Lenses
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What are the two types of lens
Concave and Convex Lens
How is the symbol for convex lens and what is their shape
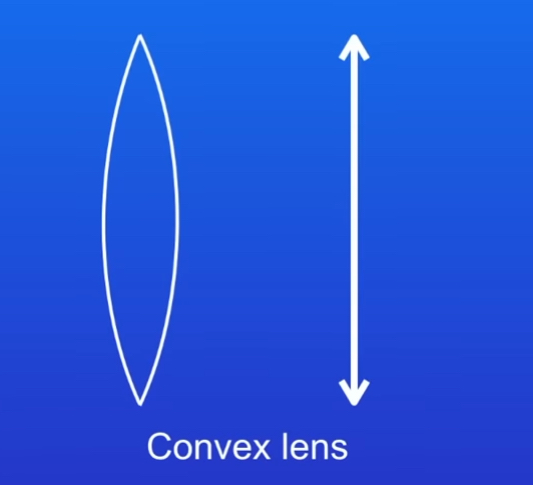
Describe convex lens thcikness
Thicker at centre then edges
What do all lenses do
They refract light to from images
What is the principal focus in a convex lens
Where rays hitting the lens parallel to the axis meet
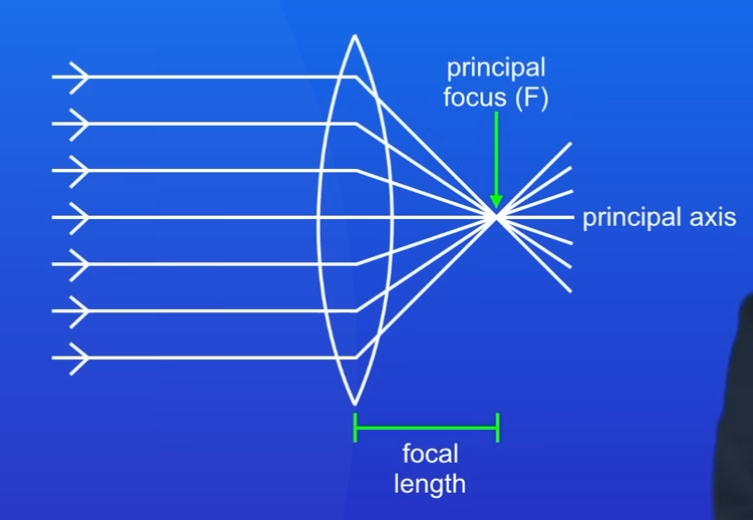
What is the focal length
The distance from the centre of the lens to the principal focus
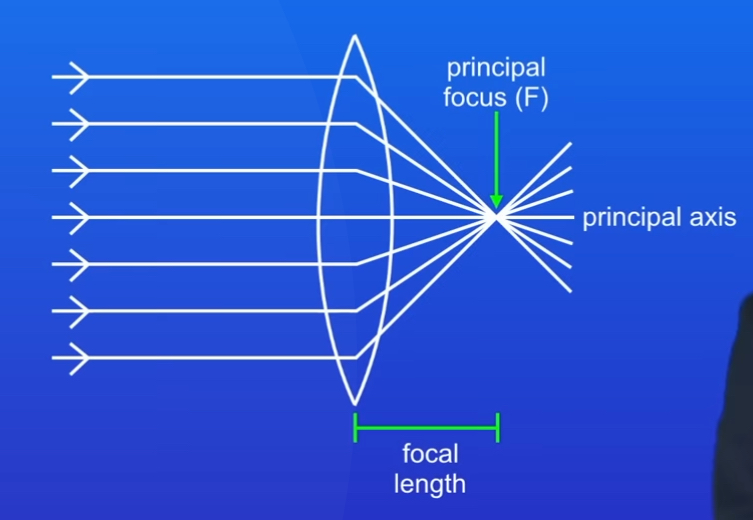
What is the Axis of a Lens
A line passing through the middle of lens, perpendicular to the lens
