ANS: Pharmacology & Pathophysiology (Apex)
1/336
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
337 Terms
What medications are considered "synthetic catecholamines"?
(1) isoproterenol
(2) dobutamine
What medications are considered "synthetic NON-catecholamines"?
(1) ephedrine
(2) phenylephrine
Which medications are considered "adrenergic agonists"?
(1) epinephrine
(2) norepinephrine
(3) dopamine
Which medications are SELECTIVE β2-adrenergic agonists?
SHORT ACTING
1) albuteroI, terbualtine, levalbuterole
LONG ACTING
(1) albuterol
(2) salmeterol
SE anxiety tremor restlessness
Used to tx asthma, COPD, airway reactivity
chronic admin can cause down rgulation of target receptors resulting in tachyphylasix.
Which medications are SELECTIVE α2-agonists?
(1) clonidine
(2) dexmedetomidine
Which beta blockers are β-ONLY antagonists?
(1) propranolol
(2) esmolol
Which beta blockers are α & β antagonists?
(1) labetalol
(2) carvedilol
Which medications are phosphodiesterase inhibitors?
(1) milrinone
(2) sildenafil
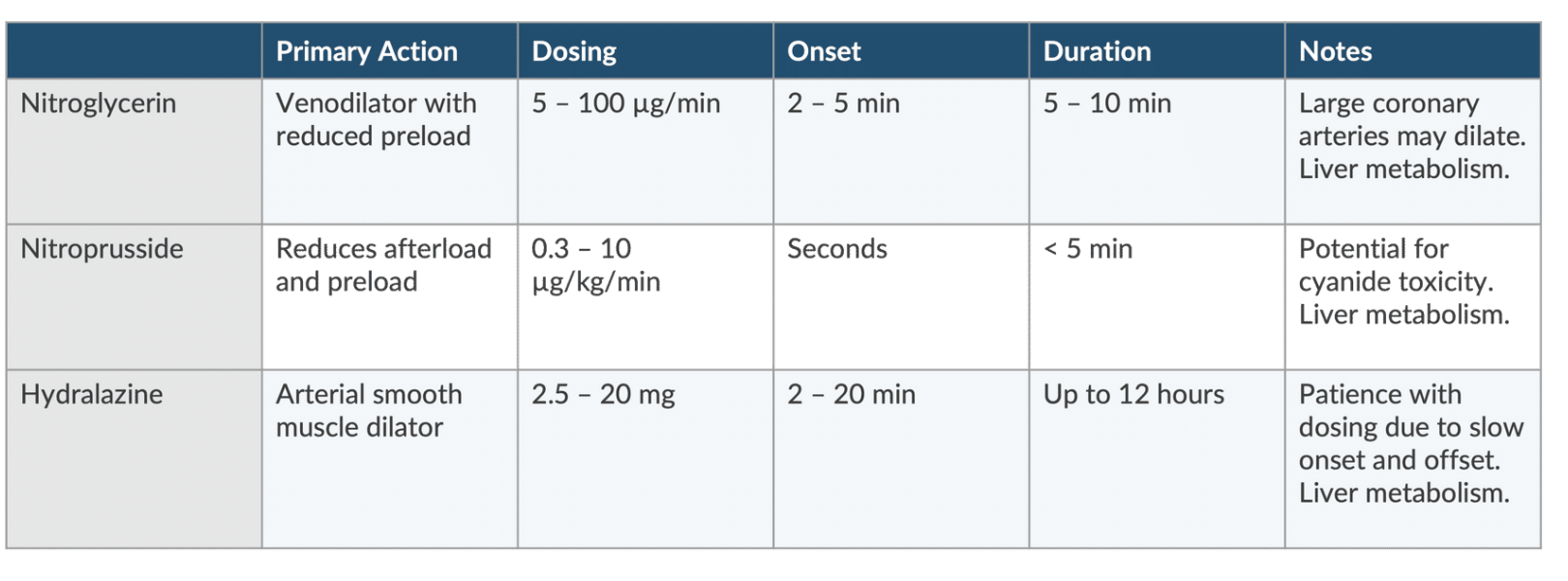
Which medications are DIRECT VASODILATORS?
(1) NTG
(2) nitroprusside
(3) hydralazine
Which medications are cholinergic AGONISTS?
(1) nicotine
(2) bethanechol
(3) physostigmine
Which medications are antimuscarinics?
