Chapter 6- Globular Proteins: Haemoproteins
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Haemoproteins
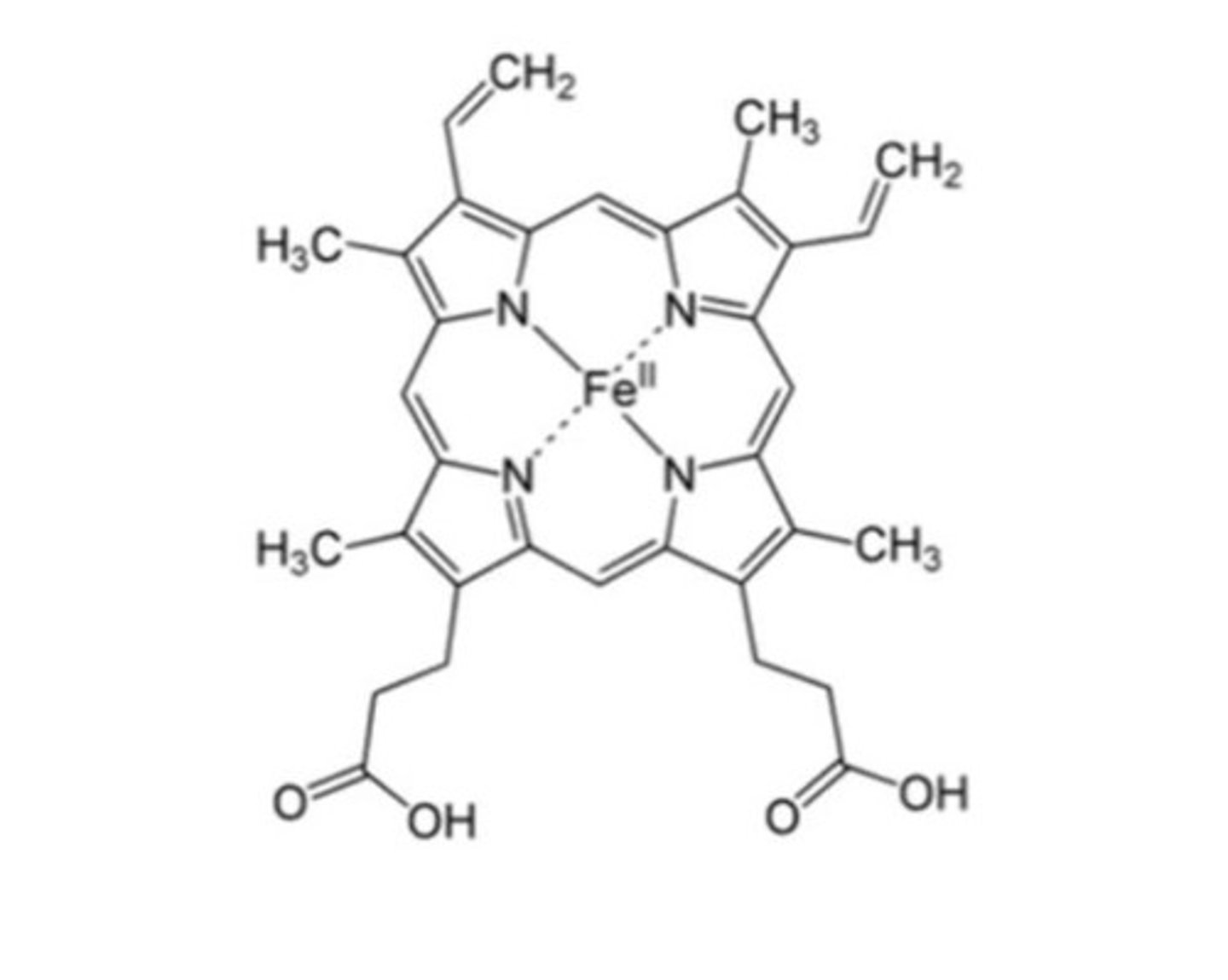
- Proteins that contain a haem prosthetic group
- Haem group binds oxygen in haemo/myoglobin
Haem composition
- Haem made of protoporphrin and ferrous iron (Fe2+)
How many bonds can iron make?
