econ unit 13 ppt
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
LABOUR MARKETS — COMPLETE STUDY NOTES
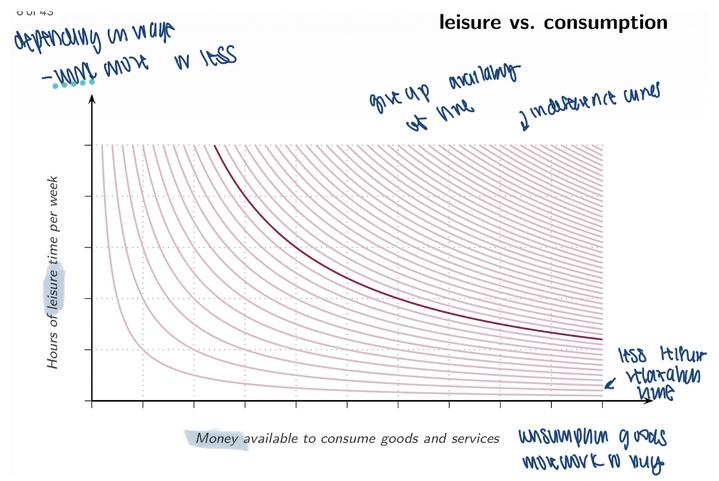
1. What is Labour Supply? People have 168 hours per week to allocate.
People choose how many hours to work vs leisure.
2. Why Do We Work?
Costs
___ of time (giving up leisure)
Disutility of ___ (working is tiring)
Benefits
Wages (money to buy goods/services)
Personal fulfillment
Social recognition
Cost of factors (work may provide benefits)
Trade-off: Leisure vs consumption
More leisure = less income; more work = more income but less leisure.
OC, effort
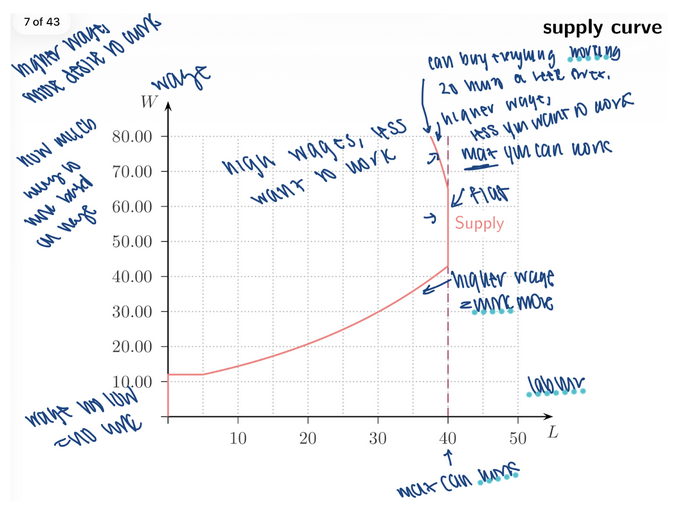
3. Labour Supply Curve
At higher wages, people supply more labour.
Upward sloping supply curve: W ↑ → Quantity of labour supplied __
increases
4. __ Labour Markets
Many firms, many workers.
Both are price takers—no one can influence the wage.
Small restaurant hiring servers
Dentist/lawyer/doctor hiring a receptionist
competitive
5. Profit Maximization by Firms
Wage (W): marginal cost (MC) of ___ labour
→ MC = ___*******Value of Marginal Product (VMP):
Marginal Benefit of hiring labour
→ VMP = MP × Price of output (P)
Decision Rule - A firm hires workers until: W = VMP
hiring, W
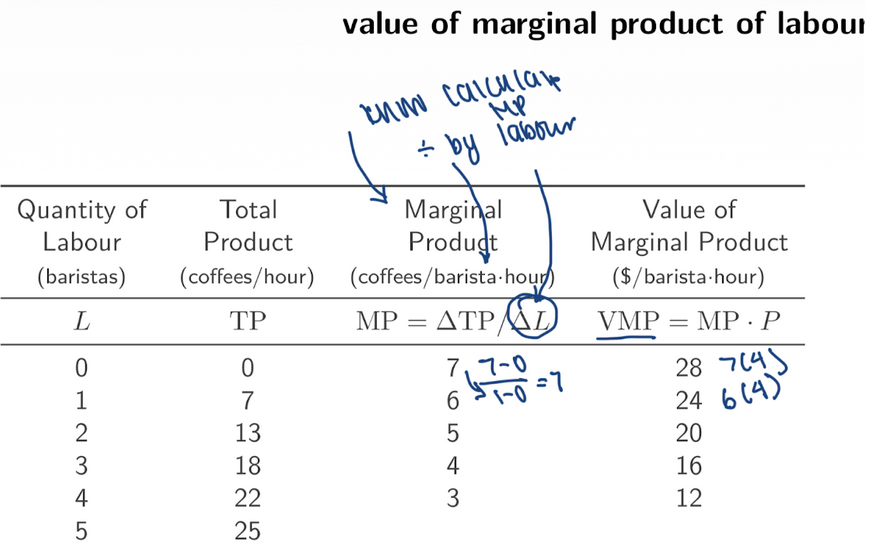
7. VMP Calculation Table
Price of coffee = $4 (because VMP = MP × P)
L | TP | MP | VMP |
0 | 0 | 7 | 28 |
1 | 7 | 6 | 24 |
2 | 13 | 5 | 20 |
3 | 18 | 4 | 16 |
4 | 22 | 3 | 12 |
5 | 25 | — | — |
This VMP curve is the labour __ curve for the firm.
