Organic chemistry
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What is an isomer ?
A molecule is an isomer of another if the two molecules have the same molecular formula but are arranged differently
What is a structural isomer ?
A compound with the same molecular formula but different structural formula
What are the 3 types of structural isomers ?
Chain ( - branch)
Positional
Functional group
Chain isomers have similar chemical properties but their physical properties are different
What is a positional isomer ?
This is an isomer where the carbon skeleton and the functional group are the same but their physical properties functional group is attached to a different carbon atom
They have _________ physical properties and slightly _________ chemical properties
They have different physical properties and slightly different chemical properties
What is a functional group isomer ?
The same atoms are arranged into different functional groups
They have very _________ physical and chemical properties
They have very different physical and chemical properties
What is a property of single c-c bonds ?
(Hint : rotational property)
Single C - C bonds are able to rotate around the bond freely without changing the chemistry of the compound
What are stereoisomers ?
Compounds with the same structural formula but with a different arrangement in space
What is an EZ isomerism ?
This is an example of stereoisomerism , in terms is restricted rotation about a double bond and the requirement for 2 different groups to be attached to each carbon atom of the c=c
What is an E - isomer ?
The 2 highest priority groups are on opposite sides to each other (entgeigen)
What is a Z - isomer ?
The 2 highest priority groups are on the same side as each other (zusammen)
What is the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rule ?
The highest priority is given to the one with the highest atomic number directly bonded to c
What is a Cis-trans isomerism ?
A special case of E/Z isomerism in which 2 of the subsitutents groups attached to each carbon atom of the c=c group are the same
What is the rule for Cis-trans isomerism ?
trans isomer (E)- groups on opposite sides
cis isomer (Z)- groups on the same side
(NB : only if there is a H on each carbon atom of the c=c)
List properties of alkanes ? (7)
They have no functional group
Undergo complete combustion
They do not react with bromine water
They are saturated
All members have the suffix ‘-Anne’
They are apart of a homogenous series (hydrocarbons)
They react with halogens to form haloalkanes
How does the chain length of a alkane affect its properties ? (3)
As chain length increases , their viscosity increases
As chain length increases , their melting point and boiling point increases
As chain length increases , their flammability decreases
Describe the process of fractional distillation ?
Crude oil is heated and vaporised before being passed into a fractionating column. The column has a temperature gradient, being hotter at the bottom and cooler at the top.
The vapour rises up the column and the different hydrocarbons condense at different heights depending on their boiling points.
Hydrocarbons with lower boiling points (smaller molecules, weaker intermolecular forces) condense near the top of the column where it is cooler.
Hydrocarbons with higher boiling points (larger molecules, stronger intermolecular forces) condense lower down where it is hotter.
Each fraction that condenses contains hydrocarbons of similar chain lengths and boiling points. The separated liquid fractions are then drawn off at different levels of the column.
What is free radical substitution ?
a reaction where a hydrogen atom in an alkane is replaced by a halogen atom (like chlorine or bromine) using energy from UV light or heat to generate highly reactive, unpaired electron species called free radicals
What are the 3 stages of free radical substitution ?
Initiation
Propagation
Termination
What is bond fission ?
Breaking a covalent bond
What is Homolytic fission ?
Each bonding atom receives 1 electron from the bonded pair. This forms 2 radicals.
What is a radical ?
A species with an unpaired electron
What is Heterolytic fission ?
1 bonding atom receives both electrons from the bonded pair
What does the curly arrow describe ?
The movement of an electron pair
What can the curly arrow show ? (2)
heterolytic fission
formation of a covalent bond
What is a reaction mechanism ?
A diagram which clearly shows the movement of electron pairs
What are reaction mechanisms used for?
They are used to explain organic reactions
What are features of a reaction mechanism ?
use curly arrows
show relevant dipoles
chlorination of alkanes …
What is a substitution reaction ?
When an atom in a compound gets swapped with another atom
What is the halogenation of alkanes ? (A type of radical substitution)
Swapping a hydrogen in an alkane with a halogen
How are alkanes turned into haloalkanes ?
Free radical substitution in the present of UV rays (ultraviolet light radiation)
How are haloalkanes turned into Aminos ?
They are dissolved in ethanol with concentrated ammonia under pressure
How are haloalkanes tuned into alcohols ? ( aka hydrolysis )
dissolve the halogenoalkanes in a small volume of ethanol
With warm aqueous alkali (NaOH or KOH)
Reflux gently (increases the rate of reaction)
How are haloalkanes turned into nitriles ?
Reacted with an aqueous solution of potassium cyanide (KCN) in ethanol
What are halogenoalkanes ?
Compounds in which a halogen atom has replaced at least one of the hydrogen atoms in an alkane chain
What is the formula for a monosubstituted halogenoalkane ?
CnH2n+1X
Show primary / secondary / tertiary halogenoalkanes ?