6- 4 with nitrogen of protoporphrin
Where is myoglobin found?
cardiac and skeletal muscle
Function of myoglobin
stores and carries oxygen in muscle cells
How many molecules of oxygen does each myoglobin molecule bind?
1
Myoglobin structure
- Made of 1 polypeptide chain, identical to haemoglobin peptide
- 140-150 AA long with 8 helices and one Haem group
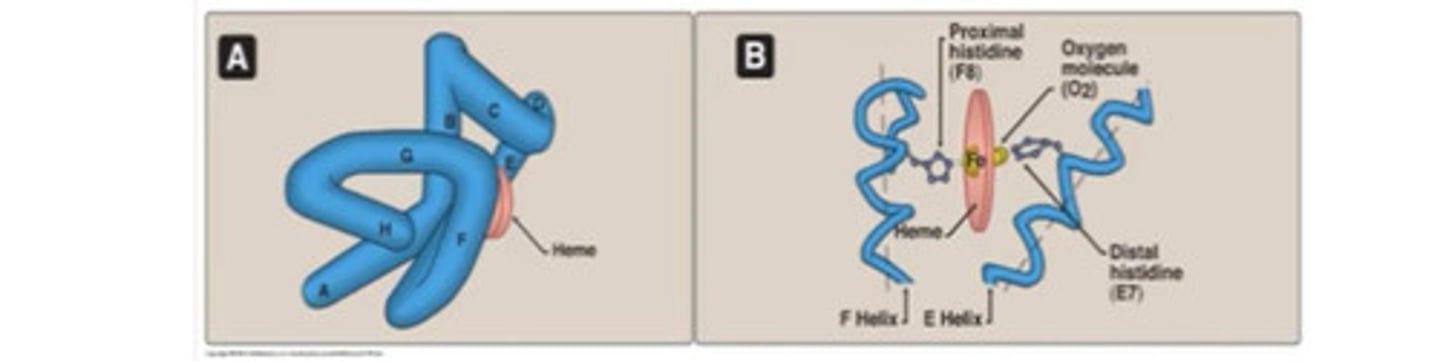
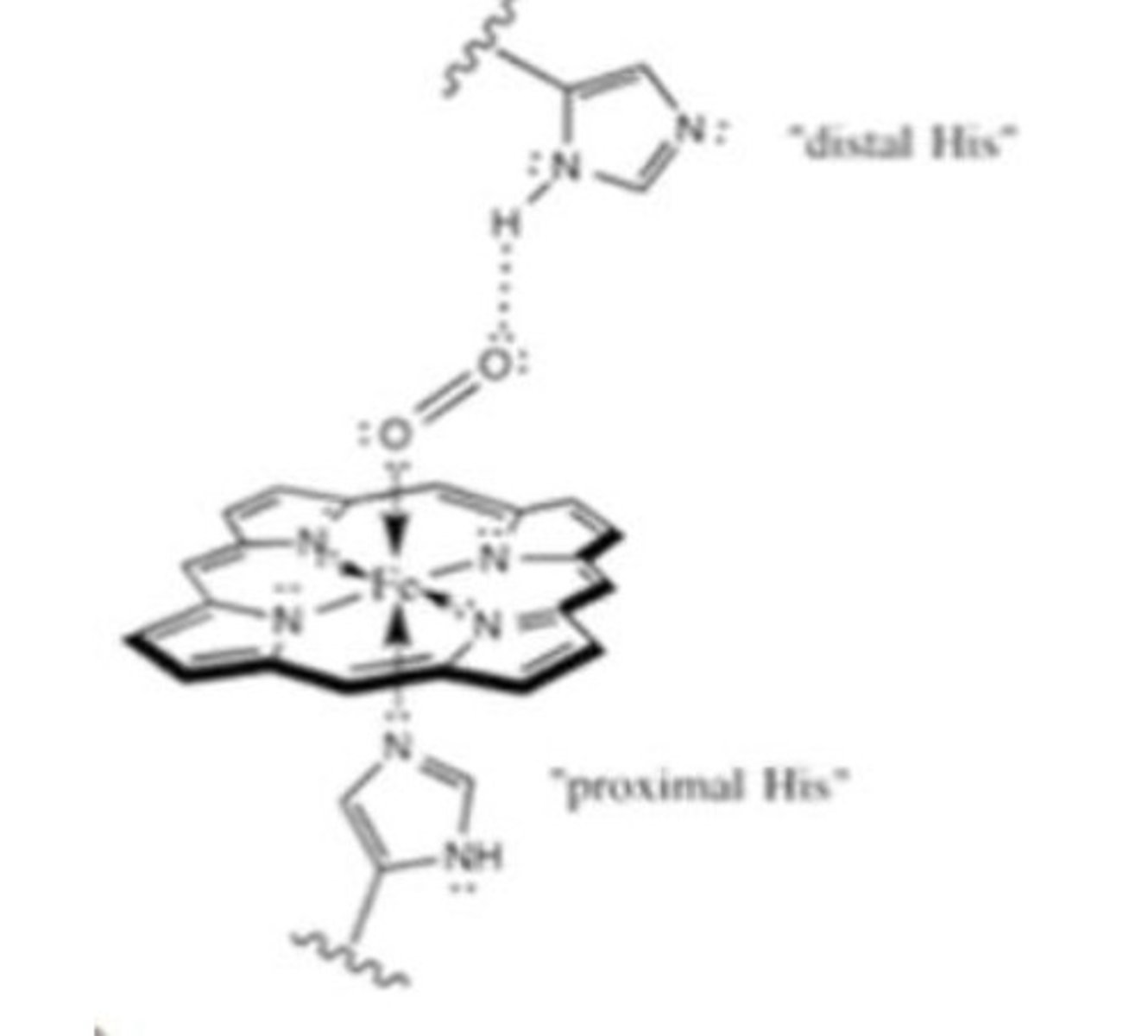
What does the oxygen bonding site involve in myoglobin?