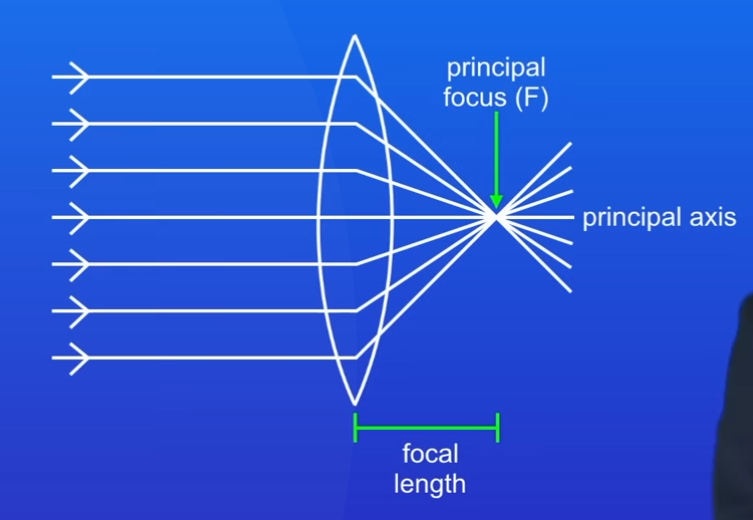
What are the three Rules for Refraction in a Convex Lens
1)An Incident ray parallel to the axis refracted through the lens and passes through the principal focus on the other side
2) An incident ray passing through the principal focus refracts through lens and travels parallel to axis
3)An incident ray passing through the centre of lens carries on in the same direction
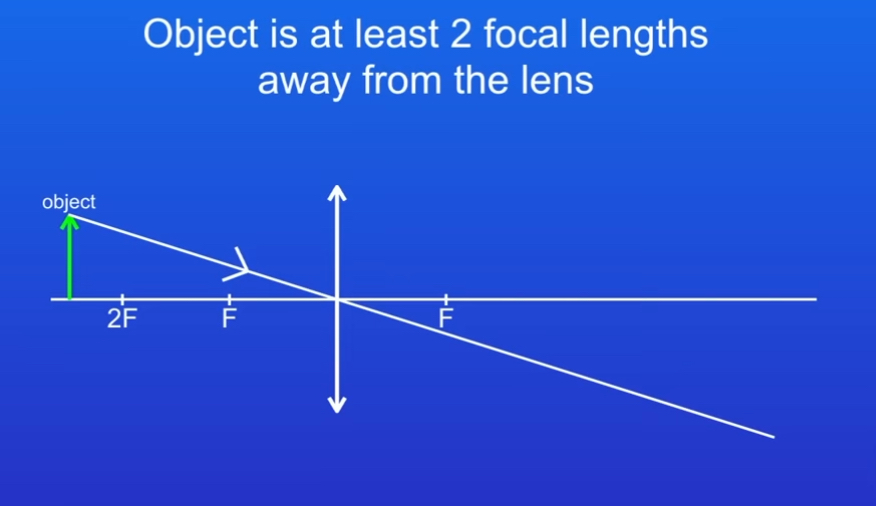
Describe how you draw a Ray diagram with convex lens STEP 1
Draw a line from top of the object passing straight through the centre of the lens without changing direction
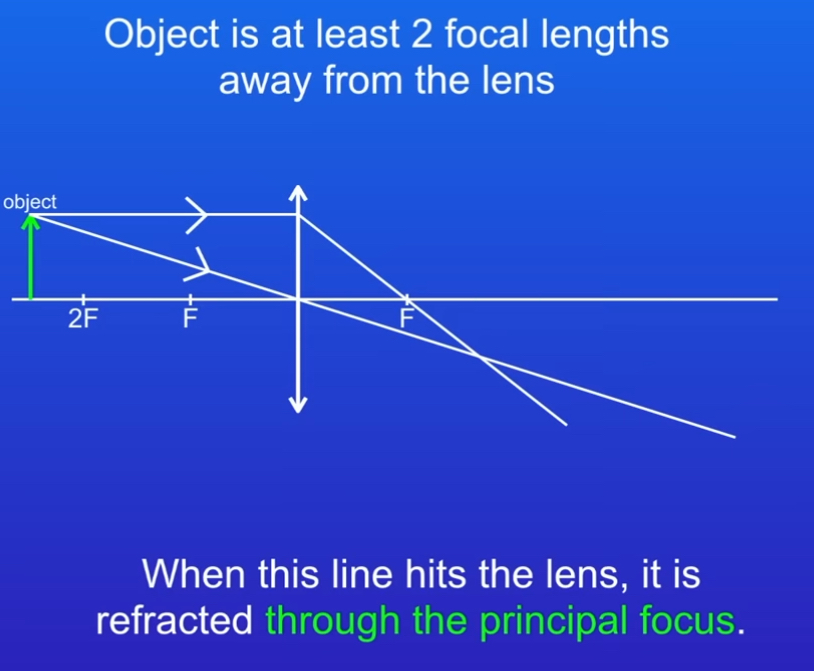
STEP 2
