Understanding Phylogenetics and Cladograms
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Fossil Record
The collection of all fossils that have been discovered across the entire Earth.
Significance of Fossil Record
The fossil record shows gradual changes in the skeletons of organisms, giving us a picture of how species have changed over time.
DNA Sequences
The order of bases that appear in a sequence for a specific protein.
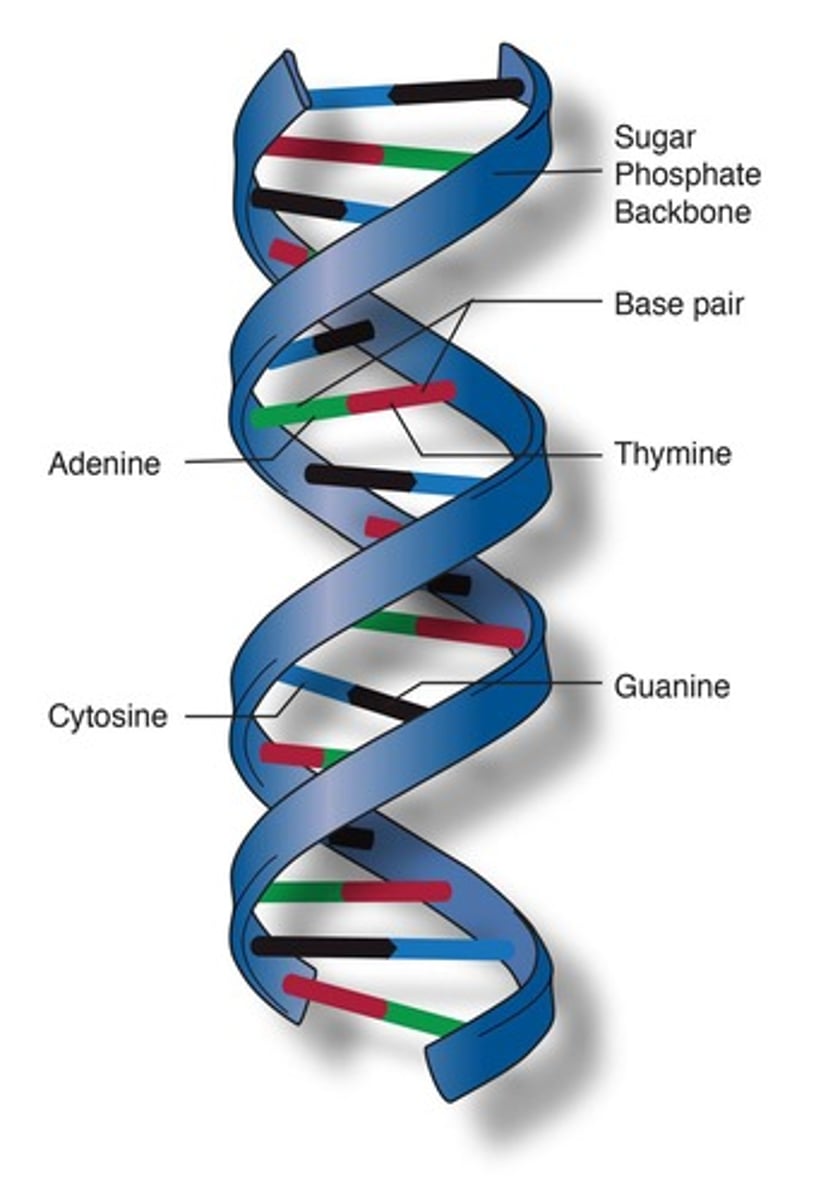
Significance of DNA Sequences
Species that are closely related to each other have DNA sequences for proteins that are almost identical! The more closely related two species are, the fewer differences they have in their DNA sequences.
Comparative Anatomy
The comparison of physical structures of organisms.
Significance of Comparative Anatomy
Identify common ancestry based on similarities and differences of physical structures.
Comparative Embryology
The comparison of the embryological development of species.
Significance of Comparative Embryology
Reveals similarities in development not seen in fully developed adults.
