Computer Science - 2B Programming Techniques
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Subroutine
giving an identifier to a block of code. Allows us to reuse that code throughout the program
Procedure
just executes code without returning a value
Function
executes code and returns a value
Parameters
data fed into a subroutine to be used within its code. Defined in the brackets after the subroutine's identifier
Return
returns a value from a subroutine
Why use subroutines? [5]
- modularised approach breaks down programs into manageable chunks of code
- helps to decompose larger problems
- programmers only need to use the interfaces of subroutines, i.e. parameters and return values
- don't need to worry about internal workings
- programs will have fewer bugs as we use structured programming techniques
Local variable
only exist inside the structure they are defined in (I.e. subroutine, while loop, if statement etc.)
Global variable
exist everywhere in the code. Must be defined outside of any structures (I.e. not indented)
Scope
the part of a program where a variable is visible and can be used by the code.
Advantage of using local variables:
keep a subroutine self-contained for use in any program, so variable names will not conflict
Structured programming techniques
techniques consisting of top-down program design, pseudocode, flowcharts, and logic structures
Data validation
ensuring that users enter the correct data type
Different validation routines [5]:
- range check
- type check
- length check
- presence check
- format check
range check
ensures a field is between a certain range of values.
type check
data is of the right type, such as integer, letter or text
length check
checks data is correct length
presence check
requires a field to be completed.
format check
checks the data is in the right format
Data verification
double-check that data has been typed in correctly
Authentication routines
used to make sure a person is who they claim to be
Examples of authentication routines [3]:
- ask for user ID and password
- biometrics
- reCAPTCHA
Maintainable code [5]:
- comments at the top for who wrote the program and when
- comments to explain complex code
- subroutines have comments to explain their use
- meaningful variable names
- modular structure
Trace table
a table that follows the values of variables to check for accuracy/function of program
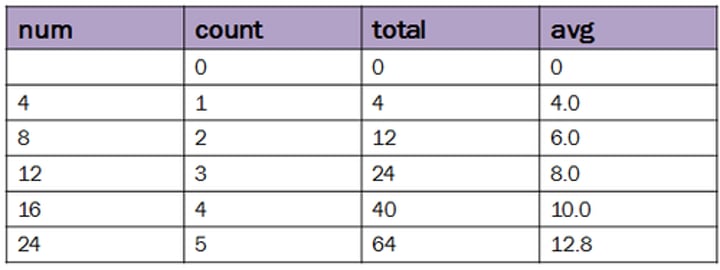
What is a trace table useful for? [3]
- determining the purpose of an algorithm
- finding the output of an algorithm
- finding errors in an algorithm
Logic error
a mistake in the algorithm or program that causes it to behave incorrectly or unexpectedly
Syntax error
an error in a program that makes it impossible to parse — and therefore impossible to interpret
What types of test data are there? [3]
- normal data
- boundary data
- erroneous data
Normal data
entering data that should be acceptable to the solution
Boundary data
data either side of the range extremes
Erroneous data
test data that a program isn't designed to accept