Draw another line from top of object which runs parallel to principal axis so when it hits lens it’s refracted through the principal focus
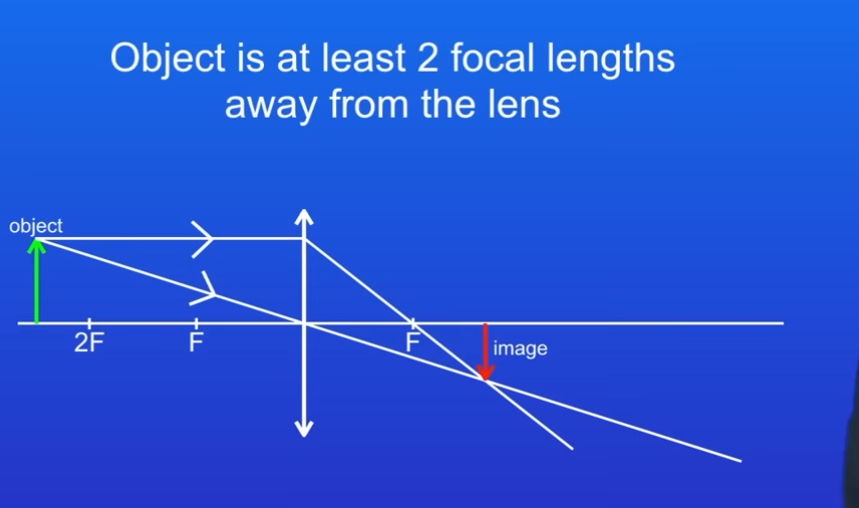
STEP 3
Where the two lines meet, shows us top of image
This image is Diminished, inverted and a real image
When you’re describing an image, what are the three things you must talk about
1)How big it is compared to the object(Has it magnified or diminished)
2)Whether it’s upside down or not(Inverted or Upright)
3)Whether it’s Real or Virtual(Real is when all the rays meet at a point. Virtual is when they don’t)
If the object is more than 2 focal lengths from the lens…
Image is diminished
Image is inverted
Image is Real
If object is between 1 and 2 focal lengths from lens then….
