biology review
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Cell prepares for mitosis
G2 phase
Centrosomes duplicated
S phase-to ensure each daughter cell daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes
ATP increased
G1- increase during the cell cycle provide energy for various cellular processes
Cytoplasm division
Cytokinesis- to form two separate daughter cells
DNA replication
S phase- ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material
Nuclear division
M phase- resulting in the separation of chromosomes and the formation of two new nuclei
Cell prepares for DNA replication
G1 phase- when the cell prepares for DNA replication by accumulating necessary enzymes and nucleotides
G1/S checkpoint
serves to prevent cells from entering S-phase in the presence of DNA damage and functions to inhibit the initiation of replication
G2/M checkpoint
prevents DNA-damaged cells from entering mitosis and allows for the repair of DNA that was damaged in late S or G2 phases prior to mitosis.
M checkpoint
whether all sister chromatids are correctly attached to the spindle microtubules that separate them.
Is cyclin a positive or negative regulators of the cell cycle
Positive
Cdks positive or negative regulators of the cell cycle?
Positive
P53 positive or negative regulators of the cell cycle?
Negative
P21 positive or negative regulators of the cell cycle?
Negative
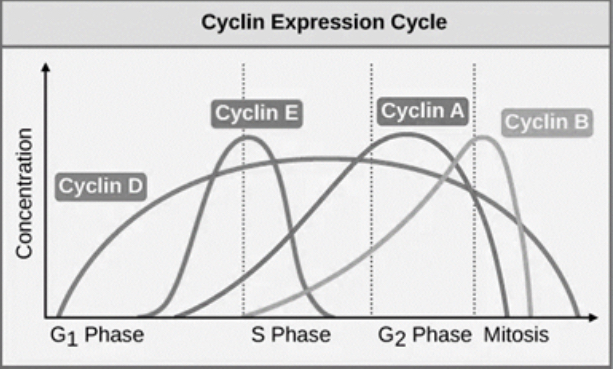
Which cyclin is important for the G2 to mitosis transition?
Cyclin B- levels are high during the G2 phase and mitosis, which is essential for the G2 to mitosis transition.
What happens after the cyclin-cds complex is phosphorylated by kinase?
Becomes fully active, allowing it to phosphorylation target proteins that promote cell cycle progression
DNA damage is detected at G1
What protein becomes active? What does it do?
p53 becomes active and initiates cell cycle arrest and DNA repair
Which cellular structure generates mitotic spindles?
Centrosome is the primary structure that organizes the mitotic spindle during cell division.
Which cellular structure is made of microtubule fibers and moves chromosomes?
Mitotic spindle- itself is made of microtuble fibers and is responsible for moving chromosomes during cell division
Which cellular structure links chromosomes to mitotic spindles?
Kinetochore- protein structure on chromosomes that attaches them to the mitotic spindle
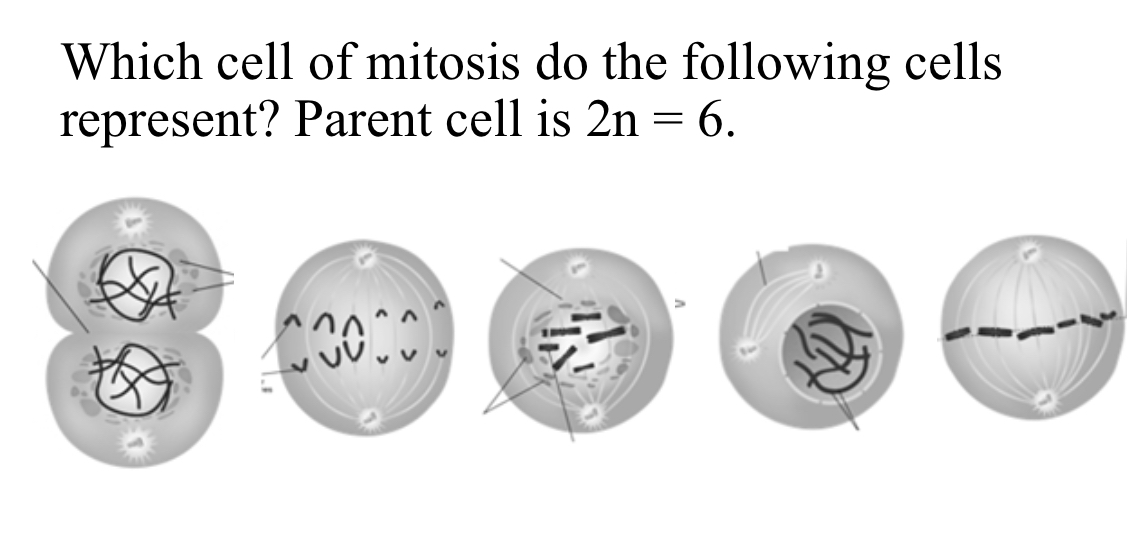
Which cell of mitosis do the following cells represent? Parent cell is 2n=6
Cytokinesis, Anaphase, Prophase, and Telophase
In which stage of mitosis does sister chromatids separate?