(1) atropine
(2) glycopyrrolate
(3) scopolamine
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) relies on two neurotransmitters. What are they?
(1) ACh → parasympathetic
(2) NE → sympathetic
ALL ganglionic neurotransmission uses __________(1) (neurotransmitter).
POSTganglionic PARASYMPATHETIC neurotransmission uses ____________ (2) (neurotransmitter).
POSTganglionic SYMPATHETIC neurotransmission uses ___________ (3) (neurotransmitter).
(1) ACh
(2) ACh
(3) NE
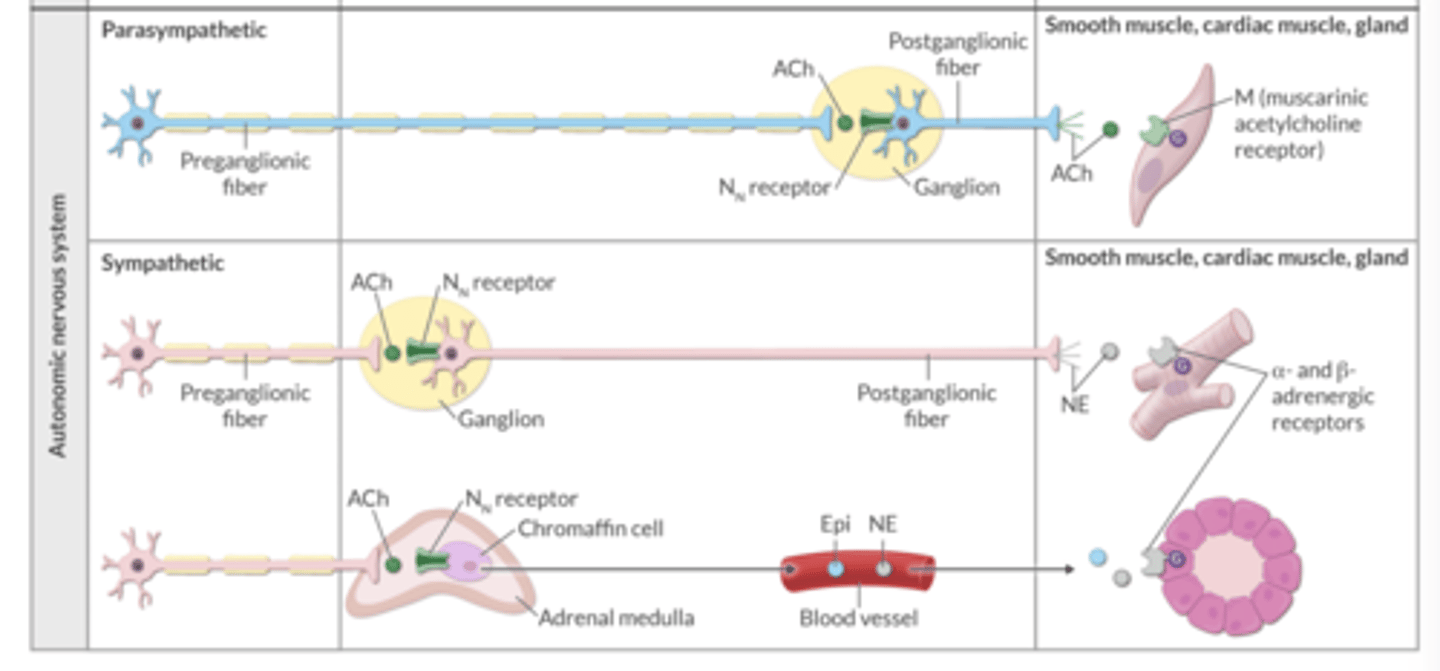
In the parasympathetic nervous system, which neuron is LONGER → the preganglionic fiber or the postganglionic fiber?
