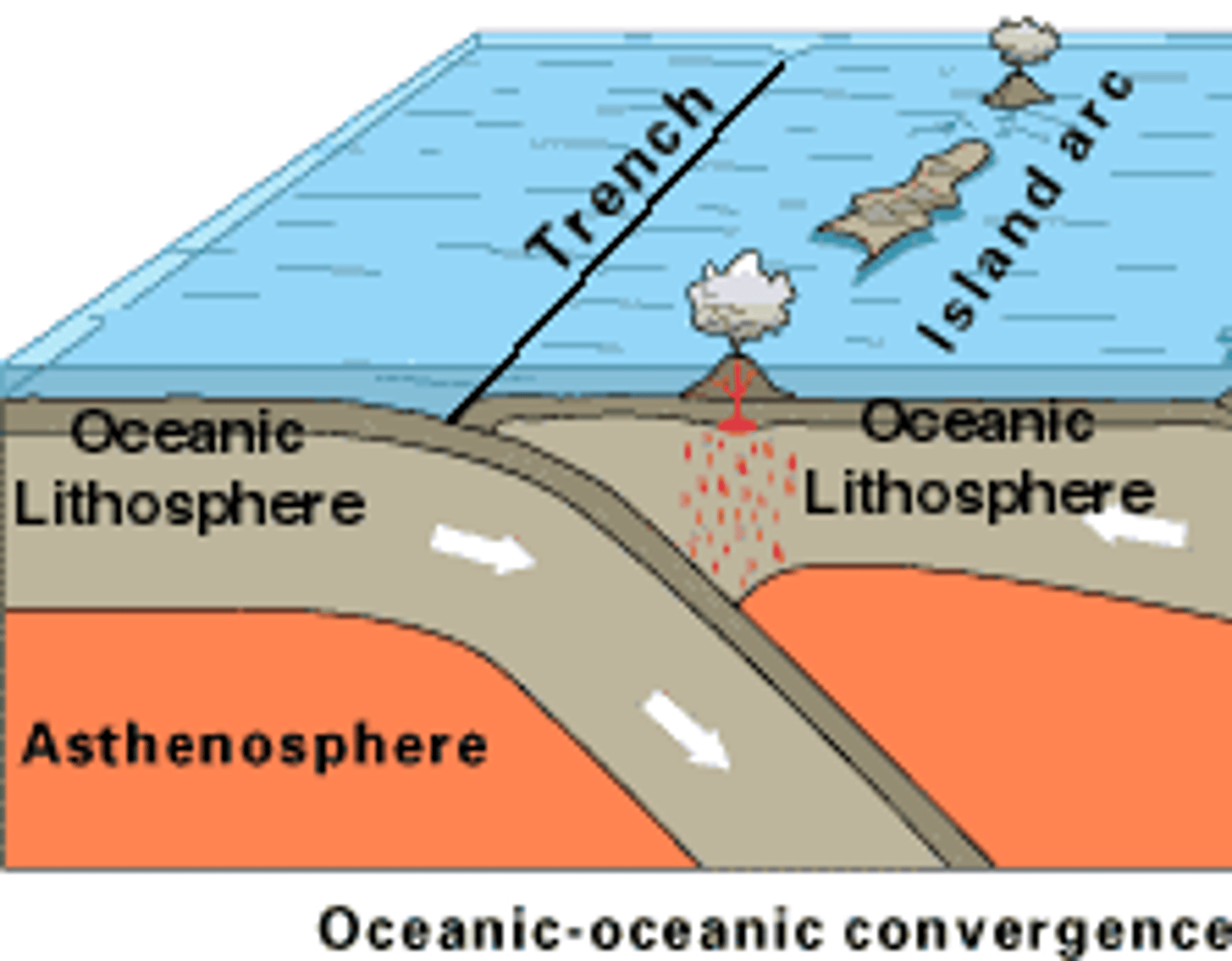
Convergent
Oceanic - Oceanic
Features: Trenches, volcanoes, volcanic islands
Examples: Japanese Islands, Ring of Fire
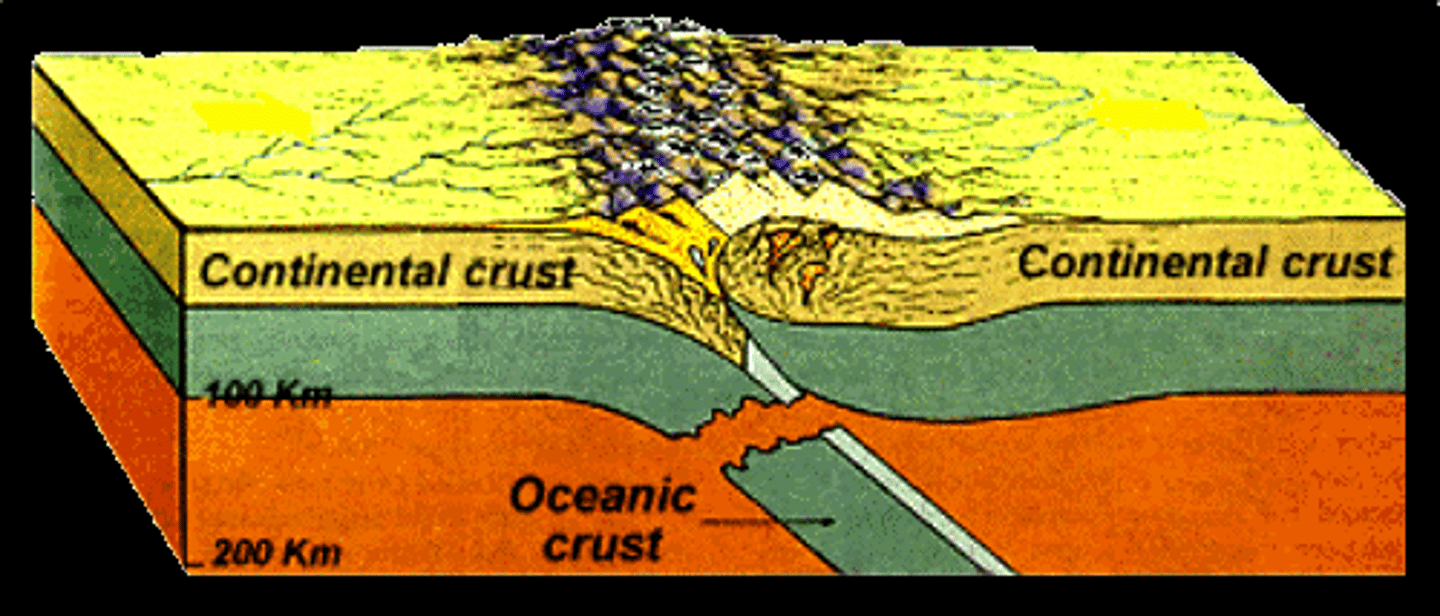
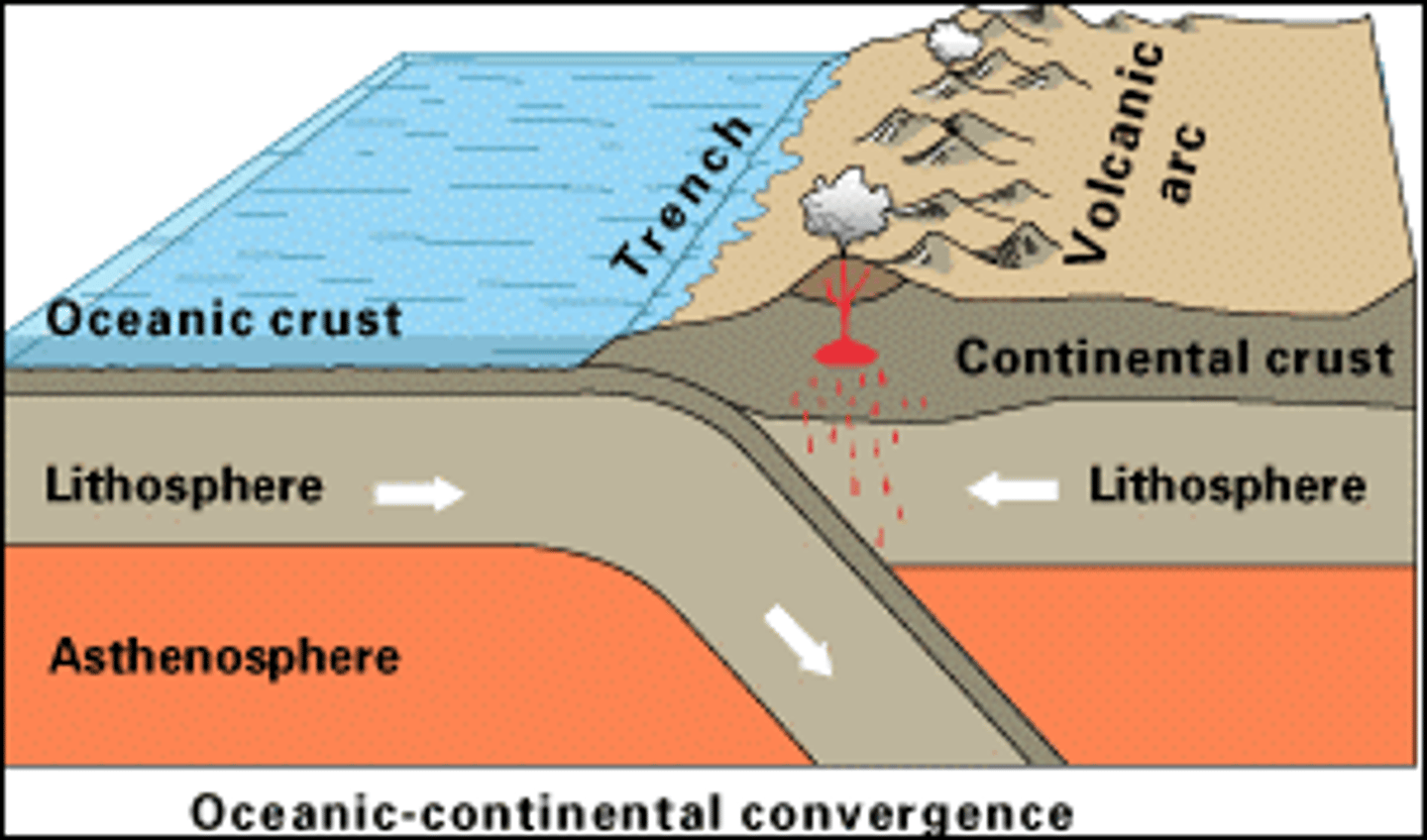
Convergent
Oceanic - Continental
Features: Volcanic Mountain Range on the coast, Trenches
Example: Andes Mountains
Volcano
A mountain or hill, typically cone-shaped, having a crater or vent through which lava, rock fragments, hot vapor, and gas erupted from the earth's crust.
Tectonic Plate
A block of lithosphere that consists of the crust and the rigid, outermost part of the mantle. It moves over time due to convection in the asthenosphere.
