Case 10: Eva Foster
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Coagulation Factor Generation
Hepatocytes:
Fibrinogen
Prothrombin
Factors V, VII, IX, X, XI, XII
Endothelial Cells:
FVIII
vWF
Extravascular/Stromal Cells: TF
Megakaryocytes: vWF
Platelet Function
Form primary hemostatic plug (white thrombus)
Increase fibrin adhesion
Coagulation Factor Function
Form secondary hemostatic plug (red thrombus)
Coagulation cascade
Increase thrombin and fibrin network formation
Fibronolysis
Hemostasis stage 5
Tissue injury = Release + activate plasminogen activators = Plasminogen → Plasmin
Plasminogen Activators:
Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)
Urokinase
Inhibited by plasminogen activator inhibitors
Plasmin break down + deactivate fibrin and fibrinogen = Release fibrin degradation products (D-dimers)
Inhibited by plasmin inhibitors
Natural Anticoagulants
Endothelial surface factors
Antithrombin III
Heparin
Natural Anticoagulant: Endothelial Surface Factors
Smooth surface prevent intrinsic pathway activation (no collagen exposure)
Glycocalyx layer repel clotting factors and platelets
Thrombomodulin
Bind thrombin = Remove thrombus
Activate plasma protein C = Inactivate FV + FVIII
Natural Anticoagulant: Antithrombin III
Bind thrombin = Inactivate + inhibit fibrinogen activation (decrease fibrin)
Natural Anticoagulant: Heparin
Combine with antithrombin III = Increase activity
Shock
Circulatory failure decreasing pressure/volume in blood vessels
Types:
Cardiogenic
Distributive
Obstructive
Hypovolemic
Cardiogenic Shock
Low CO = Hypotension
Cardiac ischemia
Arrhythmia
Treatment:
Inotropic drugs
Vasopressors
IV fluids
Distributive Shock
Fluid extravasation = Decrease intravascular fluid = Hypotension
Sepsis
Anaphylaxis
CNS injury (neurogenic)
Treatment:
IV fluids
Vasopressors
Treat underlying cause
Obstructive Shock
Physical vessel blockage = Decrease CO = Hypotension
Cardiac tamponade
Tension pneumothorax
Pulmonary embolism
Treatment:
IV fluids
Treat obstruction
Hypovolemic Shock
Intravascular volume loss = Hypotension
Fluid loss (GI, skin, kidneys)
Hemorrhage
Treatment:
IV fluids
Blood transfusion
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE): Description
Thrombus formation in venous system
Recurrent: Recurring VTE after 2 weeks of treatment
Provoked: VTE with ≥ 1 risk factors
Unprovoked/Idiopathic: VTE without risk factor
Types:
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
DVT: Description
Blood clot in deep vein
Usually in lower extremities
Proximal: Above calf vein trifurcation (knee joint)
Femoral, profunda femoris, and popliteal veins
Distal: Below calf vein trifurcation
PE: Description
Blood clot in pulmonary arteries
VTE: Epidemiology
Risk factors:
Older age (≥ 65 years)
Smoking
Obesity
Cancer
Surgery
DVT/PE history
VTE: Etiology
Thrombotic Embolisms: Virchow Triad
Endothelial damage
Venous stasis
Hypercoagulability
Nonthrombotic Embolisms:
Fat
Air bubbles
Amniotic fluid: Fetal cell + Debris from fluid → Maternal circulation
VTE Virchow Triad: Endothelial Damage
Inflammation
Trauma
VTE Virchow Triad: Venous Stasis
Slow blood flow
Varicosis
Immobilization
Travel/flights
Bed rest
VTE Virchow Triad: Hypercoagulability
Increased blood viscosity
Genetics
Thrombophilia
Increase platelet adhesion
Oral contraceptives
Pregnancy
Malignancy
DVT: Pathogenesis
