Unit 1 Transformations and Congruence
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Line
It has no thickness and it continues forever in both directions.
Line Segment
A portion of a line with two end points.
Opposite Rays
Rays with the same initial point that extend in opposite directions.
Midpoint
The point that bisects a segment. (Divides into two segments of equal length.)
Bisect
To divide something into 2 equal parts.
Perpendicular Lines
Two lines which intersect at a right angle (90 degrees).
Parallel Lines
Two lines which exist in the same plane but will never intersect.
Postulate
Something assumed as true as the basis for further reasoning, discussion, or proofs.
Midpoint Formula
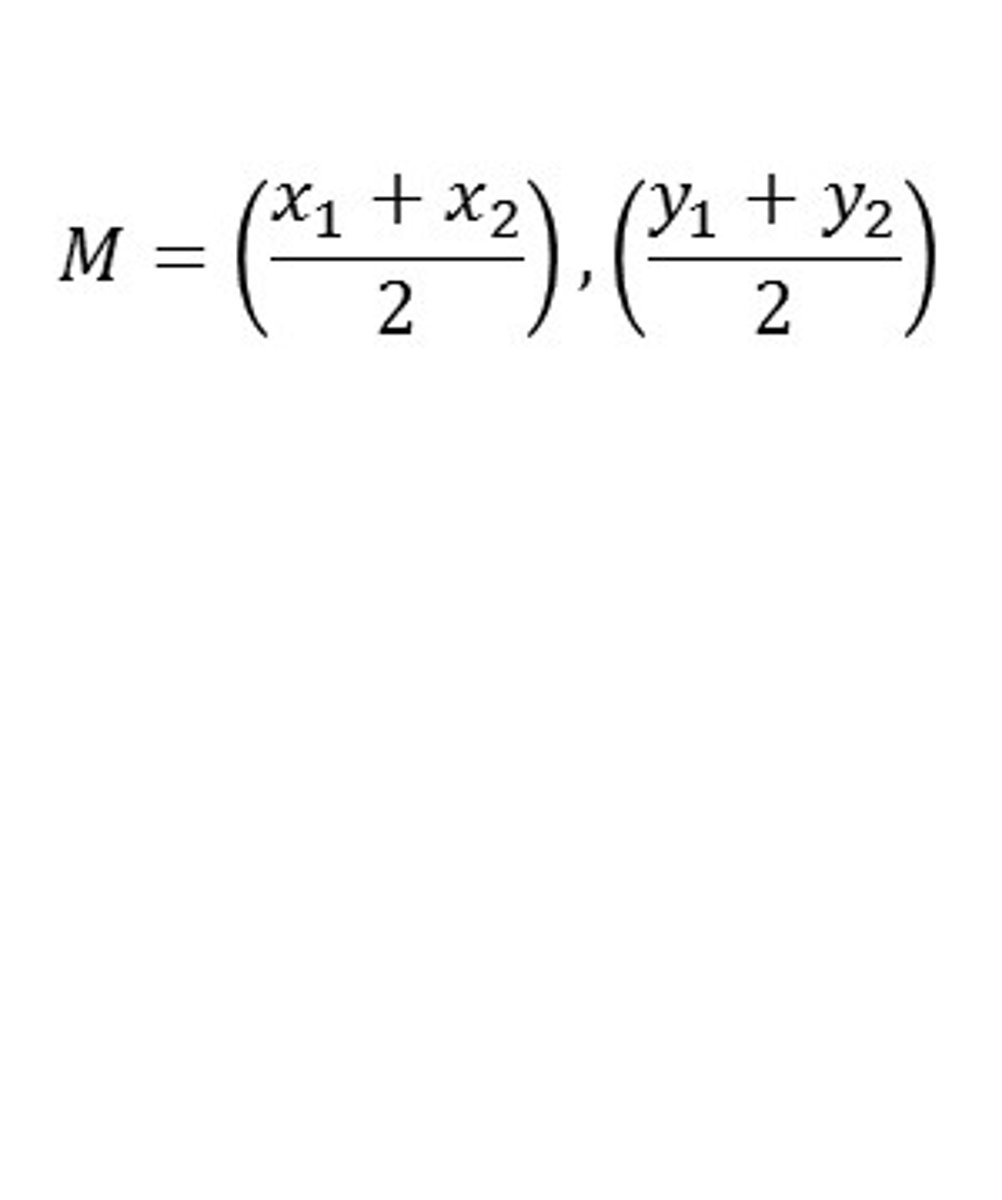
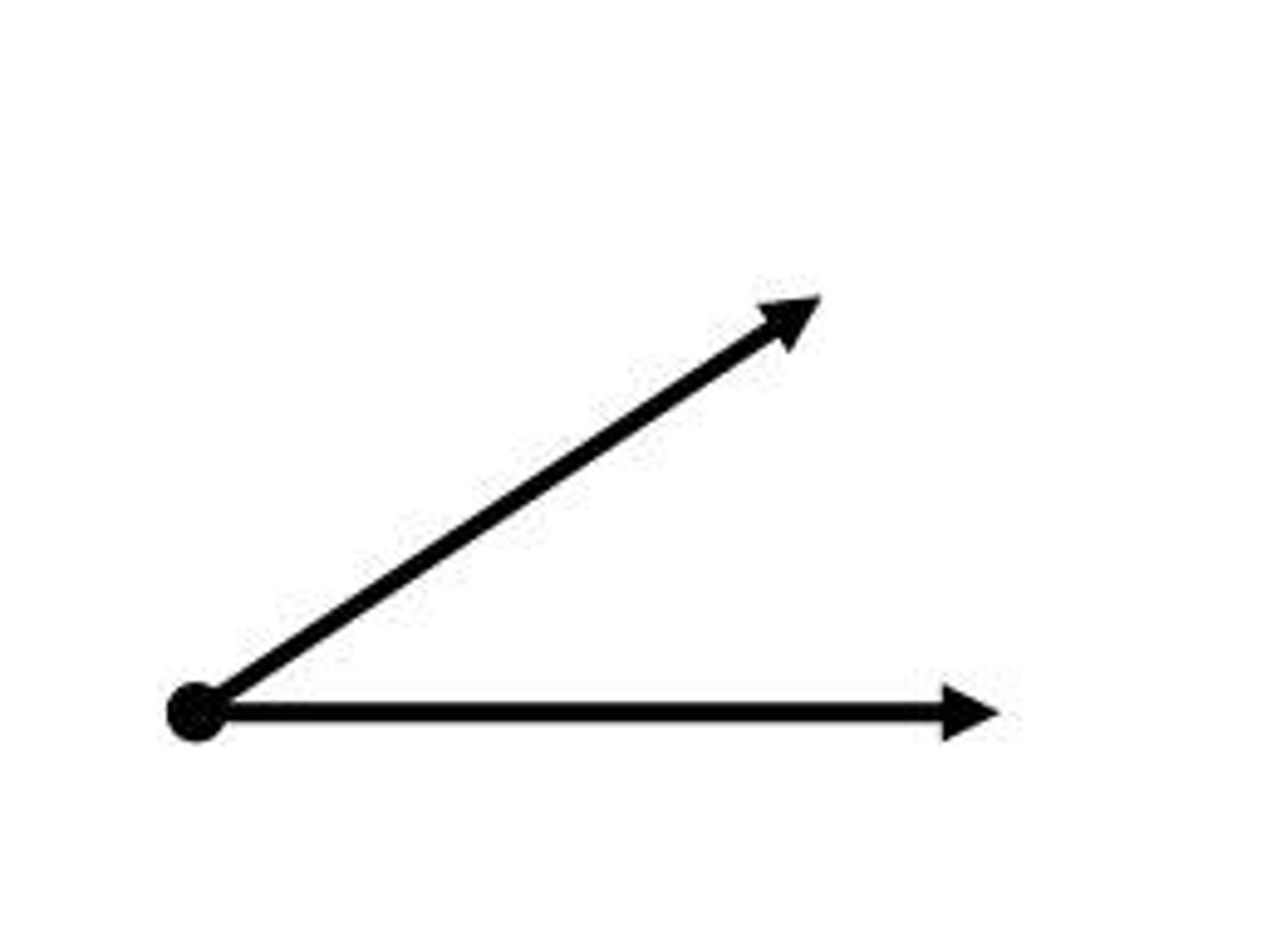
Acute Angle
An angle that measures more than zero degrees but less than 90 degrees.
