Diagnostic Imaging
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Gastric Bubble
common normal finding
Abdominal Radiograph
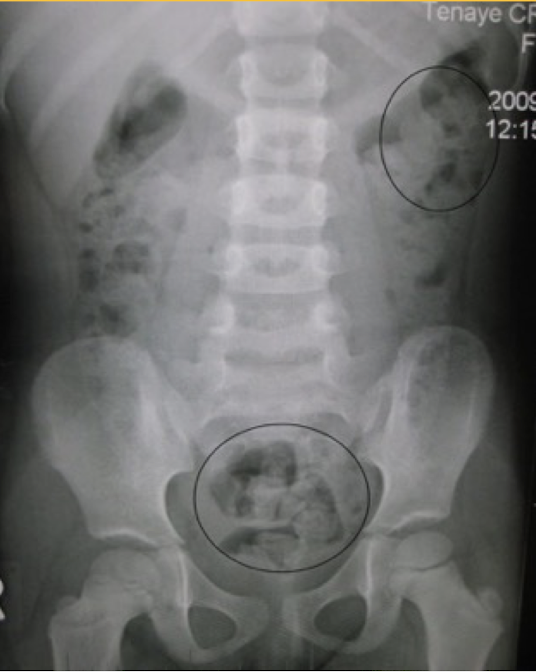
Constipation
mottled appearance of fecal material
Abdominal Radiograph
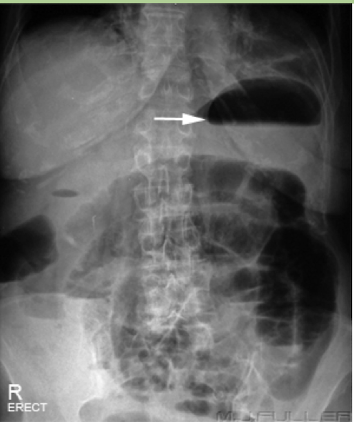
Pneumoperitonem
free air under the diaphragm
abnormal finding, perforated until proven otherwise
Abdominal Radiograph
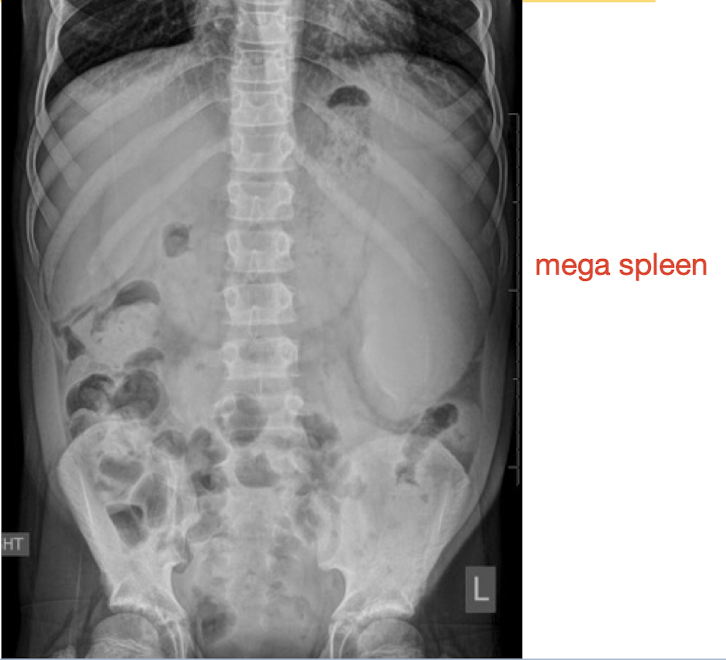
Organomegaly
abnormal finding
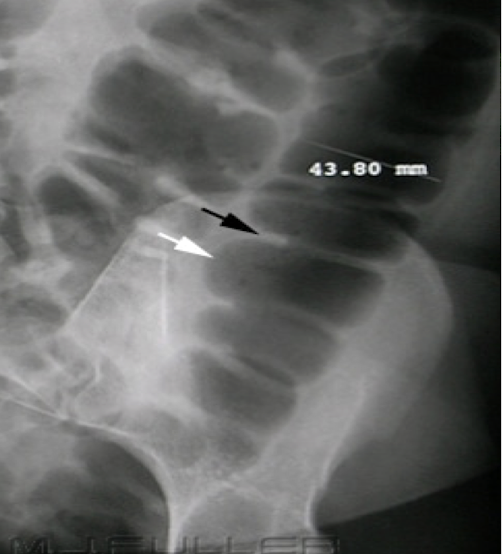
Abdominal Radiograph
Valvulae
travel entire width of the small bowel
3cm for small bowel is normal width
Abdominal Radiograph
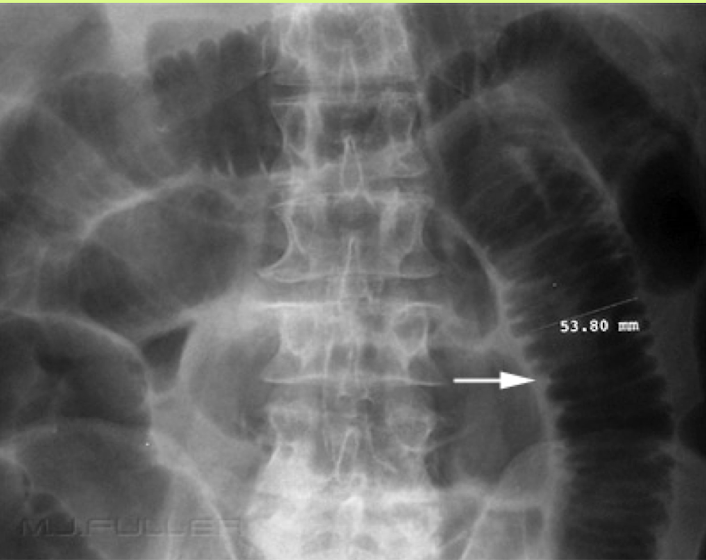
Haustra and Plicae
travel partial width of large bowel/colon
6cm for colon and 9cm for cecum is normal width
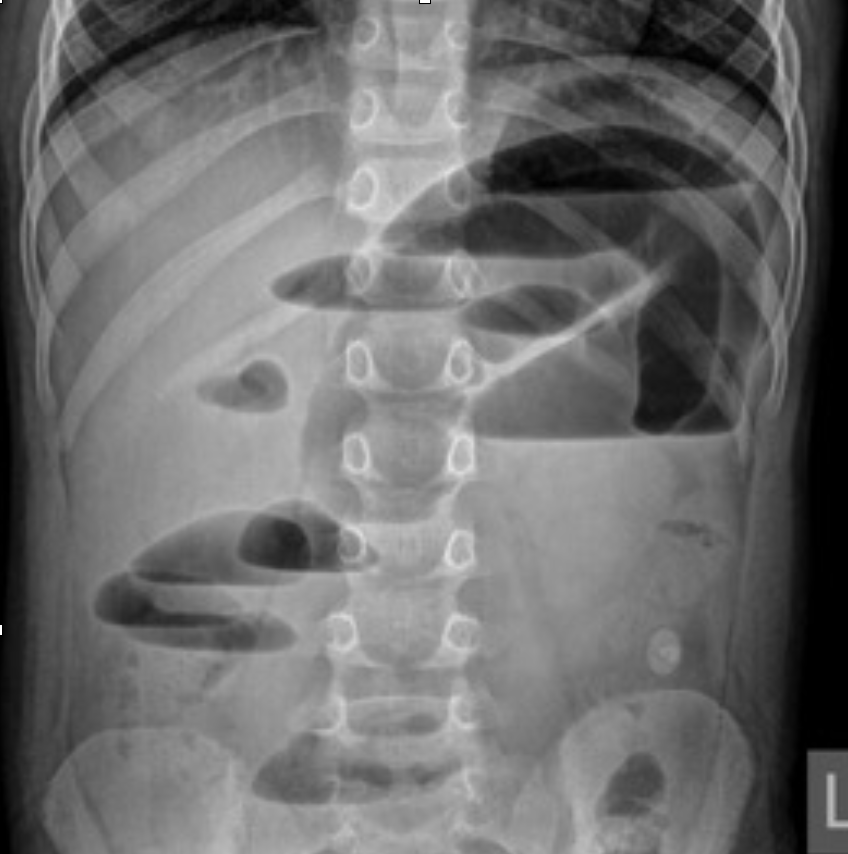
Abdominal Radiograph
