Anatomical Kinesiology
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
What is anatomical position good for?
Reference point
What is fundamental position?
Same as anatomical position but with the arms at the side with palms facing inward.
Anterior
In front or in the front
Anteroinferior
In front and below
Anterolateral
In front and to the outside
Anteromedial
In front and toward the inner side or midline
Anteroposterior
Relating to both front and rear
Anterosuperior
In front and above
Bilateral
Referring to both right and left sides of the body
Caudal
Below in relation to another structure, inferior
Caudalcephalad
Directionally from tail to head in the long axis of the body
Cephalic
Above in relation to a higher structure, higher, superior
Cephalocaudal
Directionally from head to tail in the long axis of the body
Contralateral
Opposite side of the body
ex: right arm, left leg
Deep
Beneath or below the surface
used to describe relative depth or location of muscles or tissue
Dexter
Relating to, or situated to the right or on the right side of something
Distal
Situated from the center or midline of the body, or away from the point of origin
Dorsal (dorum)
Relating to the back, being or located near, on, or toward the back, posterior part, or upper surface of, also relating to the top of the foot
Fibular
Relating to the fibular (lateral) side of the knee, leg, ankle, or foot
Interior (infra)
Below in relation to another structure, caudal
Inferolateral
Below and to the outside
Inferomedial
Below and toward the midline or inside
Ipsilateral
On the same side
ex: right arm, right leg
Lateral
On or to the side, outside, farther from the median or midsagittal
Medial
Relating to the middle or center, nearer to the median or midsagittal
Median
Relating to, located in, or extending to the middle, situated in the middle, medial
Palmar
Relating to the palm or volar aspect of the hand
Plantar
Relating to the sole or undersurface of the foot
Posterior
Behind, in back, or in the rear
Posteroinferior
Behind or in back and below
Posterolateral
Behind and to one side, specifically to the outside
Posteromedial
Behind and to the outside
Posterosuperior
Behind or in back and above
Prone
Face downward position of the body, lying on the stomach
Proximal
Nearest to the trunk or point of origin
Proximodistal
From the center of the body toward the distal ends of the appendages
Radial
Relating to the radial (radius) side of the forearm or hand
Scapular Plane
In line with the normal resting position of the scapula as it lies on the posterior rib cage
movements in the scapular plane are in line with the scapular
which is at the angle of 30-45 degrees from the frontal plane
Sinister
Related to, or situated to the left, or on the left side of, something
Superficial
Near the surface, used to describe relative depth or location of muscles or tissue
Superior (supra)
Above in relation to another structure, higher, cephalic
Superolateral
Above and to the outside
Supromedial
Above and toward the midline or inside
Supine
Face upward position of the body, lying on the back
Tibial
Relating to the tibial (medial) side of the leg, knee, ankle, or foot
Ulnar
Relating to the ulnar (medial) side of the forearm or hand
Ventral
Relating to the belly or abdomen, on or toward the front, anterior part of
Volar
Relating to the palm or the hand or palm of the foot
What are the three plane of motion?
Sagittal, Transverse (horizontal), Frontal (lateral)
Sagittal Plane
Right to left
Axis of rotation — frontal
Flexion and extension
Transverse (horizontal) Plane
Top and bottom
Axis of rotation — vertical
Internal and external rotation
Horizontal abduction and adduction
Frontal Plane
Back to front
Axis of rotation — sagittal
Abduction and adduction
Lateral Flexion
Skeletal system functions
Protection
Support
Movement
Mineral storage (calcium and phosphorus)
Hemopoiesis (production of red blood cells)
Axial Skeleton
Head, spine, thorax
Appendicular Skeleton
Upper and lower limbs, shoulder and hip girdles
Synovial Joints
Movement oriented
Designed for function and flexibility
What makes a synovial joint?
