Week 2 - Bacteria
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Magnetostatic bacteria
Use magnets formed from iron in the environment to navigate underwater, using Earth’s magnetic fields. An example of prokaryotes with membrane-bound organelles (magnetosomes)
Spherical bacteria
Coccus/cocci
Rod-shaped bacteria
Bacillus/bacilli
Comma-shaped bacteria
Vibrio/vibrios
Spiral bacteria
Spirillum/spirilla
Pleiomorphic bacteria
Varied shapes of bacteria
Hyphae
Branching filaments of cells
Mycelia
Tufts of hyphae
Trichomes
Smooth, unbranched chains of bacteria
Size of prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
Bacteria are typically 0.5 to 5 um in length, while eukaryal cells are bigger. Bacteria have extensive size variation
3 multicellular arrangements of bacteria
Diplo: pairs of cells
Strepto: chains of cells
Staphylo: clusters
Nucleoid (composition + function)
Composed of DNA, RNA, and protein, in bacterial cytoplasm
Stores genetic info, coated with proteins and RNA being synthesized
Chromosome-packaging proteins (composition + function)
Composed of protein, in bacterial cytoplasm
Protects and compacts DNA
Enzymes involved in DNA and RNA synthesis (composition + function)
Composed of proteins, in bacterial cytoplasm
Transcription
Regulatory factors (composition + function)
Composed of proteins and RNA, in bacterial cytoplasm
Control replication, transcription, and translation
Ribosomes (composition + function)
Composed of RNA and proteins, in bacterial cytoplasm
Translation
Plasmid (composition + function)
Composed of DNA, in bacterial cytoplasm
Encode non-chromosomal genes, extra pieces of DNA
Enzymes that break down substrates (composition + function)
Composed of proteins, in bacterial cytoplasm
Produce energy, provide anabolic precursors
Inclusion bodies (composition + function)
Composed of various polymers, in bacterial cytoplasm
Store carbon, phosphate, nitrogen, and sulfur
Gas vesicles (composition + function)
Composed of proteins, in bacterial cytoplasm
Maintain buoyancy, letting the cell float up or down
Magnetosomes (composition + function)
Composed of proteins, lipids, and iron, in bacterial cytoplasm
Orient the cell during movement (navigation), form long chains organized by protein filaments
Cytoskeletal structures (composition + function)
Composed of protein, in the cytoplasm
Guides cell wall synthesis and division, maintains cell shape
Polyhydroxybutyrate granules
Type of inclusion body for carbon storage. Can compose over 50% of a cell’s dry weight
Sulfur globules
Type of inclusion body for sulfur storage
Carboxysomes
Location of carbon fixation reactions (photosynthesis), in bacterial cytoplasm
Method that bacteria store large chromosomes
Supercoiling DNA in the nucleoid
FtsZ
Cytoskeleton, tubulin-related protein
Forms the Z-ring which contracts to pinch the cell in two as FtsZ breaks down
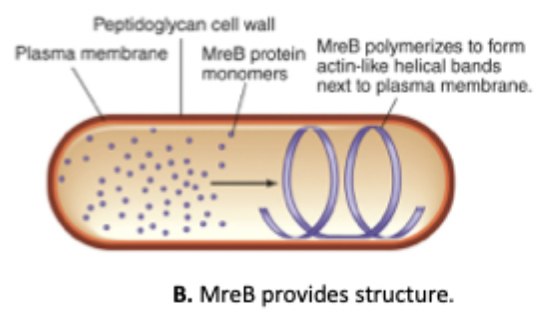
MreB
Cytoskeletal, actin-like protein
Provides structure in non-spherical bacteria by guiding cell wall synthesis and forming long helical filaments under the membrane
ParM
Cytoskeletal protein
Directs plasmid movement, ensuring plasmid segregation
MamK
Cytoskeletal, actin-like protein
Required for magnetosome function, which will disappear if MamK is mutated
FtsZ is to microtubules as MreB is to…
Microfilaments
Plasma membrane (PM)
Composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins
Separates the interior of the cell from the environment
Hopanoids
Sterol-like molecules in the PM, help with stability across temperature ranges
Hopanoids vs cholesterol
Hopanoids are abundant in prokaryotes while cholesterol is abundant in eukaryotes
Diffusion
Small gases like O2 and CO2 can diffuse across the cell membrane readily
Osmosis + related protein
The movement of water across a plasma membrane from low to high solute concentration, often through aquaporins
How do bacterial cells withstand pressure from osmosis?