Small bowel obstruction (SBO)
dilation and multiple bubbles, air fluid levels
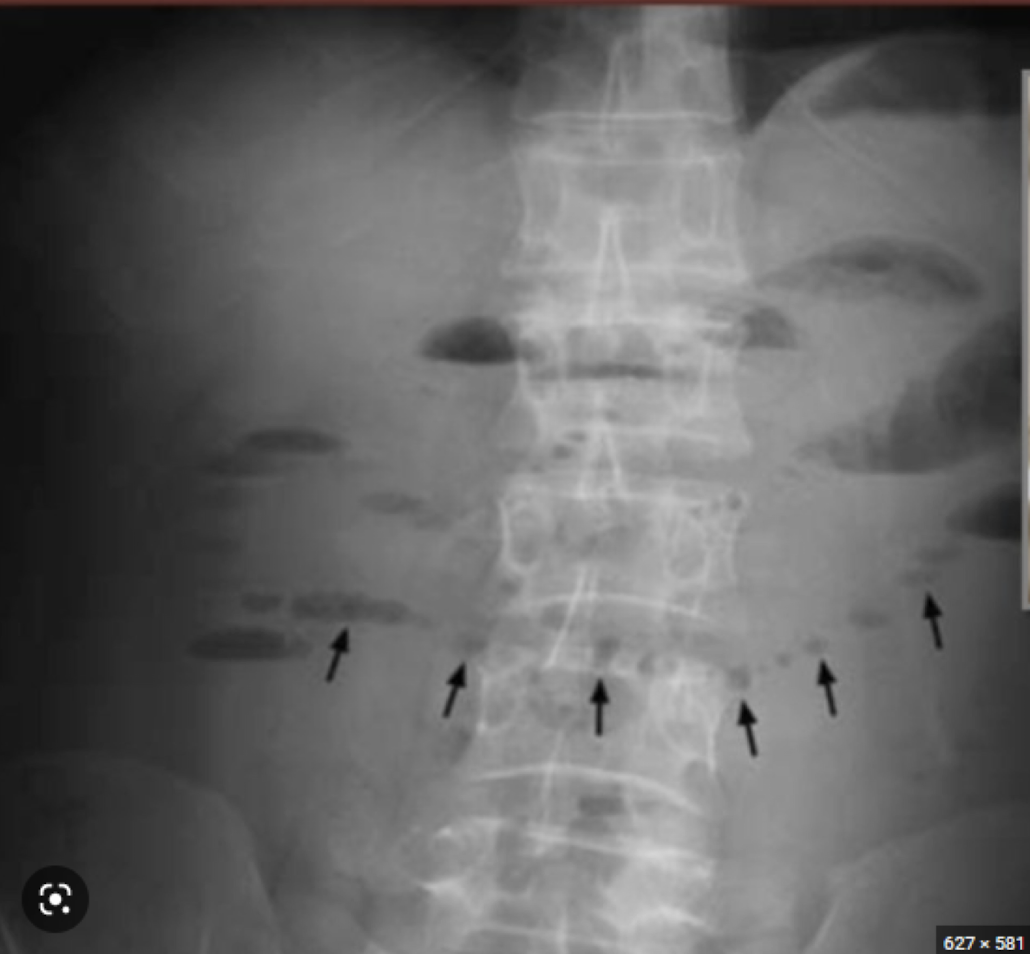
Abdominal Radiograph
Small bowel obstruction (SBO)
“string of pearls” finding
Abdominal Radiograph
Cecal volvulus
section of twisted bowel causing obstruction and strangulation
Abdominal Radiograph
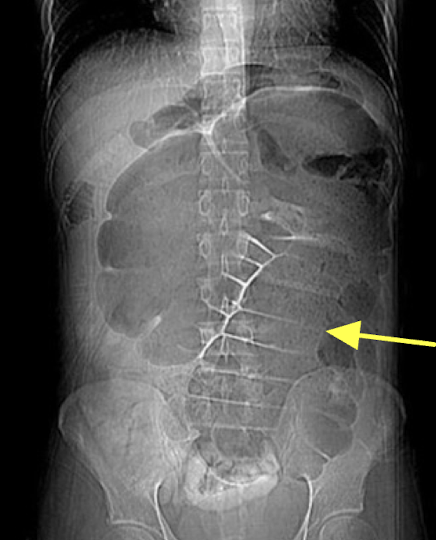
Sigmoid volvulus
“coffee bean” sign
section of twisted bowel causing obstruction and strangulation
Abdominal Radiograph
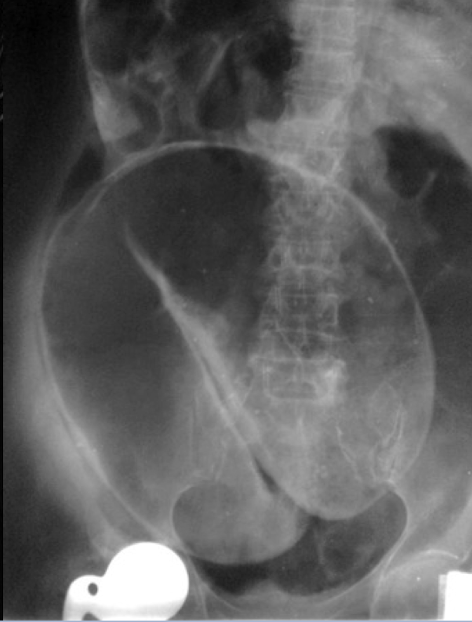
KUB (kidney, ureter & bladder)
XRAY optimized to assess the urogenital system ± GI system
Abdominal Radiograph
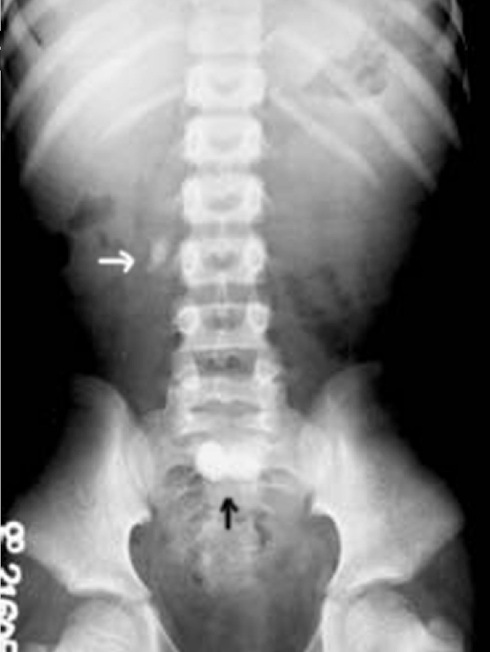
IVP (IV pyelogram)
XRAY using IV contrast material to assess kidney, ureters and bladder (less commonly used)
*CT Urogram is more common for assessing flank pain
Abdominal Radiograph