2 histidines
- Proximal His binds Fe
- Distal his stabilises O2 binding to Fe
Where is haemoglobin found?
red blood cells
Function of haemoglobin
transport oxygen
Haemoglobin structure
Tetramer consisting of two alpha and two beta chains,each globulin contains haem molecule and each haem carries one oxygen (four oxygen for each Hb molecule)
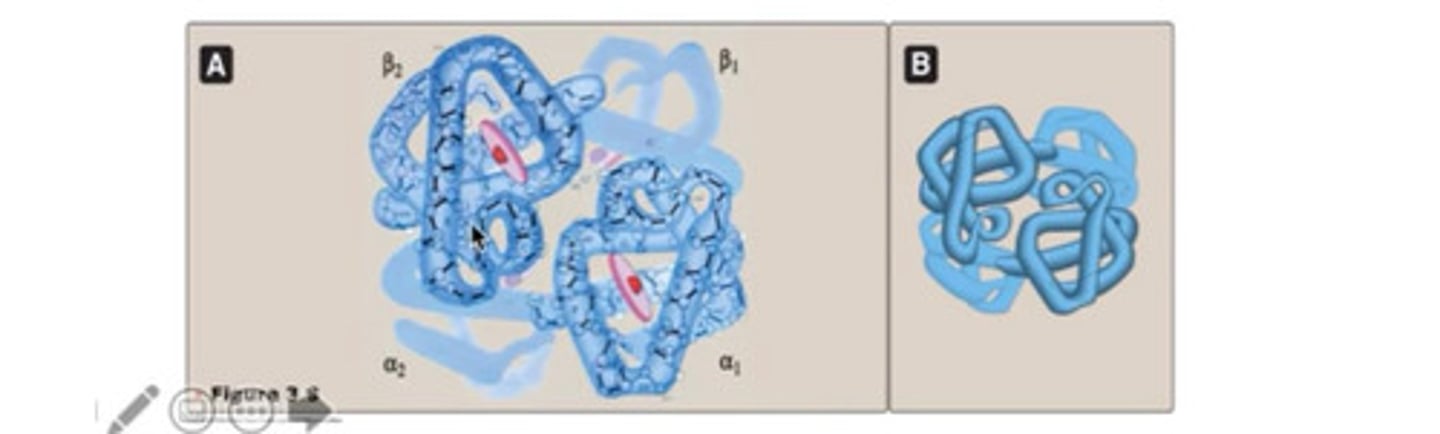
How many O2 molecules can hemoglobin carry?
four
How does haemoglobin structure change upon binding oxygen?
