Biochemistry test 1 flash cards
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
What is the one letter code for Glycine
G
What is the 3 letter code for Glycine
Gly
What is the 3 letter code for Alanine
Ala
What is the one letter code for Alanine
A
What is the 3 letter code for Proline
Pro
What is the one letter code for Proline
P
What is the one letter code for Valine?
V
What is the 3 letter code for Valine?
Val
What is the one letter code for Leucine?
L
What is the three letter code for Leucine
Leu
What is the one letter code Isoleucine?
I
What is the 3 letter code for Isoleucine
Ile (ILE)
What is the one letter code for Methionine?
M
What is the 3 letter code for Methionine?
Met
What is the 3 letter code for Phenylalanine?
Phe
What is the 1 one letter code for Phenylalanine?
F
What is the 3 letter code for Tyrosine
Tyr
What is the one letter code for Tyrosine
Y
What is the 3 letter code for Tryptophan?
Trp
what is the one letter code for Tryptophan?
W
What is the one letter code of Serine?
S
What is the 3 letter code of Serine
Ser
What is the 3 letter code of Threonine
Thr
What is the one letter code of Threonine
T
What is the three letter code of Cysteine
Cys
what is the one letter code of Cysteine
C
What is the one letter code for Asparagine
N
What is the 3 letter code for Asparagine
Asn
What is the one letter code for Glutamine
Q
What is the three letter code for Glutamine
Gln
What is the 3 letter code for Lysine
Lys
what is the one letter code for Lysine?
K
What is the one letter code for Histidine
H
what is the 3 letter code for Histidine?
His
What is the one letter code of Arginine
R
What is the 3 letter code of Arginine
Arg
What is the 3 letter code of Aspartate
Asp
What is the one letter code of Aspartate
D
What is the one letter code of Glutamate
E
What is the three letter code for Glutmate
Glu
Which amino acids have a pKr on their side chain?
Tyrosine, Cysteine, Lysine, Histidine, Arginine, Aspartate, Glutamate.
Which amino acid’s Have side chains that are capable of H bonding?
Serine and Threonine→ (OH)
Asparagine and Glutamine→ (NH2)
Tyrosine→ Phenol (Benzene ring with OH)
Which Amino acids are unlikely to be found in an alpha helix?
Glycine→ to flexible and destabilizes the structure
Proline- not flexible enough (phi and psi angles)
Which amino acids are considered aromatic by the textbook, and characteristics of them.
Tryptophan, Tyrosine , Phenylalanine
mostly nonpolar and contribute to the hydrophobic effect, absorb Ultra violet light
Which Amino acids are considered Nonpolar by the text book?
Glycine, Alanine, Proline, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine
Which amino acids are considered polar and uncharged by the text book?
Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, Asparagine, Glutamine
Which amino acids are considered Positively charged?
Lysine, Histidine, Arginine
Which amino acids are considered Negatively charged?
Aspartate Glutamate
Name differences of amino acids that are considered nonpolar.
Side chains of Alanine, valine, leucine, and Isoleucine tend to cluster together stabilizing structure.
Glycine is very small and makes no real contribution to hydrophobic affect.
Methionine- has a slightly nonpolar thioether (C-S-C) on its side chain.
Proline has a cyclic structure giving it a rigid conformation reducing flexibility in regions with proline.
Name differences and a important characteristic found in Aromatic amino acids
Tyrosine can H-bond
Tyrosine and Tryptophan are more polar than Phenylalanine, Tyrosine because of OH and Tryptophan because of the nitrogen found on the ring (indole ring).
all three absorb UV light but Phe can absorb the least significant amount
which amino acid(s) can form disulfide bonds?
Cystine
What is a Prosthetic group?
metal ion or organic compound bound to the protein and essential to its acitivity.
What is a primary structure?
the sequence of amino acid residues
What are proteases?
Enzymes that can cleave peptide bonds.
what is a Secondary structure?
the Hydrogen bonding and spatial arrangement caused from atoms and the polypeptide backbone.
how many residues are found per turn of the alpha helix?