Virchow triad induce thrombus formation (coagulation cascade) around lower extremity vein valves
More common in lower extremities from…
Immobility
Gravity-dependent blood pooling in venous valves
Low blood flow
Thrombus occlude blood vessel
PE: Pathogenesis
DVT in legs/pelvis embolize
IVC → Pulmonary arteries
Obstruct pulmonary arteries
Lung/pleural infarction + inflammation
Impair gas exchange + cardiac function
Pulmonary vasoconstriction
Thromboxane, prostaglandin, adenosine, thrombin, and serotonin secretion from platelets + thrombus
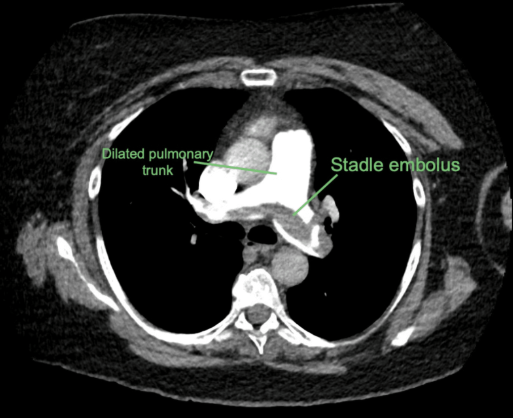
Saddle Thrombus: Clot in pulmonary trunk bifurcation = Complete obstruction = Right heart strain + Death
VTE: Clinical Presentation
DVT:
Asymptomatic
Unilateral symptoms
Swelling
Erythema
Warmth
Dull pain
Fever
PE:
Dyspnea
Tachypnea
Tachycardia → Most sensitive
Chest pain
Dizziness and syncope
Weakness
Hemoptysis
VTE: Investigations
Wells Score: Risk assessment
Diagnostic:
D-dimer
Compression US
ECG
Echo
CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA)
VTE: Wells Score
Higher score = More likely
DVT Criteria:
Medical history (cancer, previous DVT)
Immobilization
Clinical features
Tenderness
Leg + calf swelling (> 3cm)
Pitting edema
Distended superficial veins
PE Criteria:
Medical history (malignancy, pervious PE/DVT)
Immobilization
Clinical features
Hemoptysis
Tachycardia
VTE: D-Dimer
General (DVT and PE)
Negative: < 500 ng/mL
No DVT
Positive: ≥ 500 ng/mL
US
VTE: Compression US
DVT
Apply pressure on obstructed vein + Doppler
Positive:
Noncompressible
Hyperechoic mass
No venous flow
VTE: ECG
PE
Sinus tachycardia
VTE: Echo
PE
Increased RA pressure
VTE: CTPA
PE
Obstruction in pulmonary arteries
Pulmonary infarction
VTE: Treatment/Management
Temporary parenteral anticoagulant + long-term oral anticoagulant
Parenteral: Heparin
Oral: DOACs, Vit K antagonists (VKAs)
Severe:
PE: O2 therapy
Thrombolytics
Catheter-directed thrombolysis
Thrombectomy/embolectomy
VTE Treatment: Heparin
Unfractionated (UFH): Inhibit FXa and thrombin = Increase antithrombin activity (indirect) = Decrease coagulation + fibrin formation
Monitor: aPTT
Low Molecular Weight (LMWH): Bind antithrombin III = Inhibit FXa = Increase antithrombin activity (indirect) = Decrease coagulation + fibrin formation
Monitor: Anti-factor Xa activity
VTE Treatment: DOACs
Direct Thrombin Inhibitors: Inhibit thrombin = Decrease fibrin formation
Dabigatran
Direct FXa Inhibitors: Inhibit FXa = Decrease coagulation + fibrin formation
Rivaroxaban, apixaban, edoxaban
Preferred over VKAs
No monitoring
Lower bleeding risk
VTE Treatment: VKAs
Warfarin
Decrease hepatic vit K synthesis = Inhibit FII (prothrombin), FVIII, FIX, and FX activation = Decrease coagulation + fibrin formation
Monitor: PT/INR
VTE Treatment: Thrombolytics
tPA (alteplase)
Increase plasminogen → Plasmin = Increase fibrin degradation
VTE Treatment: CDT
Increase enzymes catalyzing plasminogen → Plasmin to break down clot
Streptokinase
Urokinase
rtPA
VTE Treatment: Thrombectomy/Embolectomy
If CDT contraindicated
VTE Complications
DVT:
PE
Recurrence
PE:
Recurrence
Poor oxygenation
Pulmonary artery obstruction = Increase V/Q ratio (normal ventilation + no blood flow) = Decrease O2 delivery from inspired air → Blood
Cardiovascular failure
Obstruction increase pulmonary artery pressure = Increase RV pressure + Decrease blood into LA = Decrease CO = Hypotension