Anaphase
In which stage of mitosis does chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell?
Metaphase
In which stage of mitosis does centrosomes migrate to opposite ends of the cell?
Telophase
In which stage of mitosis does the nuclear envelope reforms?
Telophase
In which stage of mitosis does mitotic spindles attach to chromosomes, moving them towards the middle of the cell?
Prometaphase
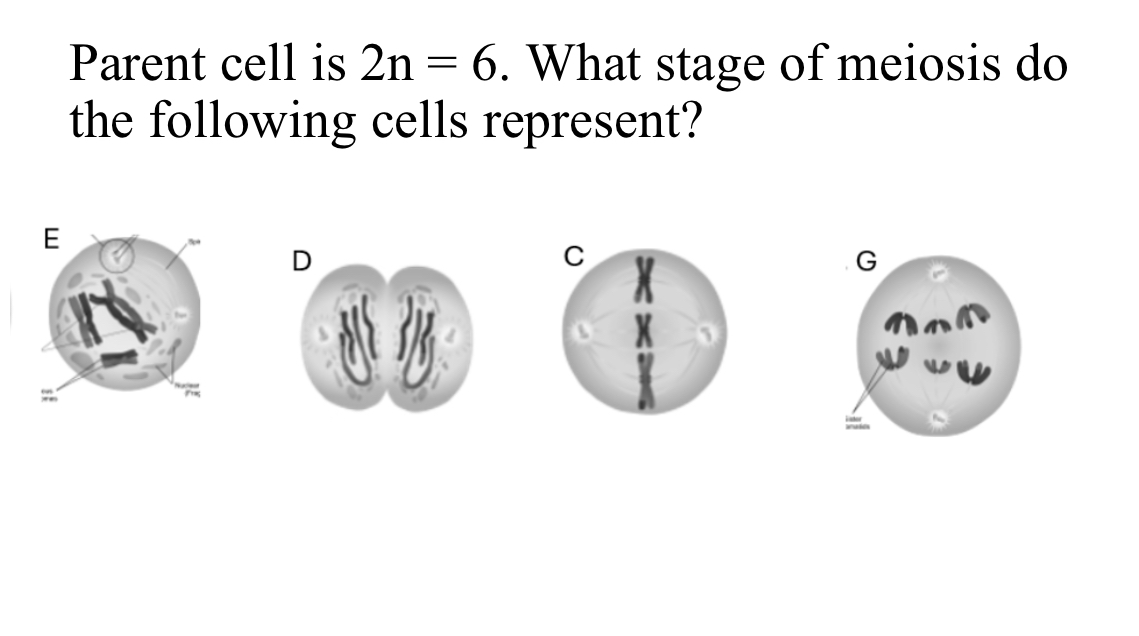
Prophase I, telophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II
What stage of meiosis does sister chromatids separate ?
Anaphase II
What stage of meiosis does homologous chromosomes separate?
Anaphase I
What stage of meiosis does chromosomes line up individually in the middle of the cell?
Metaphase II
What stage of meiosis does homologous chromosomes paired up in the middle of the cell ?
Metaphase I
What stage of meiosis does crossing over occur ?
Prophase I
What stage of meiosis does independent assortment occur ?
Metaphase I
Which statement best describe non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes exchange DNA
Crossing over
What process statements best describe homologous pairs of chromosomes line up independently of one another?
Independent assortment
Results in four daughter cells
Meiosis
2n =8 to n = 4
Meiosis
One round of division
Mitosis
Daughter cells genetically identical
Mitosis
Produced haploid cells
Meiosis
Occurs in somatic cells
Mitosis
AA x aa
Homozygous
Aa x Aa
Monohybrid cross
A_ x aa
Test cross
AaBb x AaBb
Dihybrid cross
Gamete genotypes and their probabilities ?
Aa
A ½ , a ½
Gamete genotypes and their probabilities from?
AaBb
AB ¼ , Ab ¼ , aB ¼ , ab ¼