Articular cartilage
Joint capsule
Synovial membrane
Synovial fluid
Joint cavity
6 Types of synovial joints
Hinge (ginglymus)
Ball and socket (enarthrodial)
Pivot (trochoidal)
Gliding (arthrodial)
Saddle (sellar)
Ellipsoid (condyloid)
Hinge Joint
A uniaxial joint that permits motion in one plane
Ginglymus
flexion and extension
talocrural joint
tibiofemoral joint
Ball and Socket Joint
A joint in which the ball-shaped surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone
enarthrodial
flexion and extension
abduction and adduction
glenohumeral joint
Pivot Joint
A uniaxial joint that allows for rotation around a central axis
trochoidal
atlas axis
radial ulnar joint
Gliding Joint
A nonaxial joint where flat bone surfaces glide pr slide over one another
arthrodial
acromioclavicular joint
carpals and tarsals
Saddle Joint
A biaxial joint where both articulating surfaces are shaped like a saddle, allowing for movement in two planes and some circumduction
sellar
thumb
sternoclavicular joint
Condyloid
A biaxial joint where an oval-shaped bone ends fits into a concave surface, permitting movement in two planes
ellipsoid
wrist
carpometacarpal
The 3 rules of muscles
Muscles only contract and relax
Muscles only work on joints they cross
Muscles work best of the direction of their fibers
Nervous System and motion
Receive information from sensory afferents
Interpret, organize and plan
Activate motor units via efferent motor nerves
Motor Unit
Efferent nerve
Once the motor unit turns on, muscles contract
Types of muscle actions
Concentric - active tension as it shortens, overcomes an applied resistance
Eccentric - muscles lengthening with active tension
Isometric - tension is developed in muscle without joint action
Agonist/ Prime Mover
Agonist - any muscle that contributes to a specific joint action in a plane of movement
Prime mover - main agonist
Synergist
Guiding muscle
Muscles assisting the agonist
Antagonist
Performs opposite of agonist
allows agonist to move
eccentric
Neutralizers
Muscles that contract or prevents actions of other bones/joints
Contracts to resist undesirable movement
Stabilizer
Stabilize a joint
Control arthrokinematics
Proximal stability = distal mobility
How many tarsal bones are in the foot?
26
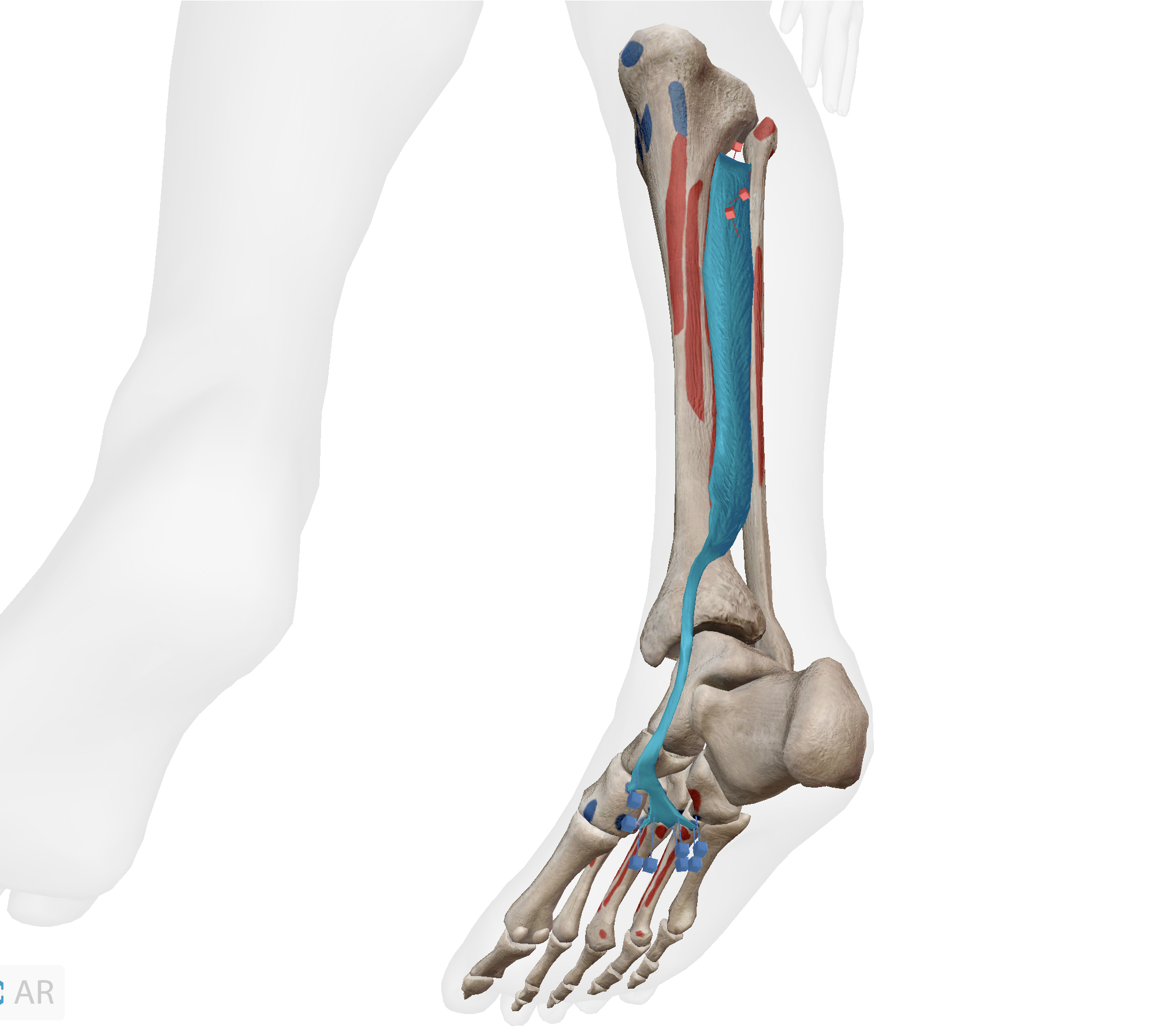
What pair of joint actions does this muscle produce?
