PS1101 HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:19 PM on 1/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
1
New cards
Evolutionary psychology
the discussion of the environmental pressure that humans may have had to adapt to and whether our psychological mechanisms were designed in a way which would have enabled us to overcome these pressures
2
New cards
historical background 1
behaviourism - complete denial of any innate influence on our behaviours
* whatever our psych competence is, is from what experiences we have been through
* we have general mechs based on associations, s-r bonds
* -we have general mechs based on associations, s-r bonds
* whatever our psych competence is, is from what experiences we have been through
* we have general mechs based on associations, s-r bonds
* -we have general mechs based on associations, s-r bonds
3
New cards
historical background 2
ethology
* reaction to environmentalism and behaviourism.
* more of a description of behaviour rather than an explanation
* reaction to environmentalism and behaviourism.
* more of a description of behaviour rather than an explanation
4
New cards
phenotype
set of behaviour and physical traits of an adult individual
5
New cards
gene
single, unbroken unit of inheritance
6
New cards
genotype
the genetic make up of a individual
7
New cards
fitness
the measure of relative reproductive success/ the no. of genes transmitted from one generation to another
8
New cards
theory of E by natural selection
based on 4 principles which have to be present for a particular behaviour to evolve through evo by natural selection
* principle of variation : refers to phenotype
* principle of inheritance: traits have to be transmittable by inheritance, doesn't need to be DNA based eg cultural transmission
\
* principle of variation : refers to phenotype
* principle of inheritance: traits have to be transmittable by inheritance, doesn't need to be DNA based eg cultural transmission
\
9
New cards
theory of E by natural selection 2
\-principle of adaptation : due to pop growth + competition for scarce resources. if someone has the traits which allow them to get the best resources--> more likely to survive + reproduce as a result of it
\-principle of evolution : relies on fitness, ppl who transmit needed traits for survival are more likely to reproduce.
\-principle of evolution : relies on fitness, ppl who transmit needed traits for survival are more likely to reproduce.
10
New cards
-principle of evolution : relies on fitness, ppl who transmit needed traits for survival are more likely to reproduce.
11
New cards
theory of E by sexual selection
- some behaviours evolved not as a result of their survival function but because they give more access to mates.
12
New cards
-intrasexual selection- based on males fighting w each other in order to prevent rivals from any access to female mates
13
New cards
- intersexual selection- if the feature is more likely to attract a mate eg between males and females
14
New cards
CASUSES OF BEHAVIOUR IN TERMS OF DIFF LVLS OF EXP
15
New cards
Proximate (lowest level)
immediate motives for behaviour
16
New cards
Ontogenetic/developmental
how behaviour is acquired through a lifespan eg the mother learned in her lifetime, through other mothers, that a way to soothe a crying baby is to feed them
17
New cards
Phylogenetic / historical
how behaviour is acquired through the development of species through history…eg changes from egg lying ancestors to mammalian species
18
New cards
Ultimate/functional level
how behaviour contributes to an individual's level of fitness eg mother increases survival chances of child carrying their genes
19
New cards
KEY CONCEPTS (david buss 2004)
20
New cards
Adaptations
inherited characteristics, which overcame environmental pressures, that developed through evolution to help survival or reproduction
21
New cards
by-products
characteristics that do not solve survival problems but come with adaptive factors (side effects) eg the whiteness of bones- its not an advantage, jus white cuz of calcium (happens to be white) which makes the bones stronger
22
New cards
Noise
random effects and chance mutations when sudden environmental changes cause chance effects with no specific functions.
23
New cards
criteria for identifying an adaptive trait
3 things, r, e and e
24
New cards
Reliability
does it develop in all members of a particular species
25
New cards
Efficiency
does it solve the adaptive problem well
26
New cards
economy
does it solve the adaptive problem without many other costs eg predatory attention
27
New cards
EEA
Environment of Evolutionary Adaptedness- selection pressures occurring when an adaptation emerges- psychological mechs are not always producing adaptive behaviour in modern society…. to do ow current environment
28
New cards
the problem of altruism
altruism- our desire to help others. but evo theory is about us needing to be selfish in order to survive
\
\
29
New cards
how do evolutionary approaches explain this
2 theories- kin selection and reciprocal altruism
30
New cards
kin selection theory 1
* helps gene survival
* shift from the individual to the gene as a unit of fitness
* important because we share our genes with our offspring and our relative (direct and indirect fitness) to maximize the no of genes which get passed on to the next generation
* this explains why we may favour some more than ourselves when it comes to giving help
* shift from the individual to the gene as a unit of fitness
* important because we share our genes with our offspring and our relative (direct and indirect fitness) to maximize the no of genes which get passed on to the next generation
* this explains why we may favour some more than ourselves when it comes to giving help
31
New cards
kin selection theory 2
altruism gene evolves whenever rB > C (the coefficient of relatedness multiplied by the benefits is greater than the costs) even if we lost offspring.
32
New cards
Reciprocal Altruism Theory
* this theory explains why we offer help to non kin
* short-term loss to the helper means that they are owed a favour in return, which could be helpful for them in the future
* this requires the complex cognitive ability to tell ppl apart and remember who owes you what
* there is risk of trust because if cheated up there will be a huge loss
* therefore we have also evolved the mechs which enable us to identify and stop cheating
* short-term loss to the helper means that they are owed a favour in return, which could be helpful for them in the future
* this requires the complex cognitive ability to tell ppl apart and remember who owes you what
* there is risk of trust because if cheated up there will be a huge loss
* therefore we have also evolved the mechs which enable us to identify and stop cheating
33
New cards
cognition : modularity
the idea that each part of the mind is modularised - relates to phrenology
34
New cards
fodor ‘83
our sensory system is modularised and domain specific but our thinking and logic is domain general
35
New cards
Karmiloff-Smith ’96
modularisation develops as time goes on, there are some moments in time where there is more modularisation than others but again higher cognition is domain general
36
New cards
tooby and comides (2000)
swiss army knife model of cognition - there are particular tools which are designed to solve particular problems and if u were to try and use these mechs on another part of the mind, it wouldnt work as well. he thought modularity applied to all forms of cognition, including higher ones
37
New cards
cognition: cheater detection 1
wason selection task ‘66 and ‘83
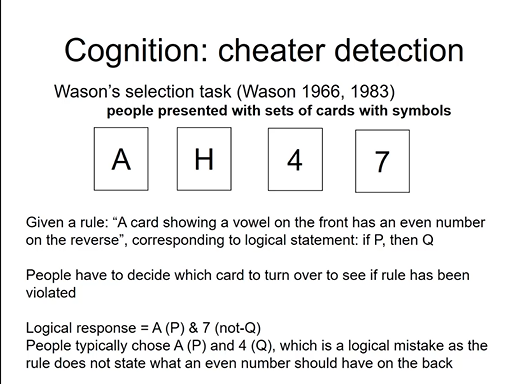
38
New cards
cognition: cheater detection 2
cosmides and tooby ‘92
