exph comps exam review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/291
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
292 Terms
1
New cards
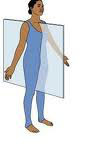
sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
2
New cards
sagittal plane movements:
flexion, extension, hyperextension, dorsi/plantarflexion
3
New cards
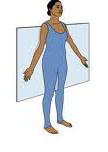
frontal plane
Divides the body into front and back portions.
4
New cards
frontal plane movements:
abduction, adduction, lateral flexion, elevation, depression, inversion, eversion, radial and ulnar deviation
5
New cards
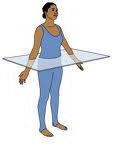
transverse plane
horizontal division of the body into upper and lower portions
6
New cards
transverse plane movements:
left and right rotation, medial and lateral rotation, supination and pronation of forearm, horizontal abduction and adduction of shoulder
7
New cards
interia
The tendency of an object to resist a change in motion
8
New cards
force
A push or a pull
=ma
=ma
9
New cards
weight
A measure of the force of gravity on an object
=mg
=mg
10
New cards
pressure
Force per unit area.
=force/area
=force/area
11
New cards
density
=mass/volume
12
New cards
torque
a twisting force
=Fd
=Fd
13
New cards
impulse
=Ft
14
New cards
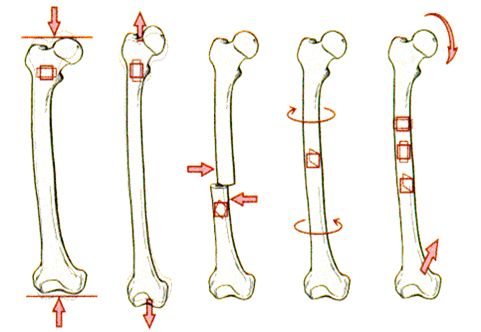
compression
pressing or squeezing force directed axially through a body
15
New cards
tension
pulling or stretching force directed axially through a body
16
New cards
shear
force directed parallel to a surface
17
New cards
stress
distribution of force within a body, quantified as force divided by the area over which the force acts
18
New cards
torsion
load producing twisting of a body around its longitudinal axis
19
New cards
bending
asymmetric loading that produces tension on one side of a body's longitudinal axis and compression on the other side
20
New cards
cortical bone
-made of calcium carbonate and calcium phosphate
-low porosity bone material found in the shafts of long bones
-low porosity bone material found in the shafts of long bones
21
New cards
trabecular bone
-made of organic material
-less compact bone with high porosity; found in the ends of long bones and the vertebrae
-less compact bone with high porosity; found in the ends of long bones and the vertebrae
22
New cards
longitudinal bone growth
occurs at epiphyseal plate
23
New cards
circumferential growth
long bones grow in diameter at the internal layer of the periosteum
24
New cards
bone modeling
formation of new bone that is not preceded by resorption
the process by which immature bones grow
the process by which immature bones grow
25
New cards
Osteoblasts
bone forming cells, stimulated by biomechinal loads
26
New cards
bone remodeling
resorption of fatigue-damaged older bone and subsequent formation of new bone
27
New cards
osteoclasts
break down bone/resorb old bone
28