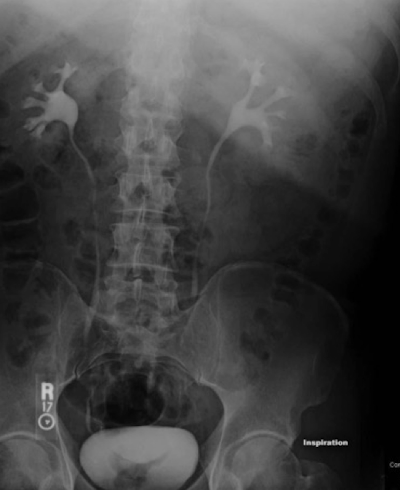
CT urography
CT scan using an IV contrast material to assess kidney, ureters, and bladder
Abdominal Radiograph
E-FAST (Extended Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma)
bedside ultrasound protocol design to detect peritoneal fluid, pericardial fluid, pneumothorax and/or hemothorax in trauma patient
RUSH Exam
ultrasound to quickly assess any patient with undifferentiated shock and hypertension
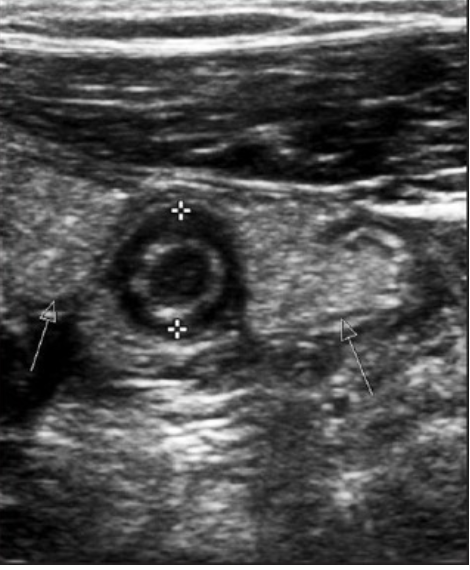
Appendicitis
“doughnut sign” or “bullseye sign” of ______ on ultrasound due to concentric alternating echogenic and hypoechoic bands
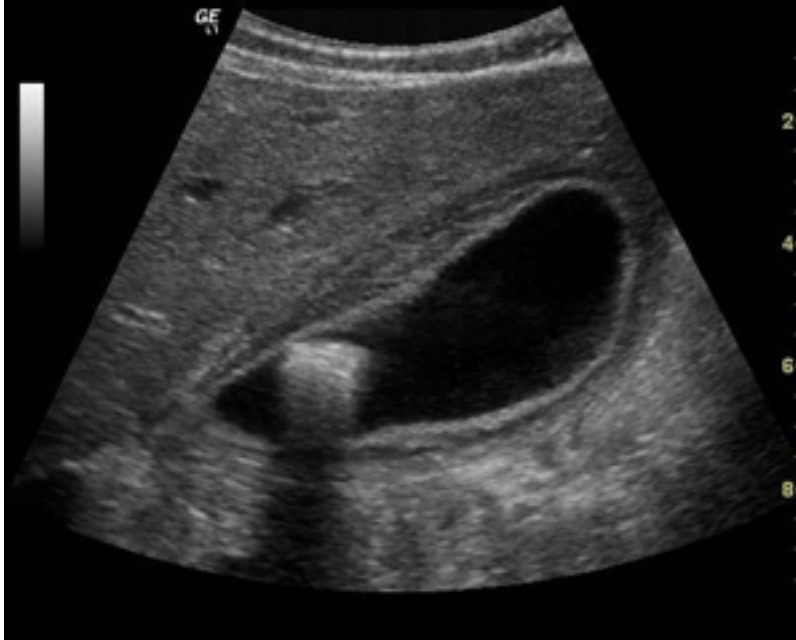
Cholelithiasis
formation of gallstones in gallbladder
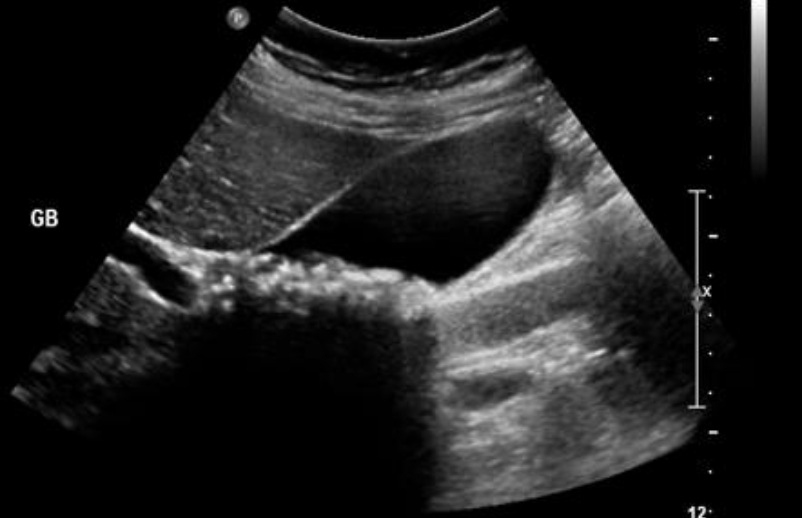
Cholecystitis
inflammation of the gallbladder
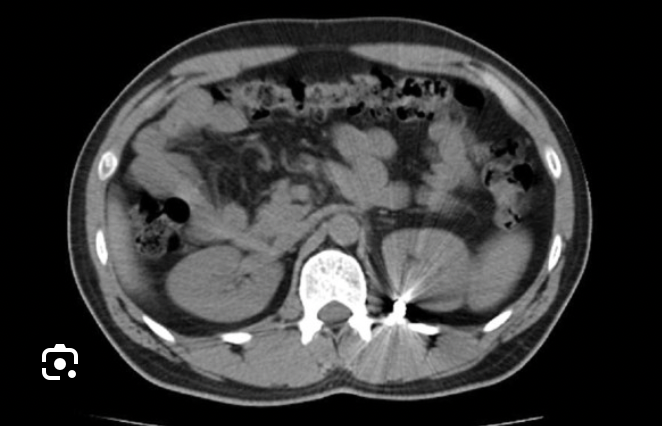
transverse
Which CT view?