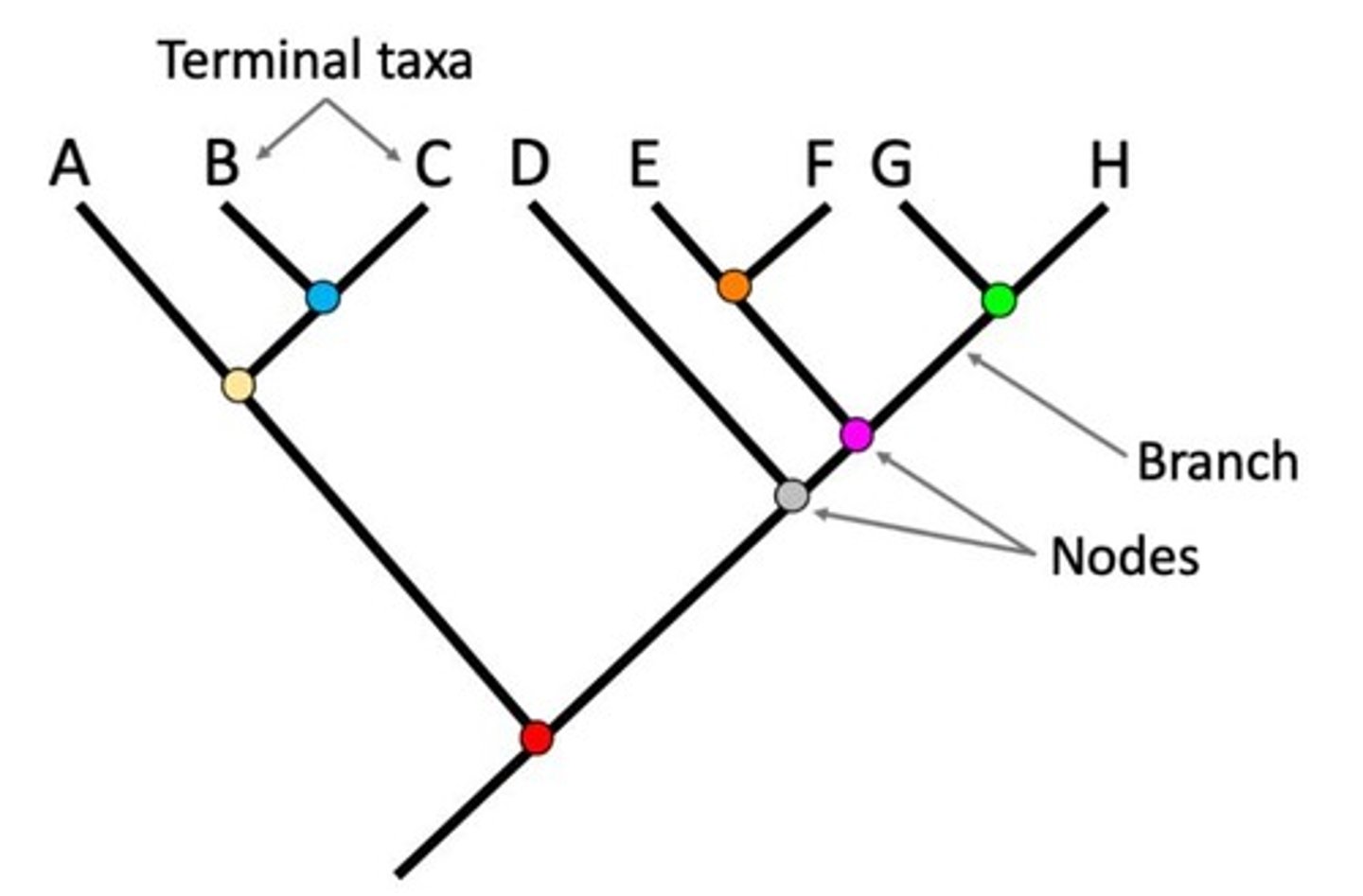
Phylogenetic Trees
A visual representation of common ancestry and evolution.
Significance of Phylogenetic Trees
Shows how closely organisms are related to each other and when different traits evolved throughout life history.
Node
Represents the last common ancestor for all species that evolved after that node.
Branch
Shows evolution of different species after a specific node.
Homologous Structures
Structures that are similar in different species due to shared ancestry.