3.6 residues
how much does an alpha helix rise per turn?
5.6 Angstrom
what interactions of amino acids can destabilize the alpha helix?
To many negatively charged carboxyl groups together
To many adjacent positively charged Residues(Lys and Arg)
The size and shape of Asn, Ser, Thr, and Cys if to close together
Which amino acids are not likely to be found in Alpha helix and why?
Proline- nitrogen atom is part of a rigid ring not allowing for the correct phi/psi angles and destabilizes the alpha helix, and also the nitrogen has no Hydrogen and can not H bond
Glycine- it has more conformational flexibility than other amino acid residues
What interactions between amino acid side chains stabilize the helix structure?
Side chains from three residues away (sometimes four). ie a Positively charged Amino acid three residues away from a negative charged amino acid.
Where does the H bond happen in backbone of the alpha helix?
H Bonding happens between the Carbonyl group of your 1st peptide and the amino group from the 5th residue (in general i+4).
Example: Residue 2 (i) of an alpha helix H bonds with residue 6 (2+4)
How does the alpha helix dipole play in stabilizing the helix?
the small electric dipole in which a positive charge is found towards the N-terminus and negative Charge towards C terminus of the helix. leading to more negatively charged amino acids being found in N terminus (Stabilizing the positive charge of the helix and more positively charged amino acids found in C terminus (stabilizing the negative charge of the helix)
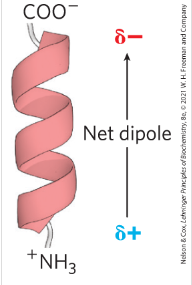
Name all 5 constraints that affect the stability of alpha helix
intrinsic propensity of amino acid residue
Interactions between R group (In particular those 3(or 4) spaces apart)
bulkiness of adjacent R groups
occurrence of Pro and Gly
Interactions between amino acids residues at ends of helical segment and electric dipole inherent to the helix
How many Amino acids are in a beta turn?
beta turns are a sequence of 4 amino acids where the carbonyl oxygen of residue 1 Hydrogen bonds with amino group hydrogen of the fourth.
Which amino acids often found in beta turns?
Glycine → most Flexible
Proline→ because peptide bonds of the amino nitrogen takes on a cis position.
What are methods or techniques used to Identify Secondary structures?
Ramachandran plots and Circular Dichroism (CD) spectroscopy
What are Ramachandran plots used for?
To verify Phi and psy angles and that the propose structure is inline with the Dihedral angles shown in the plot.
What is Circular Dichroism (CD) spectroscopy used for?
Uses UV to get a spectra of your secondary structure, and compare it with a standard of the secondary structure. to get the fraction of protein that is in common with that secondary structure.
What is a Heme group?
Consist of an organic ring (Protoporphyrin), and Iron (Fe+2)
what is a Tertiary structure?
3-D shape of a polypeptide chain
What are the designated major groups of Tertiary structures?
Fibrous proteins, globular proteins, membrane proteins, and intrinsically disordered proteins.
General shape of fibrous proteins
polypeptide chains arranged in long strands or sheets. Generally containing a single type of secondary structure.
General shape of globular proteins?
Polypeptide chains folded into a spherical or globular shape. they consist of serval type of secondary structures.
what is the shape of a intrinsically disordered proteins
polypeptide chains lacking stable tertiary structures. Lack secondary structure entirely.
What are general function of fibrous proteins?
provide support, shape, and external protection.
what is the general function of globular proteins
Enzymes
Which shapes do regulatory proteins have?
Disordered and globular
Which amino acids are found in high abundance in the Fibrous alpha-keratin?
Ala, Val, Leu, Ile, Met, and Phe
What enhances the strength of fibrous proteins?
Covalent cross linked. quaternary structure cross link with disulfide bonds from cysteines.
Properties of Collagen
It has left handed alpha helix
3 amino acids per turn (compared to 3.6).