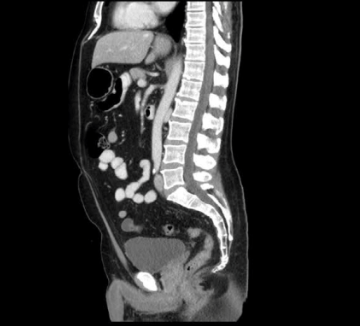
sagittal
Which CT view?
coronal
Which CT view?
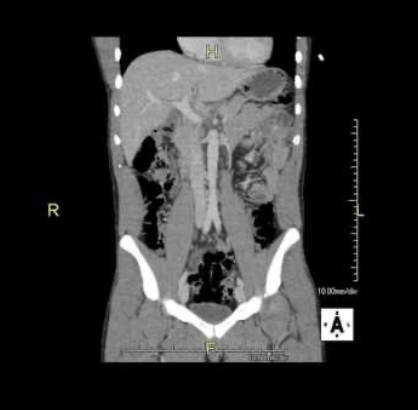
Acute appendicitis
CT Abdomen/Pelvis IV contrast
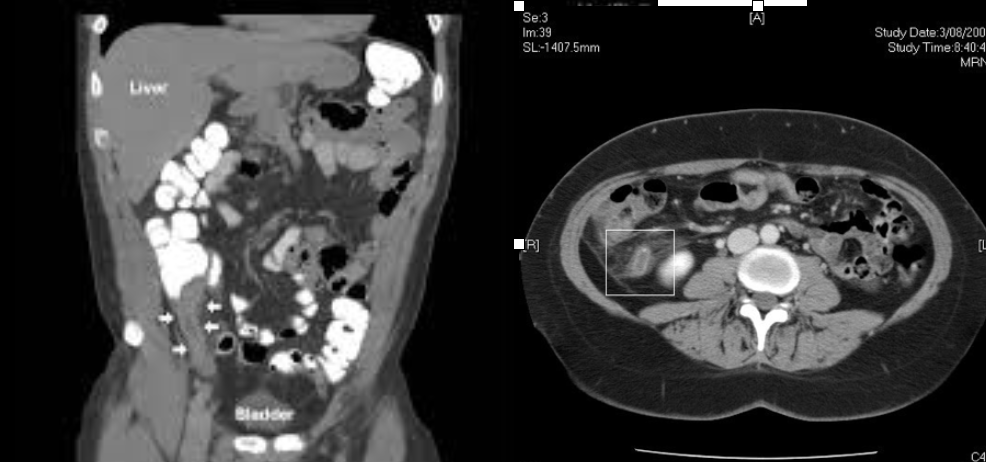
Diverticulitis
CT Abdomen/Pelvis IV contrast
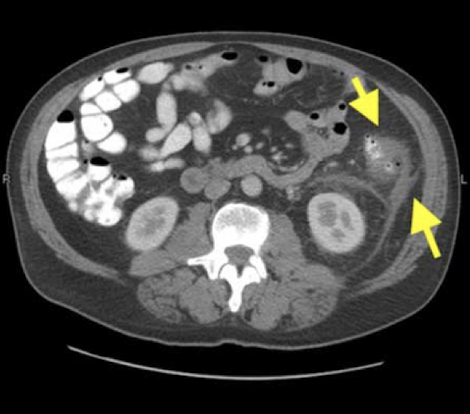
Intra-abdominal abscess
CT Abdomen/Pelvis IV contrast