T form taut
R form relaxed
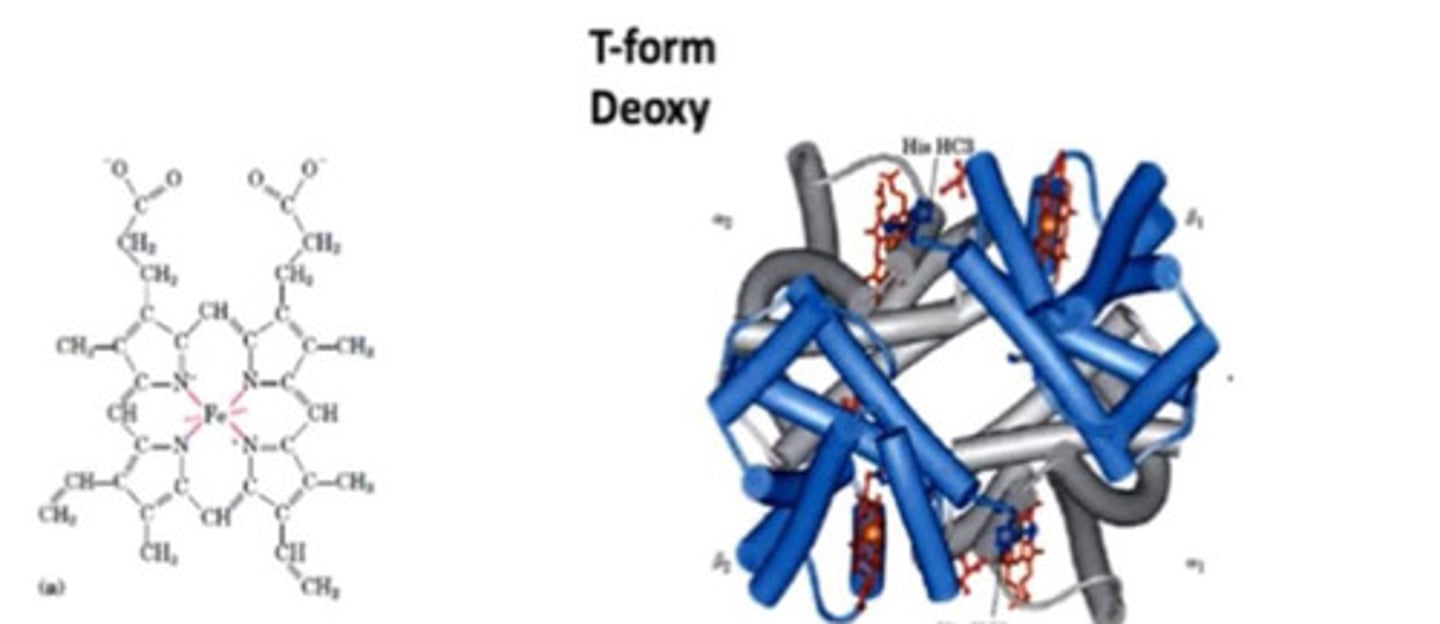
T form
- Very compact
- Deoxyhaemoglobin
- 4 haem molecules to each chain
Interactions in R form
- Some ionic and hydrogen bonds between aB dimers are broken in oxygenated state
Interactions in T form
- Weak ionic and hydrogen bonds between dimer pairs
- Strong hydrophobic interactions between a and B chains forming stable dimers
R form
- Relaxed
- Oxyhaemoglobin
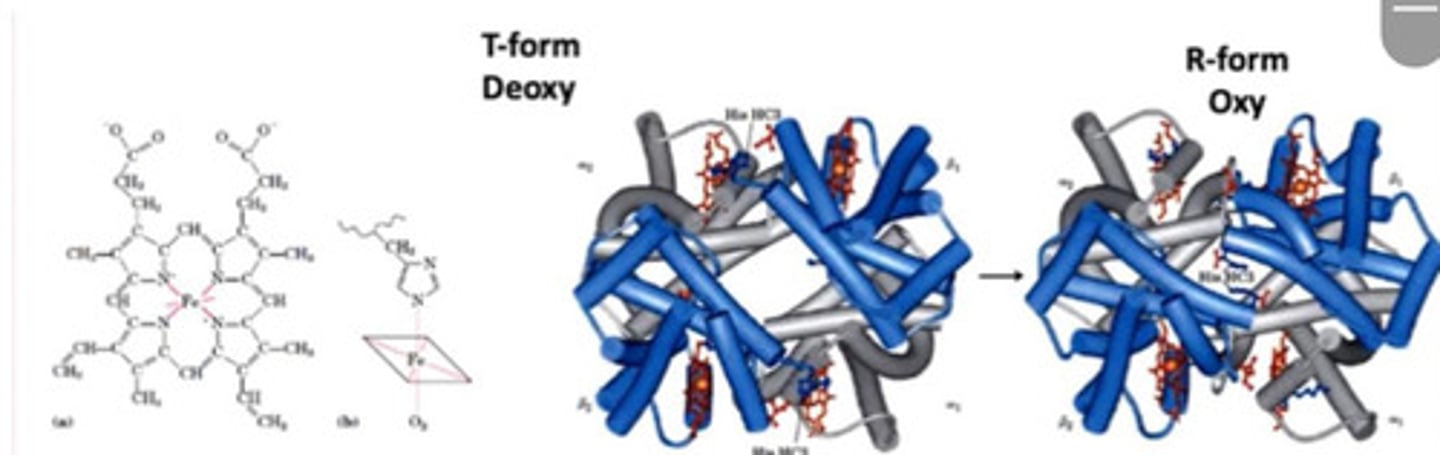
Conversion of T form to R form
- In deoxygenated form, His pushes Fe2+ out of plane of poryphyrine ring
- When O2 binds, it pulls the Fe2+ back in the plane which pulls the His with it resulting in conformational changes
- Conformation now relaxed
Oxygen transport in Hb
binds oxygen cooperatively ie binding of the first O2 enhances binding of the following ones by opening its structure
Myoglobin binding curve
-hyperbolic: has same affinity for O2 regardless of bound O2
Haemoglobin binding curve
- sigmoidal binding curve due to cooperative binding of oxygen molecules
- lower pH and higher temperature = reduced O2 affinity - exercise causes pH to drop and temperature to rise in skeletal muscle - causes a righwards shift making it easier to release O2 into the tissue
Two ways to favour unloading of O2
1. Decrease pH (when CO2 and H+ increase)
2. Increase of 2, 3 biphosphoglycerate (normal metabolic product in RBCs)