Having a strong cell well to maintain shape
Facilitated diffusion
Using a protein channcel to move particles along a concentration gradient
Active transport
Using ATP/energy to move particles against a concentration gradient
Symport/antiport
Active co-transporters where two substances are either moved in the same direction or opposite directions
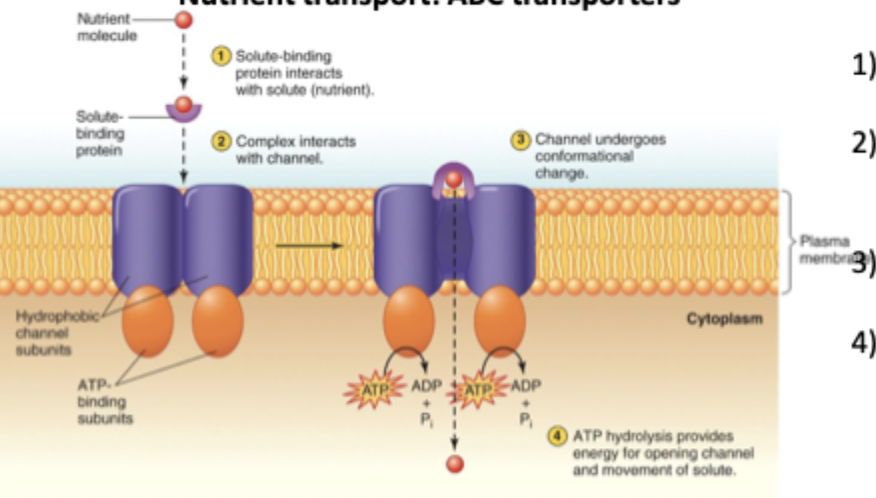
ABC transporters (4 steps)
ATP binds to these proteins to transport materials across a membrane
Binding protein grabs the solute of interest outside the cell
Binding protein delivers the solute to the ABC transporter
Transporter changes shape and opens a channel
ATP hydrolysis powers the opening/closing cycle
Electron transport chains (ETC)
Embedded in the PM, create energy (proton motive force, PMF)
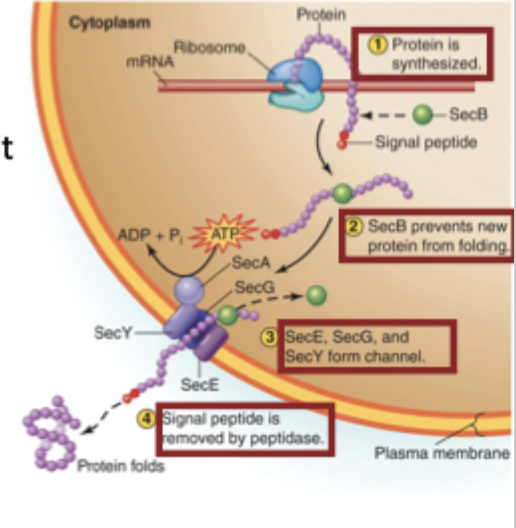
Protein secretion in the PM (4 steps)
Signal peptide marks proteins that the cell needs to secrete
SecB binds and keeps the protein unfolded
SecA uses ATP to push the protein through the SecYEG membrane channel
Once outside the membrane, the signal peptide is cut off, and the protein folds
Bacterial cell wall composition + function
Crosslinked strands of peptidoglycan subunits (NAM and NAG), giving cells their shape and protecting them from osmotic lysis
NAM vs NAG
NAM has a small peptide chain attached, which varies by species (the way they’re crosslinked can also vary)
Why are the amino acids associated with NAM unusual?