preganglionic fiber = longer
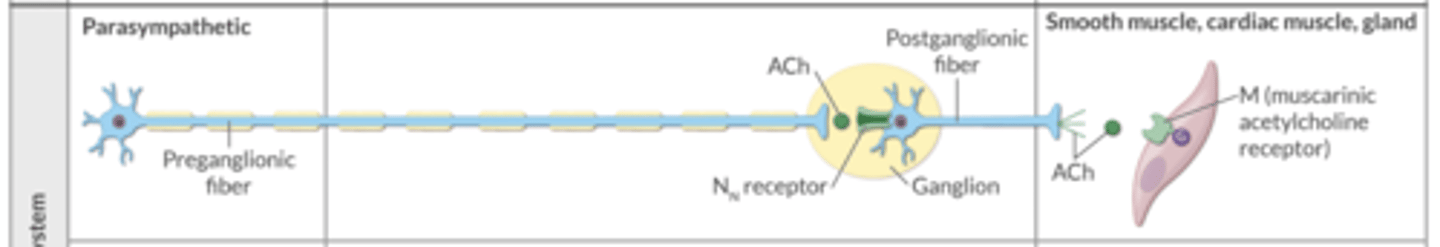
In the sympathetic nervous system, which neuron is LONGER → the preganglionic fiber or the postganglionic fiber?
postganglionic fiber = longer

In the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, ACh from the preganglionic fiber binds to ________ receptors on the postganglionic fibers.
Nn
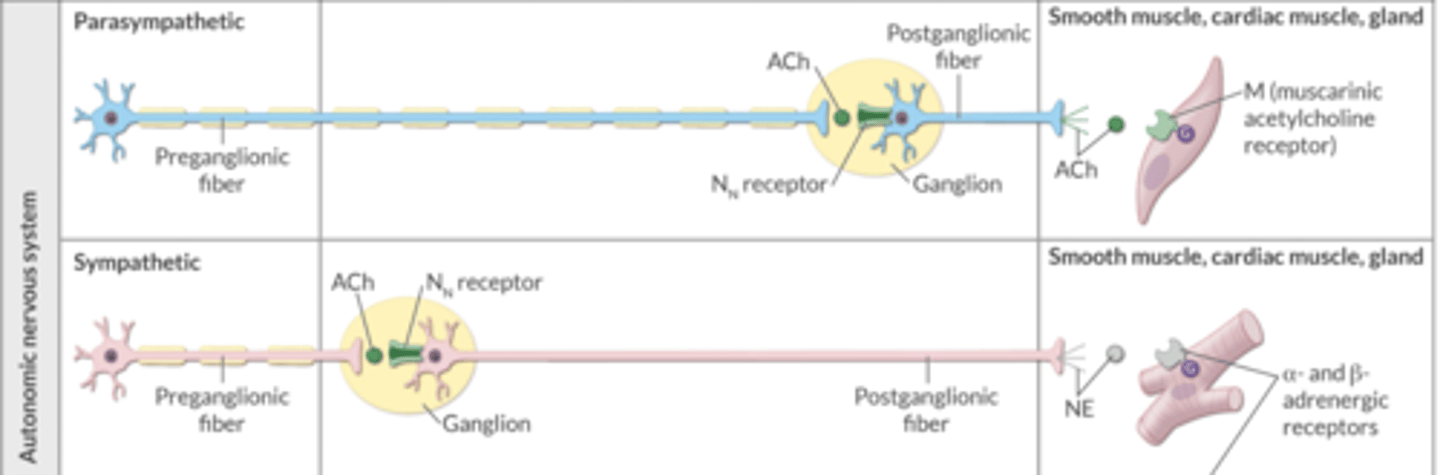
In the parasympathetic nervous system, ACh from the postganglionic fiber binds to _______ receptors on the target smooth/cardiac muscle or gland.
M (muscarinic)
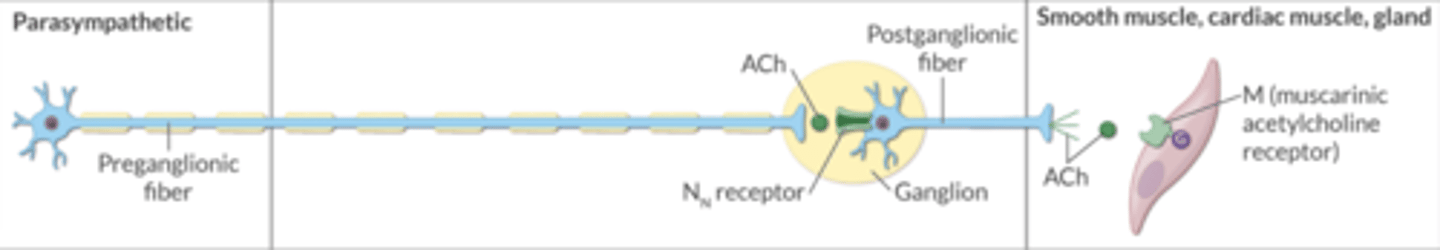
In the sympathetic nervous system, NE from the postganglionic fiber binds to what receptors on the target smooth/cardiac muscle or gland?
