AC105 - Week 5: depreciation
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What are non-current assets?
assets that provide future benefit but not trading
2 types of NCA
Finite or Infinite
meaning of finite life of a NCA
will be used up over their useful life through wear and tear
meaning of infinite life of a NCA
Benefits from assets with indefinite lives may or may not be used up over time
What is depreciation?
Accounting method that allocates cost of a tangible asset cross its useful life, reflecting gradual loss of value due to wear and tear or obsolescence
What is the NBV
cost (acq) - accumulated depreciation
What are fair values
NCA may be recorded using fair values (measured with a reasonable degree of certainty)
represent the selling price that can be obtained in an orderly transaction under current market conditions
Benefit of measuring using fair value instead of cost
more up to date information which may be more relevant to their needs
better financial figures for entity as NCA like property have increased significantly over time
What is amortisation
depreciation of intangible assets
What 4 factors have to be considered to calculate the depreciation expense
Acquisition cost of the asset
Useful life of the asset
Residual value (RV) of the asset
Approved depreciation method
What principle guides inventory write downs when market value falls below cost
Prudence principle - Inventory is valued at the lower of cost or net realisable value (NRV).
Double entry for inventory writedown
UP: Cost of Goods Sold
DOWN: Inventory
What is carrying amount
initial cost of an asset
What is the NRV of an asset
The estimated selling price minus any costs involved in selling and distributing the goods
What is PPE
PPE are tangible assets that are held for use in the production or supply of goods or services for rental to others or administrative purposes
They are expected to be used during more than one period
What does the cost of an item of PPE include
The purchase price
All costs incurred in order to bring the asset into a location and condition ready for use
What is capital expenditure
Cash spent to purchase assets, the asset is expected to provide future benefits, items last for more than a year
What is revenue expenditure
Any cash spent on day to day operations and is consumed within an accounting year
The entire amount is charged to the income statement
When and only when can subsequent expenditure on PPE be capitalised ( Added to the cost of the asset on the SOFP)
If it enhances the economic benefit of the asset
e.g. repairs will not but adding an extension will
What are the 2 ways of subsequent measurement of PPE
The cost model
OR
The revaluation model
What is the cost model
The cost model is where the asset is included in the SOFP at cost less accumulated depreciation and impairment losses
This net amount is referred to as a carrying amount or Net Book Value
What is the revaluation model
Where the asset is included on the SOFP at revalued amount (fair value) less subsequent depreciation and impairment losses
Arising revaluation gains are credited to an account 'revaluation reserve' this is part of a companys equity
Revaluation double entry
UP non-current assets
UP Revaluation Reserve
What are the 2 methods of depreciation
Straight line
Reducing balance
SL method of depreciation
Constant change over the life of the asset
Reducing balance method of depreciation
Decreasing changes over the life of the asset
Useful life of a NCA
Refers to the period over which an asset generates benefits
What is the physical life of an asset not necessarily equal to
Its economic life
What are assets depreciated based on
Their useful economic life
What does residual value refer to
The selling value of an asset at the end of its useful life
What is the formula for the depreciable amount of an asset
Initial cost - residual value
What formula does the straight line method use to calculate depreciation expense
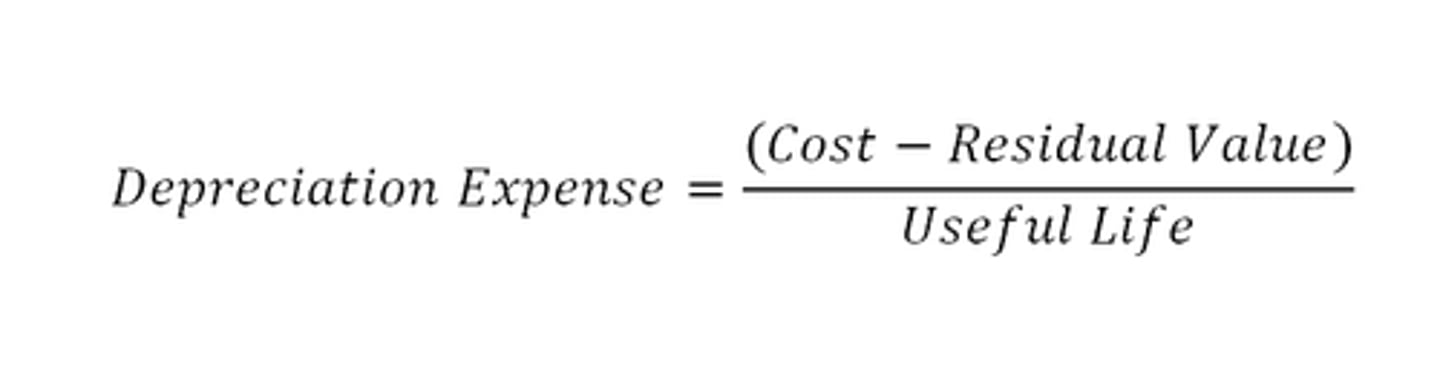
How does the rate of depreciation differ between reducing balance method and straight line method
The reducing balance method results in more depreciation in the earlier years of an assets life and less depreciation in the later years
What is the equation for depreciation expense through reducing balance method
Depreciation expense = Depreciation rate x NBV at the start of the year
What is the double entry for depreciation
Dr depreciation expense (IS)
Cr accumulated depreciation (SOFP)
What type of entry is accumulated depreciaiton
Contra account
What are the 2 accounts we use for non-current assets
Cost and Accumulated depreciation
What is the net balance of cost and accumulated depreciation
The net book value of ppe
What should the depreciation method used reflect
The pattern in which the assets economic benefits are consumed by the entity
Why do entities in the same industry usually use the same method of depreciation
improve comparability
What is an impairment of an asset
When an asset suffers a significant fall in value
What is the general rule when recording impairment
The asset on the balance sheet should be reduced to its recoverable amount and recognise an impairment loss
Double entry for impairment loss
UP Impairment loss
DOWN Equipment
Gain/loss on disposal formula
proceeds - NBV
PPE disposal steps
1) Remove disposed asset cost
2) Remove disposed accumulated depreciation
3) Record proceeds
4) Gain or loss transfer to P&L account
5) Depreciation on remaining NCA
PPE disposal steps (double entry method)
1) Remove cost of asset from PPE cost account
Dr Disposal
Cr PPE
2) Remove the accumulated depreciation
Dr Depreciation
Cr Disposal
3) Record the Cash proceed
Dr Cash
Cr Disposal
4) The benefits figure in the disposal account is the gain/loss on disposal