They appear in the D form of the molecule (the less common stereoisomer) instead of the L form
Formation of the cell wall (6 steps)
NAM is linked to a peptide in the cytoplasm
NAM-peptide attaches to bactoprenol in the membrane
NAG is added, forming the NAM-NAG unit
Bactoprenol flips the NAM-NAG unit across the membrane
The unit is added to the growing cell wall and transpeptidase crosslinks the peptides
Bactoprenol flips back to pick up the next unit
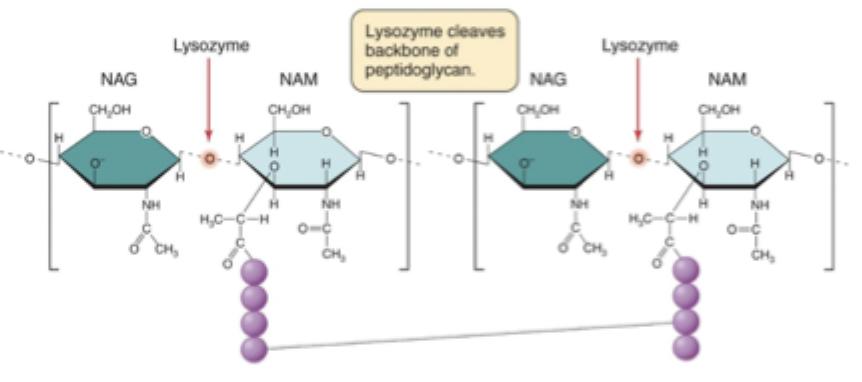
Lysozyme
Breaks the NAM-NAG B-1,4 glycosidic bond, degrading the cell wall
Lysostaphin
Cuts the glycine-glycine link in the peptidoglycan cross-bridge, causing the cell to round up into a protoplast and degrade the cell wall.
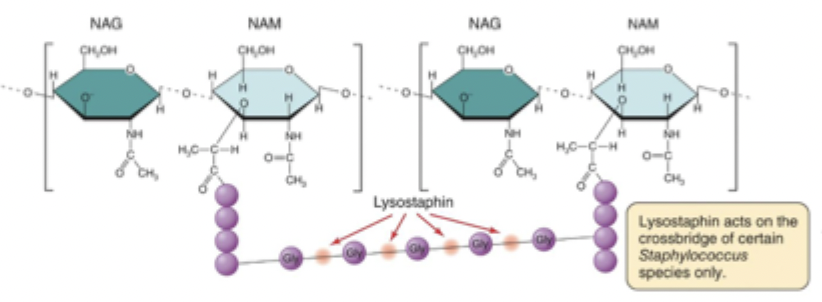
B-lactam antibiotics
Prevent the transpeptidation reaction during peptidoglycan synthesis, degrading the cell wall (ex. penicillin)
Antibiotic resistance + prevention
Bacteria produce an enzyme that destroys B-lactam, preventing cell wall degradation. Prevented by adding a second drug that inhibits the enzyme
Gram positive cells
One thick outer membrane of peptidoglycan
Very narrow periplasmic space between the outer membrane and the inner plasma membrane
LTA + teichoic acids in the peptidoglycan
Stain purple
Gram negative cells
An outer membrane of LPS and a thin inner membrane of peptidoglycan
Varying-width periplasmic space
Stains pink/red
LPS composition
Lipid A
Core oligosaccharide
Side O chain
Harmfulness of LPS in gram negative cells
Lipid A induces strong inflammatory responses
Side O chain can vary dramatically to evade host immune responses + for variation
Entry of nutrients in gram positive vs negative bacteria
Gram positive: large pores in the peptidoglycan layer
Gram negative: porin and TonB proteins in the outer membrane, then active transport from the periplasmic space into the cytoplasm
Autotransporters
Proteins that move molecules from the periplasm to the outside of the cell
Type III Secretion System (T3SS)
Single-step transport system, molecular syringe that pushes proteins from the cytoplasm and injects them directly into host cells
Flagellar Assembly
Similar to T3SS components, build flagella by having flagellin subunits travel up the hollow flagellum + add to the tip of the structure
Single step transport systems
Materials never enter the periplasm. Includes T3SS and the flagellar system
Gram staining in gram positive vs. negative cells
Gram positive: alcohol decolouration shrinks the large pores in the outer membrane, locking in the crystal violet
Gram negative: alcohol strips the outer membrane lipids, losing the crystal violet stain
LPS (composition + location + function)
Composed of lipids and proteins