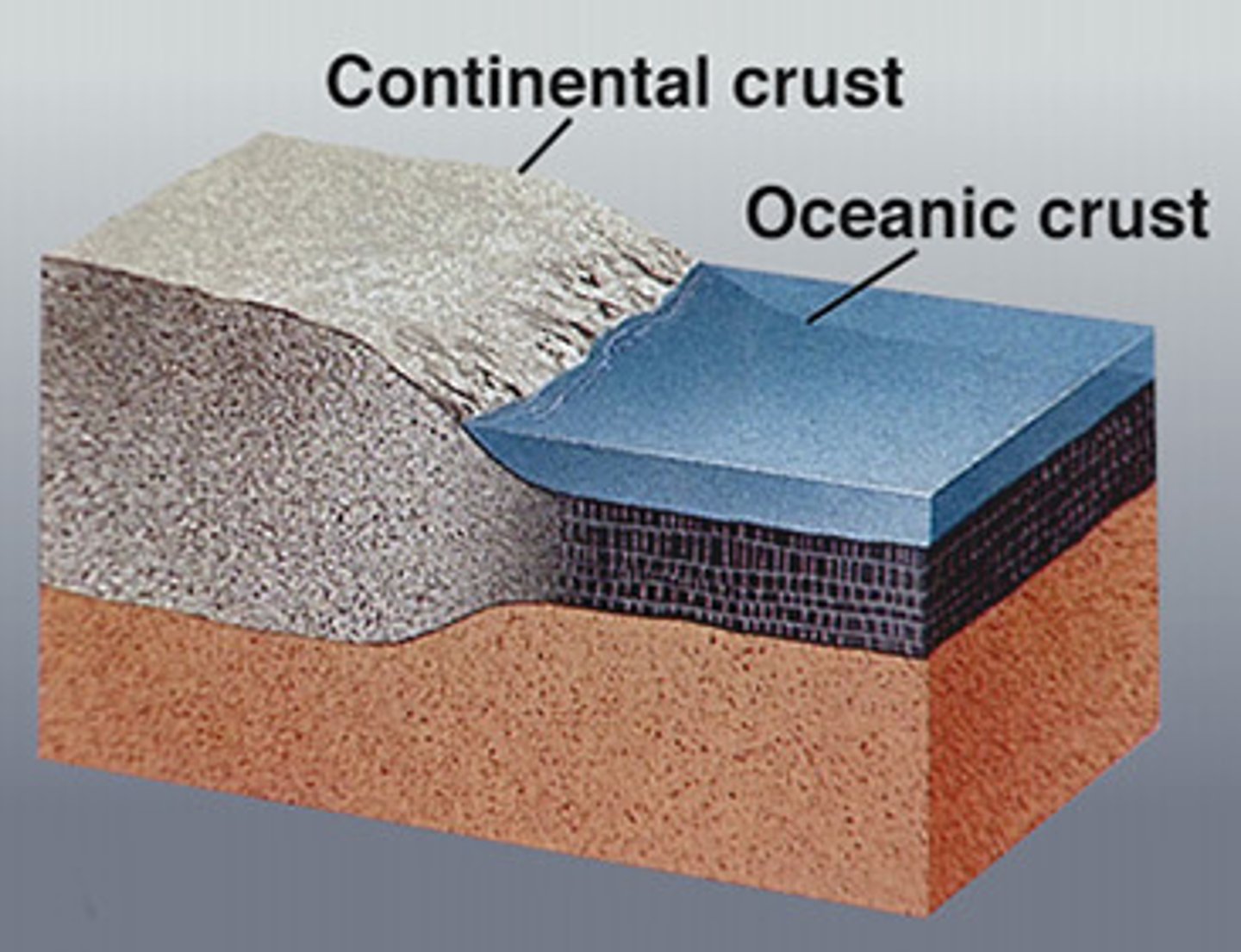
Oceanic Plate/Crust
Thin plates that form the ocean floor; more dense than continental plates.
Continental Plate/Crust
Thick plates that form the continents; less dense than oceanic plates
Tsunami
A giant wave usually caused by an earthquake beneath the ocean floor.