New cards
bone atrophy
decrease in bone mass resulting from a predominance of osteoclast activity
29
New cards
osteopenia
reduced bone mineral density
30
New cards
Osteoporosis
decreased bone mass and strength with one or more resulting fractures
health prob for elderly, women more then men
health prob for elderly, women more then men
31
New cards
female athlete triad
1. disordered eating/energy deficieny
2.amenorrhea/oligomenorrhea
3. osteoporosis
-can cause irreversible bone loss to death
2.amenorrhea/oligomenorrhea
3. osteoporosis
-can cause irreversible bone loss to death
32
New cards
greenstick fracture
incomplete, break occurs on the convex surface of the bend in the bone
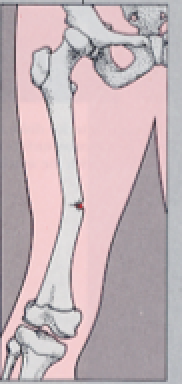
33
New cards
fissured fracture
incomplete longitudinal break
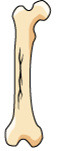
34
New cards
comminuted fracture
complete fracture that fragments the bone
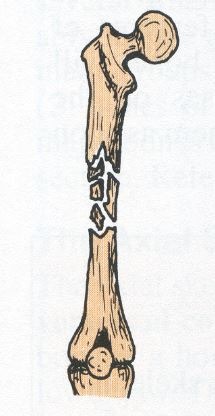
35
New cards
transverse fracture
complete fracture that is straight across the bone at right angles to the long axis of the bone
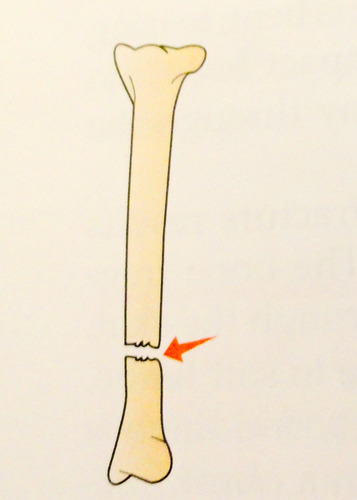
36
New cards
oblique fracture
occurs at an angle other than a right angle to the axis of the bone
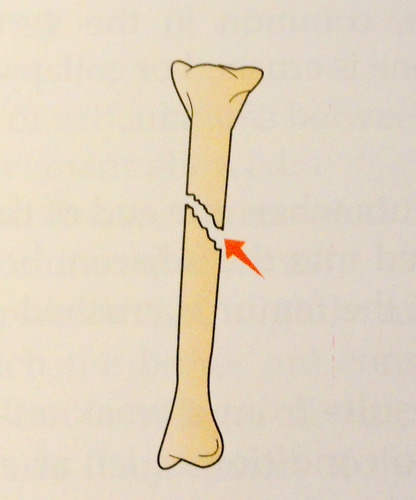
37
New cards
spiral fracture
caused by twisting a bone excessively
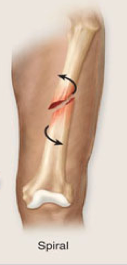
38
New cards
synarthroses
fibrous joints that can absorb shock but immoveable
ex: sutures in skull, mid-radioulnar and tibiofibular jts
ex: sutures in skull, mid-radioulnar and tibiofibular jts
39
New cards
Amphiarthrosis
cartilaginous joint having some movement at the union of two bones
ex: synchondroses (epiphyseal plates before ossification), symphyses (vertebral jts)
ex: synchondroses (epiphyseal plates before ossification), symphyses (vertebral jts)
40
New cards
Diarthroses (synovial joints)
articulating bone surfaces are covered w articular cartilage and incapsulated by a synovial membrane filled w synovial fluid
41
New cards
types of synovial joints
gliding- inter carpal and itnertarsal
hinge- interphalangeal jts
pivot- prox/distal radioulnar jts
condyloid- 2-5th metacerpophalageal
saddle- carpometacarpal jt of thumb
ball and socket- glenohumeral
hinge- interphalangeal jts
pivot- prox/distal radioulnar jts
condyloid- 2-5th metacerpophalageal
saddle- carpometacarpal jt of thumb
ball and socket- glenohumeral
42
New cards
force-velocity relationship
As velocity of contraction increases, the force it is able to exert decreases
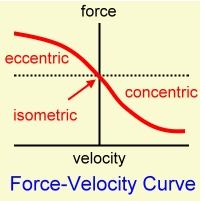
43
New cards
What are the initial gains(first 6-8 weeks) in strength and power due to?
nervous system adaptations after muscle hypertrophy
44
New cards
what kind of athletes will benefit from concurrent training?
aerobic athletes by adding strength training
45
New cards
will weightlifters or powerlifters have more adverse affects from concurrent training?