Plantar flexion, inversion
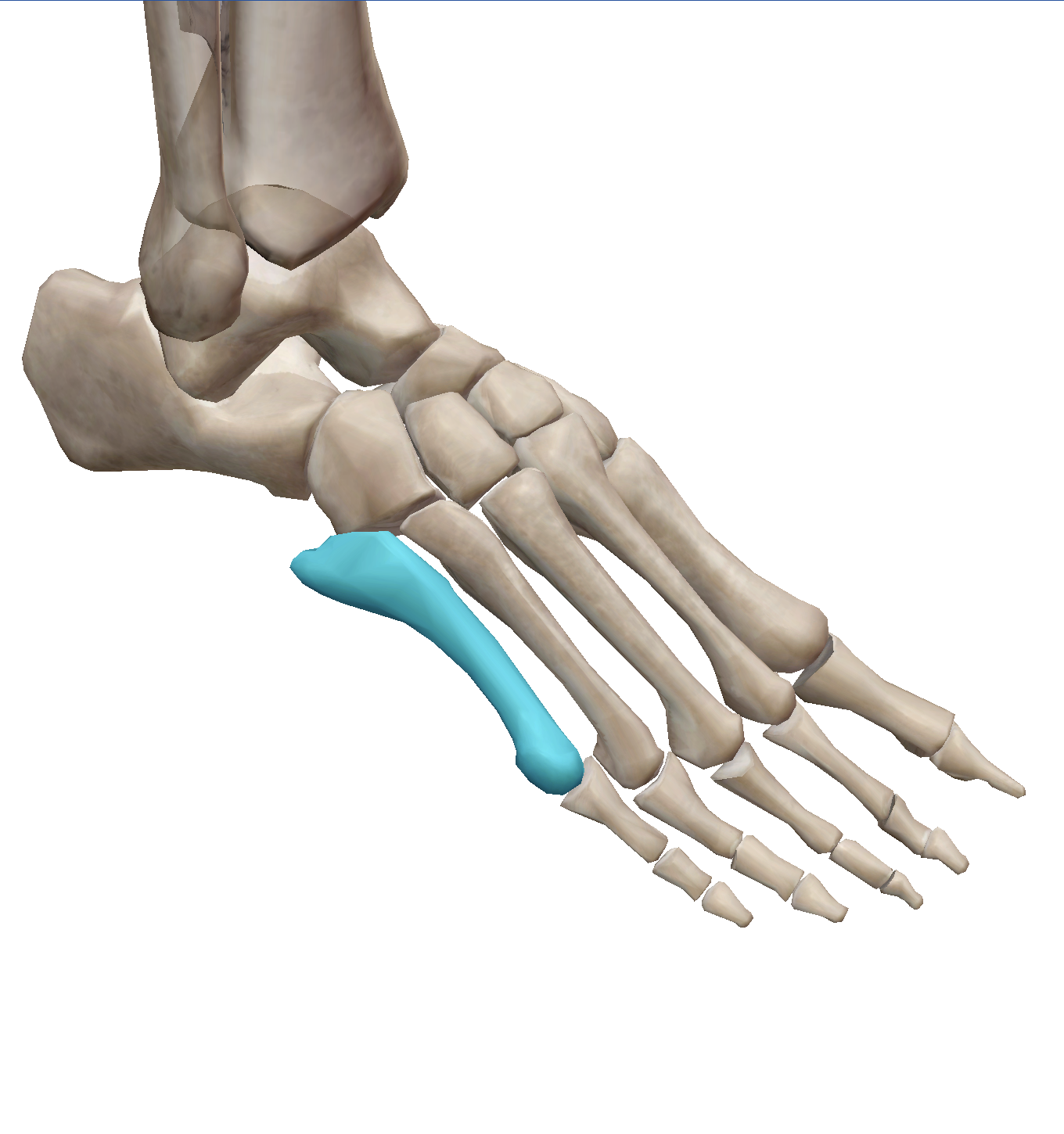
Which tendon inserts at the base of the highlighted bone?