- Both favour Deoxyhaemoglobin conformation by stabilising it
Stored blood 2, 3 biphosphoglycerate concentration
Low
Transport of CO2
- On the amino terminus of haemoglobin as a carbamate group- Carbaminohaemoglobin
Effect of CO2 on deoxyhaemoglobin
- Stabilises the deoxy form of haemoglobin and decreases its affinity for O2
- O2 disassociation curve shifts to the right
Carbon monoxide
- Binds to haem sites like oxygen
- Shifts the haemoglobin conformation to a relaxed state, so the oxygen binds with high efficiency
- O2 disassociation curve becomes hyperbolic and shifts to the left
- O2 cannot be released in tissues anymore
- O2 not delivered to tissue- toxicity of carbon monoxide
Haemoglobinopathies
Diseases caused by DNA mutations that occur in alpha and beta Globin protein genes
Normal beta globin
HbA sequence: Glutamate at position 6 (charged)
Sickle cell anaemia
HbS sequence: Valine at position 6 (hydrophobic)
HbC sequence- less severe condition
Haemoglobin C sequence: Lysine at position 6
Sickle cell anaemia
- Sickle shaped cells
- Affects red blood cells
- Point mutation DNA
- Valine at positon 6
- Hydrophobic amino acid
- Fits in hydrophobic pocket in haemoglobin
- Long rope like rigid fibres form and distort erythrocyte shape
- Occlude normal blood flow in capillaries
- Possible advantage for heterozygous carriers as have less susceptibility to malaria