Located on outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria, Lipid A portion is embedded while Side O chain sticks out
Stabilizes membrane + elicits inflammatory response in the human body
Lipoteichoic acid (LTA) (composition + location + function)
Composed of lipids and proteins
Located in peptidoglycan layer of gram positive bacteria
Unknown function, elicits inflammatory response
Peptidoglycan (composition + location + function)
Composed of protein backbone crosslinked with NAM and NAG
Located in the outer membrane of gram-positive bacteria and the inner membrane in gram negative bacteria
Maintains shape and structure to cells
Porins (composition + location + function)
Composed of proteins
Embedded in gram-negative outer membrane
Forms pores that allow for diffusion
TonB-dependent receptors (composition + location + function)
Composed of proteins
Embedded in gram-negative outer membrane
Catalyze high-affinity active transport across the outer membrane
Flagella + distribution
Spiral, hollow, rigid filaments that help a cell move. Can be polar or peritrichous, and inside the periplasm or outside the cell
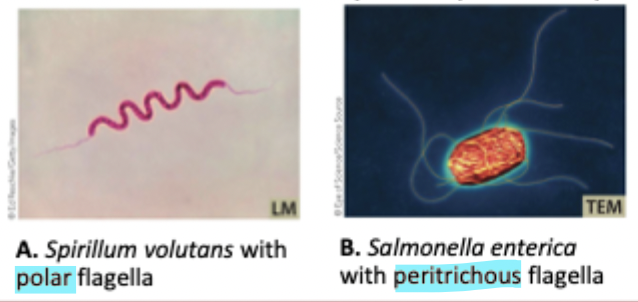
Convergent evolution and flagella
Flagella evolved independently in bacteria, archaea, and eukarya
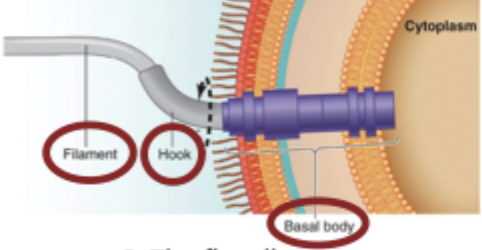
Structure of flagella
Filament: the long part of the flagella made of flagelin subunits, 5-10 um long
Hook protein: connects the filament to the basal body
Basal body: disk-like structure that wiggles the filament
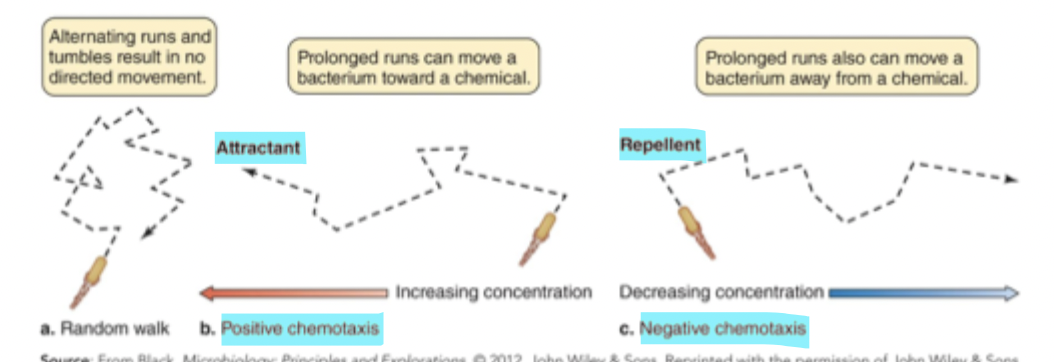
Types of movement from flagella
Powered by proton motive force (PMF), can either be directional (a run movement) or nondirectional (a tumble movement)
Chemotaxis
Directional movement of cells by using chemoreceptors to sense changes in concentrations of attractants (positive chemotaxis) or repellants (negative chemotaxis)
Gliding motility
Smooth sliding over a surface, common in cyanobacteria
Twitching motility
Slow, jerky movement using pilli that pull a cell along a surface
Actin-based motility
Cells invade a host cell, polymerize actin to form actin tails, and then propel themselves into adjacent host cells to invade
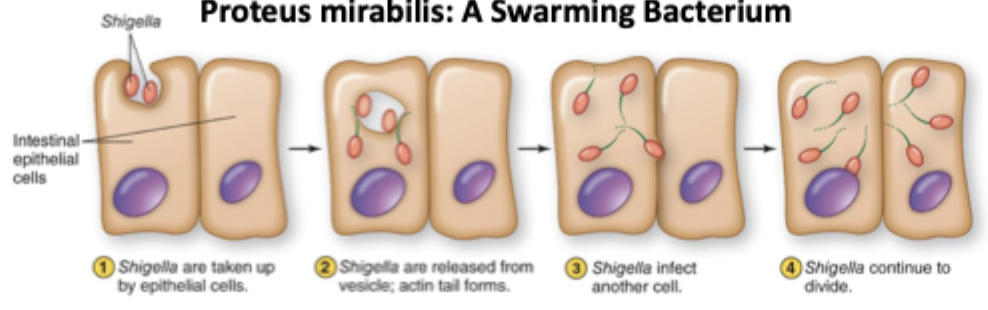
Adherence molecules
On the surface of bacteria, help them stick to surfaces using pilli or stalks
Sex pilus
Type of pilli used for conjugation (sending a DNA plasmid from one cell to another)
Pili vs fimbriae
Conjugation structures versus adherence structures
Horizontal gene transfer
Movement of DNA from one unrelated cell to another
Stalks
Adherence molecule, extension of the cell envelope tipped with sugar that provides extra surface area for the cell and adherence capability