demand
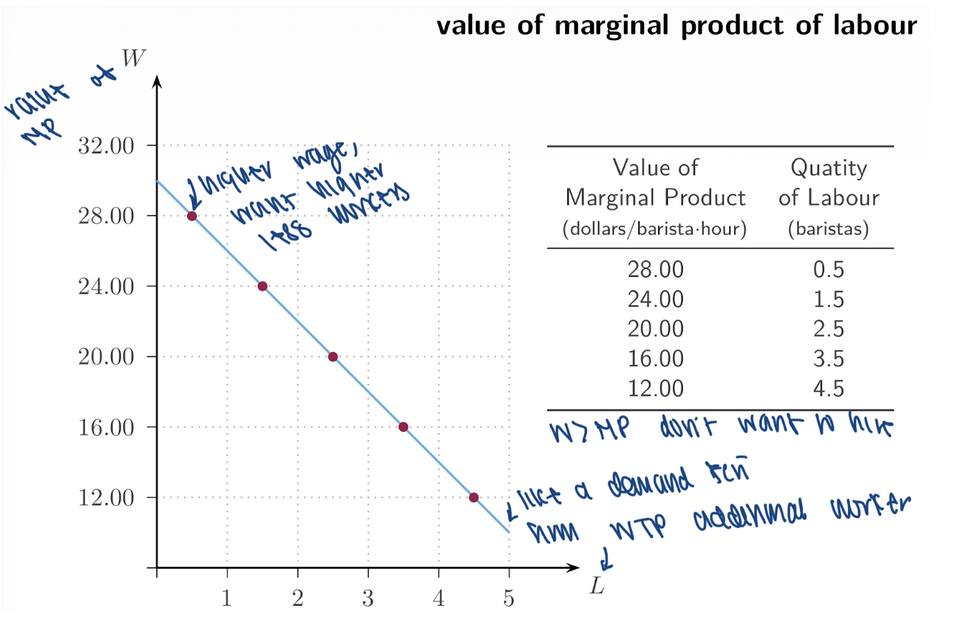
8. Labour Demand Curve & Schedule
Wage | Quantity of Labour Demanded |
28 | 0.5 |
24 | 1.5 |
20 | 2.5 |
16 | 3.5 |
12 | 4.5 |
Lower wage → more labour __
Higher wage → less labour demanded
demanded
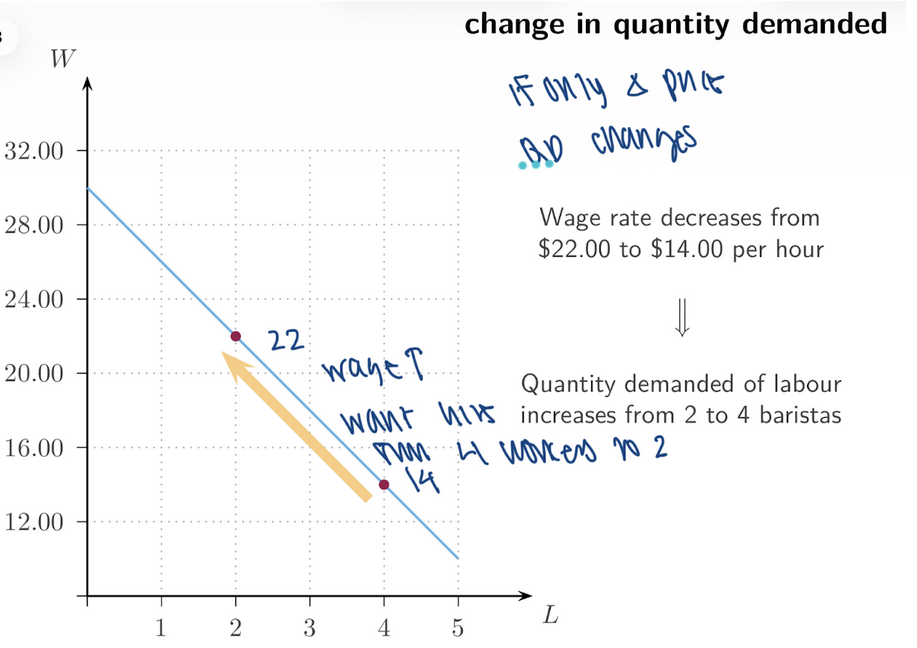
9. Change in Quantity Demanded
____ falls from $22 → $14/hour
Quantity demanded increases from 2 → 4 baristas
__ along the demand curve
wage, movement
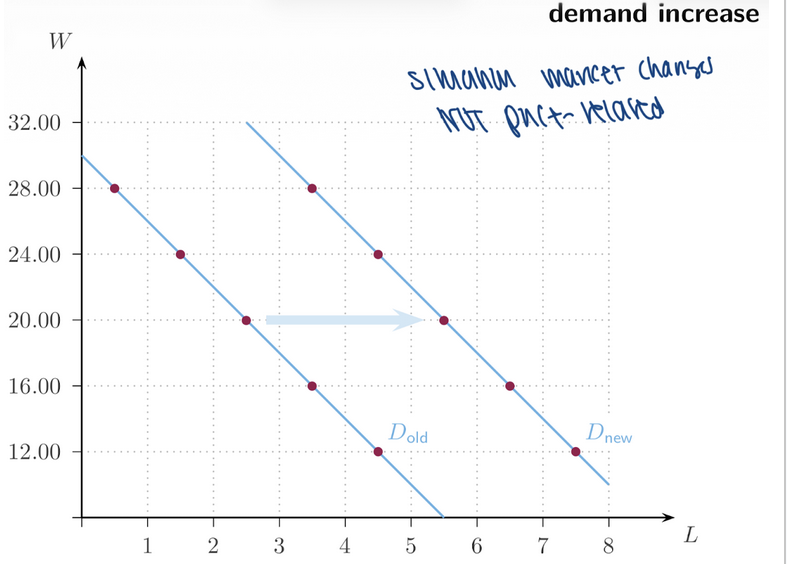
10. Increase in Labour Demand (Shift Right)
___ price of output
__ price of related factors
Lower price of ___
Better technology
higher, lower, complements
11. Market Power in Labour Markets
Most labour markets ___ competitive