Hot Spot
An area far from a plate boundary where superheated magma from deep within the mantle melts through the crust above it. Ex: Hawaii, Yellowstone Supervolcano
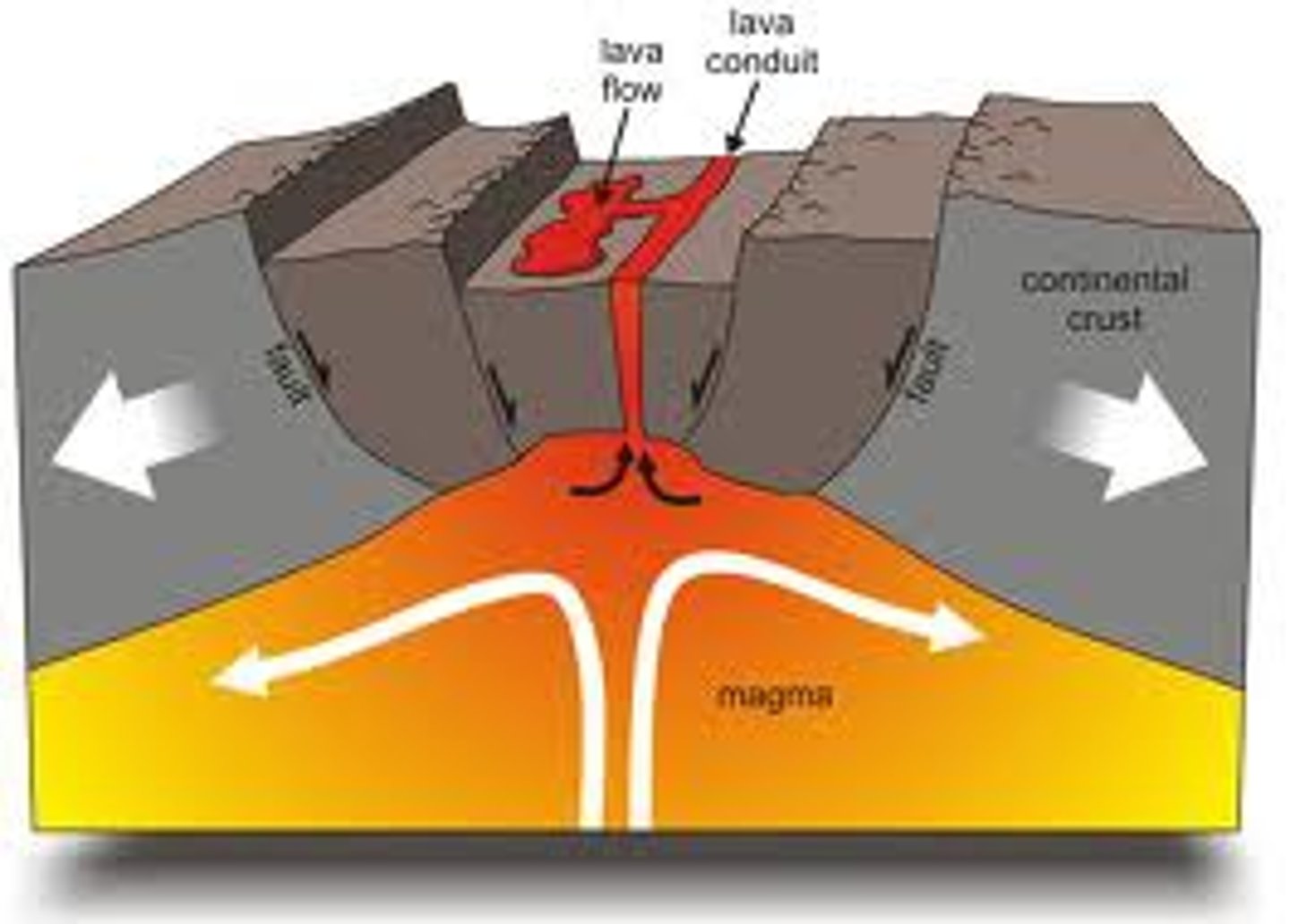
Divergent Continent-Continent
Features: Rift valley, small volcanic vents, lakes