α- and β-adrenergic receptors

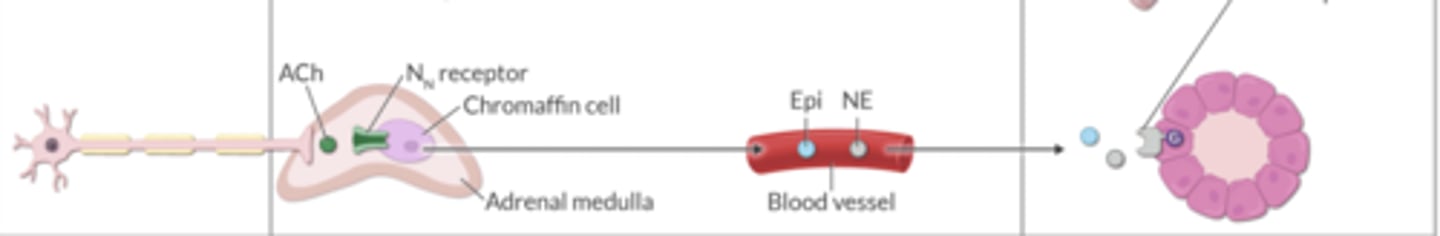
There are specific sympathetic fibers that act on chromaffin cells in the adrenal medulla.
ACh binds to Nn receptors on chromaffin cells. Then, these cells release _______ and _________, which act on blood vessels.
epinephrine, norepinephrine
T/F. Dexmedetomidine produces analgesia.
TRUE
What are the 3 α-selective drugs?
(1) phenylephrine → α1-selective
(2) clonidine → α2-selective
(3) dexmedetomidine → α2-selective
How is phenylephrine metabolized?
MAO
How is clonidine metabolized?
(1) 50% by liver
(2) 50% renal unchanged
What is the typical infusion dose of phenylephrine?
0.15-0.75 mcg/kg/min
What is clonidine primarily used to treat?
HTN
What are the s/e of clonidine?
(1) sedation
(2) rebound HTN w/ abrupt cessation
What is a typical PO dose of clonidine?
0.1-0.6 mg/day
How does phenylephrine impact renal blood flow (RBF)?
↓↓↓
How is dexmedetomidine metabolized?
CYP liver
What are the s/e of dexmedetomidine?
(1) sedation
(2) bradycardia
(3) hypotension
T/F. Dexmedetomidine produces respiratory depression.
FALSE
What is a typical bolus and infusion dose of dexmedetomidine?
(1) bolus → 1 mcg/kg over 10 minutes
(2) infusion → 0.2-0.8 mcg/kg/hr
What type of medication is phenylephrine?
(1) synthetic NON-catecholamine
(2) α1-agonist
(3) arterial & venous vasoconstriction
What IV bolus dose of phenylephrine is typically administered? What is the max dose?
(1) bolus → 40-100 mcg
(2) max → 200 mcg
What are the s/e of phenylephrine?
(1) reflex bradycardia → baroreceptor activity
(2) ↑ pulmonary artery pressure due to direct vasoconstrictive action of the drug in the lung vasculature and increase in venous return
(3) high dose/prolonged duration → risk of end-organ damage
Reflex bradycardia (from phenylephrine) is a result of the ___________ reflex.
baroreceptor
T/F. Phenylephrine is arrhythmogenic.
FALSE → unlike natural/synthetic catecholamines
Which medication can be administered in the event of a phenylephrine overdose?
nonselective alpha-antagonist (e.g., phentolamine)
What class of medications should NOT be used to treat hypertensive crisis?
beta-blockers → can cause pulmonary edema and irreversible cardiovascular collapse
T/F. The α2 receptor is present throughout the body.
TRUE
What are the different types of α2 receptors found in the body?