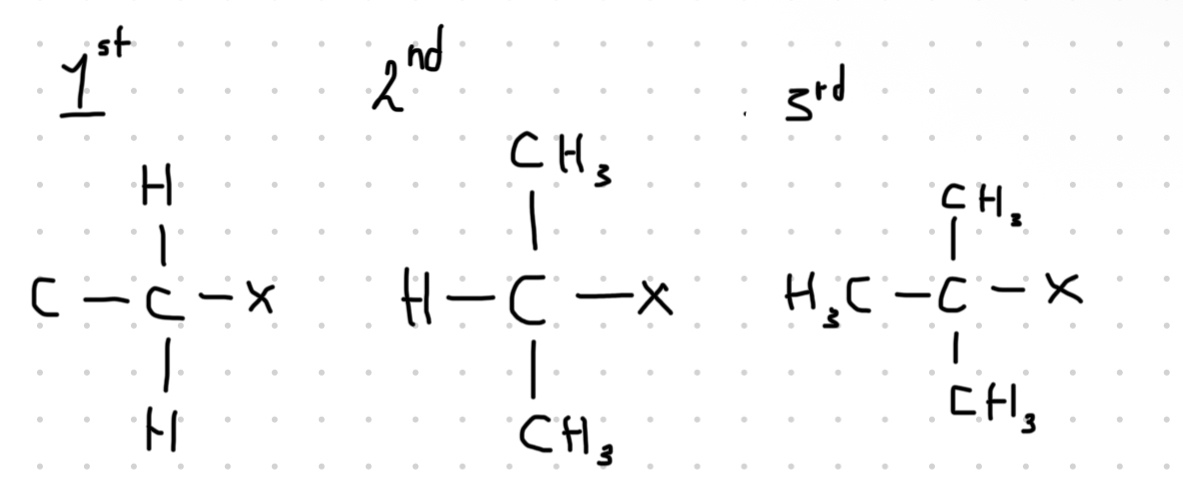
What is a polar bond ?
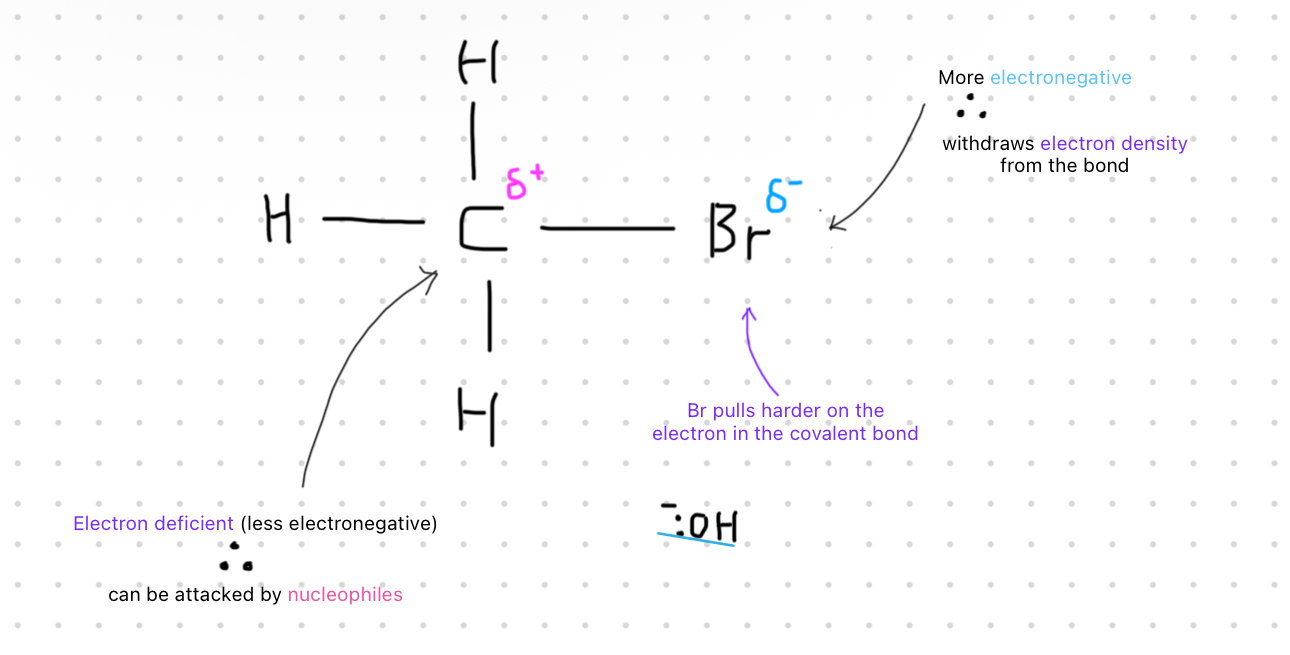
a covalent bond where electrons are shared unequallybetween two atoms due to differences in electronegativity
What is an electronegativity ?
The ability of an atom to pull a pair of electrons in a covalent bond towards itself
How is electronegativity measured ?
Pauling Scale
Where are the most electronegative elements of the periodic table ?
Top right
What is a property of halogenoalkanes ?
Contain a polar bond due to a difference in electronegativities
Explain the polar bond in 1- bromoethane ?
What is a nucleophile ?
An electron pair donor
Example of common nucleophiles ?
-CN
H2O
-OH
NH3
What does a nucleophiles do ?
It attacks and electrophile
What 2 factors affect the rate of hydrolysis ?
Polarity
Bond Enthalpy
What is the trend in polarity of the halogen group bonded with carbon ?
Electronegativity decreases down the table
How does hydrolysis occur in terms of polarity ?
The electron deficient C
attracts nucleophilesHalogenoalkanes react with these nucleophiles in substitution reactions
Nucleophiles replace The halide to form a compound with a different functional group
What is Bond Enthalpy ?
The amount of energy required to break 1 mol of a covalent bond
What is the trend in Bond Enthalpy of the halogen group bonded to carbons ?
Bond Enthalpy decreases down the table
What is the relationship between rate of hydrolysis and Bond Enthalpy ?
As Bond Enthalpy decreases , the rate of hydrolysis increases
What is the relationship between rate of hydrolysis and polarity ?
As polarity increase , the rate of hydrolysis increases
What is the most important factor in determining the rate of hydrolysis ?
Bond Enthalpy