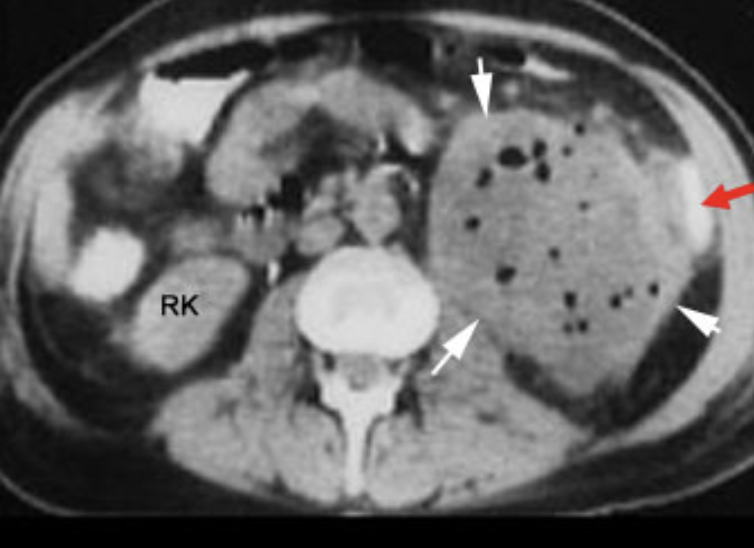
Colonic mass
CT Abdomen/Pelvis IV contrast
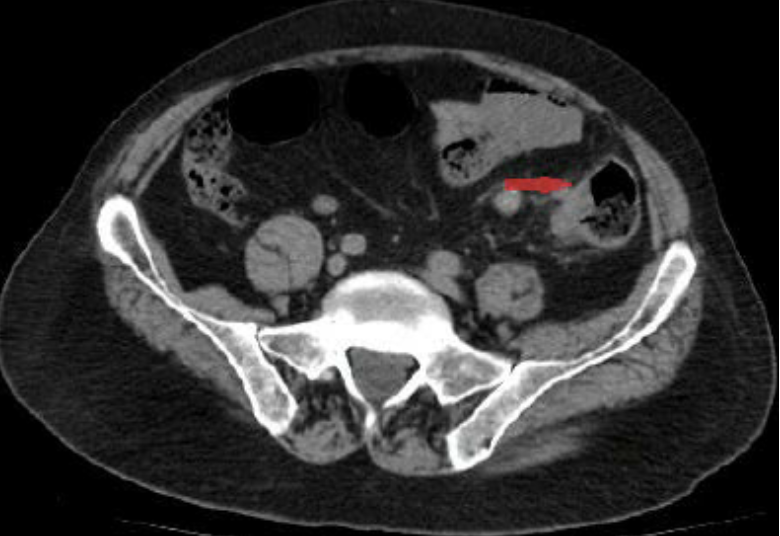
Pyelonephritis
CT Abdomen/Pelvis IV contrast
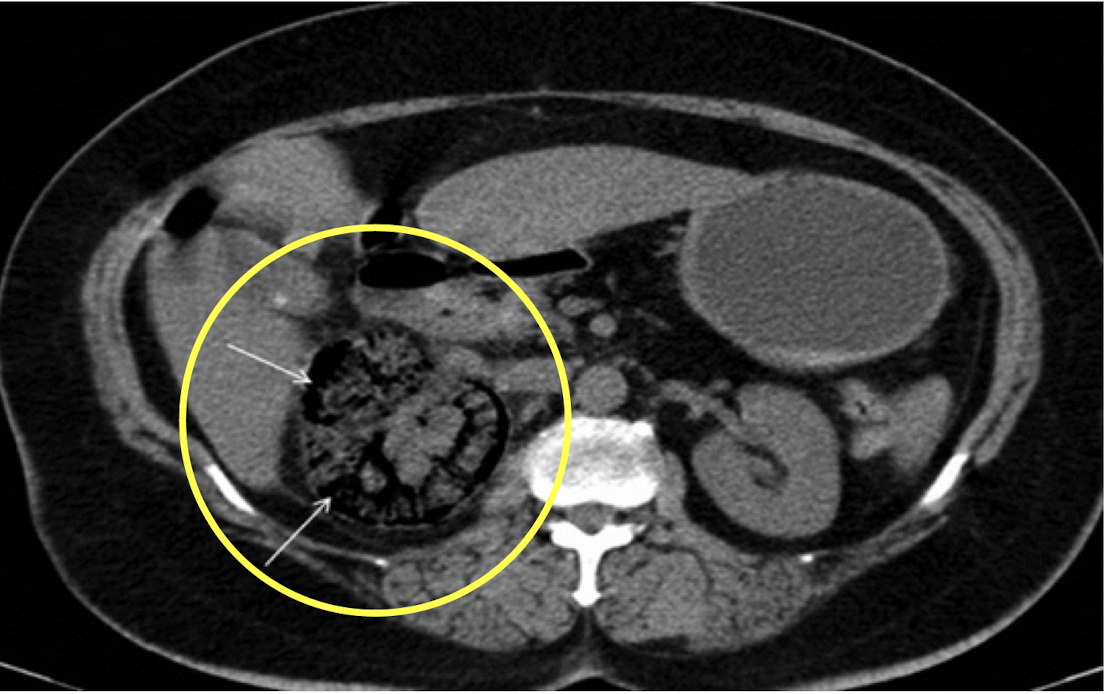
Renal cell carcinoma
CT Abdomen/Pelvis IV contrast
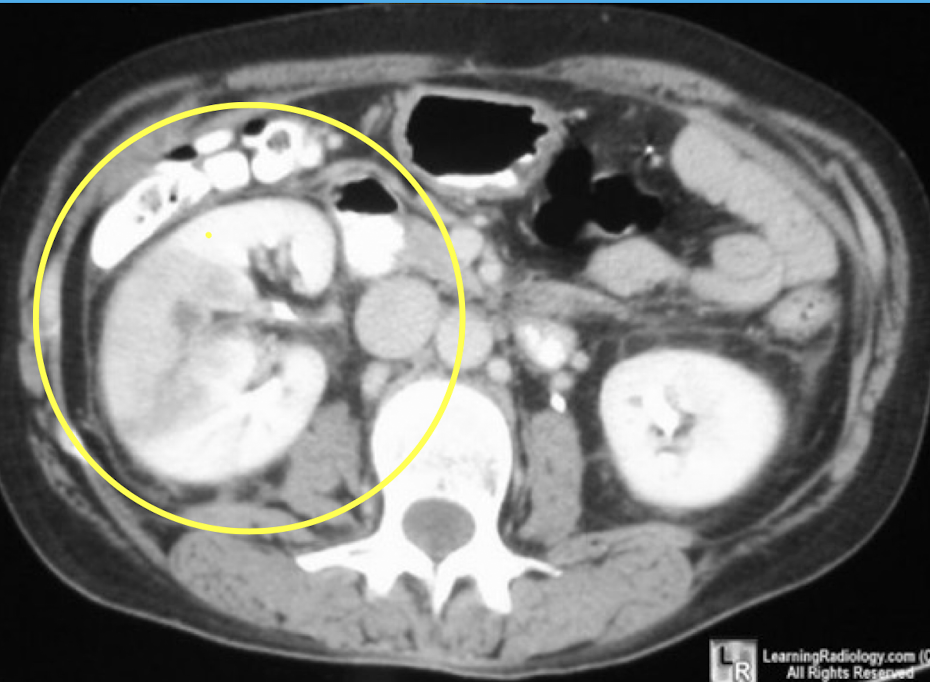
Mesenteric ischemia
CTA Abdomen/Pelvis IV contrast
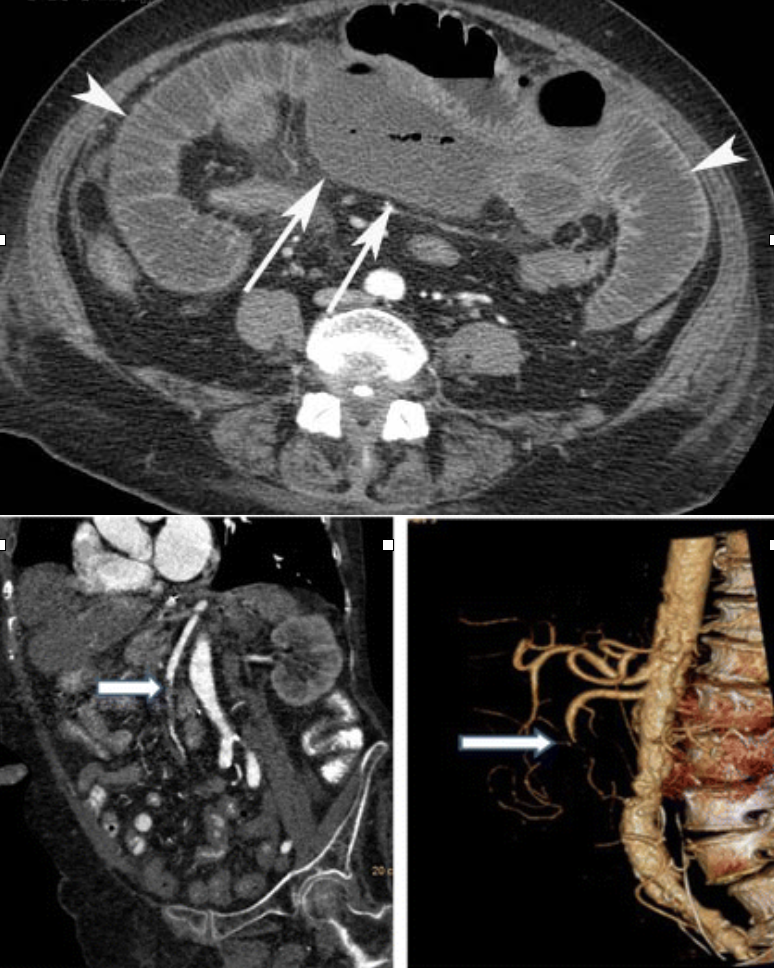