Image is magnified
Image id inverted
Image is Real
What is the Concave lens shape and symbol
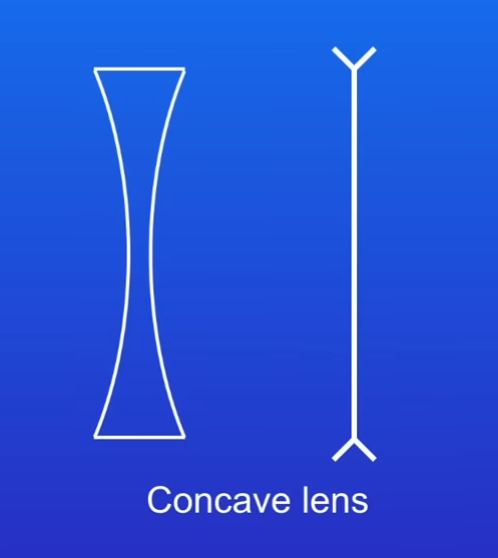
Describe Concave lens thcikness
Thicker at the edge compared to the center
What happens to light rays once they pass through concave lens
Causes Parallel rays of light to spread out (diverge)
Where is the principal focus on a concave lens
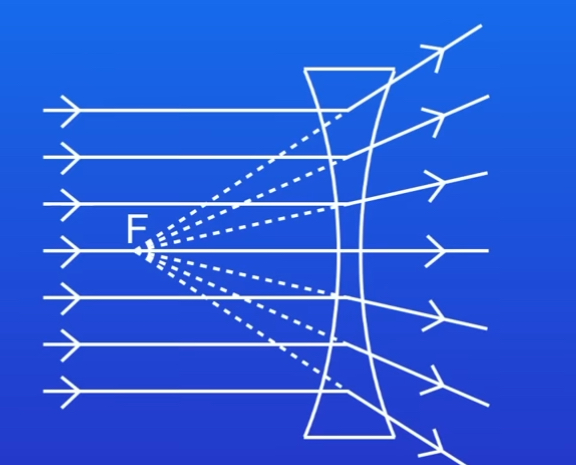
Describe the three rules for the redaction in a concave lens
1)An Incident ray parallel to the axis refracts through the lens and travels in line with the principal focus(so it appears to have come from principle focus)
2)An Incident ray passing through the lens towards the principal focus refracts through the lens and travel parallel to the axis
4)An incident ray passing though the centre of the lens carries on in the same direction
Describe how to draw a ray diagram with a concave lens STEP 1
Draw a ray from the top of the object passing through the centre of the lens without changing the direction
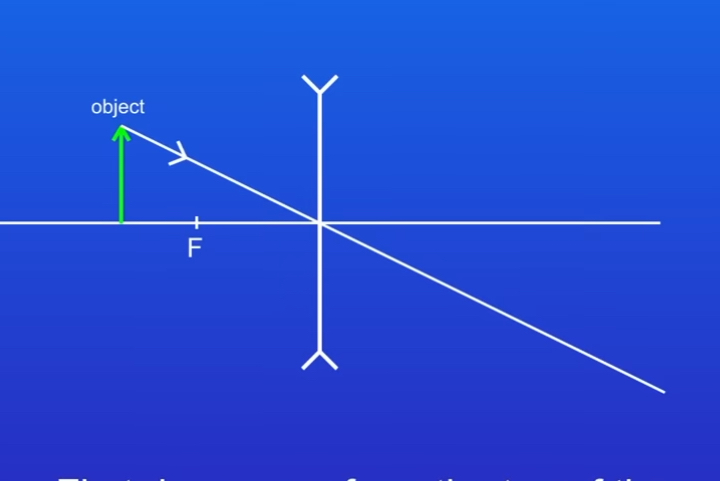
STEP 2