Follows the pattern Gly-X-Y where X is a Pro and Y is a Hyp (Hydroxyproline).
What is a Motif
A Motif or gold is a recognizable folding pattern involving two or more elements of secondary structure and the connections between them.
What is a Domain
Part of a polypeptide chain that is independently stable.
What are the several rules have merged from studies of common protein-folding patters?
Hydrophobic effect makes a large contribution to stability of protein structures.
Alpha helix and Beta sheets are found in different structural layers
Segments adjacent to each other in amino acid sequence are usually stacked adjacent to each other in a folded structure.
Beta conformation is most stable when segments are twisted slightly in a right-hand. sense.

What are the amino acid residues mostly found in a disordered structure?
High density of charged amino acids- Lys, Arg, and Glu
also has Pro residues are prominent.
What is the purpose of structural disorder and the high charge density found in it?
Can facilitate function of some proteins as spacers, insulators or linkers.
Disordered proteins can be- Scavengers binding up ions and small molecules in solution functioning as reservoirs and garbage dumps. and functions as a inhibitor due to is flexibility or as hubs or scaffolds.
The fraction of ligand-binding sites that are half occupied (Y=0.5) is when? In terms of [L]
the fraction of ligand binding sites that are half occupied is when [L] =Kd
What does a smaller Kd valuetell us?
High affinity, or high association, or low disassociation
what does a larger Kd value tell us
Low affinity, low association, or High dissociation
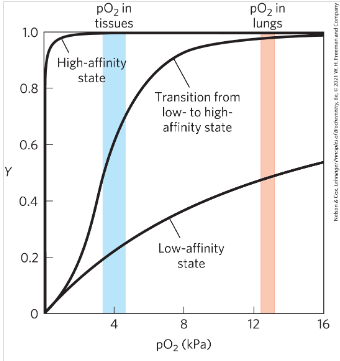
How does the R state and T state affect oxygen binding in Hemoglobin? In terms of Higher or lower affinity.
In the T state has a lower affinity for oxygen and the R state has a higher affinity for oxygen.
Why is the change of states (R→T and vice versa), or change of affinity between oxygen important?
The change of affinity allows oxygen to switch between high affinity and low affinity to make transport of oxygen to the cells possible. if it was completely low affinity not enough oxygen would bind, if it would high affinity it would not release the oxygen.
What is an allosteric protein?
A protein that when binding with a ligand changes or affect another site of the same protein.
what is a homotopic modulator?
a modulator that is the same to the normal ligand
What is heterotopic modulator
allosteric modulator that is not the normal ligand
What does the Hill coefficient tell us?
a Hill coefficient that is greater than one(+), tell us that the binding of one molecule increases/facilitates the binding of others
Coefficient of 1 tells us there is no cooperative binding (no negative or positive effect)
coefficient of negative or below 1 tells us it has negative binding or impedes bindings of others.
What is the Bohr effect?
The Bohr effect is the affect of pH and CO2 concentration affect hemoglobin.
Where it has has a higher affinity for binding to O2 at higher pH and lower affinity at lower pH.
In Ion exchange chromatography, which proteins are retained for longer for cation exchange and anion exchange respectively.
In Cation exchange chromatography- Positively charge are retained for longer (move more slowly.)
In Anion exchange- negatively charge proteins are retained for longer(move more slowly.)
Size- exclusion chromatography also known as gel filtration, which proteins go through faster or emerge sooner?
Separates proteins by size and larger proteins emerge sooner.
Electrophoresis is an analytical process that can give us what information?
When an electric current is applied for the field movements will move through the polymer, at different speeds where the lightest proteins will move down farther than heavier proteins. so we can get molecular weight and Isoelectric point.
Isoelectric focusing helps us determine what from a protein?
It helps us determine the Isoelectric point of a protein by moving through a pH gradient.
Why is Two-Dimensional electrophoresis useful with complex mixtures?
It allows the separation of protein with identical molecular weight that have different pI. and Proteins with similar pI but different molecular weight