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)
CTA Abdomen/Pelvis IV contrast
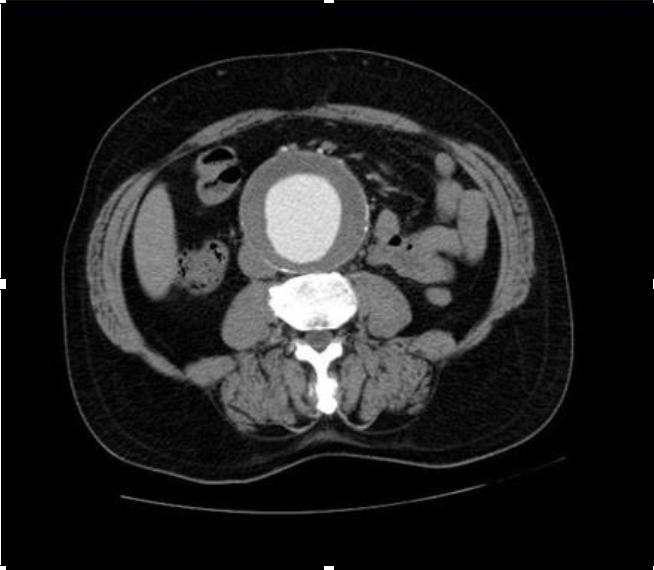
Trauma: Liver
CTA Abdomen/Pelvis IV contrast
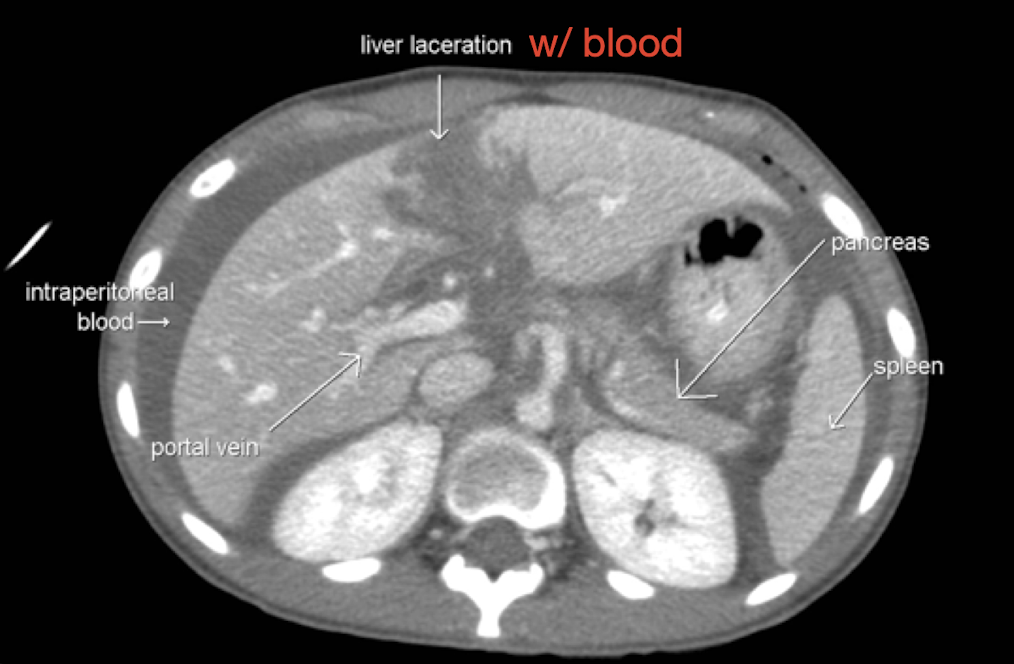
Trauma: Spleen
CTA Abdomen/Pelvis IV contrast
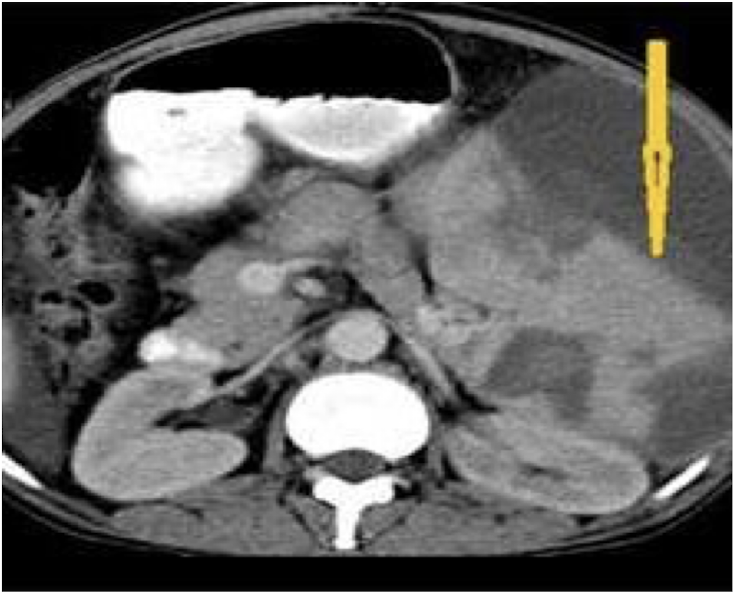
CT abdomen non-contrast
What imaging is used to visualize gallstones?