Firms often have more bargaining power:
Large firms with deep pockets
Workers are replaceable and need income
Monopsony - A labour market with a single ___ (big employer). This buyer is called the monopsonist.
aren’t, buyer
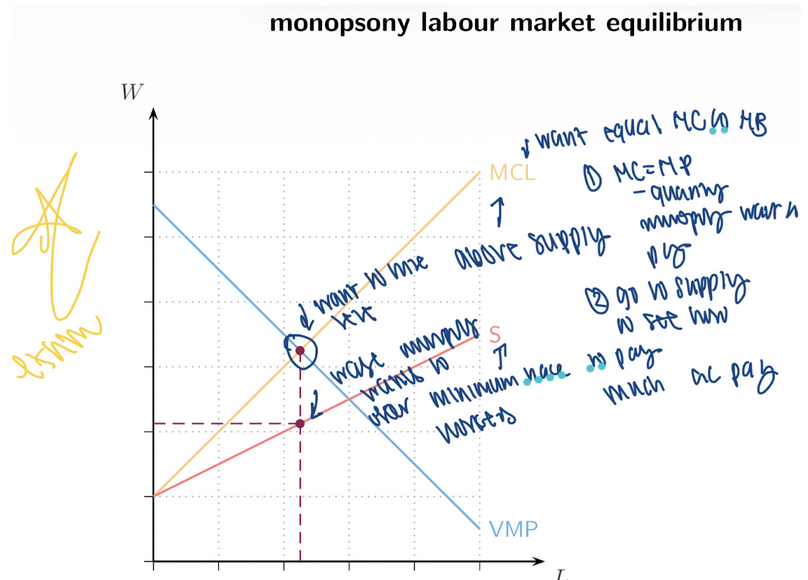
********12. Competitive vs Monopsony Employers
Competitive Firm
Pays the market wage to all employees
Marginal cost of labour = wage
→ MCL = W
Monopsony (or any employer with market power)
___ wage
Must ____ wages to hire more workers
This raises the wage for all employees
Therefore: → MCL ___ W
chooses, raise, >
13. Monopsony vs Monopoly Comparison
Market Side | Perfect Competition | Market Power |