Extensor digitorum brevis
During the lifting phase of the squat, select the correct pair of muscle contraction and muscle performing the contraction.
Gastrocnemius : concentric
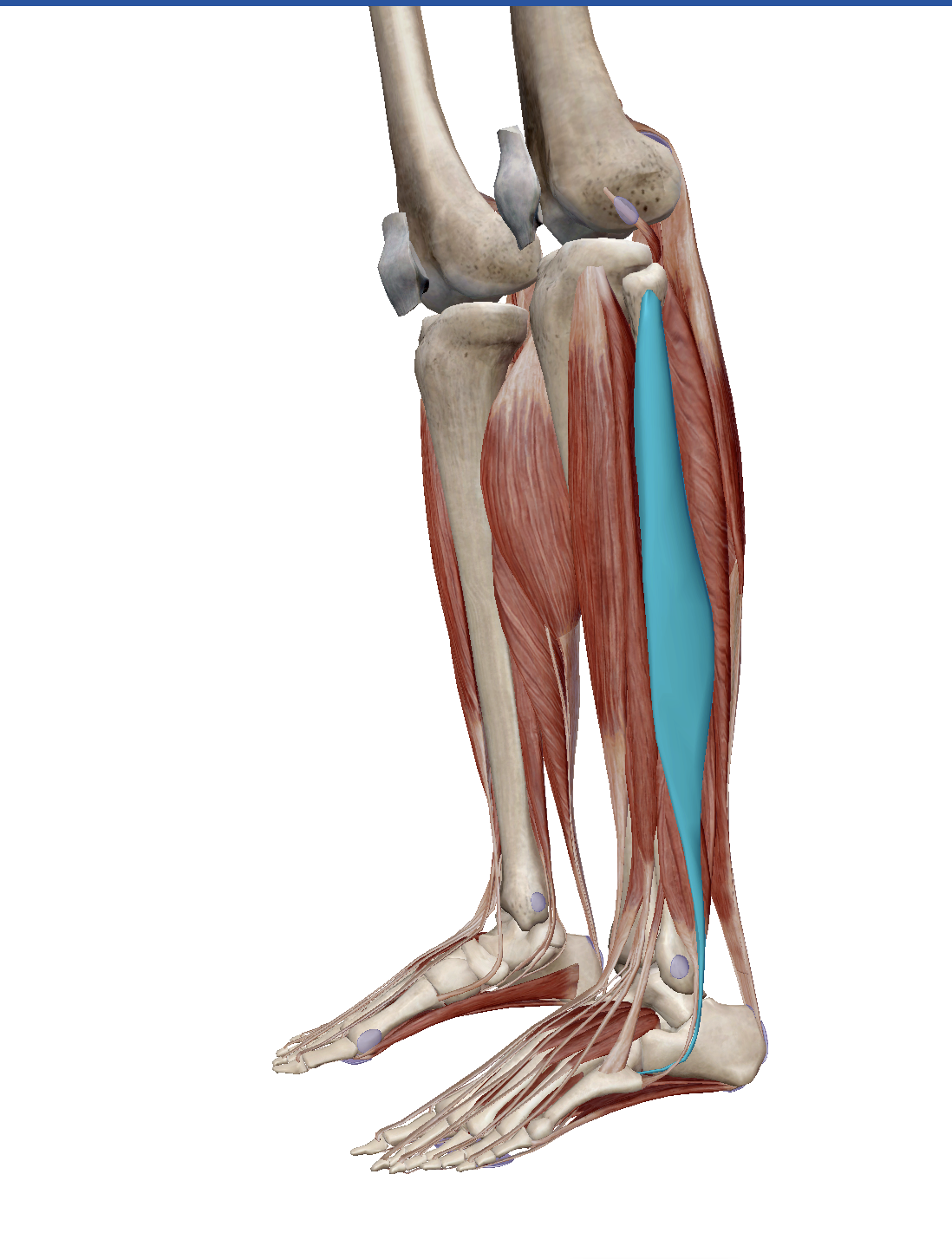
This muscle originates at the head and proximal 1/2 to 2/3 of lateral side of fibula and inserts by crossing the plantar surface of foot to attach to lateral sides of medial (1st) cuneiform and 1st metatarsal.