Draw another ray from the top of the object. This passes through the lens and is refracted. This ray must appear to have come from the principal focus so draw a dotted line to show
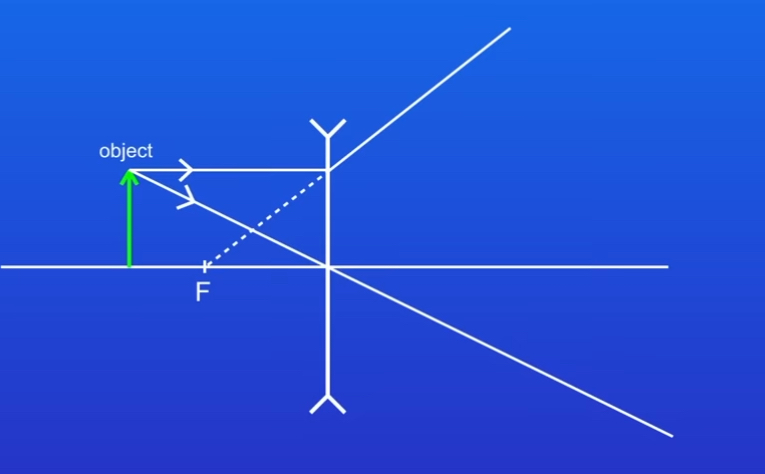
STEP 3
Where these lines meet shows us the location of the image
Image is diminished
Image is upright
Image is Virtual
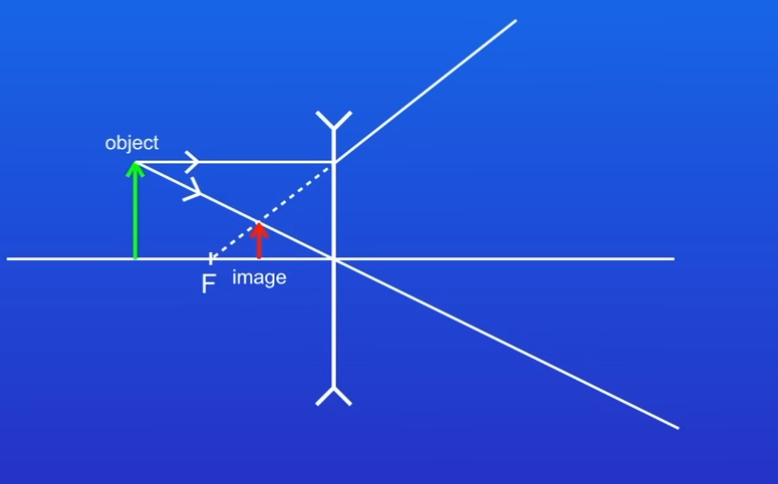
So in a Concave lens what three properties will the image always have
Always be diminished, right way up and virtual
Why are concanve lens images virtual
As we can’t see this image on a screen
Describe how to draw a ray diagram for a magnifying glass STEP 1
Object is between 1 focal length and the lens. Start by drawing a ray of light from the top of the object through the centre of the lens
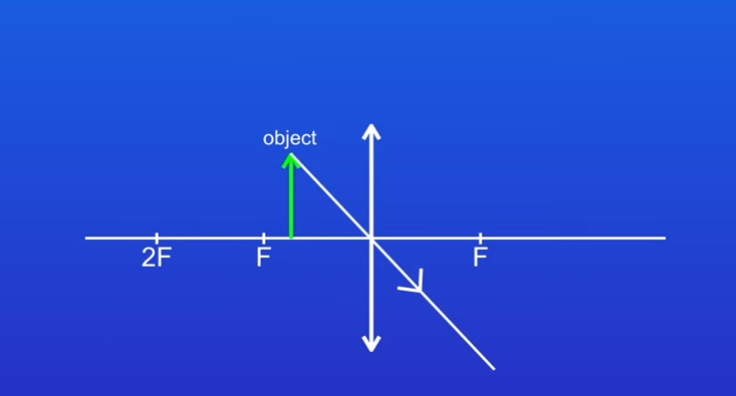
STEP 2
Draw another ray from top of object running parallel with principal axis, this ray passes though the principal focus
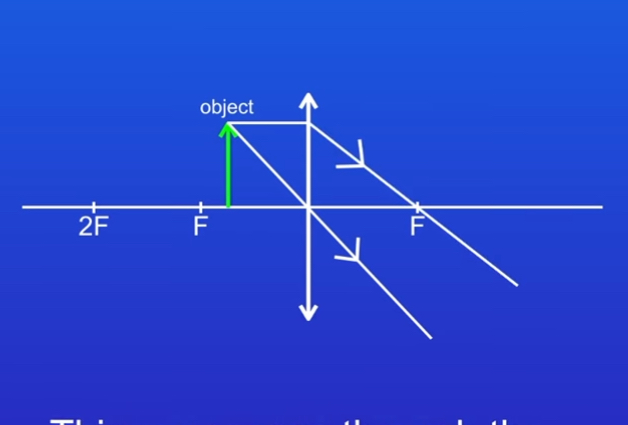
STEP 3
Draw dotted lines to extend the rays behind the lens
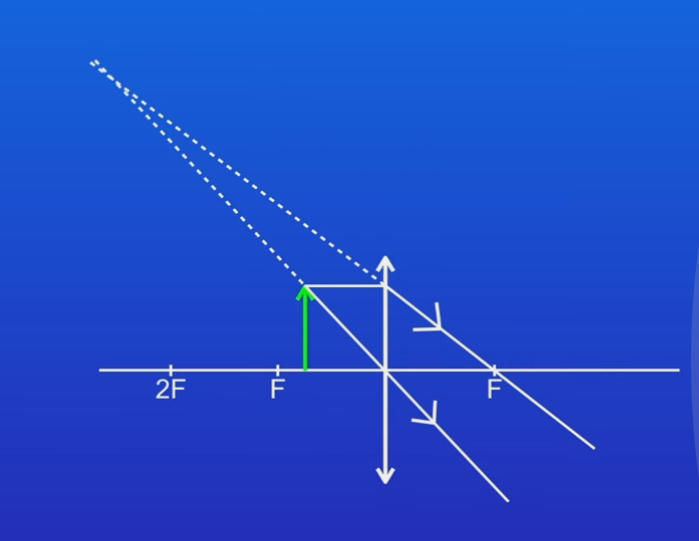
STEP 4
Where the dotted lines meet shows us us the postion of the image.