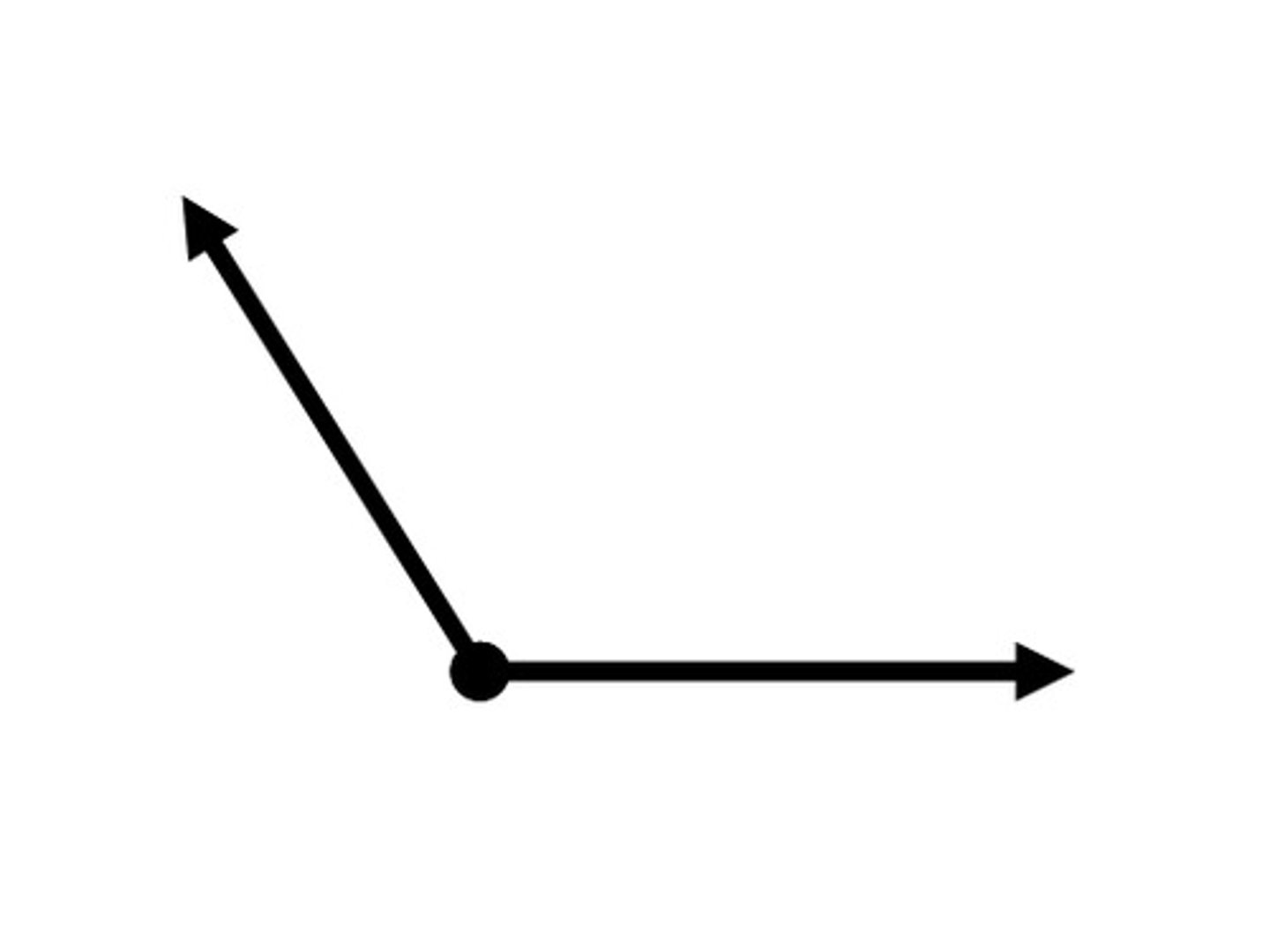
Obtuse Angle
An angle with measure greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.
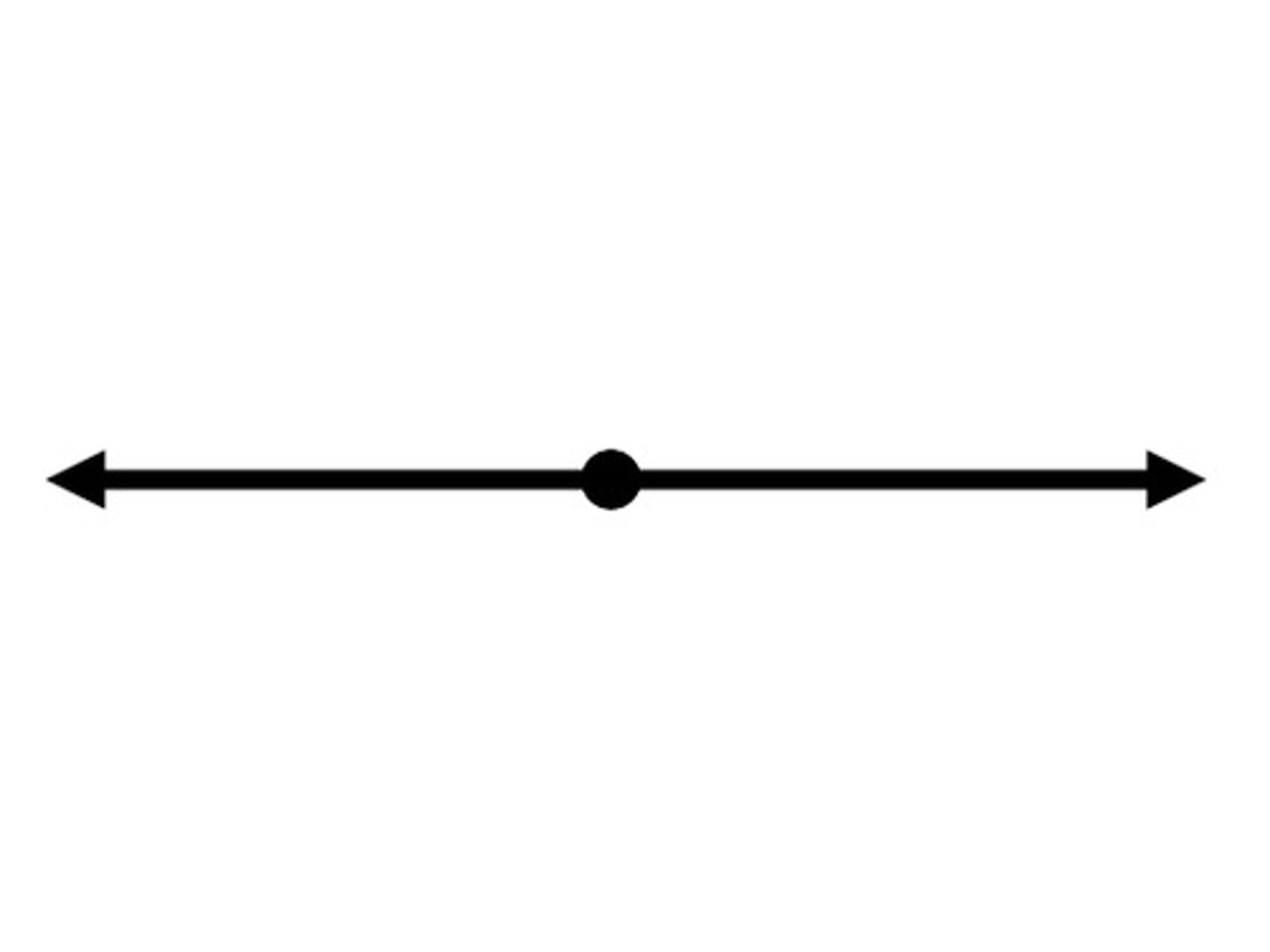
Straight Angle
An angle with measure of 180 degrees.
Right Angle
An angle with measure of 90 degrees.
Protractor
Tool used to measure angles
Collinear Points
Points lying on the same line
Supplementary Angles
Two angle measures with a sum of 180 degrees.
Complimentary Angles
Two angles with a sum of 90 degrees.
≅
Congruent
=
Equal
Congruent
Having the same size and shape
Linear Pair
Two adjacent angles that form a straight line
Angle
A figure formed by with two rays with a common endpoint.
Degree
Unit of measurement for an angle
Angle Bisector
a line or ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles
Vertex
The common endpoint of an angle
Endpoint
the point where a ray begins or the points that define a segment
Construction
a geometric drawing that uses a limited set of tools, usually a compass and a ruler
Exterior
all points not on the angle or in its interior
Interior
all points not on the sides of an angle but within the its sides
Segment Addition Postulate
If B is between A and C, then AB + BC = AC
Angle Addition Postulate
for any angle, the measure of the whole is equal to the sum of the measures of its non-overlapping parts
Vertical angles
two angles whose sides form two pairs of opposite rays
Vertical Angle Theorem
Vertical angles are always congruent
Non-rigid motion
Does not maintain shape and/or size
Point
An undefined term in geometry, it names a location and has no size.
Preimage
The original figure in a transformation.
Ray
A part of a line that starts at an endpoint and extends forever in one direction.
Reflection
A transformation across a line, called the line of reflection, such that the line of reflection is the perpendicular bisector of each segment joining each point and its image.
Rigid motion
A transformation that does not change the size or shape of a figure.
Rotation
A transformation about a point P, also known as the center of rotation, such that each point and its image are the same distance from P. All of the angles with vertex P formed by a point and its image are congruent.
Segment
A part of a line consisting of two endpoints and all points between them.
Theorem
A statement that has been proven.
Transformation
A change in the position, size, or shape of a figure or graph.
Translation
A transformation that shifts or slides every point of a figure or graph the same distance in the same direction.
Plane
a flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever
Coplanar
of the same plane
Dilation
A transformation that changes the size of an object, but not the shape.