Supply side | MR = P | MR < P |
Demand side | MCL = W | > |
MCL > W
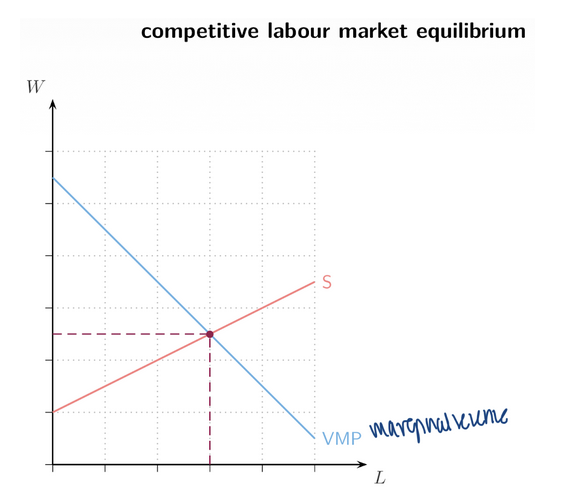
14. Competitive Labour Market Equilibrium
Intersection of ___ (Demand) and Supply
Efficient quantity and wage
VMP
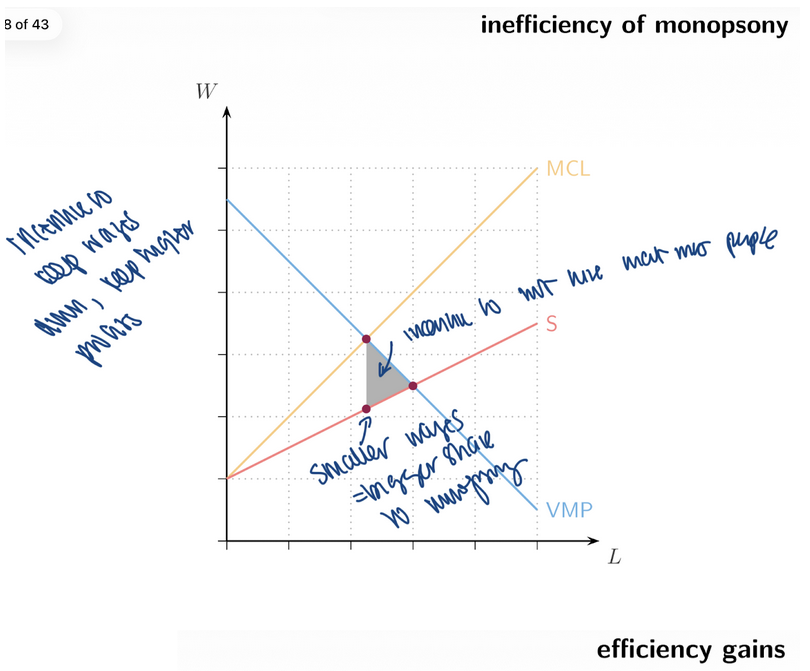
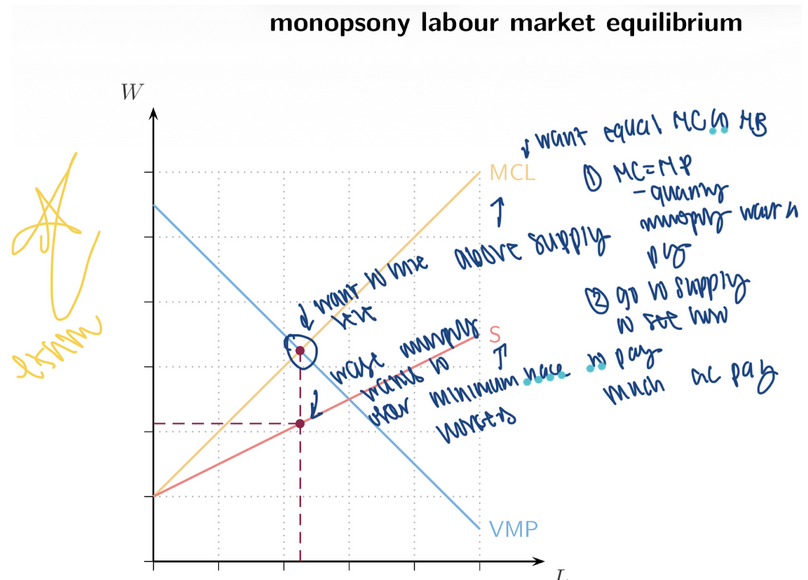
15. Monopsony Labour Market Outcome
Monopsony hires ___ labour
Pays a ___ wage
Creates ___ (inefficiency)
Monopsonist chooses:
Hire where ____ = MCL
Pay the wage from the ___ curve at that quantity
less, lower, DWL, VMP, supply
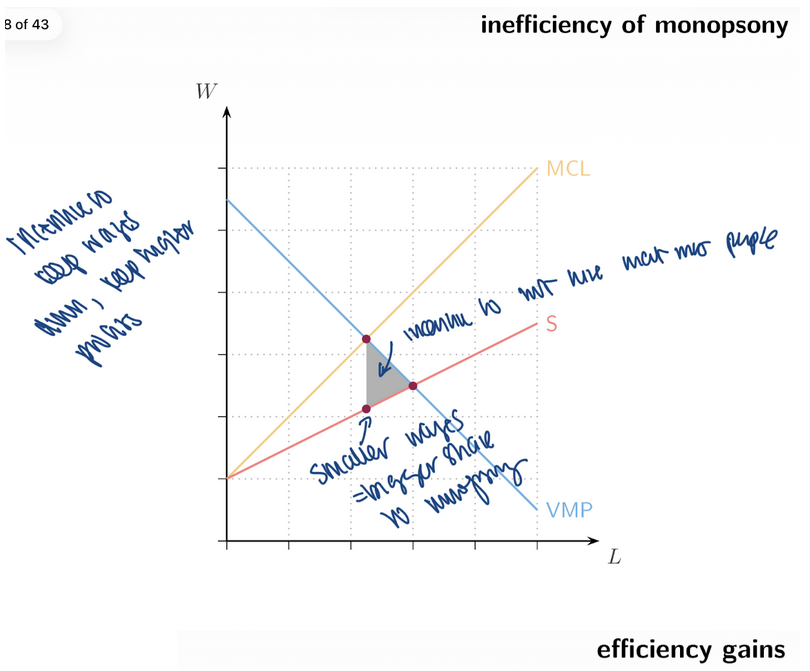
16. Monopsony Inefficiency
Too ____ employment
Wage below competitive level
Deadweight loss
Workers harmed
little