(1) presynaptic → NE-releasing neurons in the CNS/PNS (negative feedback ↓ NE release)
(2) postsynaptic → smooth muscle, organs
(3) nonsynaptic → platelets
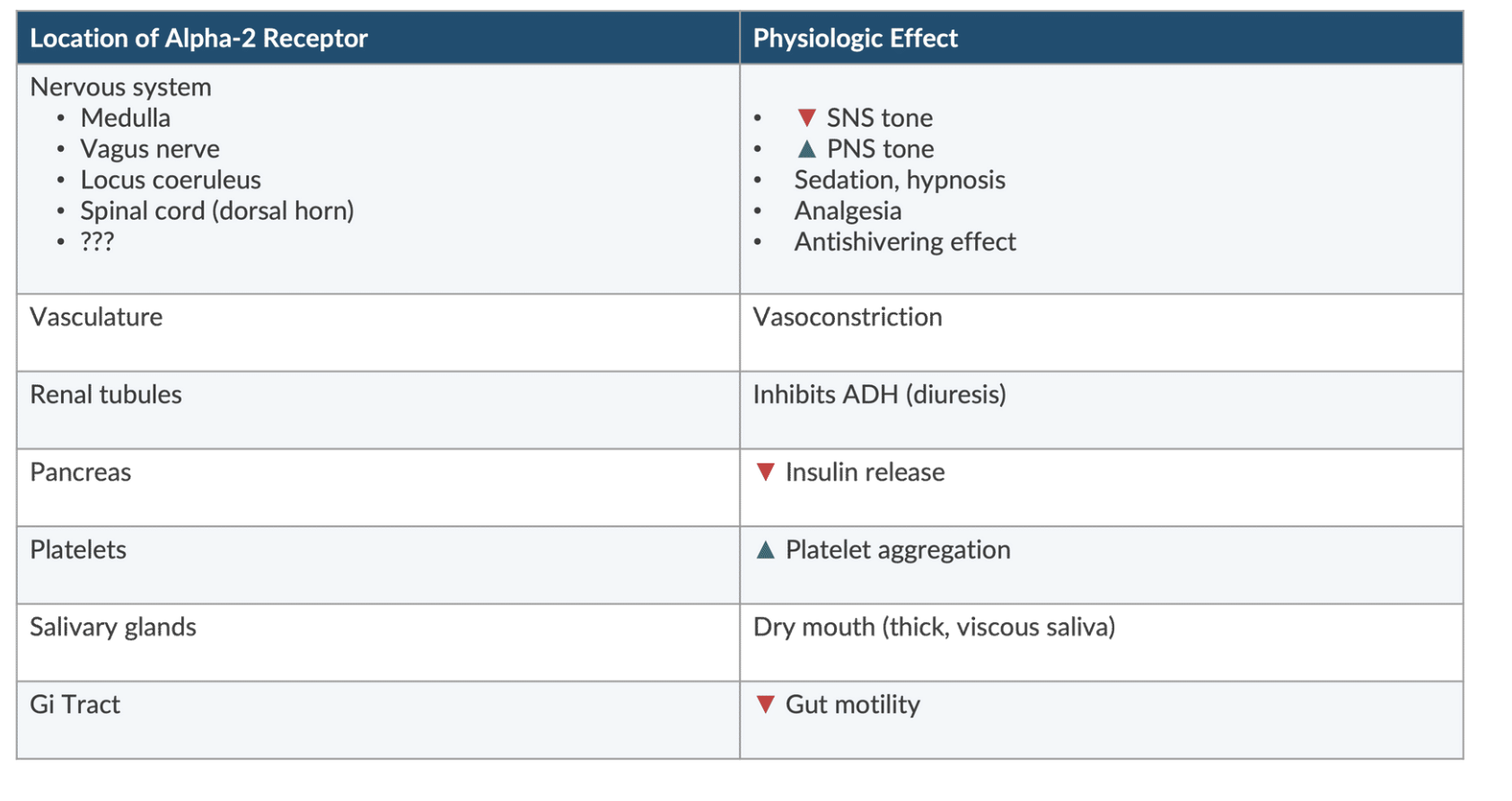
Stimulation of the α2 receptor in the vasculature causes what effect?
vasoconstriction
Stimulation of the α2 receptor in the renal tubules causes what effect?
inhibits ADH (diuresis)
Stimulation of the α2 receptor in the pancreas causes what effect?
↓ insulin release
endogenous catecholamines
epi levo, dopamine
syntheric catecholamies like dobu and isoproternol
may produce HTn, arrthmias and myocardial ischemia
Stimulation of the α2 receptor in platelets causes what effect?
