ME#3 money creation
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Assets side of CB balance sheet
Gold and currency reserves
Loans to banks
Loans to the government
Securities
Government bonds
Corporate bonds
Other securities
Liability side of CB balance sheet
▪ Cash in circulation (‘C’)
▪ Reserve accounts of banks (‘R’)
▪ Debt securities
▪ Government account
▪ Other liabilities
How is base money created
Central banks extend loans to commercial banks
CB buy securities from commercial banks/other institutions via a bank
Central bank buy foreign currencies from commercial banks
What’s money multiplier
relation btw monetary base and money in circulation
Some notes about the formula
either c or k increase → m decrease4
cashless society → m = 1/k
people wants all cash → k =1 → no money creation
Draw backs of money multiplier
strongly dependent on assumptions
much too mechanical in character
ignores demand side
ignores other sources of money creation:
banks buying assets from non-banks
cross-border transactions → changes in money supply
What's the difference btw monetary financing and QE
Monetary financing: CB creates new money (M0) to finance new gov spending (buy new gov bonds)
QE: only existing bonds are bought by CB
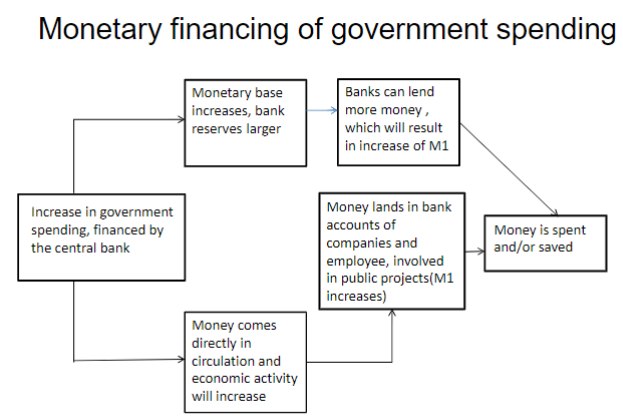
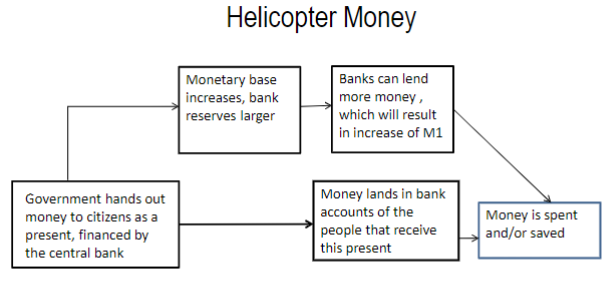
Differences btw monetary financing and helicopter money
helicopter money is given directly to people → less certain about if effectiveness
helicopter money takes effect immediately while monetary financing takes longer → helicopter money more effective in acute crisis
Pros of fractional reserve banking
flexible system
the money supply varies with the economy
money is created and destroyed on the initiative of the banks’ clients in the right amounts and in the right place in the economy
Cons of fractional reserve banking
Liquidity reserves < current accounts → all banks vulnerable for bank run (liquidity risk)
In normal times: banks with a liquidity shortage can finance themselves on the money market (borrowing from banks or other professional counterparts with cash surplus
If the money market as a whole has a liquidity shortage and/or a solvent bank has an acute liquidity shortage the central bank has to step in as ”lender of last resort” (LOLR)
Alternative system ?
full (liquidity) reserve banking
banks must cover their current liabilities with 100% liquid reserves
Bank lending has to be financed with savings that already exist
No money creation by commercial banks ==> government is given a monopoly for the creation of money
An independent government committee will announce ex-ante monetary targets
Pros of full reserve banking
Probability of a bank run (almost) fully eliminated
Liquidity risk for banks much smaller
Cons of full reserve banking
Depositors are forced to hold their savings in deposits with a longer maturity. Liquid savings should be held on an non-interest current account
(note that in today’s world this doesn’t make any difference)
Banks lose a source of income
It won’t work in a world with large cross-border financial flows
Government monopoly on money creation may be dangerous
Banks become more stable because the risks are to a large extent shifted to depositors.
It becomes more expensive to hold a bank account