Unit 0: Foundations Key Vocabulary
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/74
Earn XP
Last updated 10:15 AM on 8/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
1
New cards
Patriarchy
a system of society or government in which men hold the power and women are largely excluded from it.
2
New cards
Hinduism
allowed a individual worshippers to show their devotion to their gods directly without using priests as intermediaries
3
New cards
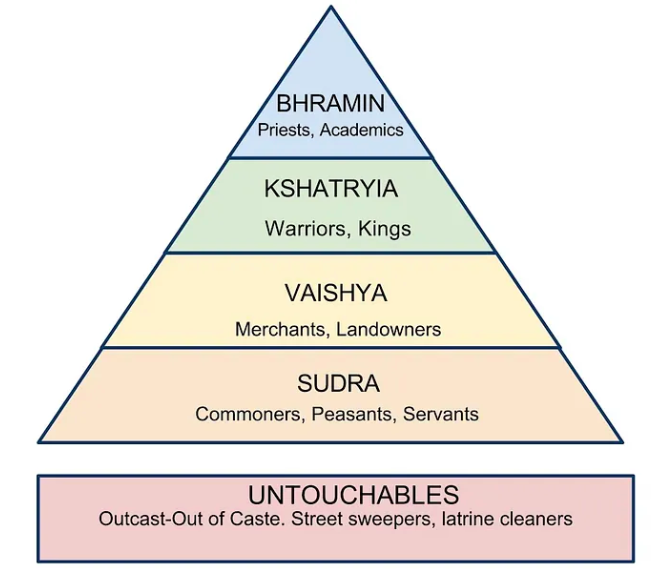
Caste System
a hindu-istic class structure that is determined by your job which is determined by your birth/past life
4
New cards
The Vedas
a body of sacred works, epics, hymns. philosophical treaises, and ritual texts created by Aryans. Oldest of the Hindu Religious Text. Primary Source of Info during Aryan era.
5
New cards
Brahmins
priests that could approach the gods and goddesses recognized by the Aryans.
6
New cards
Braman
rituals that might allow a person to achieve union with the ultimate unchanging reality that is the source of the universe
7
New cards
Karma
actions performed in one’s life determines their status in their next life.
8
New cards
Dharma
your job/duty
9
New cards
Moksha
a state of liberation, bliss, and awareness in which achieved with union of Brahman.
10
New cards
Reincarnation
an endless cycle in which souls are reincarnated through a continual process of rebirth (samsara)
11
New cards
Brahman
highest, universal in hinduism
12
New cards
Untouchables
outside the caste system; impure and did tasks that made them beneath the dignity of shrudas
13
New cards
Varnas
a social class within a hierarchical caste system
14
New cards
Sati
the practice widows dying with their husbands
15
New cards
Buddhism (1)
1. life is suffering
2. suffering is from desire
3. one must limit desire to limit suffering
4. to limit suffering, one must follow the “Eightfold Path”
16
New cards
Siddhatha Guatama
a rich sheltered prince out to the world and saw suffering and challenges. He decided leave everything to experience as those suffering and find a solution. He created Buddhism and found a solution after years of meditation.
17
New cards
Four Nobel Truths
a spiritual epiphany about the truth about the universe
18
New cards
Buddhism
teaches that by controlling desire and limit suffering leads to spiritual enlightment
19
New cards
Eightfold Path
1. Right View
2. Right Intention
3. Right Speech
4. Right Reaction
5. Right Livelihood
6. Right Effort
7. Right Mindfulness
8. Right Concentration
20
New cards
Nirvana
The Goal for Buddhist path: Enlightment or awakening
21
New cards
Mahayana Buddhism (great vehicle)
allowed people to strive for Enlightment even if they couldn’t become monks.
22
New cards
Theravada Buddhism (teaching of elders)
believed to be a closer resemblance to Buddha’s actual teachings
23
New cards
Stupas
a buddhist place of worship and houses for religious relics
24
New cards
Bodhisattva
a person who is able to reach nirvana but delays doing so out of compassion in order to save suffering beings.
25
New cards
Judaism
originated from Hebrews, a monotheistic religion about the god Yahweh
26
New cards
Hebrews
a group of people who briefly established two small kingdoms btwn the Mediterranean and Jordan River aka Canaan.
27
New cards
Ten Commandments
A series of rules of behavior for the Hebrews, created by God.