↑ platelet aggregation
Stimulation of the α2 receptor in the salivary glands causes what effect?
dry mouth
Stimulation of the α2 receptor in the GI tract causes what effect?
↓ GI motility
Stimulation of the α2 receptor in the spinal cord causes what effect?
analgesia
Stimulation of the α2 receptor in the medulla causes what effect?
↓ SNS tone
Stimulation of the α2 receptor in the vagus nerve causes what effect?
↑ PNS tone
Stimulation of the α2 receptor in the locus coeruleus causes what effect?
sedation, hypnosis
Which medication is a FULL (not partial) α2-agonist → clonidine or dexmedetomidine?
dexmedetomidine
How does the elimination ½-life compare in clonidine vs. dexmedetomidine?
(1) clonidine → 8 hours
(2) dexmedetomidine → 2 hours
How does protein binding compare in clonidine vs. dexmedetomidine?
(1) clonidine → 50%
(2) dexmedetomidine → 94%
How does the distribution ½-life compare in clonidine vs. dexmedetomidine?
(1) clonidine → >10 minutes
(2) dexmedetomidine → 5-6 minutes
Where does clonidine act?
(1) α2 agonist at central presynaptic receptors (medulla & locus coeruleus) → ↓ sympathetic outflow (sympatholysis)
(2) ↓ HR and BP
How does clonidine ↓ BP?
inhibits NE release causing vasodilation
Clonidine produces centrally mediated pain modification & analgesia via activity at the ______________.
dorsal horn (spinal cord)
What can abrupt discontinuation of clonidine lead to?
(1) rebound HTN, tachycardia
(2) arrhythmia
What is clonidine used to treat?
(1) diagnosis of pheochromocytoma
(2) HTN
(3) opiate/nicotine withdrawal symptoms
Where does dexmedetomidine work?
(1) stimulates α2 receptors in the brain and spinal cord → inhibits neuronal firing
(2) ↓ sympathetic drive → hypotension, bradycardia, sedation, analgesia
rapid infusion can stimulate post synaptic alpha 2 receptors in arterial and venous circulation leading to vasoconstriction and increased blood pressure.
The CNS effect (produces vasodilation) lags behind peripheral response. Once CNS icks in, it overpowers peripheral alpha 2 effect. Therefore making it possible fr Dex to cause transient rise in BP
How can dexmedetomidine impact the kidneys?
(1) ↓ renin release
(2) ↑ GFR
How can dexmedetomidine impact insulin release?
↓
What are the anesthetic benefits of dexmedetomidine?
(1) sedation
(2) analgesia
(3) ↓ shivering
(4) ↓ emergence agitation in adults and children
(5) ↓ neuroendocrine stress response to surgery
What symptoms can RAPID administration of dexmedetomidine lead to?
(1) can stimulate POST-synaptic α2 receptors in the arterial and venous circulation
(2) can lead to HTN and vasoconstriction
A common s/e of prazosin is...
A. diuresis
B. severe bradycardia
C. orthostatic hypotension
D. excessive energy
C - orthostatic hypotension
Which medications are considered NON-selective α1- and α2-antagonists?
(1) phenoxybenzamine
(2) phentolamine
Via what route is phenoxybenzamine administered?
PO
How does phenoxybenzamine work?
(1) non-selective α1- and α2- antagonist
(2) blocks the α-mediated activity of NE and epinephrine → ↓ PVR and BP
Phenoxybenzamine (α1- & α2-antagonist) is used almost EXCLUSIVELY to treat what?
pre-op management of pheochromocytoma → to normalize BP & prevent episodic HTN
What is the best treatment for phenoxybenzamine-induced severe hypotension?
(1) vasopressin
(2) fluids
***phenylephrine & NE are ineffective in treating severe hypotension because phenoxybenzamine IRREVERSIBLY binds to receptors
T/F. When phenoxybenzamine (α1- and α2-antagonist) binds to a receptor, it is IRREVERSIBLE.
TRUE → only the synthesis of new receptors will terminate its effect
***so, NE and phenylephrine are INEFFECTIVE in treating severe hypotension
What are the s/e of phenoxybenzamine (α1- and α2-antagonist)?
(1) ↑ HR (baroreceptor activation & ↑ NE)
(2) significant orthostatic hypotension
Phenoxybenzamine (α1- and α2-antagonist) is used almost exclusively to treat pheochromocytoma.
