SPLH 850: Cognitive-Linguistic Disorders of Adults | Final Exam
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Suppression Deficit Hypothesis
A theory that states that in RHD, the suppression of unwanted meanings is impaired
People with RHD can activate “distant” meanings, but then they can’t suppress the unwanted meanings (so multiple meanings are competing)
Example of Suppression Deficit
A topic is brought up, such as “coffee", and then the brain activates all things/memories related to that topic
Individuals with RHD can’t suppress what they don’t need to say or talk about in a conversation
Therefore, they typically say everything that comes to mind and have difficulty suppressing
Activation Deficit Hypothesis
Inefficiency or inability to activate “distant” meanings/features of words
Example of Activation Deficit
Indirect Approaches
Redundancy
Short/simple language
Reorienting implicitly
Talk slower than usual
Multimodal input
Limit number of conversational partners
Pleasant voice
Use proper nouns rather than pronouns
Reduce # of prepositions in a sentence
Not quizzing!
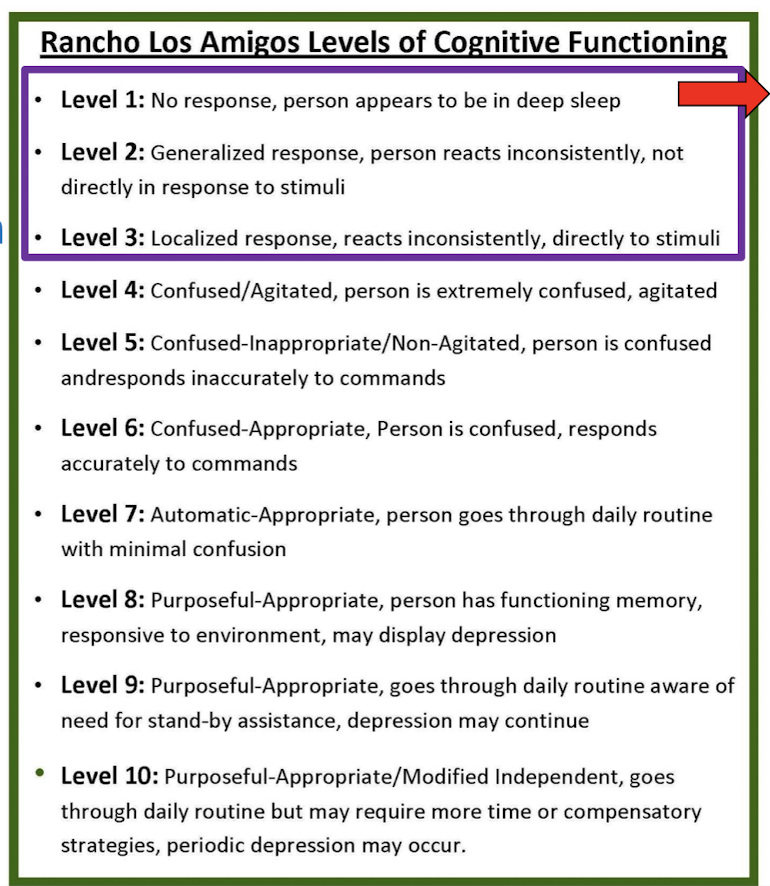
Rancho Los Amigos Scale (RLA)
Neuroanatomy of Attention Processing by Left and Right Hemispheres
Normal
Right hemisphere attends to both sides of space
Left hemisphere attends to only the right side of space
Right Hemisphere Lesion (Left Neglect)
Occurs when there is a Right CVA
Right hemisphere visual field stops working; therefore, the brain only processes objects in the right visual field (Not the left)
Left Hemisphere Lesion
Occurs when there is a Left CVA
Left hemisphere visual field stops working; however the right hemisphere can compensate, therefore, both the left and right visual fields process objects in both fields
Less common, less severe
Left neglect is…
NOT a vision deficit
Left neglect is…?
NOT denial
+Left neglect is…
Inattention to the side contralateral to the lesion
Why are computer-generated tasks and websites not recommended for therapy?
Research findings are that the patient gets better at their attention for the computer-generates TASK, not necessarily attention in general - it does not generalize!
Look at InterActAbility Training
Apply findings from non-treatment literature to your treatment needs
Coma
Consciousness: None
Sleep/Wake: Absent
Motor Function: Reflex and postural responses only
Auditory Function: None
Visual Function: None
Communication: None
Emotion: None
Vegetative State
Consciousness: None
Sleep/Wake: Present
Motor Function: Postures or withdraws to noxious stimuli; occasional non-purposeful movement
Auditory Function: Startle; brief orienting to sound
Visual Function: Startle; brief visual fixation
Communication: None
Emotion: None; reflexive crying or smiling
Minimally Conscious State
Consciousness: Partial
Sleep/Wake: Present
Motor Function: Localizes noxious stimuli; reaches for objects; holds or touches objects in a manner that accommodates size and shape; automatic movements (e.g., scratching)
Auditory Function: Localizes sound location; inconsistent command following (evidence of language functioning)
Visual Function: Sustained visual fixation; sustained visual pursuit
Communication: Contingent vocalization; inconsistent but intelligible verbalization or gesture
Emotion: Contingent smiling or crying
DoC - What to do next and why?
Using Literature from Other Populations
1) Is my patient sufficiently similar?
2) Is the nature of my client’s cognitive impairment similar?
3) Are there coexisting cognitive impairments that may interfere?
4) Is it feasible to apply the intervention in my setting?
5) What are the expected benefits and costs of this treatment?
6) Is the treatment consistent with the patient’s own preferences, values, and expectations?
Goal Attainment Scale
+2: Much better than the expected outcome
+1: Better than expected outcome
0: Expected outcome
-1: The patient’s current level of functioning
-2: Lower than the patient’s current level of functioning