Fibularis longus
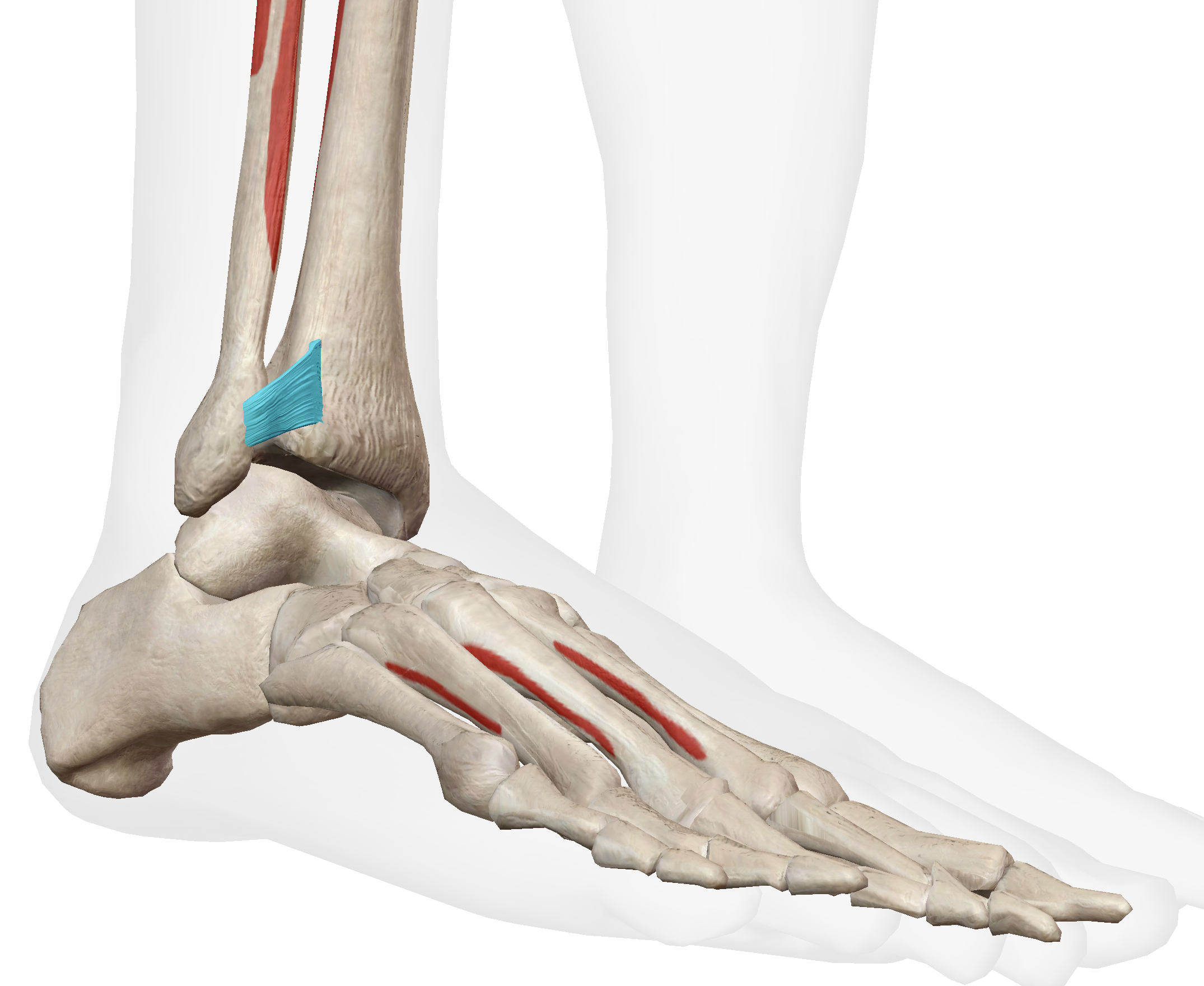
What structure is highlighted?
anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament
What joint action at the ankle is occuring during the lowering phase of a squat?