Capsules
Thick layer of sugars surrounding some cells, providing adhesion, defence against host immunity, and resisting desiccation out via biofilms
Biofilms
A sticky film formed by bacterial capsules that gives cells protection, ex. dental plaque and mold on bathroom surfaces
Surface arrays (S-layers)
Cell armour against bacteriophages, crystalline array of interlocking proteins
Bacterial flagella
Powered by PMF
Grows at tip
Made of flagellin proteins
Archaeal flagella
Powered by ATP
Grows at base
Made of archaellins
Eukaryal flagella
Powered by ATP dynein motors
Assembled within the cytoskeleton
Made of microtubules
Species
Groups of strains sharing common features while differing considerably from other strains
Genus
Group of closely related species
Order of taxonomic groups from broad to specific + what group does bacteria exclude?
Domain > kingdom > phylum > class > order > family > genus > species. Excludes kingdom
Factors bacteria are classified using (6)
Cell morphology
Colony morphology
Growth characteristics
Biochemistry
Physiology
DNA sequence data
Why are bacterial phylogenies and taxonomic classifications revised so often?
New genomic data, better resolution, improved sequencing, more accurate phylogeny, whole-genome insights
Pseudomonadota (formerly proteobacteria)
Extremely diverse gram-negative phylum including:
Pathogens
Nitrogen fixers
Photosynthetic purple bacteria
Alphaproteobacterium - ancestor of mitochondria
Cyanobacteria
Photosynthetic bacteria that use light energy to split water, producing O2
Ancestors of chloroplasts
Culture collections
Newly classified microbes must be deposited in at least 2 culture collections, maintained by the World Federation for Culture Collections
Type strain
A reference specimen deposited in a culture collection
Binomial naming system
Bacteria are named using their genus followed by their species
B-lactamase
Produced by bacteria, destroys B-lactam antibiotics like penicillin
What do NAM and NAG stand for?
N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetylglucosamine
When carrying out the Gram stain procedure, adding too little or too much alcohol to the sample is a common mistake. Suppose at student added too little alcohol to a sample of Gram-negative bacteria. What would she observe? Why?
The bacteria would appear purple, since all the bacteria would be stained by the crystal violet dye. That’s because Gram-negative bacteria do not retain the stain due to their thin peptidoglycan layer. Therefore, using too little alcohol would not remove the stain.
What is the main function of peptidoglycan (cell wall)?
Protecting against osmotic stress
Conjugation
Transfer of DNA from one bacteria cell to another via a sex pilus