weightlifters
46
New cards
ergogenic aids
any procedure or aid used to enhance performance
nutritional- creatine
mechanical- clothing
psychological- hypnosis, mental rehersal
pharmacological- anabolic steroids
physiological- ice baths, massage
biomechanical- changes in technique
nutritional- creatine
mechanical- clothing
psychological- hypnosis, mental rehersal
pharmacological- anabolic steroids
physiological- ice baths, massage
biomechanical- changes in technique
47
New cards
General Warm-Up
Low intensity exercise consisting of movements that do not necessarily relate to the more intense exercise that is to follow
48
New cards
Specific Warm-Up
Low intensity exercise consisting of movements that mimic those that will be included in the more intense exercise that is to follow
49
New cards
Should flexibility stretching be done for a warm up?
no
50
New cards
static stretching
a technique in which a muscle is slowly and gently stretched and then held in the stretched position
51
New cards
dynamic stretching
technique in which muscles are stretched by moving joints slowly and fluidly through their range of motion in a controlled manner; also called functional stretching
52
New cards
PNF stretching
requires a partner for assistance. It combines stretching with alternating contracting and relaxing of muscles
53
New cards
The ______ the cross-sectional area of a muscle the more force that muscle can generate.
larger
54
New cards
What does aerobic training compromise?
Muscle fiber hypertrophy because of the high volume loads
55
New cards
fat cals per gram
9
56
New cards
Carbs cals per gram
4
57
New cards
protein cals per gram
4
58
New cards
Macronutrients
The six key elements that organisms need in relatively large amounts: nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.
59
New cards
Micronutrients
vitamins, minerals, water
60
New cards
Most important macronutrient
Water
61
New cards
ideal body weight formula
100 pounds for first 5 feet then five pounds for every inch
62
New cards
type 1 diabetes
Diabetes of a form that usually develops during childhood or adolescence and is characterized by a severe deficiency of insulin, leading to high blood glucose levels.
63
New cards
type 2 diabetes
Diabetes of a form that develops especially in adults and most often obese individuals and that is characterized by high blood glucose resulting from impaired insulin utilization coupled with the body's inability to compensate with increased insulin production.
64
New cards
What is a normal fasting glucose?
between 70-99
65
New cards
Diabetes symptoms
thirst, excessive urination, weight loss, fatigue, nerve damage, blurred vision, poor wound healing and increased infection
66
New cards
Exercise and Diabetes
Exercise lowers the blood glucose level, encourages weight loss, reduces cardiovascular risks, improves circulation and muscle tone, decreases total cholesterol and triglyceride levels, and decreases insulin resistance and glucose intolerance.
67
New cards
overtraining
Excessive frequency, volume, or intensity of training, resulting in fatigue (which is also caused by a lack of proper rest and recovery).
68
New cards
Overreaching
excessive training on a short-term basis
69
New cards
functional overreaching
Purposely intensified training to cause a brief decrement in performance followed by a supercompensative improvement in performance.
70
New cards
nonfunctional overreaching
A long-term form of overreaching that causes stagnation and decreases in sport performance.
71
New cards
what decreases first from overtraining?
power/velocity
72
New cards
Effects of overtraining?
-decreased performance
-altered resting and ex HR
-increased Hr @ submax
-altered resting and ex BP
-increased creatine kinase
-altered cortisol
-decreased testorone
-decreased cortisol:testerone ratio
-altered resting and ex HR
-increased Hr @ submax
-altered resting and ex BP
-increased creatine kinase
-altered cortisol
-decreased testorone
-decreased cortisol:testerone ratio
73
New cards
stretch-shortening cycle
-rapid eccentric muscle action stimulates the stretch reflex and the storage of elastic energy which results in an increase in the force used in subsequent concentric muscle action
-used in plyometrics
-used in plyometrics
74
New cards
periodization phases:
hypertrophy --> basic strength --> power --> peak
75
New cards
hypertrophy phase
high vol
low-mod intensity
low-mod intensity
76
New cards
Basic strength phase
mod-high vol
high intensity
high intensity
77
New cards
power phase
low vol
low-high intensity
low-high intensity
78
New cards
Peak phase
very low vol
v high to v low intensity
v high to v low intensity
79
New cards
cluster sets
-combat fatigue induced alterations in technique
-enhance velocity of movement w higher loads
-rest between reps
-enhance velocity of movement w higher loads
-rest between reps
80
New cards
how often should plyos be done?