-Draw an eye between two rays at bottom
Results should be Image is Magnified, upright and virtual
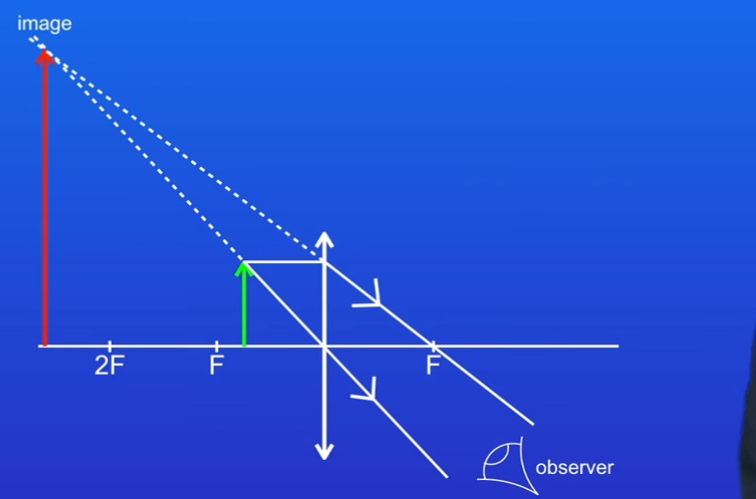
Why can’t see a virtual image on a screen
As the only time that a convex lens lrucrds a virtual image is when it’s used as a magnifying glass
A magnifying glass is used to view an object which has a height of 0.5cm
The image has a height of 3.5cm
Calculate the magnification
Magnification = 3.5/0.5 =7X
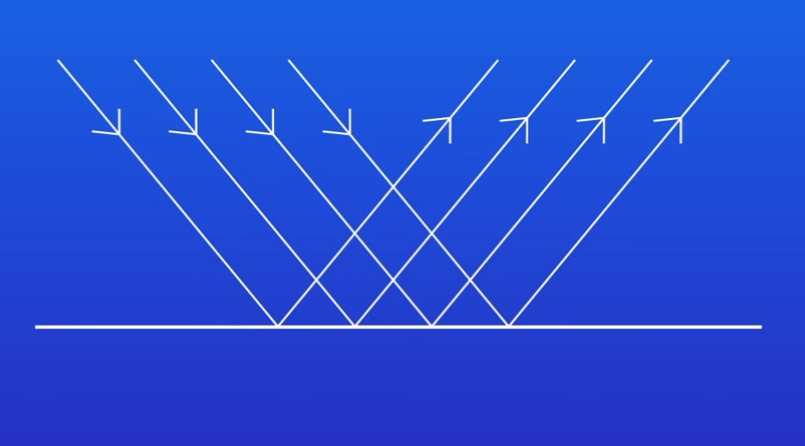
What is Specular reflection
Reflection from a smooth surface in a single direction which produces an image

What if Diffuse Reflection
Reflection from a through surface that doesn’t produce an image
What is white light
A mixture of all the different colours
What happens if we pass white light through a prism
Then it splits into a spectrum
What does the colour of an object depend on
Which wavelengths of light are reflected,transmitted or absorbed
How do colour filters work
They absorbs specific wavelengths and transmitting (Allowing through) other wavelengths
Describe how a red filter would work
1)Shine white light onto the filter
2)The filter then absorbs all the colours of visible light apart from red
3)So only red light transmitted though the filter
Objects that transmit light can be either…
Transparent(Can easily see though object)
Translucent(These objects scatter the light rays so we can’t see though them clearly)
What are Opaque objects
Objects that we cannot see through at all so light can’t pass through
Why do white objects appear white
Because they reflect all of the wavelengths of visible light equally
Why do objects appear black
Because they absorb all the wavelengths of visible light
Why does a object appear red colour
As when white light is shining onto a red object the red object absorbs all all the colours of white light apart from red which is reflected
Why does a red object appear red through a red filter
The Red filter absorbs all the colours of white light apart from red which is transmitted and then red light is reflected off the red object so it appears red
Describe what you’ll see with a green object and a red filter
Red filter allows red light to be transmitted however green object absorbs all the red light so none is reflected so green object will appear black as it is reflecting no light at all
The colour of a opaque object depends on what