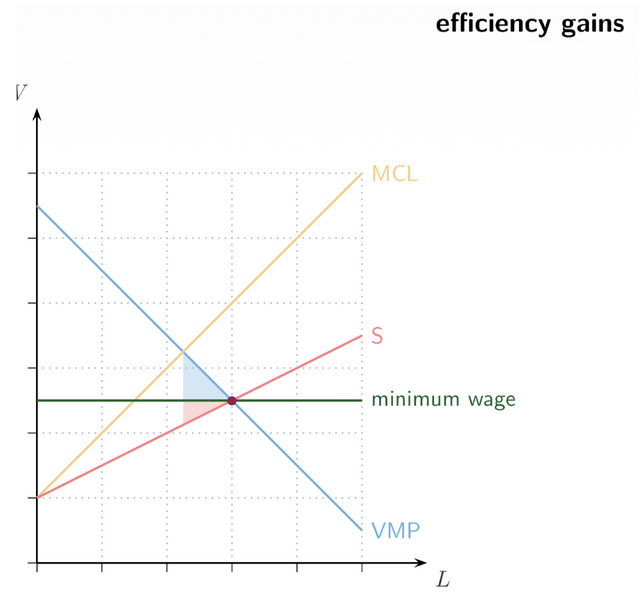
17. Minimum Wage in Monopsony
Key claim from slides: Minimum wages can increase employment and ___ if the labour market isn’t competitive.
A minimum wage set between ____wage and __ wage:
Increases __
Reduces inefficiency
Raises worker welfare
surplus, competitive, monopsony, employment
18. Elasticity of Low-Wage Labour Supply
Low-wage workers often have ___ labour supply
Inelastic supply amplifies firm power
inelastic
19. Wage Discrimination
1. By __
__ pay
Productivity bonuses
2. By __
Secret __
Different pay for similar work based on __
quantity, overtime, identity, identity
20. Bargaining
Bargaining = process by which agents split economic ___.