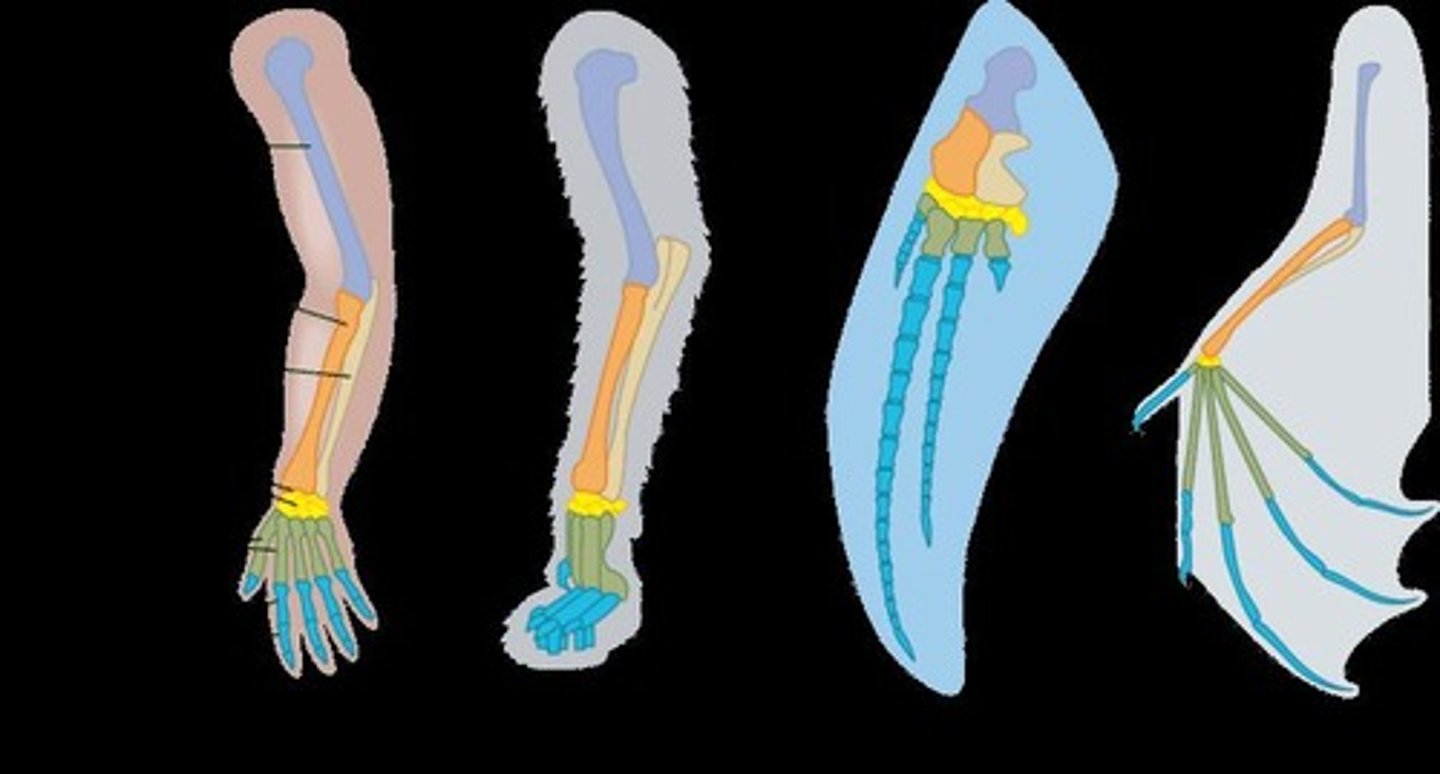
Analogous Structures
Structures that serve similar functions but evolved independently in different species.
Vestigial Structures
Structures that have lost most or all of their original function through the course of evolution.
Driving Question
How do the fossil record, anatomical structures, and DNA evidence support the theory of evolution?
Check for Understanding
Questions to assess comprehension of cladograms and phylogenetic trees.
Cladogram
A diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among various biological species based on similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics.
Common Ancestry
The concept that different species share a common ancestor from which they evolved.
Evidence of Evolution
Data and observations that support the theory of evolution, including fossil records, DNA sequences, and comparative anatomy.
Phylogenetics
The study of evolutionary relationships among biological entities, often using a phylogenetic tree.
Amino Acid Differences
Variations in the sequence of amino acids in proteins that can indicate how closely related different species are.
Exit Ticket
An assessment tool used to gauge students' understanding of the day's lesson.