Business 3.5
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is a budget?
A financial plan that forecasts revenue from sales and expected costs over a time period
What is a cash flow forecast?
It shows the movement of cash in and out of a business over a time period
Definition of cash flow?
The movement of cash into and out of a business over a period of time
Why is cash flow important?
If there is not enough cash flowing into and out if a business then it may be forced into liquidation even if it is profitable
What is the formula for contribution per unit (CPU)?
Revenue per unit - variable costs per unit
What is the formula for total contribution?
Contribution per unit x number of units sold
How do you calculate profit using total contribution?
Contribution - fixed costs
What is contribution?
The difference between sales revenue and variable costs of production
What is the formula for breakeven output?
Fixed costs / contribution per unit
Break even chart and labels
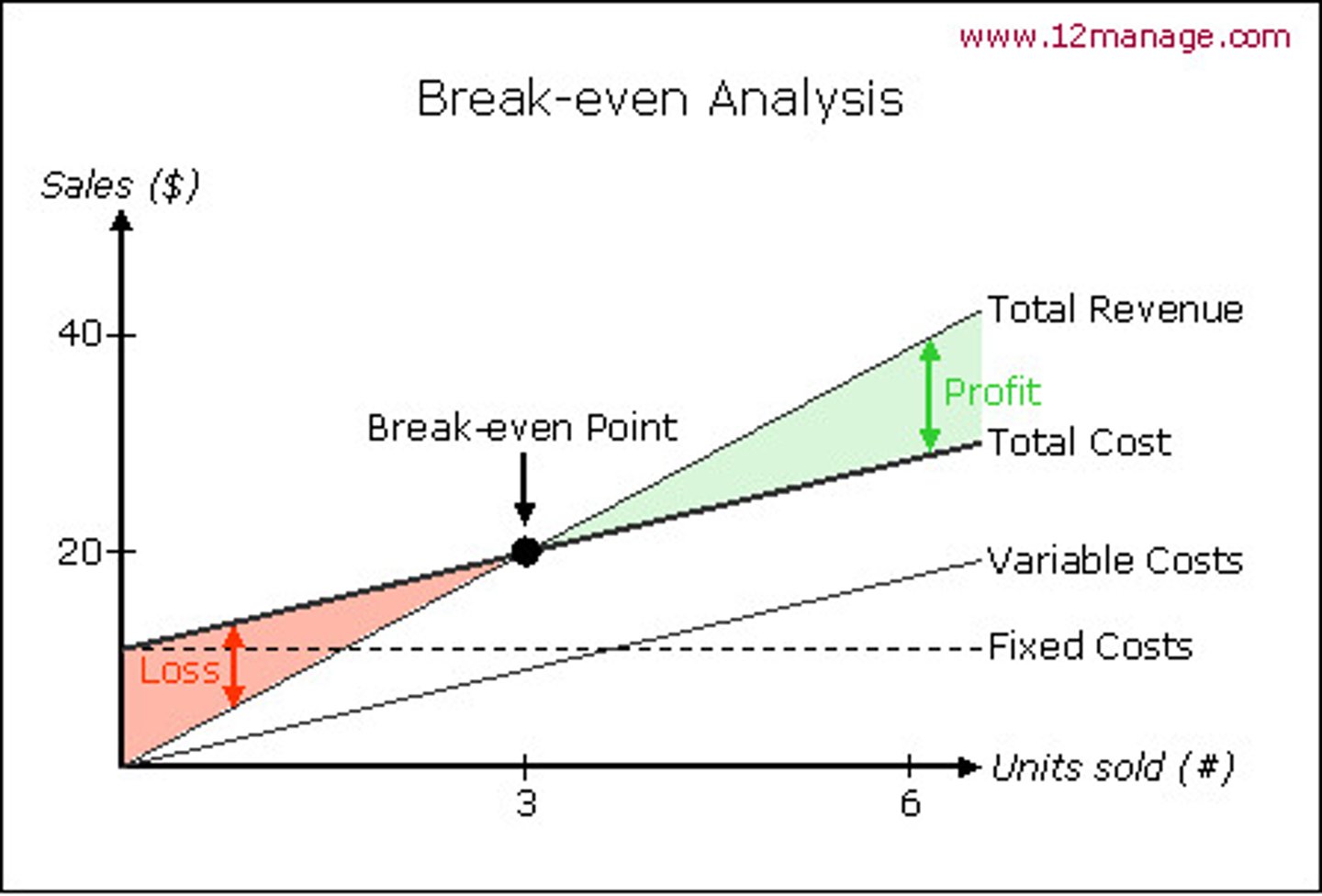
What is margin of safety?
The amount by which the existing level of output is greater than the break even point
What is variable costs?
Costs that change as output changes (e.g. raw materials, wages)
What are fixed costs?
Costs that do not vary with the quantity of output produced
What are total costs?
Fixed costs + variable costs
What is revenue for a business?
The total amount of money brought in by company's operations
How do you calculate revenue?
Price x Quantity
What is the selling price per unit?
The amount a customer pays for each unit bought
How do you calculate selling price per unit?
Total costs / number of units bought
What is variance analysis?
It shows the comparison between the budgeted figure and the actual figure achieved. This analysis helps identify any discrepancies and assesses their impact on financial performance.
What is the expenditure budget?
A sum of money to be spent at a given time period by a department of business
What is a budget holder?
A person who is accountable for seeing that a budget is kept to
What is income budget?
The sales revenue target for a department or whole new business during a specific time period. It outlines the expected income and plays a key role in financial planning.
What is the delegated budget?
Giving some control in the setting and spending of budgets to departments or individuals
What is profit budget?
The target profit for the business over a given period of time - this is created by combining expenditure and income budgets
What is it when you are monitoring budgets?
Keeping a check on progress towards achieving targets during the budget period
Why is budgeting important when financial planning?
To reduce costs
To make sure you are spending as much as you are earning
So the business doesn’t experience loses
Benefits of budgets?
It is required for lenders and investors
Increases staff performance so they can achieve objectives
Controls finances
Prevents risk of overspending
Drawbacks of budgeting?
Possible unexpected costs
Short term budget costs may lead to long term problems
Demotivated staff
Departments may compete for funding
What is favourable variance?
When the actual figure is better than the budgeted figure, resulting in an increase in profit or a reduction in costs.
What is adverse variance?
When the actual figure is worse than the budgeted figure
What could cause favourable variance?
Increase in demand
Revenue increase
Lower costs
What is zero budgeting?
A budgeting approach where all expenses must be justified for each new period, starting from a base of zero.
What is the benefit of analysing budgets?
Shareholder trust
Target levels will be met
Money is being spent on the correct items
Why is budgeting important for a business
Helps to allocate recourses efficiently
Improves financial control
Helps planning strategy
Makes sure financial goals are being met
What are financial objectives?
Capital structure objectives
Revenue objectives
Cost objectives (minimise them)
Profit objectives
Possible cash flow
Return on investment