Dorsiflexion
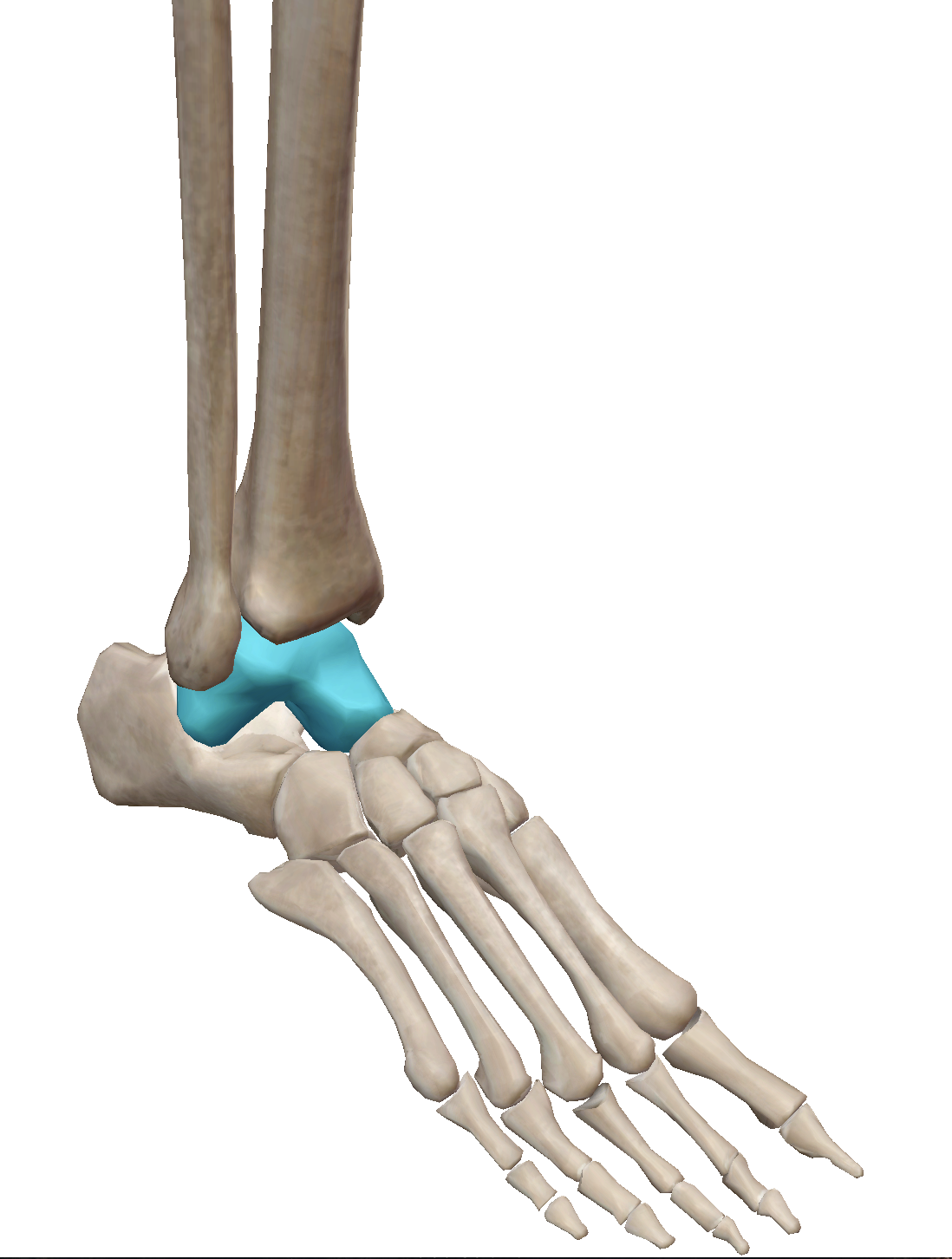
What structure is highlighted?
Talus
Select the lateral ligaments of the ankle joint. (multiple answer)
calcaneofibular ligament, posterior talofibular ligament, anterior talofibular ligament
Inversion and eversion at the ankle take place at the talocrural joint.
False
During the lowering phase of the squat, select the correct pair of muscle contraction and muscle performing the contraction.
Gastrocnemius : eccentric
Which of the following correctly lists the compartments of the lower leg?
Anterior, Lateral, Superficial Posterior, Deep Posterior
When concentrically contracted the anterior tibialis can create both dorsiflexion and inversion.
True
The tibialis anterior attaches distally into which bone?
Medial cuneiform
Please check all the muscles that invert the foot. (multiple answer)
Tibialis posterior, Flexor hallucis longus, Tibialis anterior