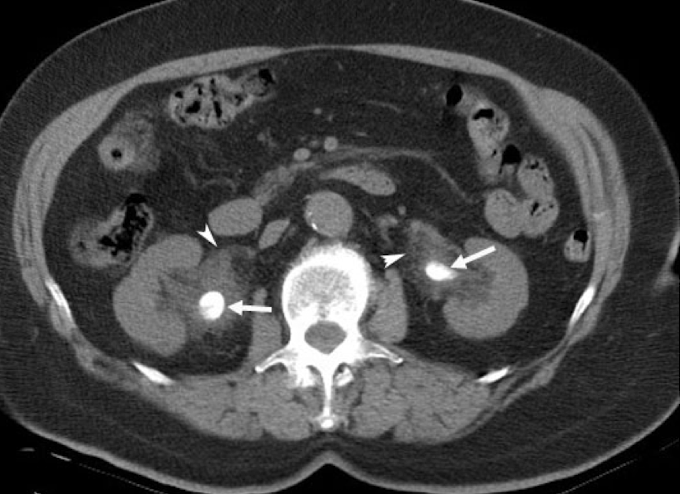
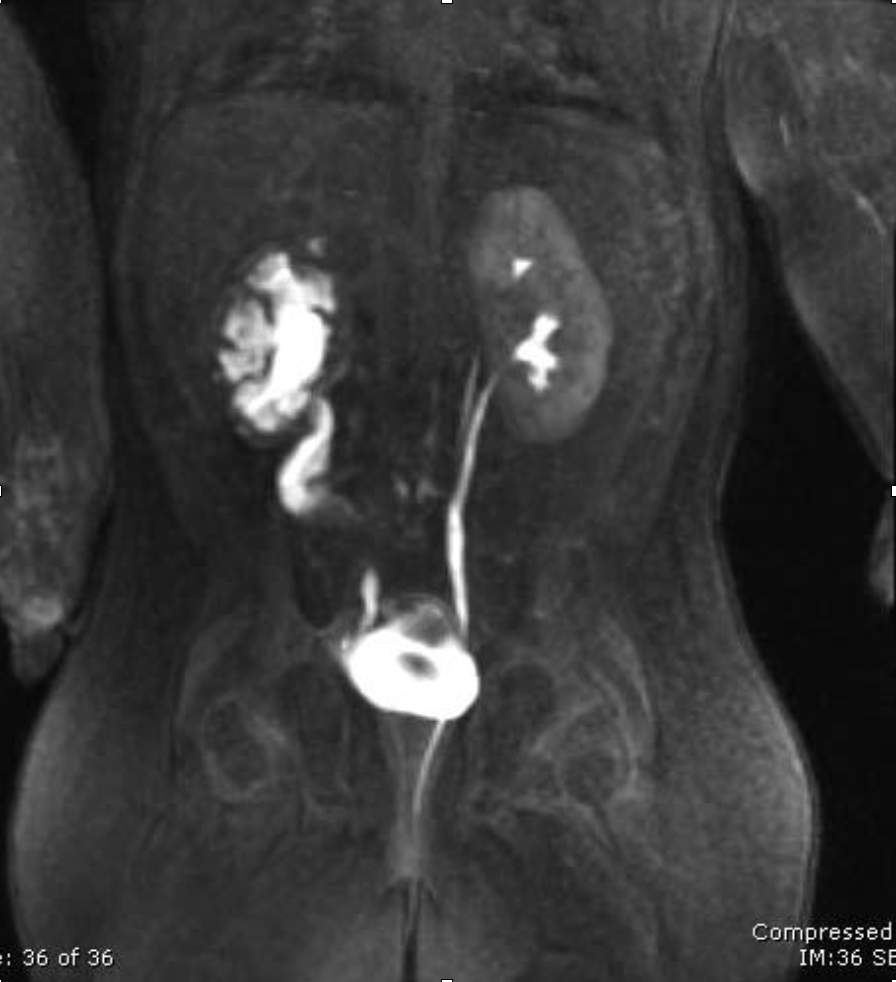
CT urogram
Which imaging is used to visualize ureteral stricture?
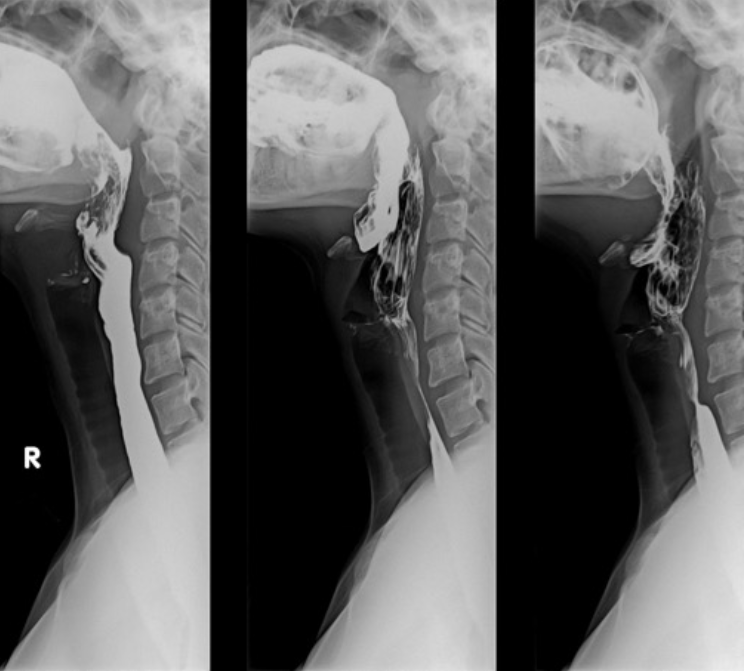
Upper GI Series (Barium swallow)
What imaging is used to assess for esophageal stricture or dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), may include fluoroscopy?
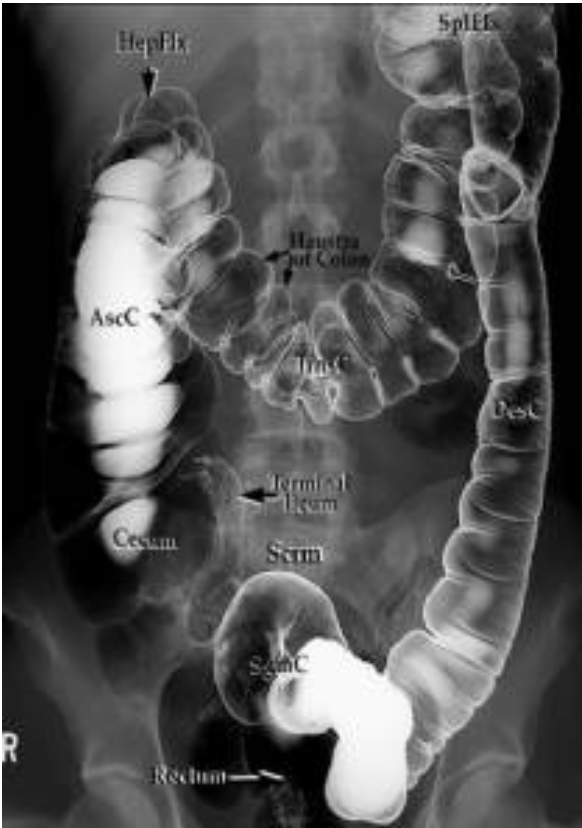
Lower GI series (Barium enema)
What imaging to assess for obstructions in large bowel?