28
New cards
Diasporic Communities
Communities that spread out of their origin homeland
29
New cards
Abraham
tribal leader of the Hebrews that spoke to God (mentioned in abrahamic religions: Judaism, Christianity and Islam)
30
New cards
Israel
the land God promised the Jews through Abraham
31
New cards
Christianity
a abrahamic and monotheistic religion in the belief of Jesus of Nazareth dying for sins
32
New cards
Jesus of Nazareth
(3 BCE - 29 CE) born to religious parents and began ministry at age 30
33
New cards
Salvation
Sins
34
New cards
Universal Religion
a religion with a goal to welcome more followers into the religion
35
New cards
Monastic Life
living in isolation/self-discipline to devote oneself to religion
36
New cards
Great Schism (1054)
the separation of the Catholic church of the West from the Orthodox churches of the East
37
New cards
Orthodox Church
The East Religion, idk what they believe in but i’ll ask
38
New cards
Roman Catholic Church
The West Religion, idk what they believe in even tho its my religion lolol
39
New cards
Crusades
a series of military expeditions/wars
40
New cards
Islam
monotheistic and abrahamic religion that’s centered the belief of god (Allah). Guidance in Qu’ran
41
New cards
Muhammad
born in Arabia (570 - 632 CE) and was 40 when he experienced religious visons. Founder of Islam and received revelation from God, which he described in the Qur’an
42
New cards
Five Pillars
1. the profession of faith in God and in Muhammad as God’s prophet
2. regular prayer at home or in \n mosques
3. fasting during the sacred month of Ramadan
4. giving alms (charity) to the poor
5. and a pilgrimage to Mecca, if possible
43
New cards
Shar’ia
Muslim laws or sacred laws
44
New cards
Haji
pilgrimage to the holy city of Mecca in Saudi Arabia
45
New cards
Jizya
tax towards the non-muslim population
46
New cards
Dhimmi
legal protection for non-muslims in islamic states
47
New cards
umma
refers to the islamic or muslim community formed by Muhummad in Medina
48
New cards
Allah
Islam’s word for God
49
New cards
Mecca
located in Saudi Arabia, holy islamic city
50
New cards
Medina
where muhummad first started
51
New cards
Hadiths
traditions attributed to the Prophet Muhammad that include his sayings, acts, and approval or disapproval of things
52
New cards
Caliph
successor of the prophet Muhammad, muslim ruler
53
New cards
caliphate
state ruled by a caliph, a Muslim ruler who is both the ruler of a state and the leader of the entire ummah
54
New cards
Qur’an
the direct words of God from the Prophet Muhummad
55
New cards
Dar al Islam (House of Islam)
refers to states that are majority islam
56
New cards
Ulama
Muslim scholars trained in Islam and Islamic law
57
New cards
Jihad
arabic word for struggle
58
New cards
Harem
a part of a house set apart for women in islamic household
59
New cards
Sufis
emphasized personal spiritual experience; divine revelation can be reached when losing oneself and uniting with God
60
New cards
Sunni/Shia
divisions and have different religious beliefs for Islam. Sunni is majoirty, Shia is minority
61
New cards
Confucianism
stressed the importance of complementary relationships
62
New cards
Confucius
educated man born in wealthy family, lived during political turmoil of Eastern Zhou Dynasty (constant war with states), inspired him to create Confucianism
63
New cards
Filial Piety
respect and honor for elder family members
64
New cards
Mandate of Heaven
there could be only one legitimate ruler of China at a time, and that this ruler had the blessing of the gods. If he did not fulfill their duties to the people, the people were allowed to rebel
65
New cards
Civil Service Exam
Taken by young Chinese men and is tested for the knowledge of Confucianism; must pass for government employment
66
New cards
Scholar Gentry
idk high top people
67
New cards
Daoism
68
New cards
The Dao
The Way; an Chinese belief system which emphasizes harmony with the natural balanced order o the universe
69
New cards
Yin and Yang
the idea that all things exist as entwined, complementary (harmonous) opposites
70
New cards
Laozi (the elder)
Chinses scholar created Daoism in book Dao De Jing
71
New cards
Bureaucracy
72
New cards
Empire
control over terriotry to a great extent
73
New cards
Shamanism
a tradition of part-time religious specialists who establish and maintain personalistic relations/ connections with specific spirit from other worlds
74
New cards
Ancestor Veneration
the practice of honoring one's ancestors
75
New cards
Syncretism
a blend of different beliefs