How can we prevent significant hypotension with initiation?
low-dose initiation that is gradually ↑ over several days
When an alpha-blocker is used (e.g., phenoxybenzamine) the use of epinephrine may worsen hypotension. Why?
(1) unopposed β2 stimulation → "epinephrine reversal"
(2) a reversal of epi's pressor response (mediated by α receptors) to a depressor response (mediated by β2 receptors)
What type of medication is phentolamine?
competitive non-selective α-antagonist
Receptor interaction can be overcome using alpha recetor agonists like neo or levo (unline phenoxybenzamine)
Shorter half life <10 minutes
Use in caution with patients with limited flow CAD due to rapid activng IV vasodilators that cuases baroreceptor mediated reflex tachycardiac
benefiical in refractory HTN seen with abrupt dc in clonidine dc
Used in IV extravasation like epi or norepi to prevent tissue necrosis
Has affinity of 5-HT receptors whic sitmulates stomach acid secretion, and induces mast cell degranulation
Hypotension resulting from administration of _____________ (phentolamine, phenoxybenzamine) can be reversed by phenylephrine or NE.
phentolamine → phenoxybenzamine causes irreversible α-receptor antagonism
Which non-selective α-antagonist has a shorter duration of action → phenoxybenzamine or phentolamine?
phentolamine (½-life <10 min)
Which medication may be used to treat refractory HTN that results from abrupt clonidine discontinuation?
phentolamine → non-selective α-antagonist
What mediation can be administered after IV extravasation of a vasoconstrictor (e.g., epinephrine, NE) to prevent tissue necrosis?
phentolamine (non-selective α-antagonist)
What are the potential s/e of phentolamine (non-selective α-antagonist)?
(1) reflex tachycardia (baroreceptor mediated) → use with caution in those with CAD
(2) affinity for 5HT₃ receptors:
a. ↑ stomach acid
b. mast cell degranulation
Which medications are SELECTIVE α-antagonists?
(1) prazosin
(2) terazosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin
(3) Yohimbe
What type of medication is prazosin?
highly-selective α1-antagonist
What are the s/e of prazosin (α1-antagonist)?
orthostatic hypotension
What is prazosin used to treat?
(1) highly-selective α1-antagonist
(2) ↓ PVR in arterioles and veins (↑ venous capacitance)
(3) ↓ preload and BP with little change in HR
What are terazosin, doxazosin, and tamsulosin used to treat (α1-antagonists)?
prostate hypertrophy → note: anesthesia-induced hypotension may be exacerbated in these patients
What is Yohimbe?
(1) selective α2 antagonist
(2) widely marketed for...
a. erectile dysfunction
b. athletic performance
c. weight loss
d. HTN
e. diabetic neuropathy
(3) ↑ parasympathetic and ↓ sympathetic activity
What are the anesthesia considerations for patients on Yohimbe (α2-antagonist)?
may ↓ the effect of antihypertensive medications
What are some potential indications for β-blockers?
(1) HTN
(2) SVT
(3) afib
(4) CHF
(5) ischemic heart disease
(6) ↓ myocardial O₂ consumption & improve perfusion
(7) glaucoma
What are the potential s/e of β-blockers?
(1) bradyarrhythmias
(2) heart block
(3) HF
(4) bronchoconstriction
(5) hypoglycemia
What can abrupt discontinuation of β-blockers lead to?
rebound tachycardia and HTN
Which beta-blockers act as antiarrhythmics?
(1) certain beta-blockers (e.g., propranolol, acebutolol, carvedilol) have membrane stabilizing activity (MSA)
(2) beta-blockers with MSA can act as antiarrhythmics
Which β-blockers are NON-SELECTIVE?
(1) propranolol
(2) carvedilol
(3) nadolol
(4) pindolol
(5) sotalol
(6) timolol
Which non-selective β-blocker has a very long ½-life?
nadolol
Propranolol can be administered via which routes?
PO, IV
Which conditions might propranolol (non-selective β-blocker) aggravate?
(1) Raynaud's
(2) PVD
How do non-selective β-blockers (e.g., propranolol) work?
prevents the action of epinephrine, NE, dopamine, dobutamine, and isoproterenol at β-receptors
Which non-selective β-blocker does not ↓ HR and BP to as significant of an extent?
Which selective β-blocker also has less of an impact on HR and BP?
(1) non-selective → pindolol
(2) selective → acebutolol