Which wavelengths of light are most strongly reflected E.g a red apple appears red because the wavelengths corresponding to the red part of the visible spectrum are most strongly reflected, the others are absorbed
Which surface it the best absober and best emitter of infrared radiation
Matt Black surface
What do all bodies(objects) do
Emit and absorbed infrared radiation
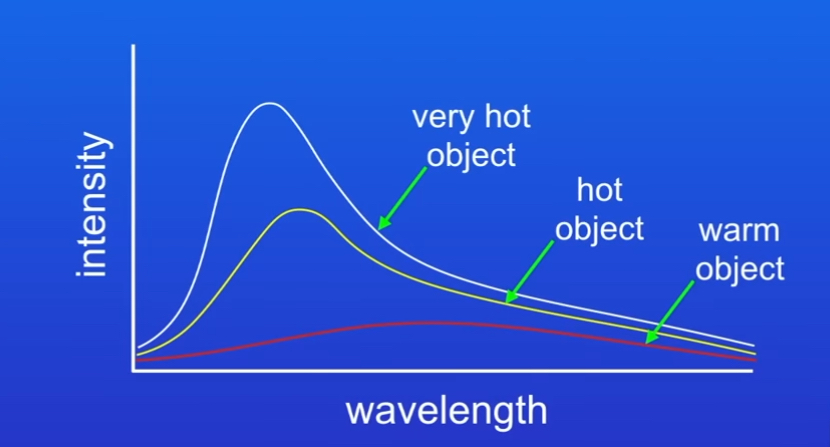
The hotter an object is…
The more infrared radiation is emitted in a given time compared to a cooler object
Both the wavelength and intensity of radiation depend on…
The temperature of the object
What else do very hot objects emit
Short wavelength
As object gets hotter what happens to wavelength and what does it produce
Wavelength gets shorter,producing visible light
An object that’s hotter than its surroundings..
Emits more IR radiation than it absorbed as it cools down(E.g cup of tea on table is warmer than the air around it so it gives out more IR radiation than it absorbs which cools it down)
An object that’s cooler than its surroundings…
Absorbs more IR radiation than it emits as it warms up(E.g cold glass water on a sunny day)
Objects at a constant temperature
Emit IR radiation at the same rate it absorbs its
What is silver surfaces best at and worst at
Best at reflection while being worst for emitting and absorbing.
What is a perfect black body
Absorbs all of the radiation that hits it. No radiation is reflected or transmitted
A perfect black body is all the best…
Possible emitter of radiation
How does the earth gain or lose energy
By absorbing or emitting radiation
What does the sun emit
Short wavelength radiation which travels to Earth
What happens to radiation emitted from sun
Some is sent to the earth
Some is reflected by clouds
Remaining radiation can be absorbed by the surface of the earth causing the temperature of Earth to increase causing the Earth to emit infrared reaction back into space
Why is human activity that increases level of greenhouse gases bad
-Some of the energy of the infrared emitted by Earth is trapped by greenhouses gases in atmosphere like carbon dioxide meaning more heat energy is trapped in the atompshere and less is radiated into space
Why are cloudy nights more warmer than clear nights
As clouds can reflect infrared back to the Earth and prevent it being radiated into space
What factors affect how much energy is radiated from the earth
Cloud cover