Outcomes depend on __ power
Can lead to inefficiency
Monopoly/monopsony
Labour strikes
War
Catennaccio (soccer strategy metaphor)
surplus, bargaining
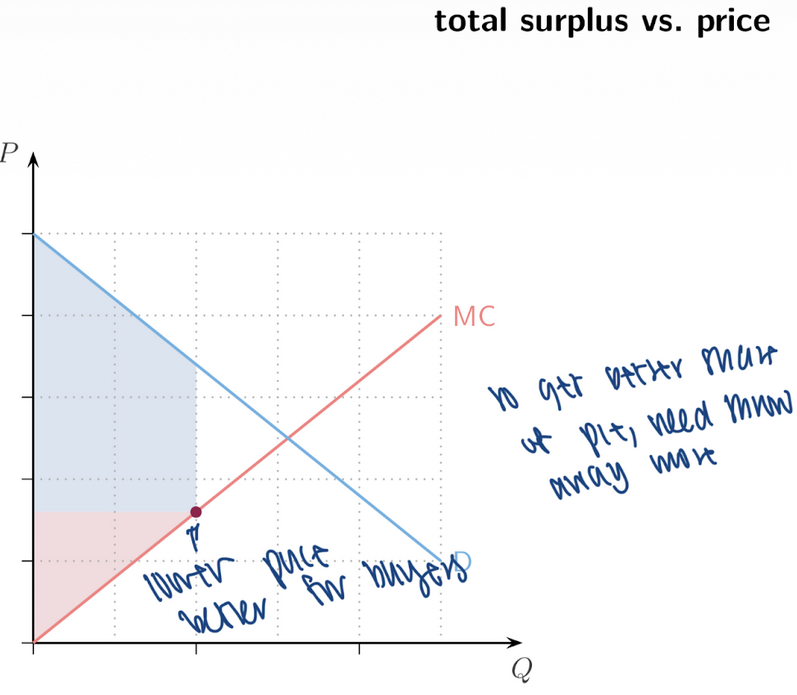
21. Bargaining and Prices
Trade Generates Surplus
__ parties can benefit
Amount traded influences surplus ____
Role of Price - Determines how the surplus is __
both, size, split
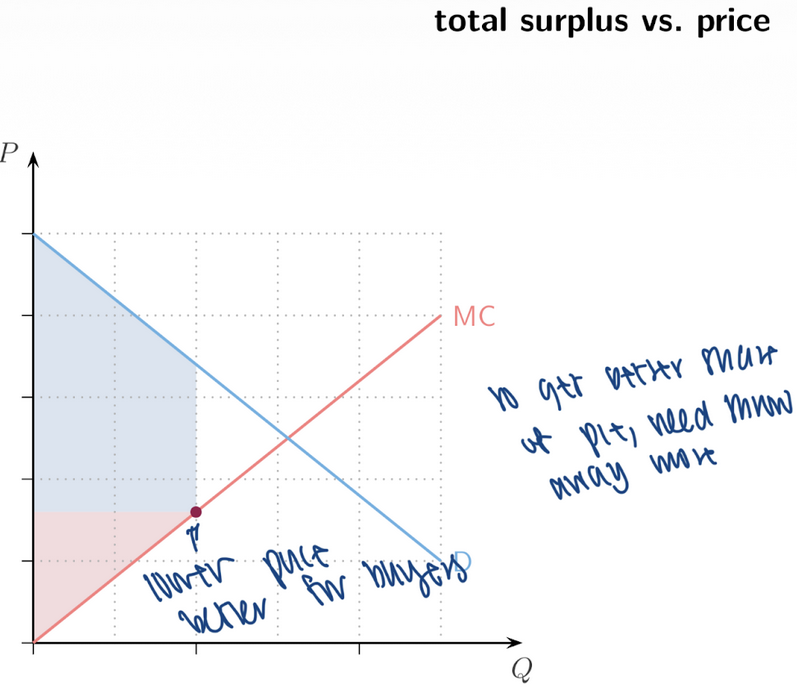
22. Total Surplus vs Price
Repeated diagrams show:
Demand curve (D)
Marginal cost (MC)
Surplus area changes depending on ___
Key message: Price affects the __ of surplus but not necessarily total surplus (unless prices distort quantity).
price, split
23. Bargaining Asymmetry
Firms generally have more power: Large corporations vs households
Wages often favour __
Outcomes may be inefficient or unfair
employers