Example: Iceland, Great African Rift
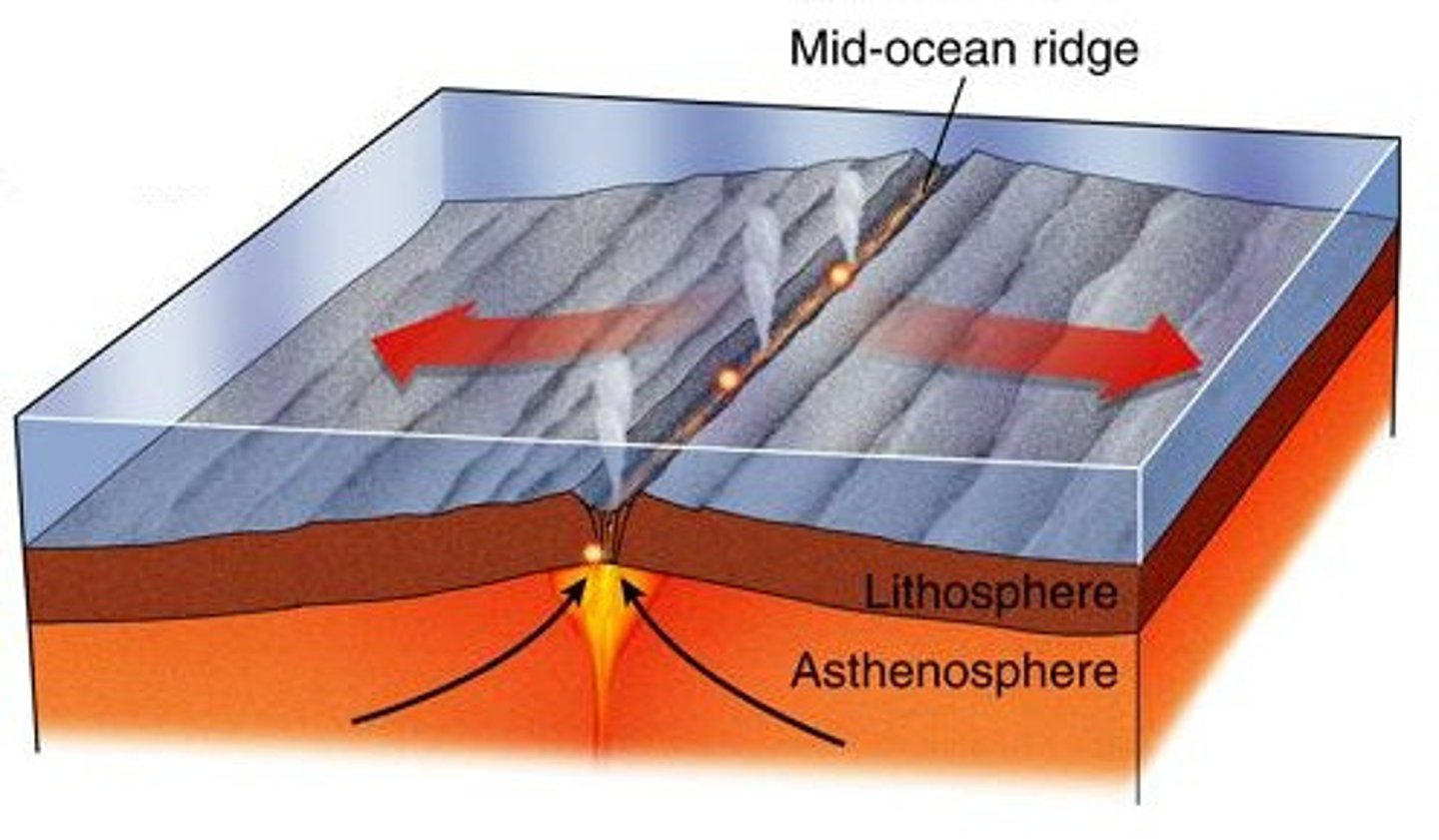
Divergent Ocean-Ocean
Features: Mid-ocean ridge, underwater volcanoes
Example: Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Transform Boundary
Features: Major earthquakes, fault line, ridge or low mountains
Example: San Andrean Fault