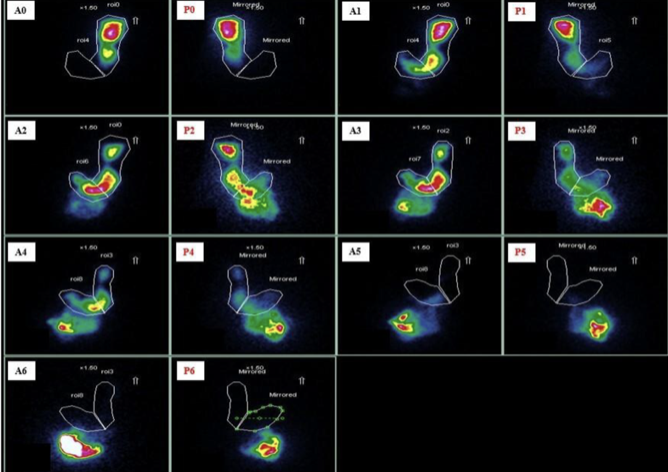
Scintigraphy
Which imaging to assess for gastric emptying for gastroparesis?
radioactive scrambled eggs ☢
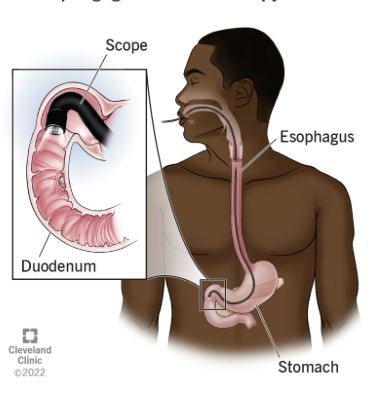
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
Which imaging to assess the upper GI tract including esophagus, stomach, and duodenum looking for ulceration?
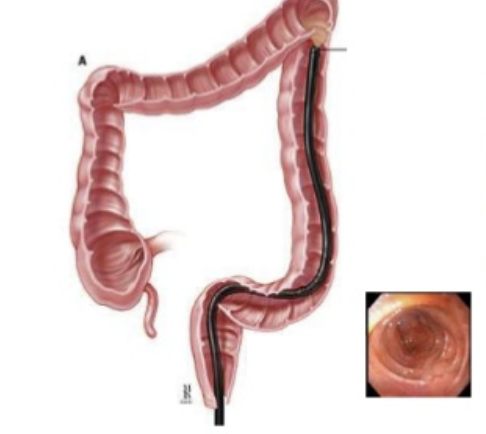
Flexible sigmoidoscopy
visualize part of the colon using less sedation and cleanout prep
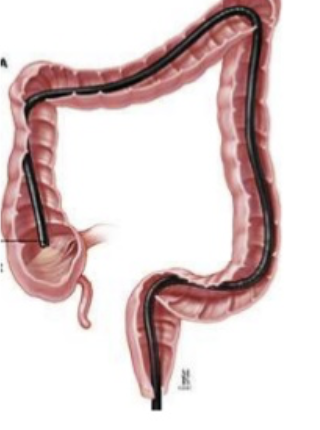
Colonoscopy
visualize the entire colon looking for polyps, malignancy, diverticulitis, requires full sedation and cleanout
T1 weighted
Which type of CT contrast highlights fat and anatomy: fat is bright; water is dark?
T2 weighted
Which type of CT contrast highlights fluid and pathology: water is bright, fat is bright
ERCP
-invasive, involves sedatives, radiation and more costly
-can cause pancreatitis, infection, bleeding
-diagnostic and therapeutic (stent, remove gallstones)
-gold standard for diagnosis of biliary obstruction
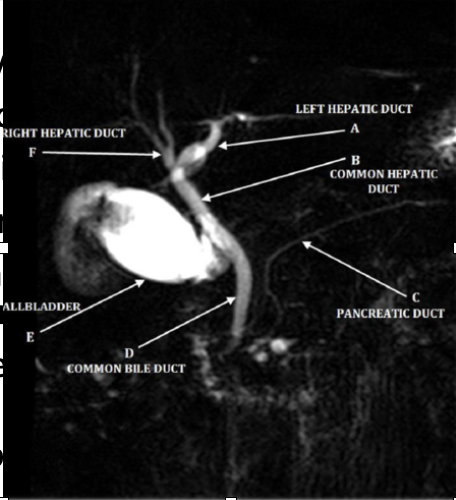
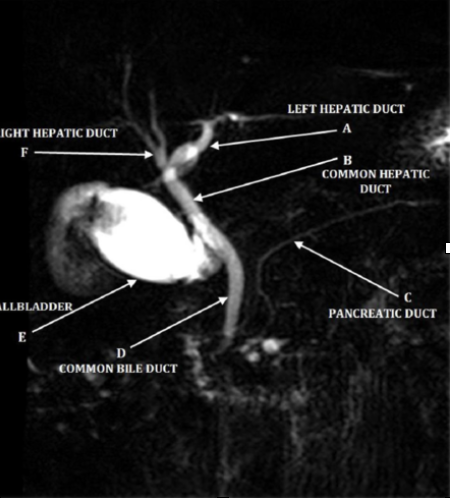
MRCP
-noninvasive, without anesthesia or radiation, cheaper
-improved visualization
-contraindicated with pacemakers and cochlear implant
-diagnostic but NOT therapeutic (delays treatment)
Positron emission tomography (PET)
nuclear medicine study that uses injectable radiotracer with a scan to evaluate function (blood flow, O2 use, glucose metabolism) visualizing uptake of radiotracer and look for metastasis
-assesses ischemic areas of heart
-used in neurology to evaluate tumors, seizure
Radiographs (KUB and ABD series with upright chest)
What imaging is used to assess for foreign body, bowel gas patterns, and obstruction?
Ultrasound
What imaging is used to visualize the gallbladder, appendix, complete abdomen, kidneys and lungs for pneumothorax (eFAST/RUSH), skin and soft tissue?
Computerized Tomography (CT)
What imaging is used to assess:
-with contrast (IV/ ± PO or rectal: vasculature, bowel, trauma
-without: stone protocol, spine trauma can also get reconstructions
*AVOID IV contrast with suspected perforation
Barium Studies
Which imaging can be fluoroscopy (real time) or radiographs?
-barium swallow: dysphagia, esophageal stricture
-barium enema: intussusception, other
-upper and lower endoscopy
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Which imaging includes:
• MRCP (choledocholithiasis)
• Pregnancy abdominal pain (appendicitis)