2-3 times per week
81
New cards
Best way to perform plyos?
UB plyos w LB resistance and LB plyos w UB resistance
82
New cards
Exercise for pediatrics:
60 mins/day x 3 week
-strength gains are due to nervous system adaptations
-strength gains are due to nervous system adaptations
83
New cards
Exercise for adults:
30-60 min/day and 150 min/week of mod intensity
OR
20-60 min/day and 75 min/week of high intensity
OR
20-60 min/day and 75 min/week of high intensity
84
New cards
kcal
one cal is the heat needed to raise the temp of 1 kg ( 1 L) of water 1 C
85
New cards
first law of thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed
**theory of conservation of energy**
**theory of conservation of energy**
86
New cards
potential energy
stored energy that results from the position or shape of an object
-when it is released its transformed into kinetic energy
-when it is released its transformed into kinetic energy
87
New cards
kinetic energy
the energy an object has due to its motion
88
New cards
2nd law of thermodynamics
tendency of potential energy to degrade to kinetic energy w a lower capacity to do work
-increases entropy
-increases entropy
89
New cards
Gibbs free energy
energy available to do work
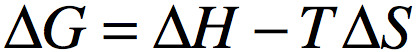
90
New cards
entropy
a measure of the disorder of a system
increases in a random fashion
increases in a random fashion
91
New cards
enzymes
-lower activation energy and catalyze rxns faster
-rxn rate effected by: pH, temp, availability of substrates
-rxn rate effected by: pH, temp, availability of substrates
92
New cards
oxidation reaction
loss of electrons with a gain in valence electrons
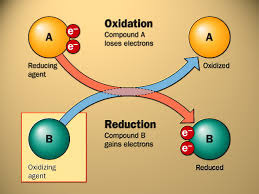
93
New cards
products of glycolysis
2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 NADH
(gross ATP 4)
-glucose-->pyruvate
-anaerobic breakdown occurring in the cytoplasm of the cell
(gross ATP 4)
-glucose-->pyruvate
-anaerobic breakdown occurring in the cytoplasm of the cell
94
New cards
krebs cycle
pyruvate --> acetyl-CoA
acetyl-CoA then enter the Krebs cycle
acetyl-CoA then enter the Krebs cycle
95
New cards
oxidative phosphorylation
NADH and FADH2 undergo this to donate electrons.
anaerobic yield: 2 ATP (glycolysis)
2 ATP (Krebs)
4 TOTAL
anaerobic yield: 2 ATP (glycolysis)
2 ATP (Krebs)
4 TOTAL
96
New cards
what's the total aerobic yield?
2 ATP (glycolysis)
4 ATP (from 2 NADH formed during glycolysis)
6 ATP (2 NADH from pyruvate --> acetyl-coA rxn)
2 ATP (Krebs)
22 ATP (6 NADH and 2 FADH2 from Krebs that go to ETC)
36 TOTAL
4 ATP (from 2 NADH formed during glycolysis)
6 ATP (2 NADH from pyruvate --> acetyl-coA rxn)
2 ATP (Krebs)
22 ATP (6 NADH and 2 FADH2 from Krebs that go to ETC)
36 TOTAL
97
New cards
When are fatty acids used?
During caloric deficits/low-mod intensity exercise.
If not being used they are stored as triglycerides.
If not being used they are stored as triglycerides.
98
New cards
What does "fat burns in a carb flame" mean?
Degradation of FA via Krebs only continues if there is oxaloacetate available. oxaloacetate comes from pyruvate during glucose breakdown.
99
New cards
Lactic acid
=NADH + H +Pyruvate
can be converted to glucose via the Cori cycle.
can be converted to glucose via the Cori cycle.
100
New cards
Protien daily intake:
0.83 g/kg body mass
intense training: 1.2-1.8 g
intense training: 1.2-1.8 g